用cocos2dx引擎简单实现了一下navmesh的多边形划分,然后基于划分多边形的a*寻路。以及路径拐点优化算法
用cocos主要是方便使用一些渲染接口和定时器。重点是实现的原理。
首先画了一个带有孔洞的多边形
//多边形的顶点数据
Vec2(100, 100),
Vec2(300, 200),
Vec2(500, 50),
Vec2(650, 300),
Vec2(900, 200),
Vec2(1100, 30),
Vec2(1230, 400),
Vec2(1050, 550),
Vec2(850, 450),
Vec2(700, 600),
Vec2(500, 600),
Vec2(420, 270),
Vec2(350, 300),
Vec2(250, 550),
Vec2(200, 400),
Vec2(50, 300),
//孔洞的顶点数据
Vec2(550, 400),
Vec2(970, 230),
Vec2(800, 450),
Vec2(700, 420),
Vec2(580, 550),
Vec2(150, 150),
Vec2(250, 220),
Vec2(200, 300)
注意都是逆时针顺序
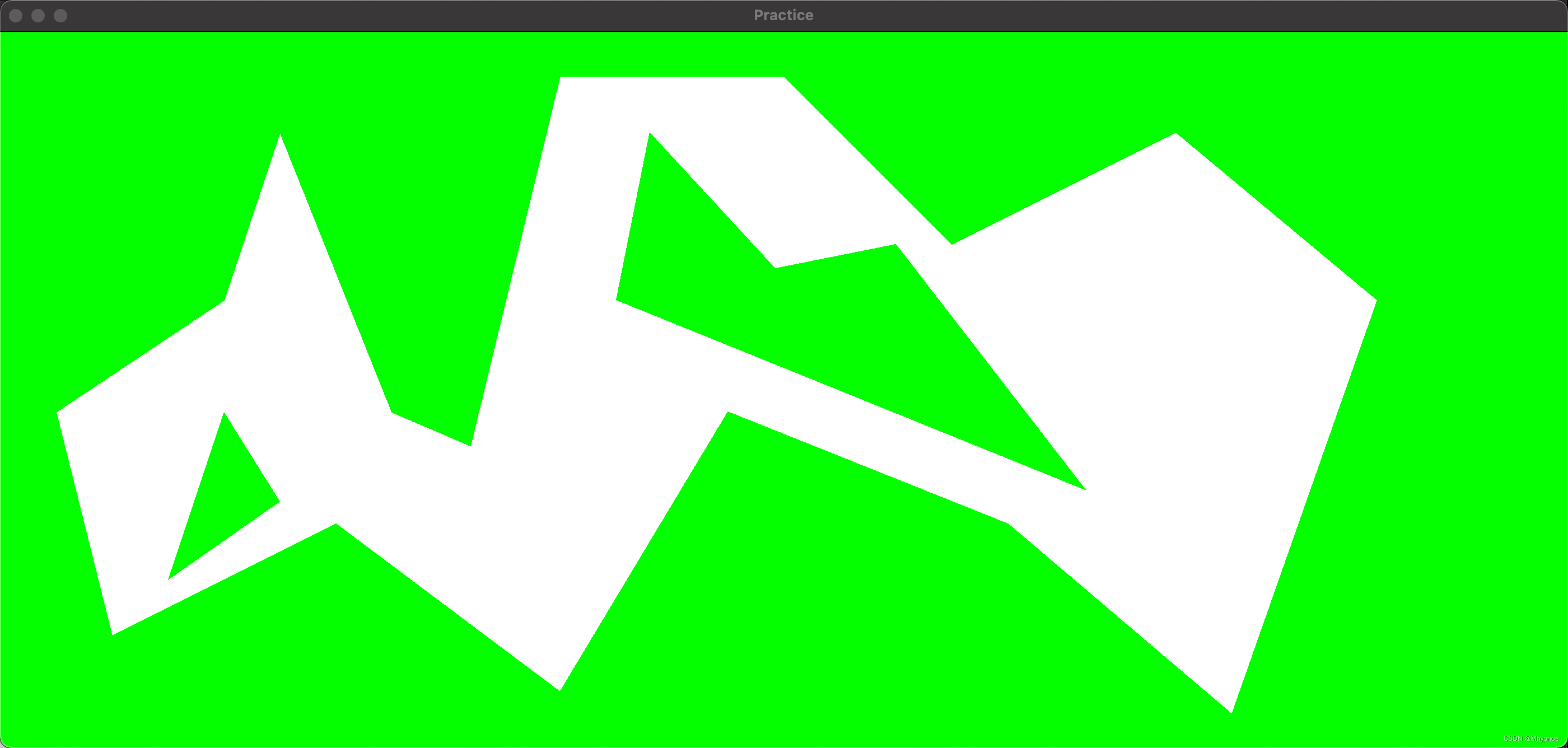

孔洞和整体多边形都是一个双向链表结构
void PolygonClass::insert(int id, Vec2 pos) {
Vertex* vert = new Vertex(id, pos);
if (_head == nullptr) {
_head = vert;
_head->next = vert;
_head->prev = vert;
}else {
Vertex* tail = _head->prev;
tail->next = vert;
vert->next = _head;
vert->prev = tail;
_head->prev = vert;
}
}
链表的节点Vertex即是地图上各个点的数据
class Vertex
{
public:
Vertex(int id, Vec2 pos) {
this->id = id;
this->pos = pos;
}
bool isSameVert(Vertex* vert) {
return vert->id == id && vert->pos == pos;
}
bool isSamePos(Vertex* vert) {
return vert->pos == pos;
}
int id;
Vec2 pos;
Vertex* next;
Vertex* prev;
};
孔洞连接
带有孔洞的多边形,首先要将孔洞和整体多边形连接起来。
孔洞是否在多边形内部
我在连接前加入了一个孔洞是否包含在多边形内部的逻辑判断
即相当于判断孔洞的所有顶点是否都在多边形内部
// 判断多边形hole是否被polygon完全包含
bool PolygonClass::isInnerHole(PolygonClass* hole) {
// hole的所有点都被polygon包含
Vertex* cur = hole->getHead();
if (_head == nullptr) return false;
do {
if (!this->isInnerVert(cur)) return false;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(hole->getHead()));
return true;
}
判定一个坐标点是否在一个多边形内部:从坐标点向右发射一条水平射线,判定水平射线与多边形所有边的交点数目,奇数则在内部,偶数则在外部。
bool PolygonClass::isInnerVec2(Vec2 vec) {
//从 顶点 向右 发射一条向右水平射线, 水平射线与所有边的交点数目,为奇数,则在内部, 为偶数,则在外部
Vertex* cur = _head;
int intersectLines = 0;
do {
if (GeometryMath::isRayIntersectLine(vec, cur->pos, cur->next->pos)) intersectLines++;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return intersectLines % 2 == 1;
}
判断一个射线与一条线段相交
线段与射线的几种关系:
1.射线与线段水平或重合,视作不相交。
