类
将同一类对象的所有属性都封装起来。
类中最基础的内容包括两部分,一个是属性、一个是行为。
● 属性:表示一些特征项的数值,比如说:身高、体重、性别、肤色。这些属性都是名词。属性一般都以名词存在。属性的数值,也被称为“成员变量”。
● 行为:表示能执行的动作,能干什么?比方说:吃饭、睡觉、唱跳rap,篮球。打游戏。打架。这些行为一般通过函数实现,也被称为“成员函数”。行为一般以动词存在。
成员 = 成员变量+成员函数。
定义
class 类名
{
访问权限:
成员属性;
访问权限:
成员方法;
};
封装
封装指的是,将类的一些属性和细节隐藏,重新提供外部访问的接口。封装可以提升代码的安全性,并且可以让程序员更关注于上层架构而非内部细节。
访问权限:public、private、protected
public:共有的,类内、类外和子类中都可以访问
private:私有的,类内可以访问,类外和子类中都不能访问(类中的默认权限是私有权限)
protected:受保护的,类内和子类中可以访问,类外不可以访问
类和结构体的区别
1、类的封装性比结构体更好,类中的默认权限是私有权限,结构体中默认权限是公有权限;
2、结构体默认是公有继承,类默认是私有继承;
3、C++中,类就是由结构体演变来的;
4、结构体一般用于实现某种数据结构,类一般用于描述一类对象的性质(属性、方法的封装);
对象的创建
C++中存在两种类型对象:
● 栈内存对象
对象所在的 {} 执行完毕后,自动被销毁。
● 堆内存对象
必须使用 new 关键字创建,使用指针保存。如果不使用 delete 关键字将其销毁,则堆内存对象会持续存在。
堆内存对象调用成员,使用 "->"。
栈内存对象调用成员,使用 "."。
💡 练习 1
定义一个长方形类,包含 私有属性:长、宽;
公有方法:设置长和宽,
定义一个 show 函数,获取长方形的长和宽;
输出长方形的面积和周长。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
public:
void set(float new_width, float new_height);
void show();
float area();
float perimeter();
};
void rectangle::set(float new_width, float new_height)
{
width = new_width;
height = new_height;
}
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
}
float rectangle::area()
{
return width * height;
}
float rectangle::perimeter()
{
return (width + height) * 2;
}
int main()
{
rectangle rec;
float w, h;
cout << "Input width and height:" << endl;
cin >> w >> h;
rec.set(w, h);
rec.show();
cout << "S = " << rec.area() << endl;
cout << "C = " << rec.perimeter() << endl;
return 0;
}
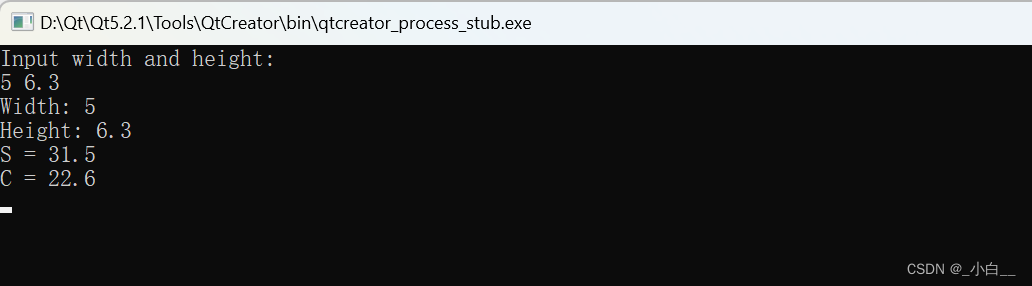
运行结果如下:
💡 练习 2
在 练习1 的基础上,设置新的函数,判断两个类对象是否完全相等(长 = 长,宽 = 宽)。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
public:
void set(float new_width, float new_height);
/* void show();
float area();
float perimeter(); */
