日期类的实现
- 一,声明
- 二,函数成员定义
- 2.1构造函数
- 2.2获取月份天数
- 2.3比较运算符
- 2.3.1等于和大于
- 2.3.2其他
- 2.4计算运算符
- 2.4.1 +=&&+
- 2.4.2-=&&-
- 2.5日期-日期
一,声明
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);
//打印
void Print();
//获取月份天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
//比较运算符
bool operator==(const Date& y);
bool operator!=(const Date& y);
bool operator>(const Date& y);
bool operator<(const Date& y);
bool operator>=(const Date& y);
bool operator<=(const Date& y);
//计算运算符
int operator-(const Date& d);
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator-(int day);
Date& operator++();
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
二,函数成员定义
2.1构造函数
Date::Date(int year,int month,int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (_year < 1 || _month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
Print();
cout << "日期非法" << endl;
}
}
这里要注意,构造函数的声明定义分离,给缺省值的时候,只在声明的地方给,不然会出错。
2.2获取月份天数
//获取月份天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);
int monthArray[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
return 29;
return monthArray[month];
}
2.3比较运算符
2.3.1等于和大于
bool Date::operator==(const Date& y)
{
return _year == y._year
&& _month == y._month
&& _day == y._day;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& y)
{
if (_year > y._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == y._year)
{
if (_month > y._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_month == y._month)
{
if (_day > y._day)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
写完了这两个那么其他的运算符我们都可以复用来简化代码。
2.3.2其他
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& y)
{
return !(*this == y);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& y)
{
return (*this > y || *this == y);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& y)
{
return !(*this>=y);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& y)
{
return!(*this > y);
}
2.4计算运算符
2.4.1 +=&&+
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= (-day);
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_month = 1;
_year++;
}
}
return *this;
}
+可以复用+=
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
补充:这里除了+去复用+=,可以反过来吗?
这里我们就要从效率的角度去看待这个问题。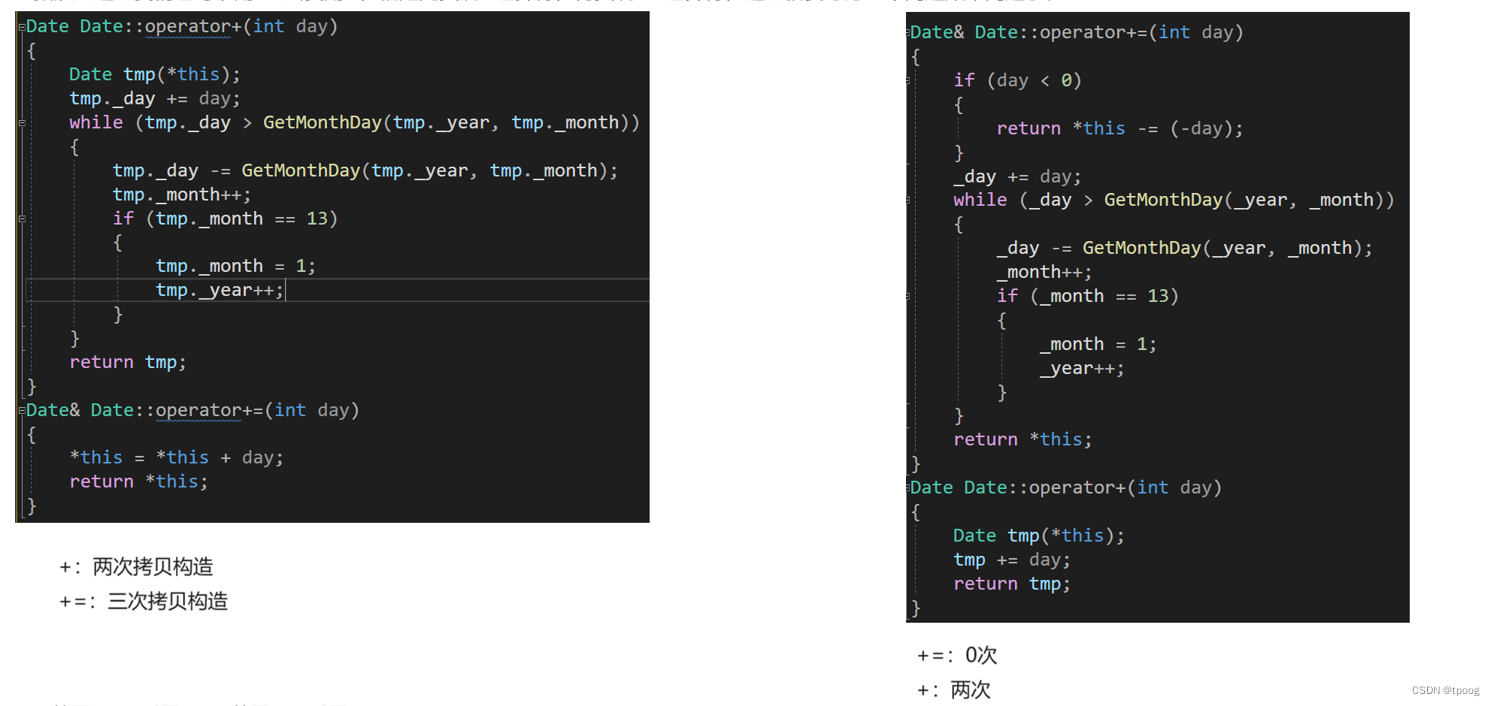
我们分别对比,他们的拷贝构造,可以看出用+=去复用+资源更浪费。
2.4.2-=&&-
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += (-day);
}
_day -= day;
while (_day<=0)
{
_month--;
if (_month < 1)
{
_month = 12;
_year--;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
一样的复用
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
2.4.3(前置++&&后置++)&&(前置–&&后置–)
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return* this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
为例区分前置和后置,我们会在后置的参数部分加一个参数类型。
2.5日期-日期
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
int flag = 1;
Date Max = *this;
Date Min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
Max = d;
Min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (Max != Min)
{
++Min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
找出两个天数中大的那个,然后让小的天数一直++,直到相等。