2.线段在射线的上方或下方,不相交。
3.线段下方端点在线上, 与 线段上方端点的在线上的情况,即线段只有一个端点在射线上,只能选择一种作为相交,另一种作为不相交,如图下,
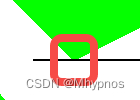

这两种情况,相邻两条线都是上端点或下端点在射线上,无论视作相不相交,都不影响结果的判断

但是如果是从中间穿过的话,一个是上端点在射线上,一个是下端点在射线上,只能取一种情况作为相交
4.线段两个端点分别在射线的上下方,则求线段在射线水平线上的x点,如果x点在向右的射线范围内则相交,否则不相交
bool GeometryMath::isRayIntersectLine(Vec2 vR, Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2) {
//线段水平,与射线重合或平行
if (vL1.y == vL2.y) return false;
//线段在 水平射线上方
if (vL1.y > vR.y && vL2.y > vR.y) return false;
//线段在 水平射线下方
if (vL1.y < vR.y && vL2.y < vR.y) return false;
float minY = min(vL1.y, vL2.y);
float maxY = min(vL1.y, vL2.y);
/*线段下方端点在线上, 与 线段上方端点的在线上的情况,只能选择一种作为相交,另一种作为不相交
否则射线穿过的顶点的相交判断会有问题
即maxY 或者 minY 只选择一种做判断*/
if (maxY == vR.y) return false;
//线段两个端点分别在 射线的上下, 求线段在 射线的水平线上的x点,判断x点与 射线起点x轴坐标(射线方向向右)
float offsetY = vL2.y - vR.y;
float offsetX = offsetY / (vL2.y - vL1.y) * (vL2.x - vL1.x);
float x = vL2.x - offsetX;
return x >= vR.x;
}
连接孔洞
连接孔洞与多边形,在孔洞上寻找一点v1,然后在多边形上寻找一点v2,保证v1与v2的连线不与任何孔洞以及多边形的边相交(两点的相邻边除外),并且连线在v2为顶点的角的内部以及在v1为顶点的角的外部。
// 从hole 选择一个顶点pA
// 从polygon选择一个顶点pB,保证与pA连线不与polygon以及hole上的任意非相邻边相交
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> NavMeshScene::getLinkHoleVertex(PolygonClass* polygon, PolygonClass* hole) {
Vertex* vertHole = hole->getHead();
do {
Vertex* vertPolygon = polygon->getHead();
do {
bool isInAngle = polygon->isLineInInnerAngle(vertHole, vertPolygon) && !hole->isLineInInnerAngle(vertPolygon, vertHole);
if (isInAngle) {
bool noIntersect = polygon->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole) && hole->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole);
for (auto hole = _holes.begin(); hole != _holes.end(); hole++) {
if (!(*hole)->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole)) {
noIntersect = false;
break;
}
}
if (noIntersect) return make_pair(vertPolygon, vertHole);
}
vertPolygon = vertPolygon->next;
} while (!vertPolygon->isSameVert(polygon->getHead()));
vertHole = vertHole->next;