bool whether_same(rectangle &r1, rectangle &r2); // 也可以定义为全局函数
// 但需要额外定义获取长、宽的方法
// float get_wid();
// float get_hgt();
};
void rectangle::set(float new_width, float new_height)
{
width = new_width;
height = new_height;
}
float rectangle::get_wid()
{
return width;
}
float rectangle::get_hgt()
{
return height;
}
bool rectangle::whether_same(rectangle &r1, rectangle &r2) // 也可以定义为全局函数
{ // 但需要调用获取长、宽的方法
return (r1.width == r2.width && r1.height == r2.height);
// return (r1.get_wid() == r2.get_wid() && r1.get_hgt() == r2.get_hgt());
}
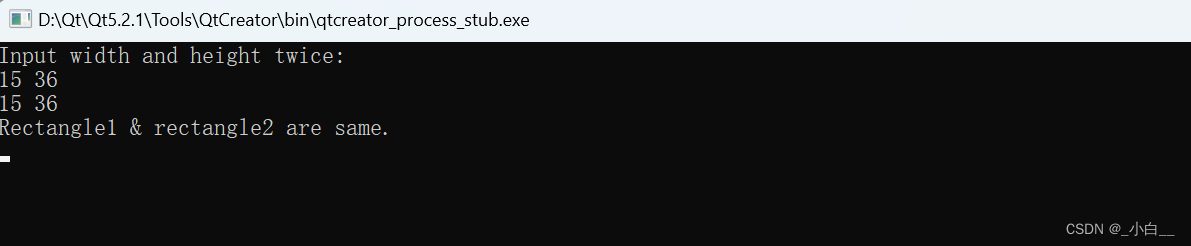
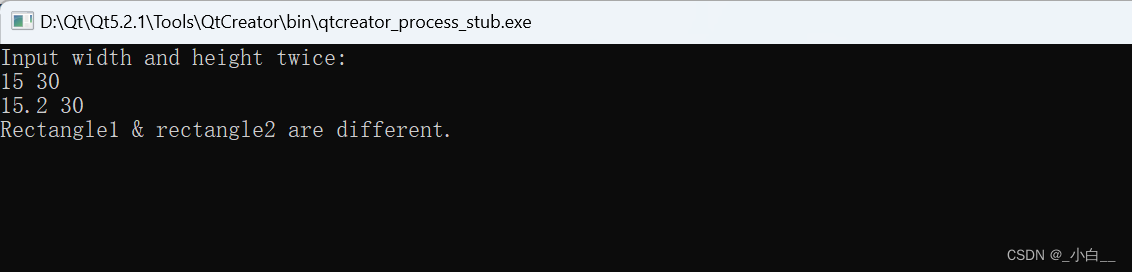
int main()
{
rectangle rec1, rec2, rec;
float w1, h1, w2, h2;
cout << "Input width and height twice:" << endl;
cin >> w1 >> h1;
cin >> w2 >> h2;
rec1.set(w1, h1);
rec2.set(w2, h2);
if (rec.whether_same(rec1, rec2)) // 若定义为全局函数,则不需要利用对象 rec 调用
cout << "Rectangle1 & rectangle2 are same." << endl;
else
cout << "Rectangle1 & rectangle2 are different." << endl;
return 0;
}
this 指针
每一个类中的非静态成员函数,都有一个 this 指针,指向调用者(谁调用 this 就指向谁)。
this 指针是一个特殊的指针,指向当前类对象的首地址。只能在类内使用。
成员函数(包括构造函数与析构函数)中都有 this 指针,this 指针指向的就是当前运行的成员函数所绑定的对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
string name;
public:
Test(string n)
{
name = n;
}
void test_this()
{
cout << this << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t1("小明");
cout << &t1 << endl; // 0x61fe84
t1.test_this(); // 0x61fe84
cout << "-----------" << endl;
Test *t2 = new Test("张三");
cout << t2 << endl; // 0x742698
t2->test_this(); // 0x742698
delete t2;
return 0;
}
原型:
类的类型 *const this; // 指针的指向不能修改
使用 this 指针的场合:
1、当形参和成员属性同名;

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
public:
void set(float width, float height);
void show();
float area();
