包装类和泛型
- 1. 包装类
- 1.1 基本数据类型和对应的包装类
- 1.2 装箱和拆箱
- 1.3 自动装箱和自动拆箱
- 1.4 自动装箱实际上是调用了valueOf()
- 1.5 Integer包装类赋值注意点
- 2 什么是泛型
- 3 引出泛型
- 4 泛型的使用
- 4.1 语法
- 4.2 类型推导
- 5 裸类型
- 6 泛型如何编译
- 6.1 擦除机制
- 7 泛型的上界
- 写一个泛型类, 求一个数组当中的最大值
- 另一个类作为参数实例化时要引用它对应的接口和重写对应的方法
- 8 泛型方法
- 设为静态方法static
1. 包装类
在Java中,由于基本类型不是继承自Object,为了在泛型代码中可以支持基本类型,Java给每个基本类型都对应了一个包装类型。
1.1 基本数据类型和对应的包装类
基本数据类型 --> 包装类
byte --> Byte
short --> Short
int --> Integer
long --> Long
float --> Float
double --> Double
char --> Character
boolean --> Boolean
除了 Integer 和 Character, 其余基本类型的包装类都是首字母大写。
1.2 装箱和拆箱
装箱/装包:把一个基本类型转变为包装类型
拆箱/拆包:把一个包装类型转变为基本类型
1.3 自动装箱和自动拆箱
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
Integer ii = a; //自动装箱
Integer ii2 = new Integer(10);
int b = ii2; //自动拆箱
System.out.println(ii); // 10
System.out.println(b); // 10
}
1.4 自动装箱实际上是调用了valueOf()
public static void main2(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
//Integer ii = a; //自动装箱
Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(a); // 手动装箱
Integer ii2 = new Integer(10);
//int b = ii2; //自动拆箱
int b = ii2.intValue(); // 手动拆箱
double d = ii2.intValue();
System.out.println(ii); // 10
System.out.println(b); // 10
System.out.println(d); // 10.0
}
1.5 Integer包装类赋值注意点
public static void main(String[] args) {
// i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high
// 在 Integer valueOf方法中 的int i取值范围是 -128~127
// 在这个返回返回的是 -128 到 127 中 255 个地址 存放100
// IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)] 即返回的地址为同一个地址
// 而200不属于这个取值范围里面 返回的是 一个新的 值 new Integer(i)
/*Integer ii = 100;
Integer ii2 = 100; //true */
Integer ii = 200;
Integer ii2 = 200; //false
System.out.println(ii == ii2);
}
2 什么是泛型
一般的类和方法,只能使用具体的类型: 要么是基本类型,要么是自定义的类。如果要编写可以应用于多种类型的代码,这种刻板的限制对代码的束缚就会很大。
泛型是在JDK1.5引入的新的语法,通俗讲,泛型:就是适用于许多许多类型。从代码上讲,就是对类型实现了参数化。
3 引出泛型
实现一个类,类中包含一个数组成员,使得数组中可以存放任何类型的数据,也可以根据成员方法返回数组中某个下标的值?