} while (!vertHole->isSameVert(hole->getHead()));
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
判断线段是否在角的内侧
bool PolygonClass::isLineInInnerAngle(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2) {
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2)) return false;
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2->prev)) return false;
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2->next)) return false;
Vec2 vecL2Prev = vertL2->prev->pos;
Vec2 vecL2= vertL2->pos;
Vec2 vecL2Next = vertL2->next->pos;
Vec2 vecL1 = vertL1->pos;
if (GeometryMath::isInLeft(vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next)) return GeometryMath::checkVectorInConvexAngle(vecL1, vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next);
return GeometryMath::checkVectorInConcaveAngle(vecL1, vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next);
}
判断线段在劣角内部
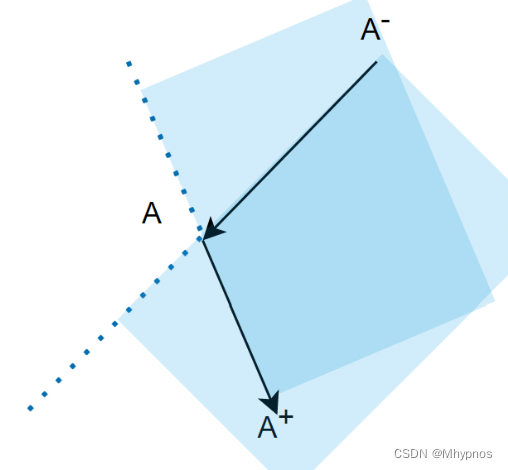
// 小于180°的角 ∠abc,点a,点b,点c是逆时针,判定线vb在角内, 线需在ab的左边,并且在bc的左边
bool GeometryMath::checkVectorInConvexAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return isInLeft(a, b, v) && isInLeft(b, c, v);
}
判断线段在优角内部
//大于180°的角 ∠abc,点a,点b,点c是逆时针,判定线vb在角内,即线不在∠abc的外侧,即线不在∠cba里
bool GeometryMath::checkVectorInConcaveAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return !checkVectorInConvexAngle(v, c, b, a);
}
角度大小判断
通过角的两条的相邻边的叉积判断
// 点 c 在a到b向量的左边, 即∠abc 小于180°
bool GeometryMath::isInLeft(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
float e = getVectorCross(a, b, c);
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) < 0;
}
// 点 c 在a到b向量的右边, 即∠abc 大于180°
bool GeometryMath::isInRight(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) > 0;
}
// 点 c 与a到b向量共线, 即∠abc 等于180°
bool GeometryMath::isCollineation(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) == 0;
}
int GeometryMath::getVectorCross(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
Vec2 vectorBA = a - b;
Vec2 vectorBC = c - b;
return vectorBA.cross(vectorBC);