float perimeter();
bool whether_same(rectangle &r1, rectangle &r2);
};
void rectangle::set(float width, float height)
{
this->width = width;
this->height = height;
}
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
}
2、函数,需要返回自身的引用;
支持链式调用的成员函数特点:返回值是当前类的引用。
■ 返回值是当前类的引用。
■ return *this;
1)拷贝赋值函数
2)其他链式调用
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
int val = 0;
public:
Test &add(int i)
{
val += i; // val = val + i;
return *this; // this是一个指针,需要解引用返回对象的引用
}
int get_val()
{
return val;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t1;
t1.add(1);
t1.add(2);
t1.add(100);
cout << t1.get_val() << endl; // 103
// 链式调用
Test t2;
cout << t2.add(2).add(3).add(200).get_val() << endl; // 205
return 0;
}
类中的特殊成员函数
类中会默认提供一些特殊的成员函数:构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数、拷贝赋值函数。
构造函数(支持函数重载、默认参数)
在实例化类对象时,系统默认调用无参构造函数。若自定义了构造函数,则系统将不提供构造函数。
类名()
{
// 函数体
}
------------------------------------------
类名(参数列表)
{
// 函数体
}
显示调用 & 隐式调用
显示调用:类名 对象名(实参列表);
隐式调用:类名 对象名 = {实参列表}; | 类名 对象名 = 实参;
建议使用显示调用,可以使用 explicit 关键字屏蔽隐式调用语法:
explicit 类名(参数列表)
{
// 构造函数
}
调用时机
类的嵌套:内层类先构造,外层类后构造;
类的继承:父类先调用构造,子类后调用构造
栈区:实例化类对象时(不初始化),调用无参构造函数
堆区:使用 new 申请空间时(不初始化),调用无参构造函数
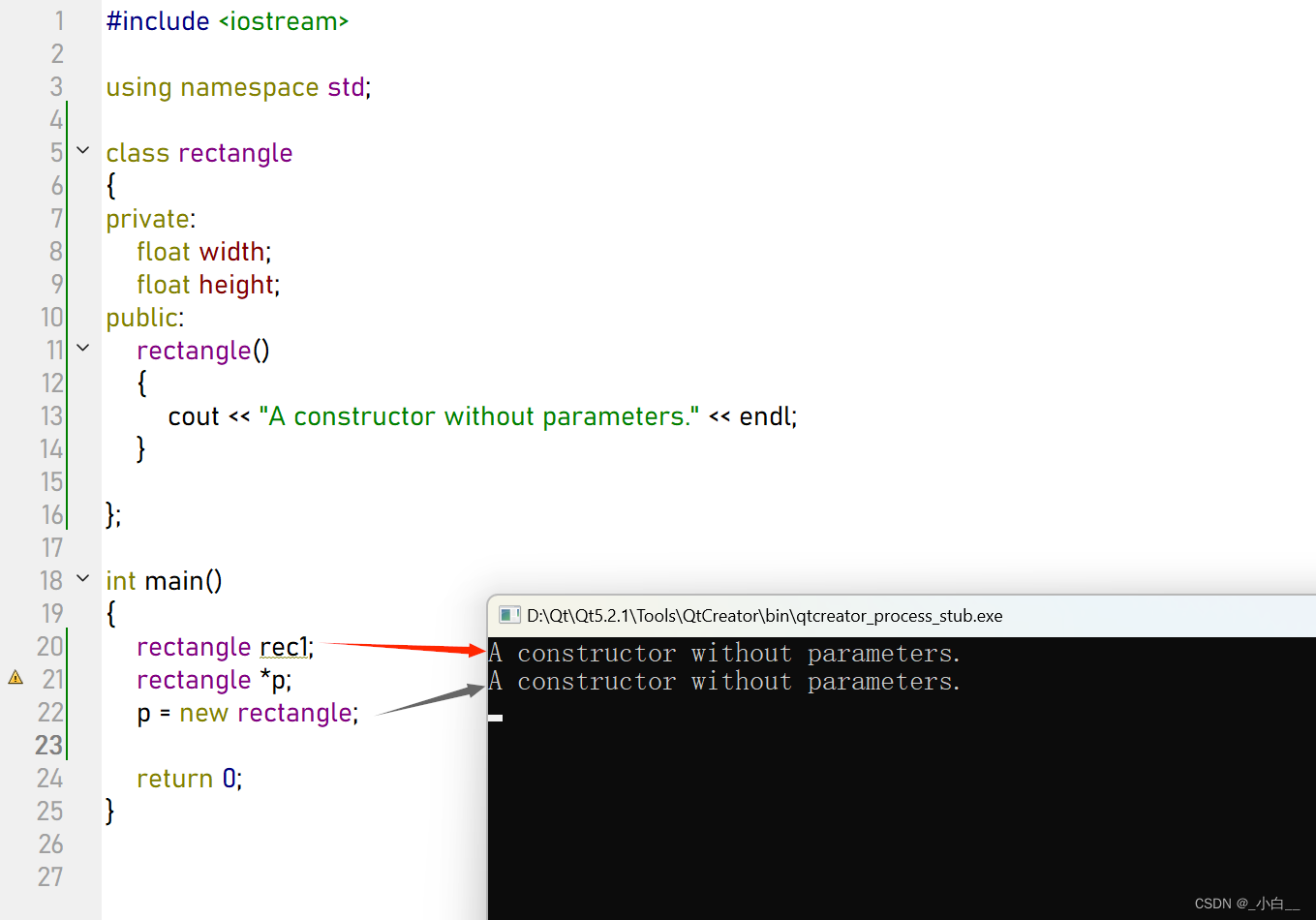
初始化列表的机制
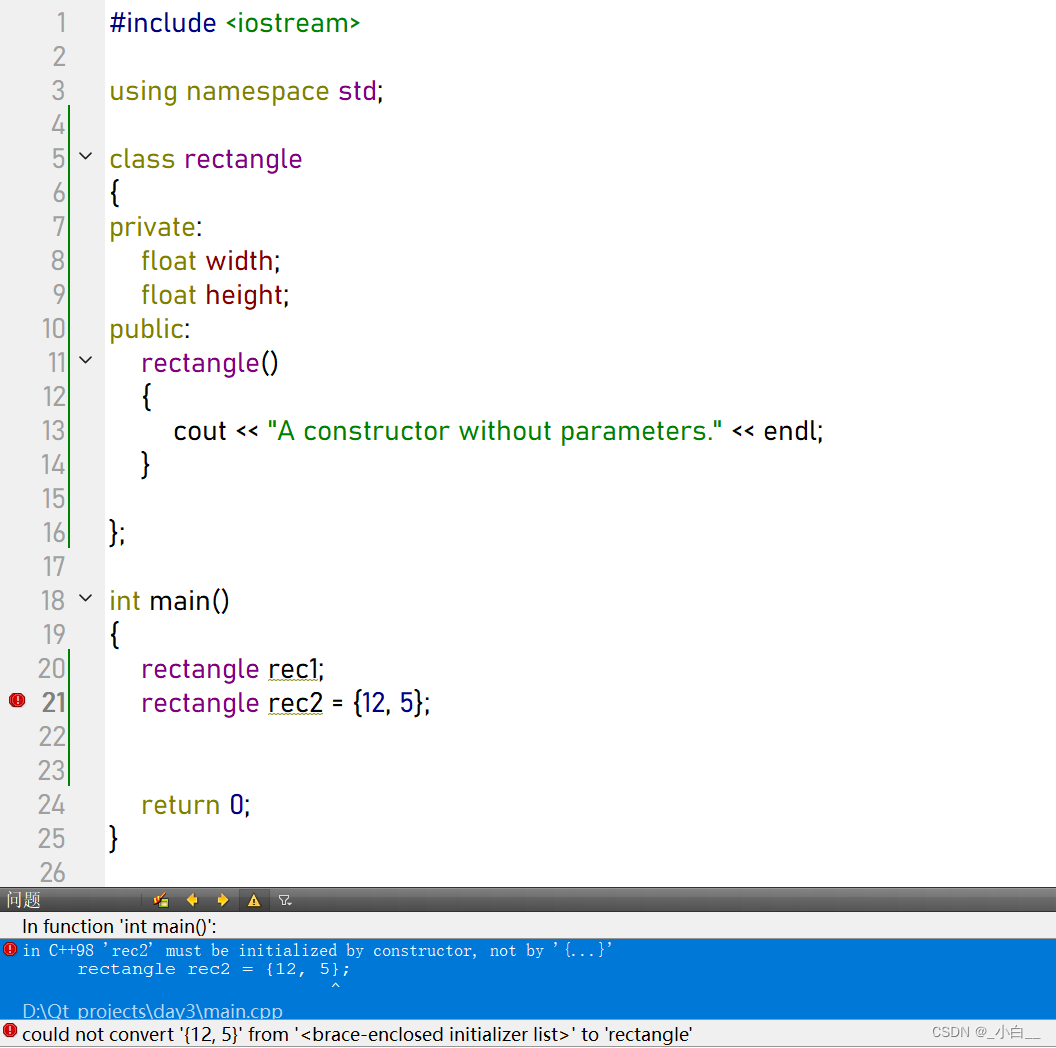
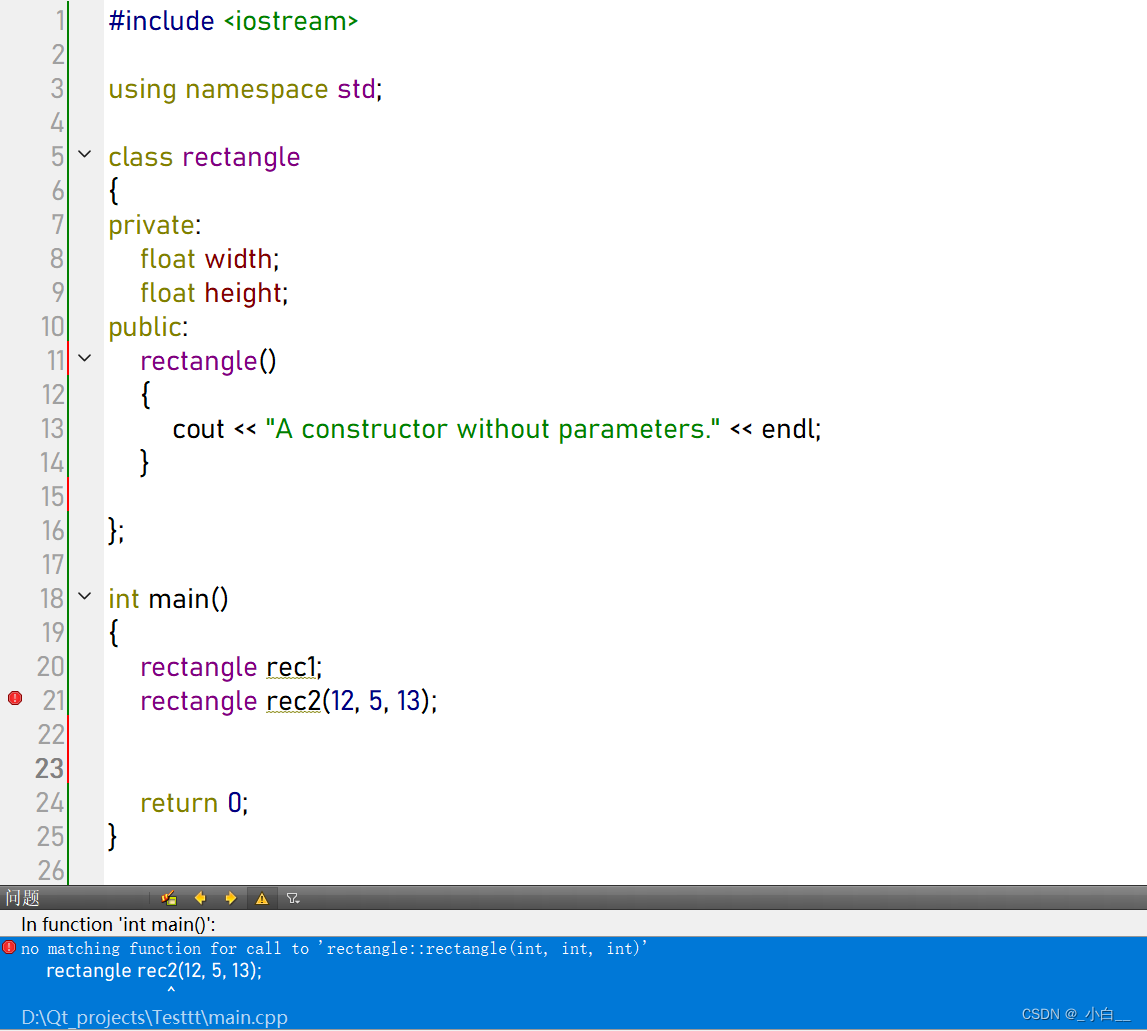
在函数体内部给成员属性赋值,是一个赋值的过程,不是初始化的过程。
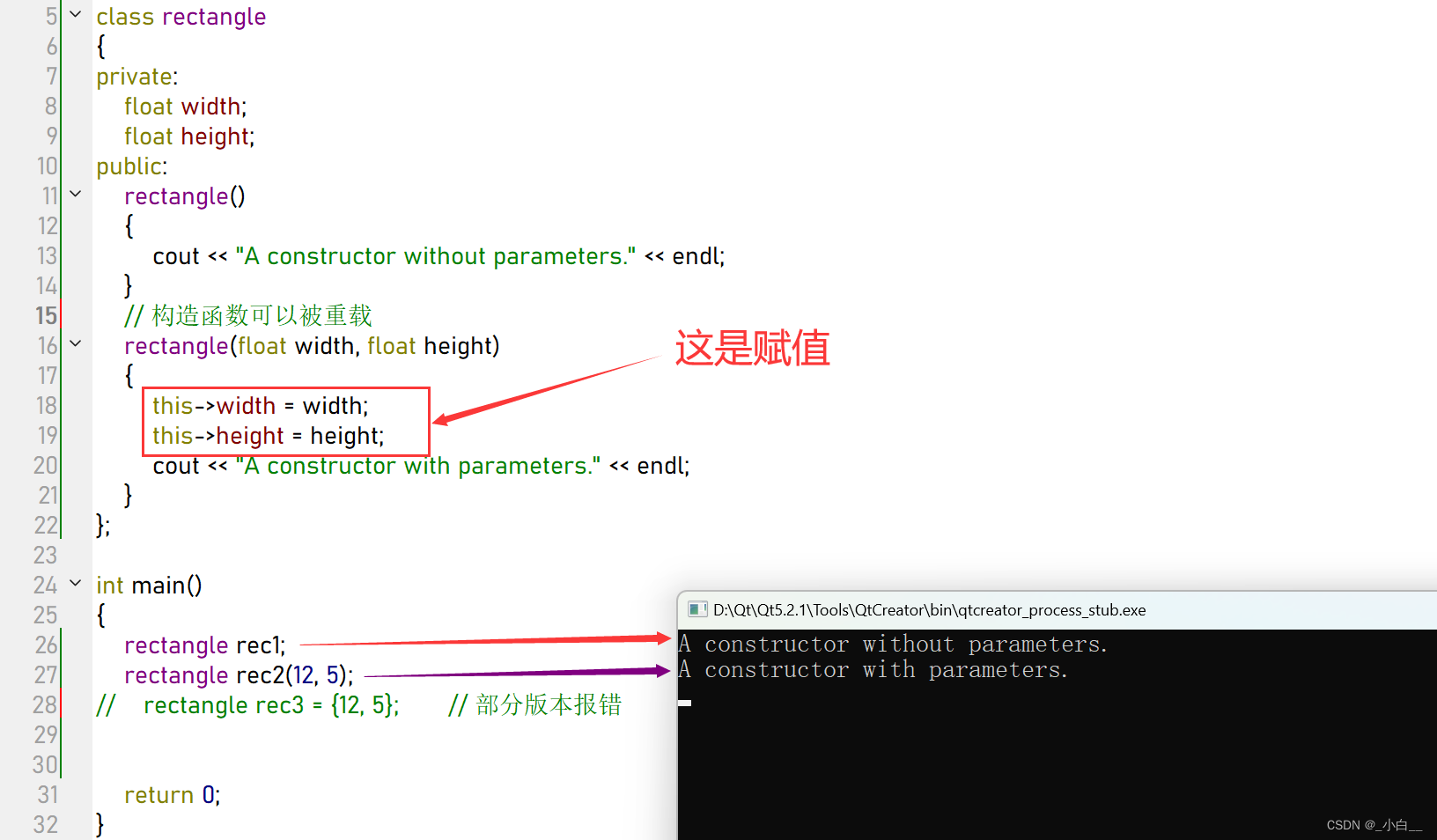
类名(参数列表):成员1的属性(形参1的值), 成员2的属性(形参2的值), …
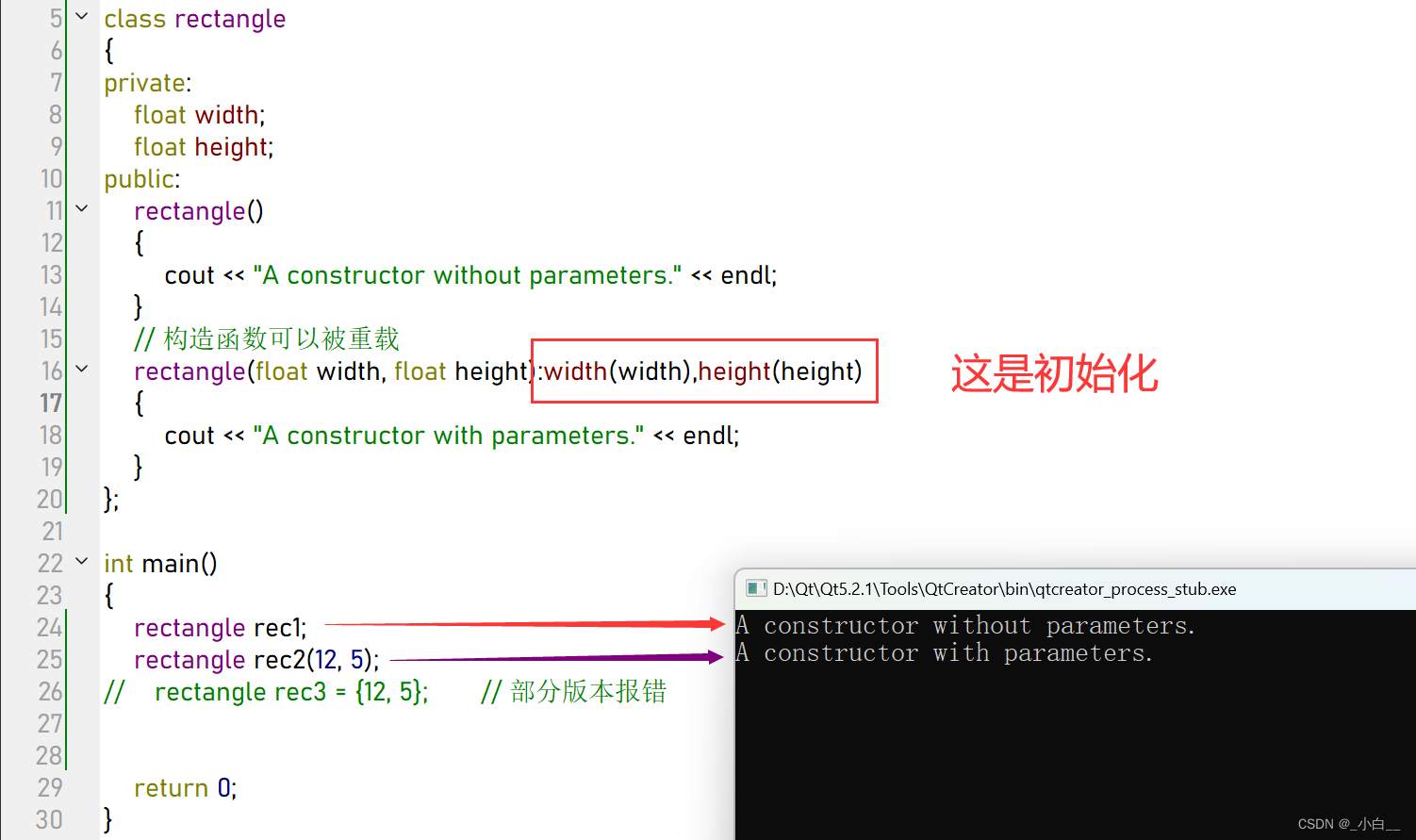
需要使用初始化列表的情况
1、形参和成员属性同名
2、类中有引用成员时,必须使用初始化列表
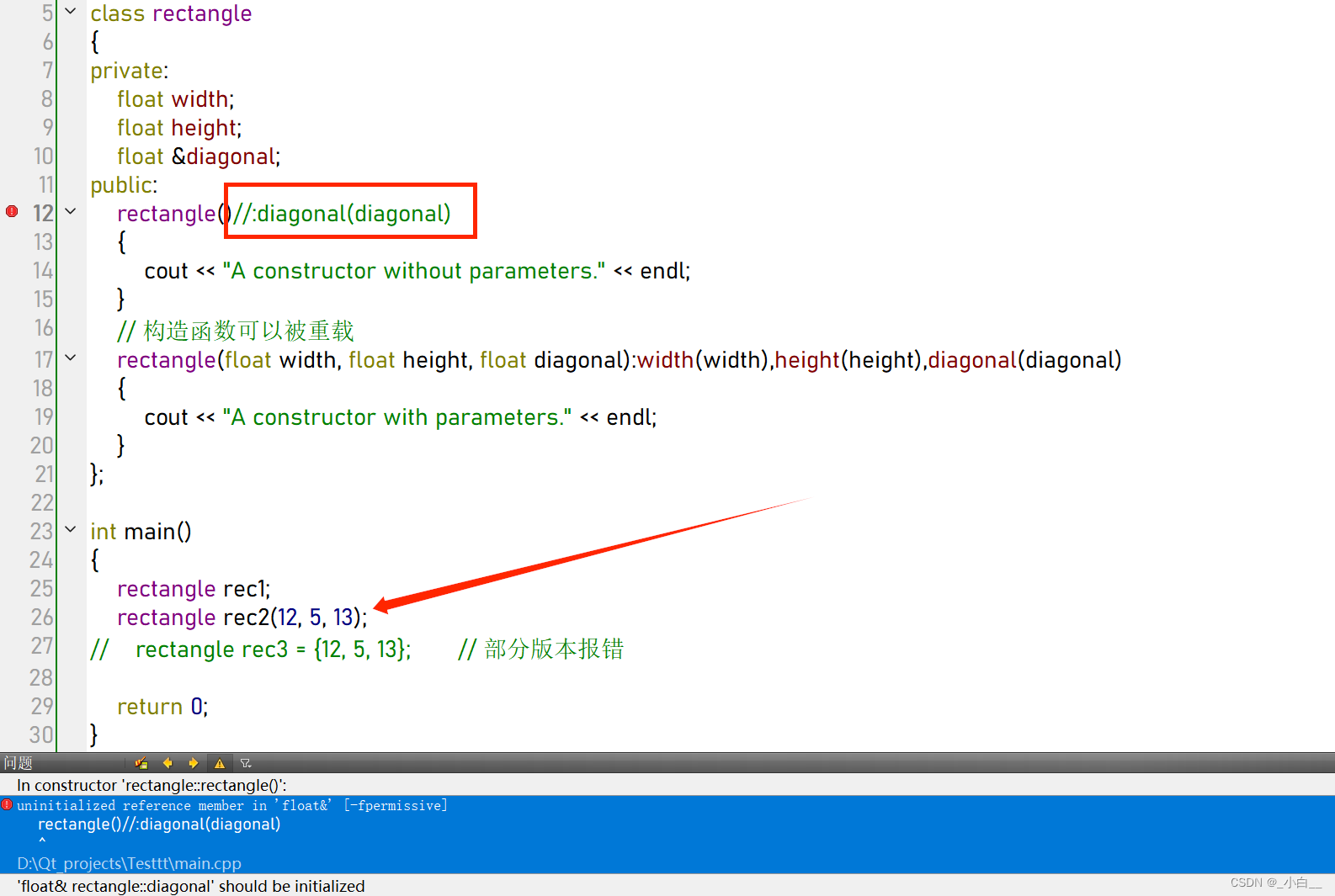
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
float &diagonal;
public:
rectangle():diagonal(diagonal)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
// 构造函数可以被重载
