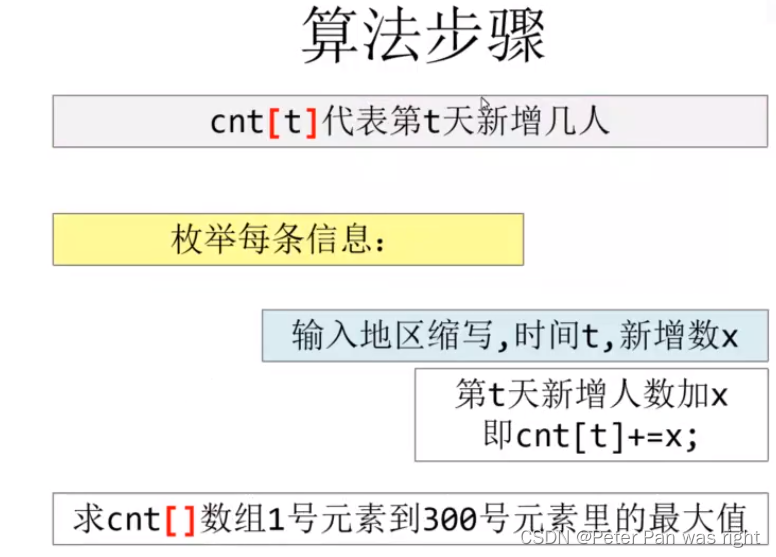
学习参考来自:
- Image Style Transform–关于图像风格迁移的介绍
- github:https://github.com/wmn7/ML_Practice/tree/master/2019_06_03
文章目录
- 风格迁移
风格迁移
风格迁移出处:
《A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style》(arXiv-2015)


风格迁移的实现

让 Random Image 在内容上可以接近 Content Image,在风格上可以接近 Style Image,当然, Random Image 可以初始化为 Content Image
导入基本库,数据读取
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.models as models
import numpy as np
import copy
import os
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def image_loader(image_name, imsize):
loader = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(imsize), # scale images
transforms.ToTensor()
])
image = Image.open(image_name).convert("RGB")
image = loader(image).unsqueeze(0)
return image.to(device, torch.float)
def image_util(img_size=512, style_img="./1.jpg", content_img="./2.jpg"):
"the size of style_img and contend_img should be same"
imsize = img_size if torch.cuda.is_available() else 128 # use small size if no gpu
style_img = image_loader(style_img, imsize)
content_img = image_loader(content_img, imsize)
print("Style Image Size:{}".format(style_img.size()))
print("Content Image Size:{}".format(content_img.size()))
assert style_img.size() == content_img.size(), "we need to import style and content images of the same size"
return style_img, content_img
定义内容损失

"content loss"
class ContentLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target):
super(ContentLoss, self).__init__()
self.target = target.detach()
def forward(self, input):
self.loss = F.mse_loss(input, self.target)
return input
定义风格损失
def gram_matrix(input):
a, b, c, d = input.size() # N, C,
features = input.view(a * b, c * d)
G = torch.mm(features, features.t())
return G.div(a * b * c * d)

Gram Matrix 最后输出大小只和 filter 的个数有关(channels),上面的例子输出为 3x3
Gram Matrix 可以表示出特征出现的关系(特征 f1、f2、f3 之间的关系)。
我们可以通过计算 Gram Matrix 的差,来计算两张图片风格上的差距

class StyleLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target_feature):
# we "detach" the target content from the tree used to dynamically
# compute the gradient: this is stated value, not a variable .
# Otherwise the forward method of the criterion will throw an error
super(StyleLoss, self).__init__()
self.target = gram_matrix(target_feature).detach()
def forward(self, input):
G = gram_matrix(input)
self.loss = F.mse_loss(G, self.target)
return input
写好前处理减均值,除方差
"based on VGG-16"
"put the normalization to the first layer"
class Normalization(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
super(Normalization, self).__init__()
# view the mean and std to make them [C,1,1] so that they can directly work with image Tensor of shape [B,C,H,W]
self.mean = mean.view(-1, 1, 1) # [3] -> [3, 1, 1]
self.std = std.view(-1, 1, 1)
def forward(self, img):
return (img - self.mean) / self.std
定义网络,引入 loss
"modify to a style network"
def get_style_model_and_losses(cnn, normalization_mean, normalization_std,
style_img, content_img,
content_layers,
style_layers):
cnn = copy.deepcopy(cnn)
# normalization module
normalization = Normalization(normalization_mean, normalization_std).to(device)
# just in order to have an iterable acess to or list of content / style
# losses
content_losses = []
style_losses = []
# assuming that cnn is a nn.Sequantial, so we make a new nn.Sequential to put
# in modules that are supposed to be activated sequantially
model = nn.Sequential(normalization)
i = 0 # increment every time we see a conv
for layer in cnn.children():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
i += 1
name = "conv_{}".format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
name = "relu_{}".format(i)
layer = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
name = "pool_{}".format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.BatchNorm2d):
name = "bn_{}".format(i)
else:
raise RuntimeError("Unrecognized layer: {}".format(layer.__class__.__name__))
model.add_module(name, layer)
if name in content_layers:
# add content loss
target = model(content_img).detach()
content_loss = ContentLoss(target)
model.add_module("content_loss_{}".format(i), content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
if name in style_layers:
# add style loss
target_feature = model(style_img).detach()
style_loss = StyleLoss(target_feature)
model.add_module("style_loss_{}".format(i), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
# now we trim off the layers afater the last content and style losses
for i in range(len(model)-1, -1, -1):
if isinstance(model[i], ContentLoss) or isinstance(model[i], StyleLoss):
break
model = model[:(i+1)]
return model, style_losses, content_losses
def get_input_optimizer(input_img):
optimizer = optim.LBFGS([input_img.requires_grad_()])
return optimizer
def run_style_transfer(cnn, normalization_mean, normalization_std, content_img, style_img, input_img, content_layers,
style_layers, num_steps=50, style_weight=1000000, content_weight=1):
print('Building the style transfer model..')
model, style_losses, content_losses = get_style_model_and_losses(cnn, normalization_mean, normalization_std,
style_img, content_img, content_layers,
style_layers)
optimizer = get_input_optimizer(input_img) # 网络不变,反向传播优化的是输入图片
print('Optimizing..')
run = [0]
while run[0] <= num_steps:
def closure():
# correct the values of updated input image
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
model(input_img) # 前向传播
style_score = 0
content_score = 0
for sl in style_losses:
style_score += sl.loss
for cl in content_losses:
content_score += cl.loss
style_score *= style_weight
content_score *= content_weight
# loss为style loss 和 content loss的和
loss = style_score + content_score
loss.backward() # 反向传播
# 打印loss的变化情况
run[0] += 1
if run[0] % 50 == 0:
print("run {}:".format(run))
print('Style Loss : {:4f} Content Loss: {:4f}'.format(
style_score.item(), content_score.item()))
print()
return style_score + content_score
# 进行参数优化
optimizer.step(closure)
# a last correction...
# 数值范围的纠正, 使其范围在0-1之间
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
return input_img
搭建完成,开始训练,仅优化更新 input image(get_input_optimizer),网络不更新
# 加载content image和style image
style_img,content_img = image_util(img_size=270, style_img="./style9.jpg", content_img="./content.jpg") # [1, 3, 270, 270]
# input image使用content image
input_img = content_img.clone()
# 加载预训练好的模型
cnn = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features.to(device).eval()
# 模型标准化的值
cnn_normalization_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).to(device)
cnn_normalization_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).to(device)
# 定义要计算loss的层
content_layers_default = ['conv_4']
style_layers_default = ['conv_1', 'conv_2', 'conv_3', 'conv_4', 'conv_5']
# 模型进行计算
output = run_style_transfer(cnn, cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std,
content_img, style_img, input_img,
content_layers=content_layers_default,
style_layers=style_layers_default,
num_steps=300, style_weight=100000, content_weight=1)
image = output.cpu().clone()
image = image.squeeze(0) # ([1, 3, 270, 270] -> [3, 270, 270])
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage()
image = unloader(image)
import cv2
image = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite("t9.jpg", image)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
"""VGG-19
Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(17): ReLU(inplace=True)
(18): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(19): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(24): ReLU(inplace=True)
(25): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(26): ReLU(inplace=True)
(27): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(31): ReLU(inplace=True)
(32): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(33): ReLU(inplace=True)
(34): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(35): ReLU(inplace=True)
(36): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
"""
"""modify name, add loss layer
Sequential(
(0): Normalization()
(conv_1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_1): StyleLoss()
(relu_1): ReLU()
(conv_2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_2): StyleLoss()
(relu_2): ReLU()
(pool_2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_3): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_3): StyleLoss()
(relu_3): ReLU()
(conv_4): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(content_loss_4): ContentLoss()
(style_loss_4): StyleLoss()
(relu_4): ReLU()
(pool_4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_5): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_5): StyleLoss()
(relu_5): ReLU()
(conv_6): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_6): ReLU()
(conv_7): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_7): ReLU()
(conv_8): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_8): ReLU()
(pool_8): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_9): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_9): ReLU()
(conv_10): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_10): ReLU()
(conv_11): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_11): ReLU()
(conv_12): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_12): ReLU()
(pool_12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_13): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_13): ReLU()
(conv_14): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_14): ReLU()
(conv_15): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_15): ReLU()
(conv_16): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(relu_16): ReLU()
(pool_16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
"""
"""after trim
Sequential(
(0): Normalization()
(conv_1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_1): StyleLoss()
(relu_1): ReLU()
(conv_2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_2): StyleLoss()
(relu_2): ReLU()
(pool_2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_3): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_3): StyleLoss()
(relu_3): ReLU()
(conv_4): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(content_loss_4): ContentLoss()
(style_loss_4): StyleLoss()
(relu_4): ReLU()
(pool_4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv_5): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(style_loss_5): StyleLoss()
)
"""
原图,花宝叽

不同风格

产生的结果

更直观的展示