}
判断线段是否与多边形非相邻边相交
bool PolygonClass::isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2) {
Vertex* cur = _head;
do {
if (!vertL1->isSamePos(cur) && !vertL1->isSamePos(cur->next) && !vertL2->isSamePos(cur) && !vertL2->isSamePos(cur->next)) {
if (GeometryMath::checkTwoVectorIntersect(vertL1->pos, vertL2->pos, cur->pos, cur->next->pos)) return false;
}
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return true;
}
判断两条线段是否相交
// 检查 vectorAB 与 vectorCD 相交
bool GeometryMath::checkTwoVectorIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd) {
if (isStrictlyIntersect(va, vb, vc, vd)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(va, vb, vc)) {
return true; }
if (isVertexInLine(va, vb, vd)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(vc, vd, va)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(vc, vd, vb)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
判断两条线段严格相交
其中一个线端有某个端点与另一条线段共线,或者一条线段两个端点都在另一条线段的另一边,则不严格相交
// 检查 vectorAB 与 vectorCD 严格相交, 点va,点vb在 线vectorCD 两侧, 且点vc,点vd 在线vectorAB 两侧
bool GeometryMath::isStrictlyIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd) {
if (isCollineation(va, vb, vc)) return false;
if (isCollineation(va, vb, vd)) return false;
if (isCollineation(vc, vd, va)) return false;
if (isCollineation(vc, vd, vb)) return false;
if (isInLeft(va, vb, vc) == isInLeft(va, vb, vd)) return false;
if (isInLeft(vc, vd, va) == isInLeft(vc, vd, vb)) return false;
return true;
}
判断点在线段内
// vert 在 vectorL12 线段之间
bool GeometryMath::isVertexInLine(Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2, Vec2 vert) {
if (!isCollineation(vL1, vL2, vert)) return false;
if (vL1.x == vL2.x) return (vert.y >= min(vL1.y, vL2.y)) && (vert.y <= max(vL1.y, vL2.y));
else return (vert.x >= min(vL1.x, vL2.x)) && (vert.x <= max(vL1.x, vL2.x));
}
获取到连线点v1,v2后,要复制两个连线点帮助接入孔洞顶点,孔洞的顶点要以顺时针的方式插入多边形的顶点。如图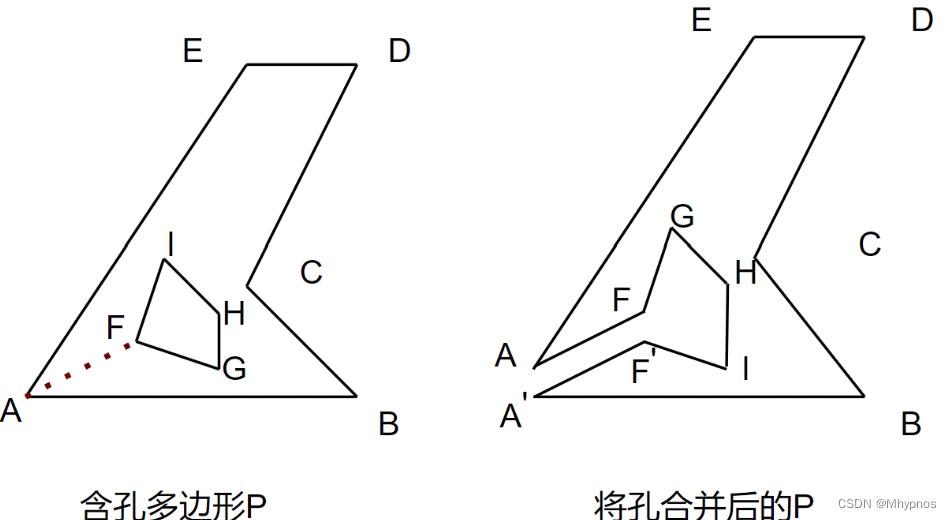
void NavMeshScene::linkHole() {
while (!_holes.empty()) {