rectangle(float width, float height, float diagonal):width(width),height(height),diagonal(diagonal)
{
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
rectangle rec2(12, 5, 13);
// rectangle rec3 = {12, 5, 13}; // 部分版本报错
return 0;
}
3、类中有 const 修饰的成员时,必须使用初始化列表
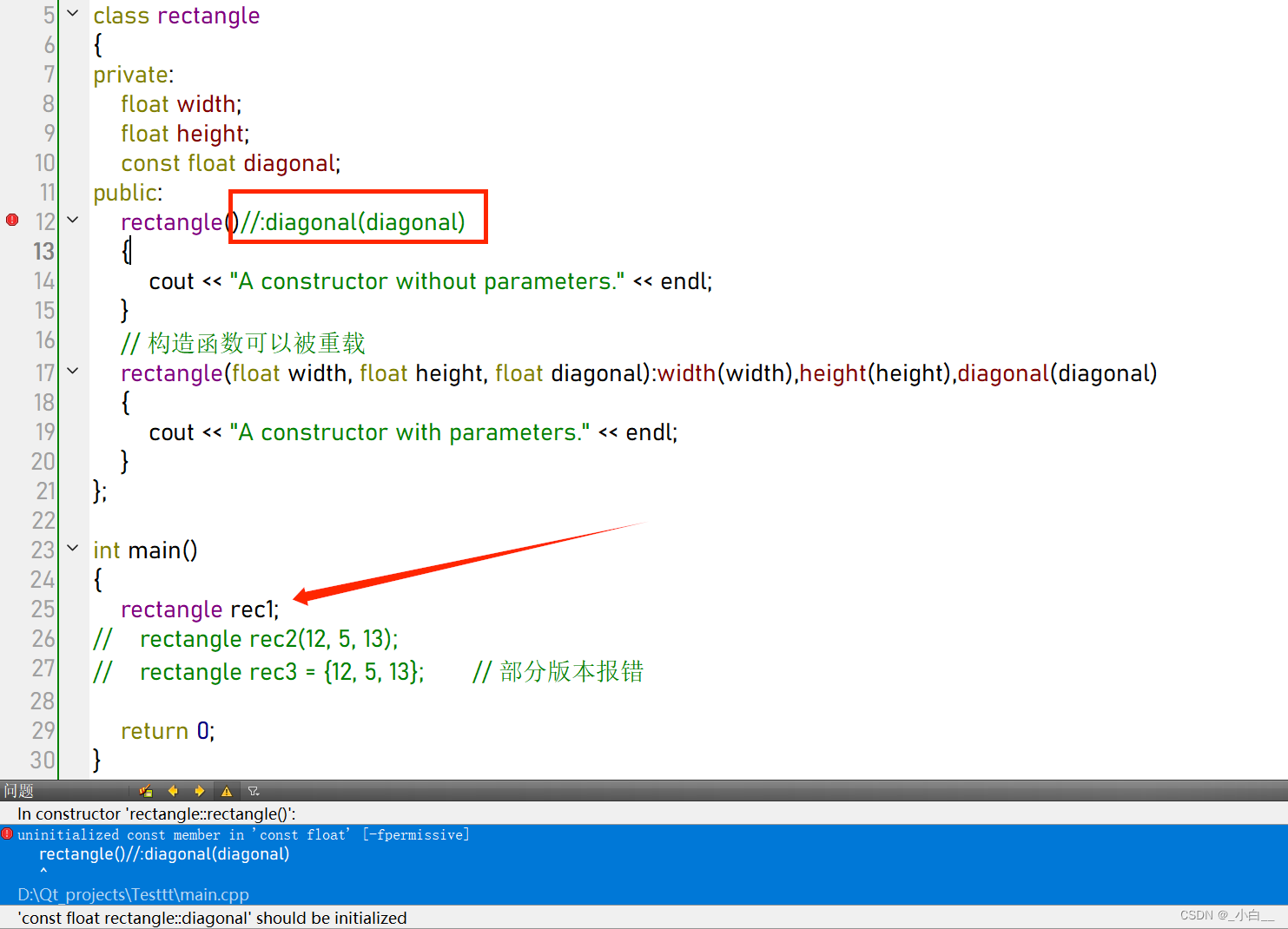
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
const float diagonal;
public:
rectangle():diagonal(diagonal)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
// 构造函数可以被重载
rectangle(float width, float height, float diagonal):width(width),height(height),diagonal(diagonal)
{
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
rectangle rec2(12, 5, 13);
// rectangle rec3 = {12, 5, 13}; // 部分版本报错
return 0;
}
4、类中含有其他类的子对象时,必须使用初始化列表
如果内部类只有有参构造,需要在外部类的有参构造、无参构造的初始化列表中宏显性调用;
如果内部类存在无参构造,外部类可以不写无参构造的初始化列表。
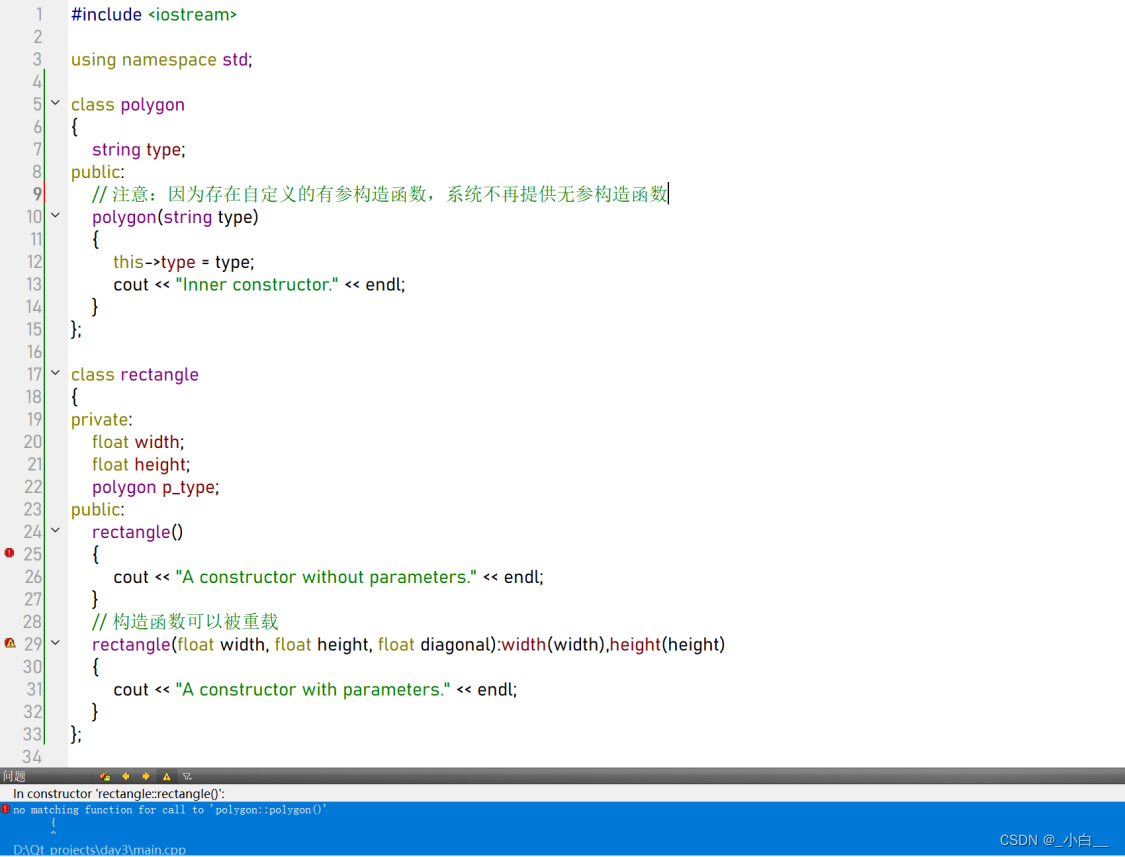
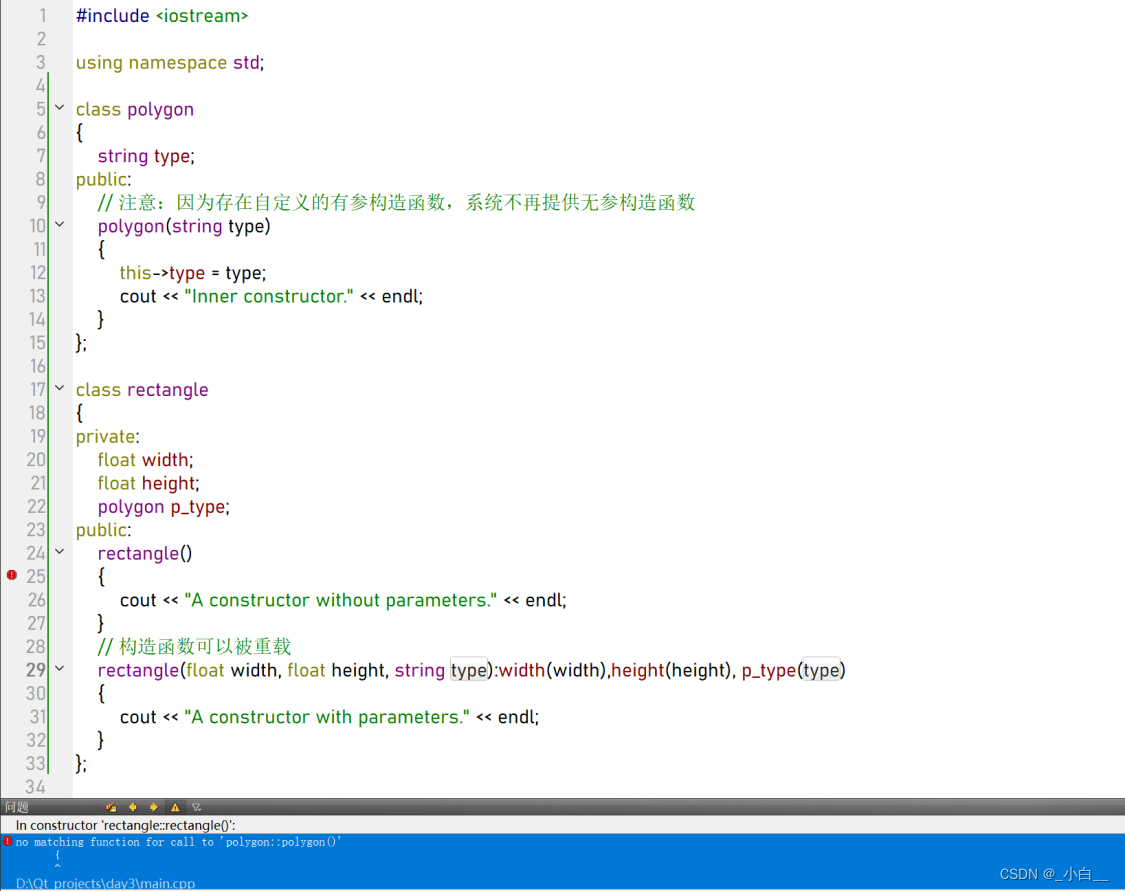
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class polygon
{
string type;
public:
// 注意:因为存在自定义的有参构造函数,系统不再提供无参构造函数
polygon(string type)
{
this->type = type;
cout << "Inner constructor." << endl;
}
};
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
polygon p_type;
public:
rectangle():p_type("a default value") // 注意此行
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
// 构造函数可以被重载
rectangle(float width, float height, string type):width(width),height(height), p_type(type)
{
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
rectangle rec2(12, 5, "rectangle");
// rectangle rec3 = {12, 5, "rectangle"}; // 部分版本报错
return 0;
}
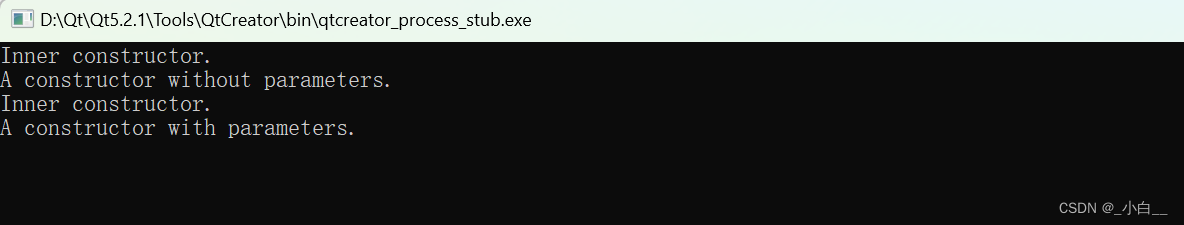
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class polygon
{
string type;
public:
// 注意:加上自定义的无参构造函数后,外部类可以不写无参构造的初始化列表。见 L27.