class MyArray <T>{
// <T> 占位符 是一个泛型类
// 泛型的意义:1. 在编译的时候 检查数据类型是否正确 2.在编译的时候 帮助进行类型转化
//public Object[] array = new Object[10];
// 不能实例化一个泛型类型的数组
// public T[] array = new T[10];
//public T[] array = (T[])new Object[10];
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public void setValue(int pos,T val) {
array[pos] = val;
}
// 在java中不能将整个数组进行强转
public T getValue(int pos) {
return (T) array[pos];
}
}
class Person {
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray<Integer> myArray = new MyArray<>();
//MyArray<int> myArray = new MyArray<>(); //<>里面不能是基本数据类型
myArray.setValue(1,90); // 直接放int 会发生自动装箱
//裸类型 不加包装类型
MyArray myArray1 = new MyArray<>();
myArray1.setValue(0,1);
}
//目的:想存放指定的元素
public static void main4(String[] args) {
MyArray<String> myArray = new MyArray<>();
myArray.setValue(0,"hello");
MyArray<Integer> myArray2 = new MyArray<Integer>();//类型后加入<Integer> 指定当前类型
myArray2.setValue(0,99);
myArray2.setValue(1,20);
MyArray<Person> myArray3 = new MyArray<>();
}
}
- 类名后的 代表占位符,表示当前类是一个泛型类
了解: 【规范】类型形参一般使用一个大写字母表示,常用的名称有:
- E 表示 Element
- K 表示 Key
- V 表示 Value
- N 表示 Number
- T 表示 Type
- S, U, V 等等 - 第二、第三、第四个类型
- 不能new泛型类型的数组
- 类型后加入 指定当前类型
- 不需要进行强制类型转换
4 泛型的使用
4.1 语法
//泛型类<类型实参> 变量名; // 定义一个泛型类引用
//new 泛型类<类型实参>(构造方法实参); // 实例化一个泛型类对象
MyArray<Integer> myArray = new MyArray<>();
泛型只能接受类,所有的基本数据类型必须使用包装类!
4.2 类型推导
MyArray<Integer> list = new MyArray<>(); // 可以推导出实例化需要的类型实参为 Integer
5 裸类型
//裸类型 不加包装类型
MyArray myArray1 = new MyArray<>();
myArray1.setValue(0,1);
总结:
- 泛型是将数据类型参数化,进行传递
- 使用表示当前类是一个泛型类
- 泛型的优点:数据类型参数化,编译时自动进行类型检查和转换
6 泛型如何编译
6.1 擦除机制
在终端通过命令:javap -c 查看字节码文件,所有的T都是Object。
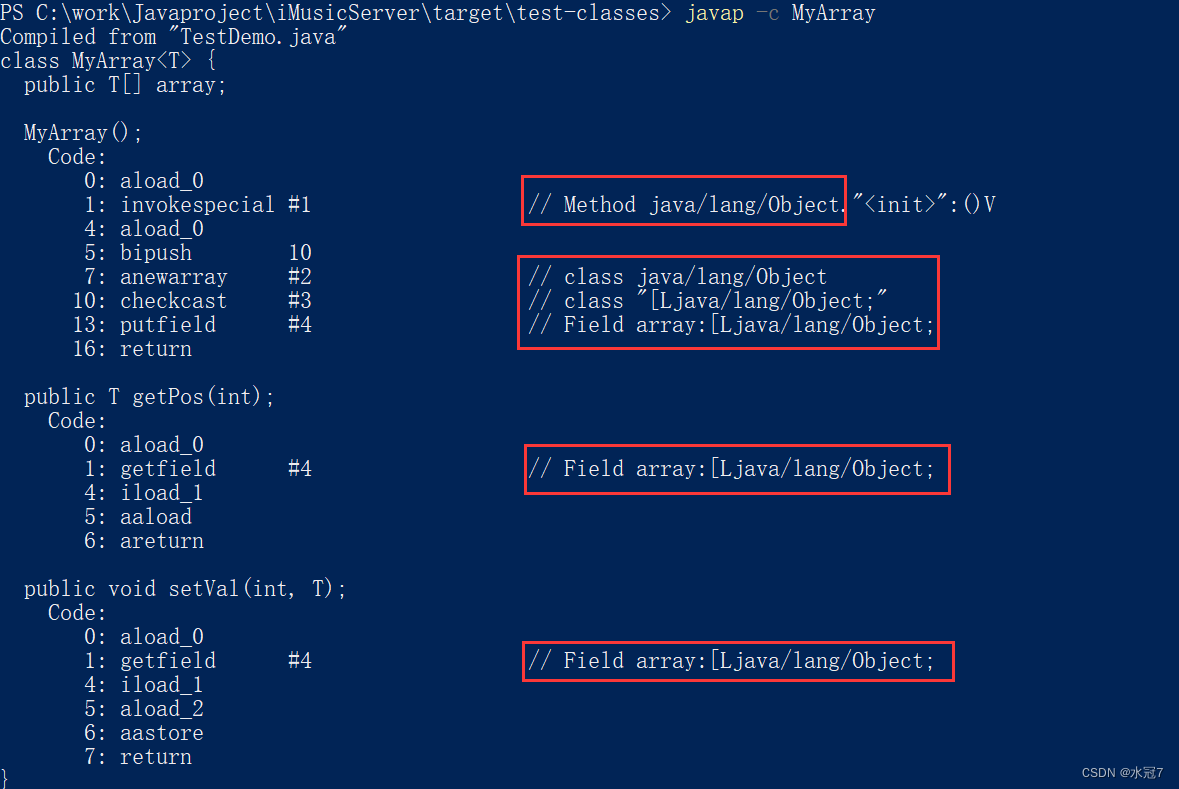
在编译的过程,将所有的T替换为Object这种机制,称为:擦除机制。
即可以直接写成:
class MyArray <T>{
//public T[] array = (T[])new Object[10];
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public void setValue(int pos,T val) {
array[pos] = val;
}
public T getValue(int pos) {
return (T) array[pos]; //加(T) 转一下
}
public T[] getArray() {
return (T[]) array;
}
}
7 泛型的上界
class MyArray <T extends Number>{ // T 一定是Number或者是Number的子类如Integer