polygon()
{
cout << "There's nothing." << endl;
}
polygon(string type)
{
this->type = type;
cout << "Inner constructor." << endl;
}
};
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
polygon p_type;
public:
rectangle()//:p_type("a default value")
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
// 构造函数可以被重载
rectangle(float width, float height, string type):width(width),height(height), p_type(type)
{
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
rectangle rec2(12, 5, "rectangle");
// rectangle rec3 = {12, 5, "rectangle"}; // 部分版本报错
return 0;
}
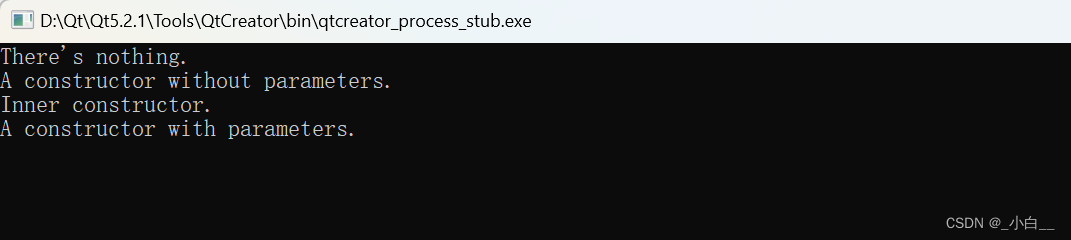
构造函数 v.s. 析构函数
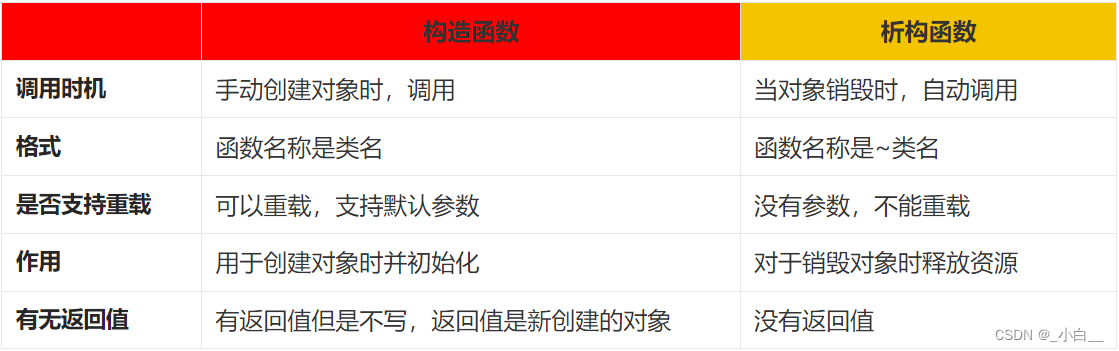
析构函数(不支持重载)
在类对象空间消亡时,系统自动调用。
~类名()
{
// 函数体
}
调用时机(先构造的后析构,后构造的先析构)
栈区:类对象消亡时,系统自动调用
堆区:使用 delete 释放空间时,系统调用析构函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class polygon
{
string type;
public:
polygon()
{
cout << "There's nothing." << endl;
}
~polygon()
{
cout << "Destructor of polygon." << endl;
}
};
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
polygon p_type;
public:
rectangle()
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
rectangle *p;
p = new rectangle;
delete p;
return 0;
}
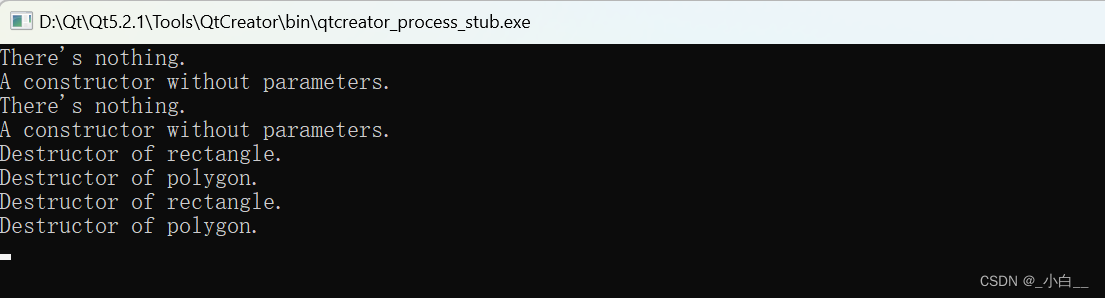
需要显性写出析构函数的情况(类指针成员指向堆区空间)
类中有指针成员,并且指针成员指向堆区空间。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
rectangle():ptr(new int) // 保证指针成员 指向 堆区空间
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
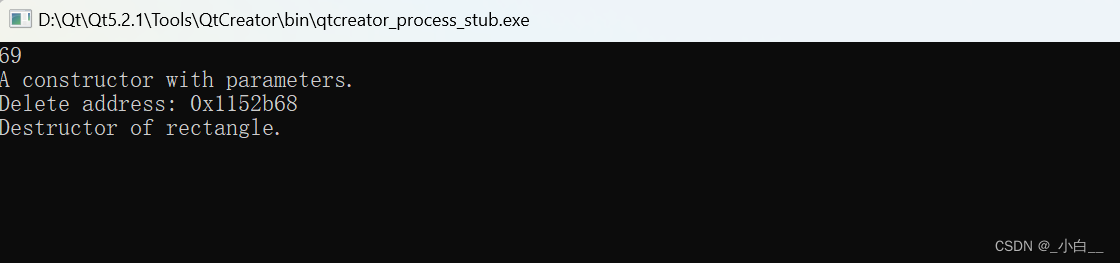
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
rectangle rec1;
return 0;
}
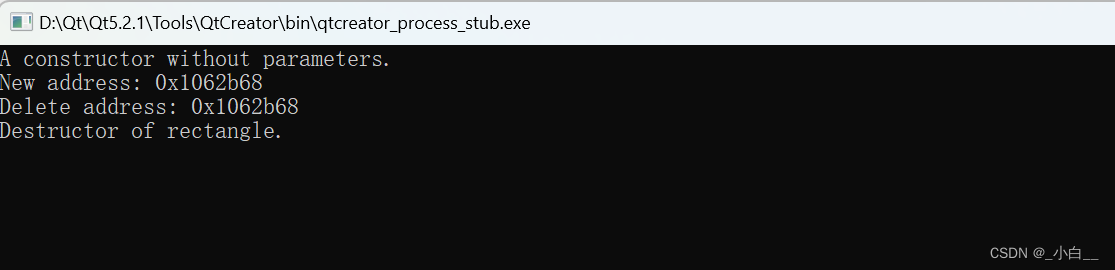
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
rectangle():ptr(new int) // 保证指针成员 指向 堆区空间
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{ // 不能用 int *ptr
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
int num = 69;
int *p = #
rectangle rec1(12, 5, *p);
return 0;
}
拷贝构造函数
利用 一个类对象 给另一个类对象初始化时,自动调用拷贝构造函数(浅拷贝)。
如果自定义了拷贝构造,则系统不再提供默认的拷贝构造。
类名 ( 被拷贝的同类对象的引用 )
{
// 函数体
}
浅拷贝构造(系统自动完成)
// 浅拷贝构造(系统自动完成)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
void show();
rectangle():ptr(new int) // 保证指针成员 指向 堆区空间
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Ptr = " << ptr << endl;
}
int main()
{
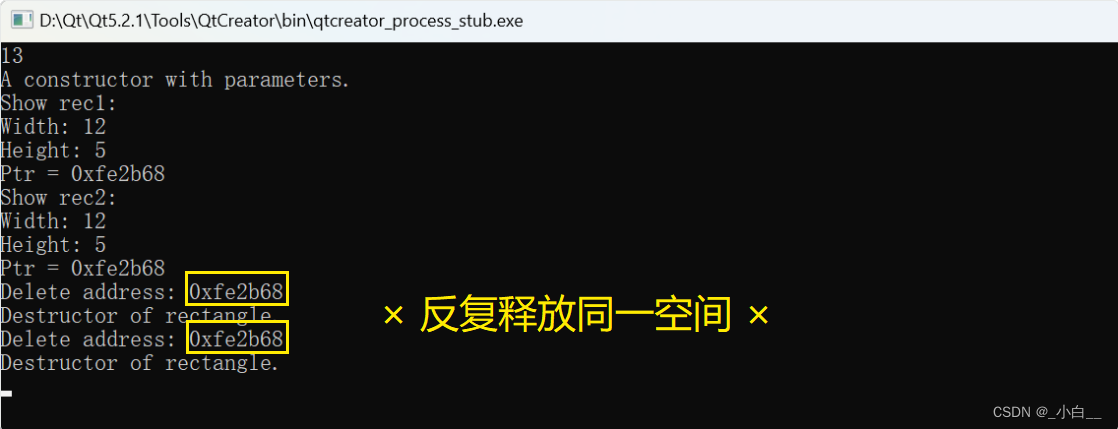
rectangle rec1(12, 5, 13);
cout << "Show rec1: " << endl;
rec1.show();
rectangle rec2 = rec1;
cout << "Show rec2: " << endl;
rec2.show();
return 0;
}
尝试手动添加拷贝构造函数
// 半成品(累了请忽略)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
void show();
rectangle():ptr(new int)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
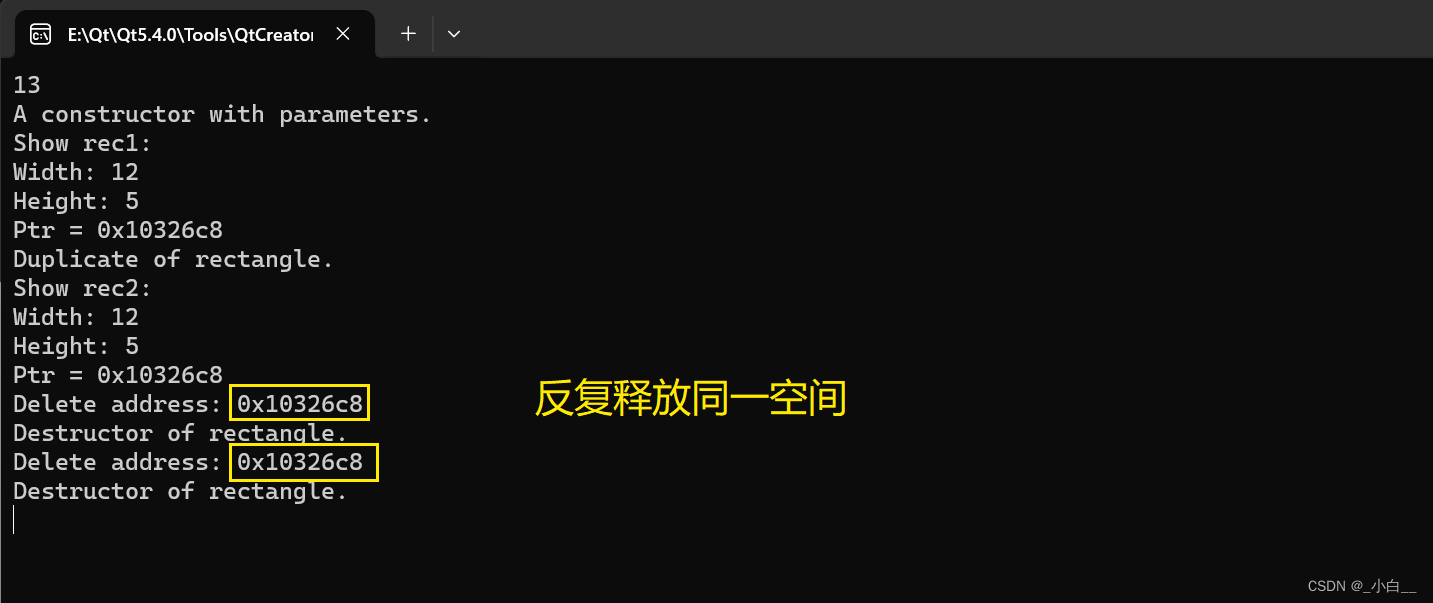
rectangle(rectangle &other) // 注意此行
{
this->width = other.width;
this->height = other.height;
this->ptr = other.ptr;
cout << "Duplicate of rectangle. " << endl;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Ptr = " << ptr << endl;
}
int main()
{
rectangle rec1(12, 5, 13);
cout << "Show rec1: " << endl;
rec1.show();
rectangle rec2 = rec1;
cout << "Show rec2: " << endl;
rec2.show();
return 0;
}
深拷贝构造
// 深拷贝构造
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
void show();
rectangle():ptr(new int)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
rectangle(rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height), ptr(new int(*(other.ptr)))
{ // 使用同类其他对象的指针成员解引用后的值,给自己的指针成员的内容初始化
// this->width = other.width;
// this->height = other.height;
// this->ptr = new int (*(other.ptr)); // 也可以,是赋值,不是初始化列表
cout << "Duplicate of rectangle. " << endl;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Ptr = " << ptr << endl;
}
int main()
{
rectangle rec1(12, 5, 13);
cout << "Show rec1: " << endl;
rec1.show();
rectangle rec2 = rec1;
cout << "Show rec2: " << endl;
rec2.show();
return 0;
}
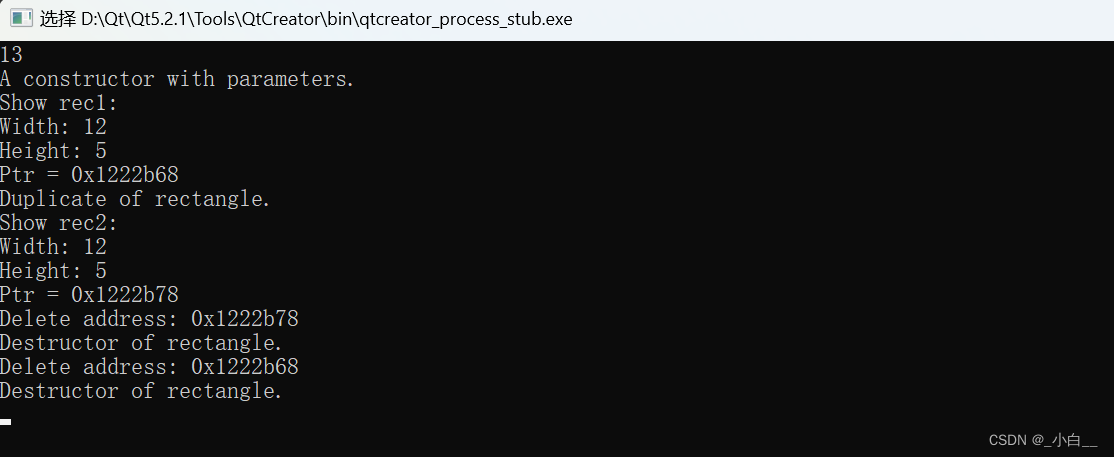
【思考】 深拷贝的代码是否存在隐患?
存在,new 开辟的空间无法释放,造成内存泄漏的问题。所以需要显性写出析构函数(见上面)。
调用时机(利用 一个类对象 给另一个类对象初始化)
1、使用已有的类对象,给新的类对象初始化
2、函数的参数是一个类对象时,也会调用拷贝构造函数
3、函数的返回值是一个类对象时,也会调用拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
public:
void show();
rectangle()
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height):width(width), height(height)
{
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
rectangle(rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height)
{
cout << "Duplicate of rectangle. " << endl;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
}
rectangle fun(rectangle s1) // 应该这样写:rectangle &fun(rectangle &s1)
{
return s1;
}
int main()
{
rectangle s(12, 5);
fun(s).show();
// rectangle s2(fun(s)); // 会报错,因为 fun(s) 的返回值是一个临时值,不能引用
return 0;
}
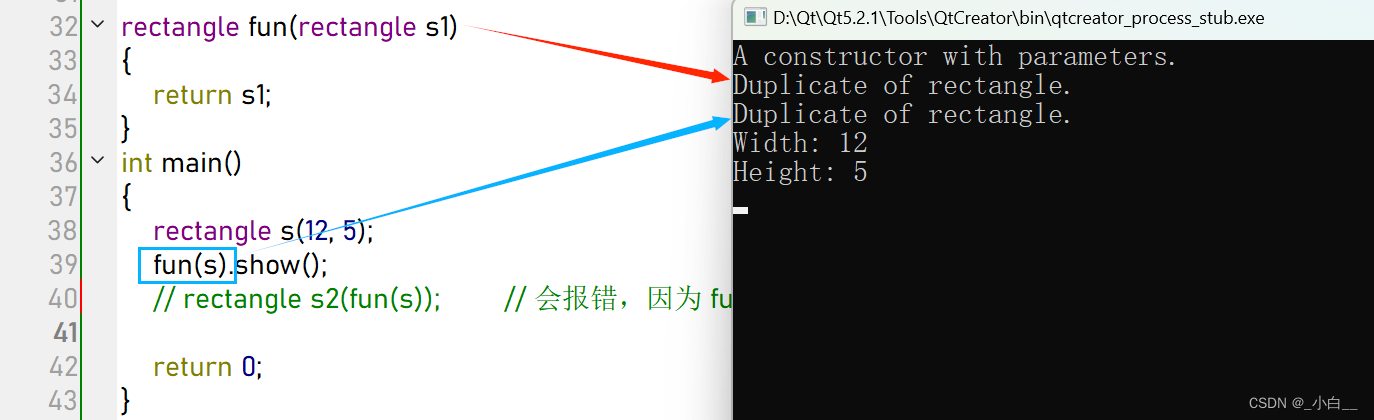
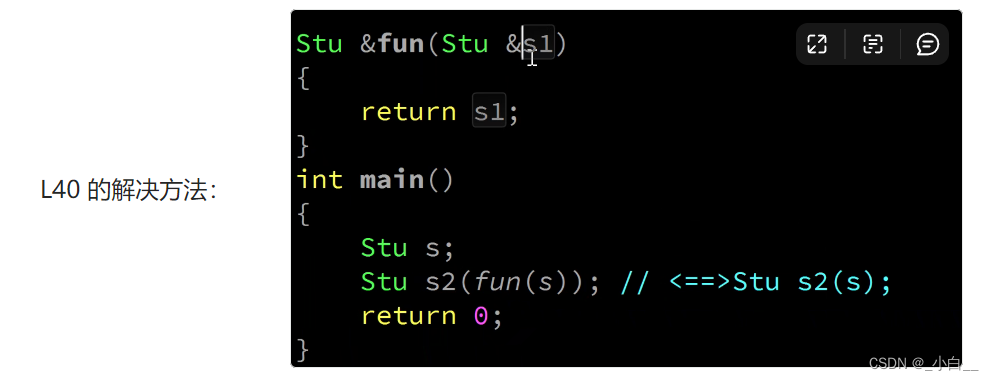
深浅拷贝问题**
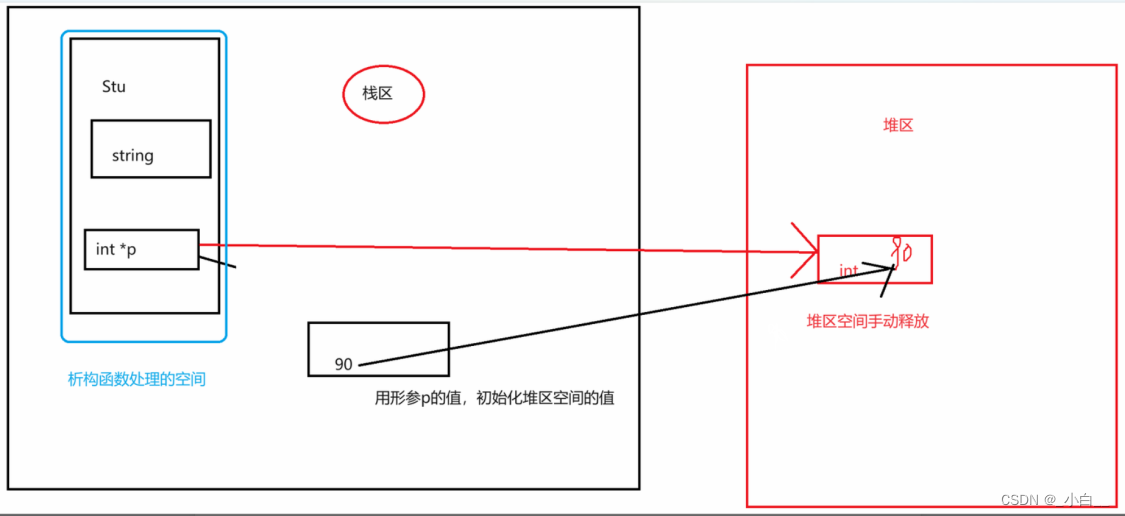
当类中有指针成员,会涉及到深浅拷贝问题。
默认的拷贝构造函数会导致两个对象的成员变量指向同一处。不符合面向对象的设计规范。这种现象被称为“浅拷贝”。
必须手动重写拷贝构造函数,使每次赋值都创建一个新的副本,从而每个对象单独持有自己的成员变量。这种方式就是“深拷贝”。
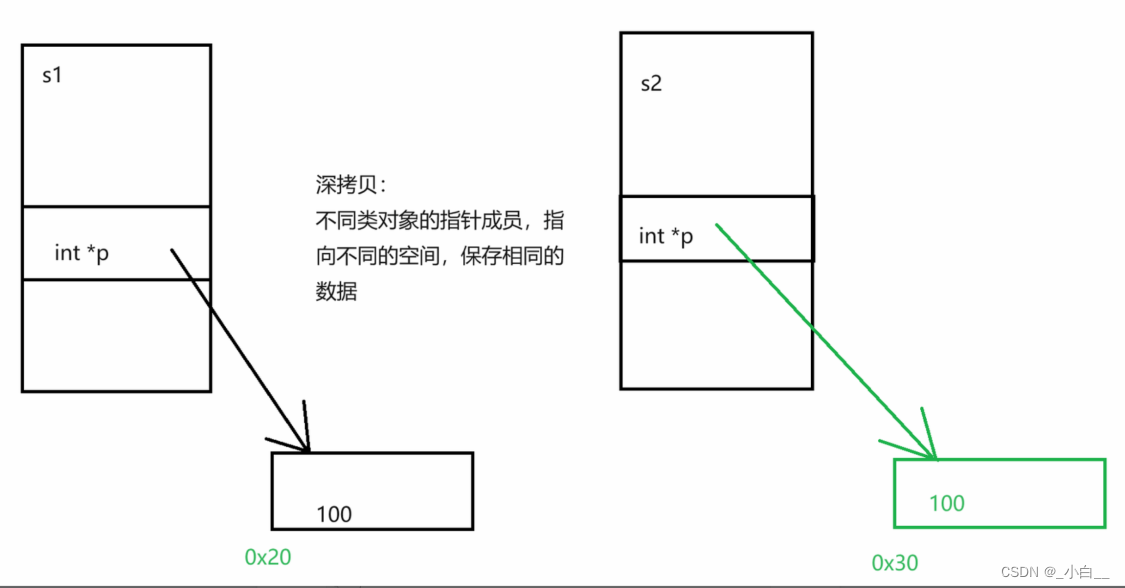
浅拷贝:两个(多个)对象的指针成员,指向同一片空间。
(不写拷贝构造函数或拷贝赋值函数,系统自动生成)
产生问题:同一片空间被两个不同的类对象占用,发生资源抢占。析构时会发生二次释放问题。
深拷贝:两个(多个)对象的指针成员,指向不同的空间,但保存的是同样的数据。
(手动书写拷贝构造函数或拷贝赋值函数)
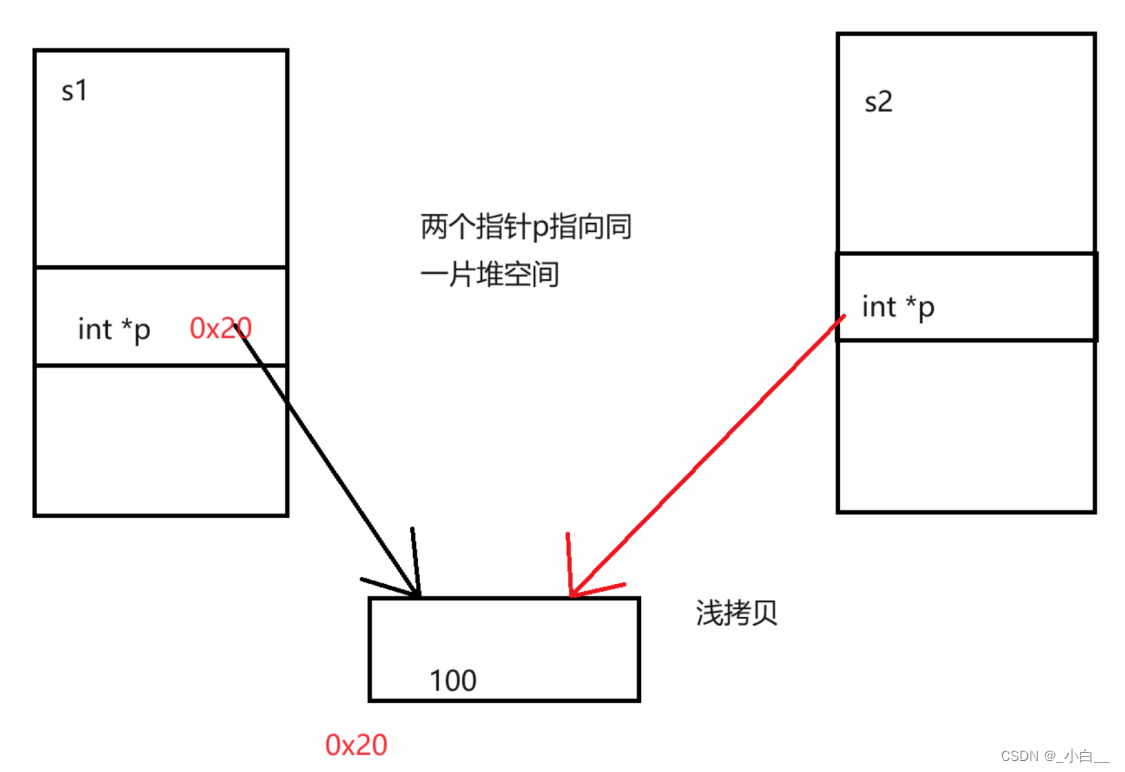
● 在需求不受影响的前提下,可以直接通过屏蔽拷贝构造函数(私有化)来解决浅拷贝问题,但不建议如此。
拷贝赋值函数
使用 已有的类对象 给另外一个已有的类对象 赋值。系统默认提供一个拷贝赋值函数。
本质:赋值运算符的重载。
类名 &operator = (const 类名 &other)
{
// 函数体
}
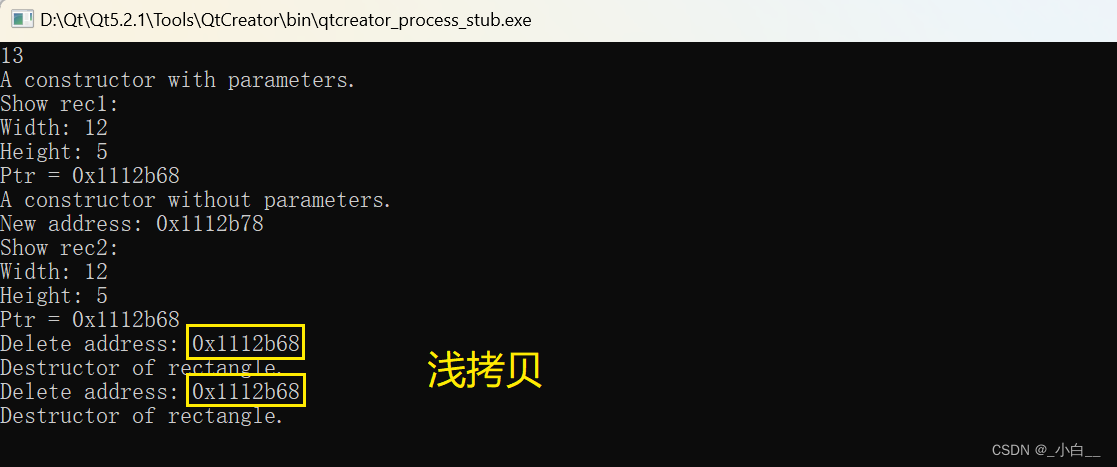
浅拷贝赋值
// 浅拷贝赋值(默认缺省,系统自动完成)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