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public void setValue(int pos,T val) {
array[pos] = val;
}
public T getValue(int pos) {
return (T) array[pos];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray<String> myArray = new MyArray<>(); // 报错 String不是Number的子类
// String[] ret = (String[])myArray.getArray(); //会报错 在java中不能将整个数组进行强转
// 数组是一种单独的数据类型
Object[] ret = myArray.getArray();
}
写一个泛型类, 求一个数组当中的最大值
//写一个泛型类, 求一个数组当中的最大值
class Alg<T extends Comparable<T>> { // 泛型的上界
public T findMaxVal(T[] array) {
T max = array[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//if (array[i] > max) { // 引用类型不能直接通过 大于等于号进行比较
//这个时候就需要 写一个Comparable<T> 上界
if (array[i].compareTo(max)>0){
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] array = {1,2,8,5,3};
Alg<Integer> alg = new Alg<>();
System.out.println(alg.findMaxVal(array));
}
}
另一个类作为参数实例化时要引用它对应的接口和重写对应的方法
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return 0;
}
}
//写一个泛型类, 求一个数组当中的最大值
class Alg<T extends Comparable<T>> { // 泛型的上界
public T findMaxVal(T[] array) {
T max = array[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//if (array[i] > max) { // 引用类型不能直接通过 大于等于号进行比较
//这个时候就需要 写一个Comparable<T> 上界
if (array[i].compareTo(max)>0){
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] array = {1,2,8,5,3};
Alg<Integer> alg = new Alg<>();
System.out.println(alg.findMaxVal(array));
//如果定义一个类 作为Alg实例的话 这个类必须实现Comparable接口并且重写compareTo方法
Alg<Person> alg1 = new Alg<Person>();
}
}
8 泛型方法
在定义方法的时候加
class Alg2 {
public<T extends Comparable> T findMaxVal(T[] array) {
T max = array[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i].compareTo(max)>0){
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Alg2 alg2 = new Alg2();
Integer[] array = {1,2,8,5,3};
alg2.<Integer>findMaxVal(array); //可以不加<Integer>会通过实参的值自动推导
alg2.findMaxVal(array);
}
}
设为静态方法static
class Alg3 {
public static <T extends Comparable> T findMaxVal(T[] array) {
T max = array[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i].compareTo(max)>0){
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] array = {1,2,8,5,3};
Alg3.<Integer>findMaxVal(array); //直接通过类名调用方法
}
}