void show();
rectangle():ptr(new int)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
rectangle(rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height), ptr(new int(*(other.ptr)))
{
cout << "Duplicate of rectangle. " << endl;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Ptr = " << ptr << endl;
}
int main()
{
rectangle rec1(12, 5, 13);
cout << "Show rec1: " << endl;
rec1.show();
rectangle rec2;
rec2 = rec1;
cout << "Show rec2: " << endl;
rec2.show();
return 0;
}
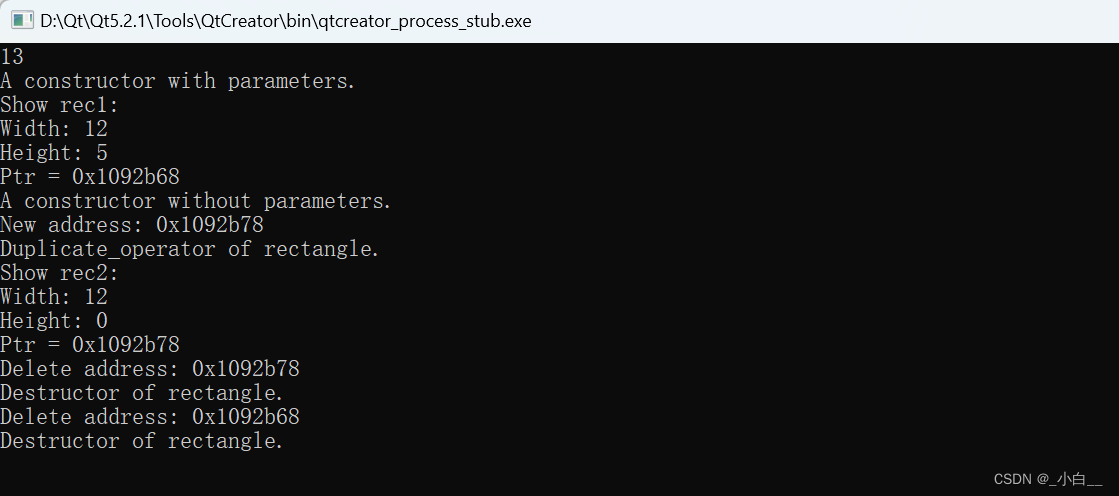
深拷贝赋值
// 深拷贝赋值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rectangle
{
private:
float width;
float height;
int *ptr;
public:
void show();
rectangle():ptr(new int)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "New address: " << ptr << endl;
}
rectangle(float width, float height, int ptr):width(width), height(height), ptr(new int(ptr))
{
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
~rectangle()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << ptr << endl;
delete ptr;
cout << "Destructor of rectangle." << endl;
}
rectangle(rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height), ptr(new int(*(other.ptr)))
{
cout << "Duplicate_constructor of rectangle. " << endl;
}
rectangle &operator = (const rectangle &other)
{
this->width = other.width;
// this->height = other.height;
*ptr = *(other.ptr);
cout << "Duplicate_operator of rectangle. " << endl;
return *this;
}
};
void rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Width: " << width << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Ptr = " << ptr << endl;
}
int main()
{
rectangle rec1(12, 5, 13);
cout << "Show rec1: " << endl;
rec1.show();
rectangle rec2;
rec2 = rec1; // 注意:拷贝构造函数是定义对象的同时初始化,拷贝赋值函数是先定义对象再赋值
cout << "Show rec2: " << endl;
rec2.show();
return 0;
}
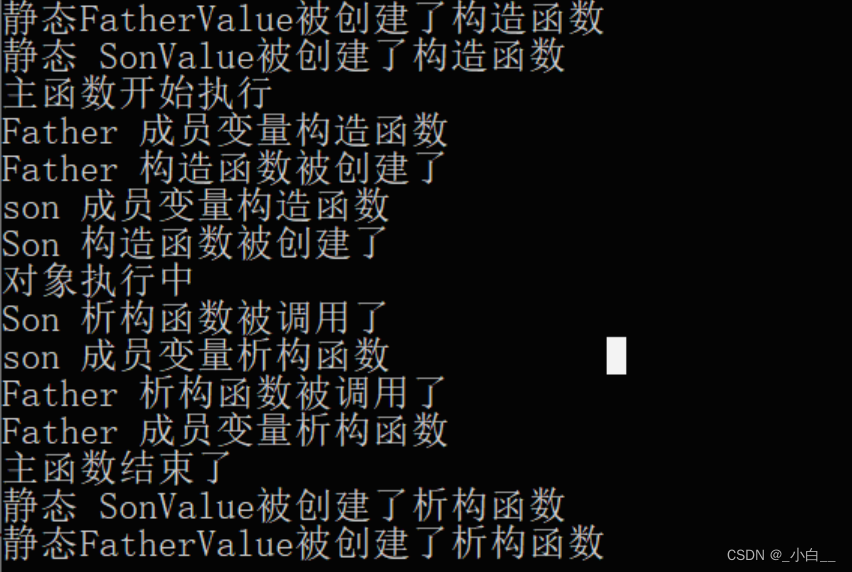
对象的创建与销毁流程
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Value
{
private:
string str;
public:
Value(string str):str(str)
{
cout << str << "构造函数" << endl;
}
~Value()
{
cout << str << "析构函数" << endl;
}
};
class Father
{
public:
static Value s_value;
Value val = Value("Father 成员变量");
Father()
{
cout << "Father 构造函数被创建了" << endl;
}
~Father()
{
cout << "Father 析构函数被调用了" << endl;
}
};
Value Father::s_value = Value("静态FatherValue被创建了");
class Son:public Father
{
public :
static Value s_value;
Value val = Value("son 成员变量");
Son()
{
cout << "Son 构造函数被创建了" << endl;
}
~Son()
{
cout << "Son 析构函数被调用了" <<endl;
}
};
Value Son::s_value = Value("静态 SonValue被创建了");
int main()
{
cout << "主函数开始执行"<< endl;
{
Son s;
cout << "对象执行中"<<endl;
} // Son s 的生命周期到此为止
cout << "主函数结束了" << endl;
return 0;
}
匿名对象
没有对象名,通过类名实例化出来的对象,生命周期短。 e.g. rectangle();
用作全局函数传参
// 方法一:
class rectangle
{
// ......
rectangle(rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height), ptr(new int(*(other.ptr)))
{
cout << "Duplicate_constructor of rectangle. " << endl;
}
// ......
}
void func(rectangle &&rec) // 注意此行
{
// ......
}
int main()
{
func(rectangle());
return 0;
}
// 方法二:
class rectangle
{
// ......
rectangle(const rectangle &other):width(other.width), height(other.height), ptr(new int(*(other.ptr)))
{
cout << "Duplicate_constructor of rectangle. " << endl;
}
// ......
}
void func(rectangle rec)
{
// ......
}
int main()
{
func(rectangle());
return 0;
}
临时使用类中的成员函数
rectangle().show();
给类对象的数组赋值
rectangle arr[2] = {rectangle(12, 5), rectangle(3, 4)};
给新的类对象赋值
rectangle recn(rectangle(6, 8));
💡 练习
定义一个 Person 类,包含私有属性:姓名、年龄、身高(通过指针实现)、性别(const成员)。
要求:写出类的构造函数,析构函数,拷贝构造函数 和 拷贝赋值函数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class person
{
private:
string name;
int age;
float *height;
const string gender;
public:
void show();
person();
person(string name, int age, float height, string gender);
~person();
person(person &other);
person &operator = (const person &other);
};
void person::show()
{
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
cout << "Age: " << age << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
cout << "Gender: " << gender << endl;
}
person::person():height(new float)
{
cout << "A constructor without parameters." << endl;
cout << "Height: " << height << endl;
}
person::person(string name, int age, float height, string gender):name(name), age(age), \
height(new float(height)), gender(gender)
{
// cout << height << endl;
cout << "A constructor with parameters." << endl;
}
person::~person()
{
cout << "Delete address: " << height << endl;
delete height;
cout << "Destructor of person." << endl;
}
person::person(person &other):name(other.name), age(other.age), \
height(new float(*(other.height))), gender(other.gender)
{
cout << "Duplicate_constructor of person. " << endl;
}
person &person::operator = (const person &other)
{
this->name = other.name;
this->age = other.age;
*height = *(other.height); // *(this->height) = *(other.height);
string *p = (string *)&this->gender;
*p = other.gender;
cout << "Duplicate_operator of person. " << endl;
return *this;
}
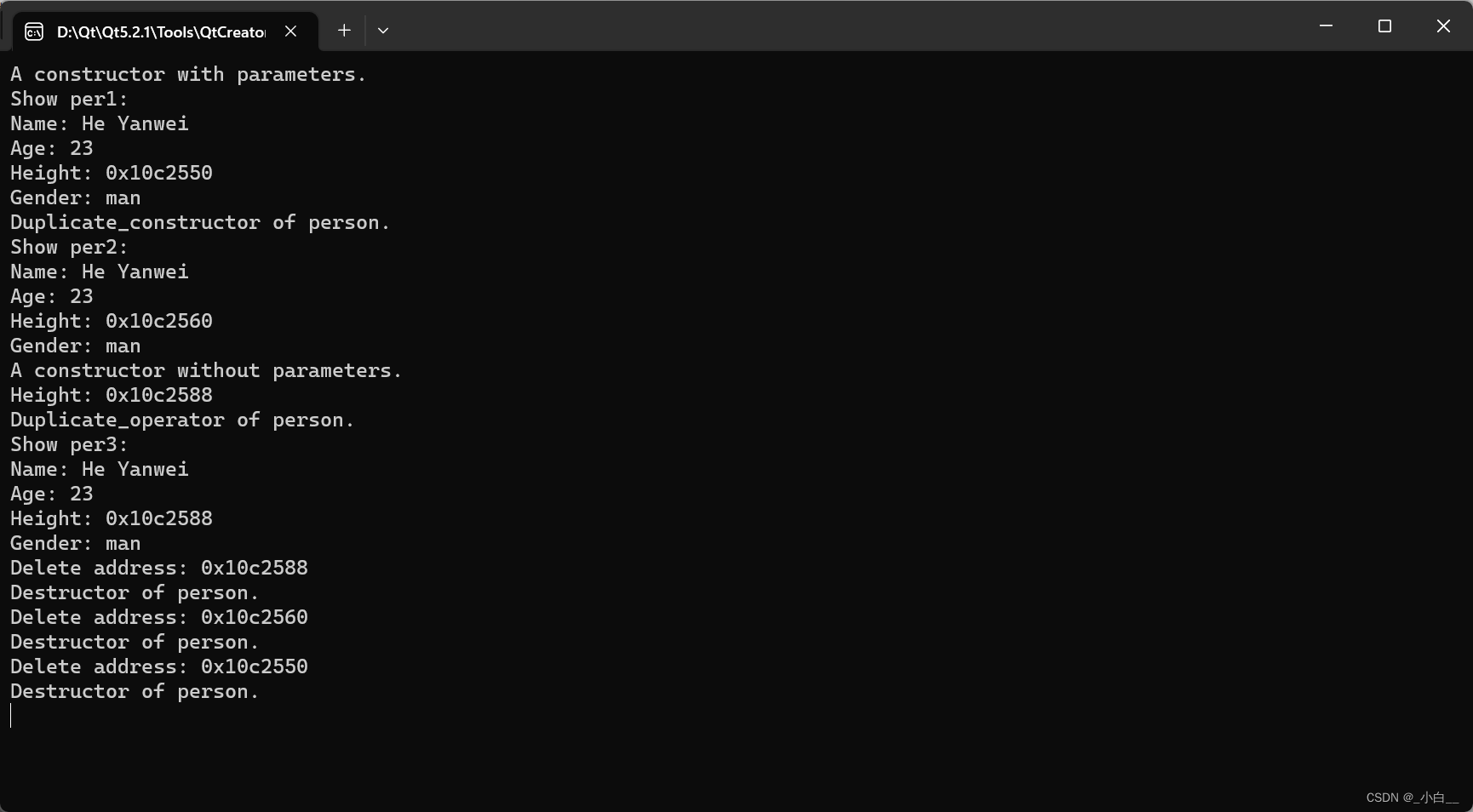
int main()
{
person per1("He Yanwei", 23, 180, "man");
cout << "Show per1: " << endl;
per1.show();
person per2 = per1;
cout << "Show per2: " << endl;
per2.show();
person per3;
per3 = per1;
cout << "Show per3: " << endl;
per3.show();
return 0;
}