PolygonClass* hole = _holes[0];
_holes.erase(_holes.begin());
if (_polygons.front()->isInnerHole(hole)) {
auto verts = getLinkHoleVertex(_polygons.front(), hole);
if (verts.second == nullptr || verts.first == nullptr) _holes.push_back(hole);
else {
auto drawNode = DrawNode::create();
drawNode->drawSegment(verts.first->pos, verts.second->pos, 0.5, Color4F(1, 0, 0, 1));
this->addChild(drawNode);
Vertex* vPolygon = verts.first;
Vertex* vertPolygonNext = vPolygon->next;
//hole的顶点需要顺时针插入polygon
Vertex* vHole = verts.second;
do {
Vertex* vert = new Vertex(vHole->id, vHole->pos);
vPolygon->next = vert;
vert->prev = vPolygon;
vPolygon = vert;
vHole = vHole->prev;
} while (!vHole->isSameVert(verts.second));
_newPointId++;
Vertex* newVHole = new Vertex(_newPointId, verts.second->pos);
newVHole->prev = vPolygon;
vPolygon->next = newVHole;
_newPointId++;
Vertex* newVPolygon = new Vertex(_newPointId, verts.first->pos);
newVHole->next = newVPolygon;
newVPolygon->prev = newVHole;
newVPolygon->next = vertPolygonNext;
vertPolygonNext->prev = newVPolygon;
float len = verts.first->pos.getDistance(verts.second->pos);
_linkHoleLines.emplace(new Line(verts.first, verts.second, len, drawNode));
delete hole;
hole = nullptr;
}
}
}
_isLinkHole = true;
}

分割凸多边形
找到多边形上的一个凹点,在寻找多边形内部与该凹点不相邻的一点,确保两点的连线完全在多边形内部,将此作为分割线把多边形分割成两个新的多边形。再对新分割出来的多边形进行循环操作,直到新分割的多边形里找不到凹点,即为凸多边形。
寻找分割点
分割线在多边形内部的判断:
1.即为分割线在以两个分割点为顶点的角的内部
2.分割线不与多边形任一条边相交(分割点相邻边除外)。
注意这里有一个重点,如果是有孔洞的多边形,经过上文的孔洞连线处理。会有同位置的重复顶点。如果这个顶点刚好是凹点,做非相邻边判断时要特殊处理。
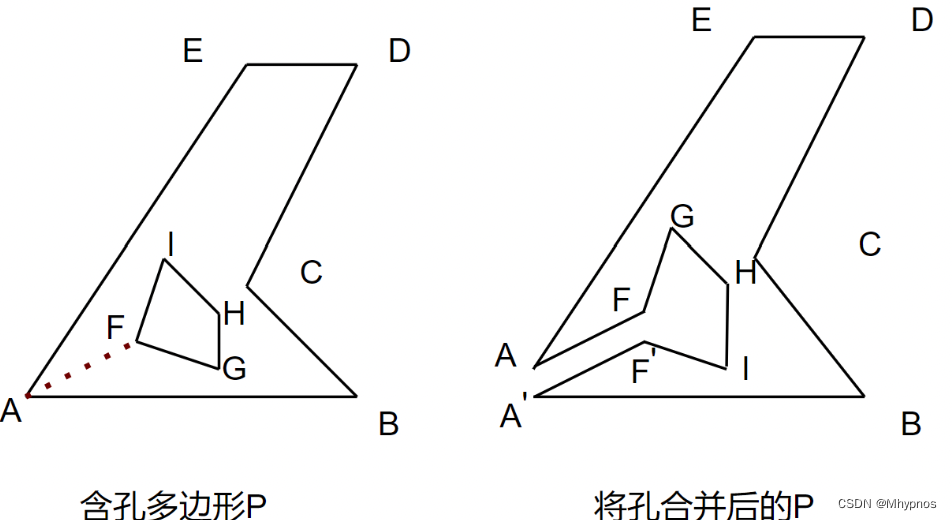
依旧是这张图,连接孔洞划分出的∠AFG,如果是凹点,那需要从F点出发找内部对角线。A′ F′ 不算F点的相邻边,但是又和F点同位置。此时如果分割线是往上,与A′ F′ 是不相交,如果是往下,与A′ F′ 又应该是相交的。
如果凹角是公共点,那新的内部对角线判断和其他边相交的时候,要忽略复制点连接的两条线。
例如从F出发寻找的内部对角线,相交线判断要忽略IF′ 和F′ A′ ,因为分割线必须在∠AFG内
如果A′ 是凹点,从A′ 出发的线,相交线判断要忽略EA和AF,因为线必须在∠F′ A′ B
//找到一个凹角顶点a
//从点a 找到一个 不相邻点b 且能连接成完全在内部的对角线,
//因为a为凹角,所以从a出发一定在∠a内, 则需要对角线在目标点的∠B内,且不与任何非相邻边相交
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> PolygonClass::findClipVert() {
auto srcVert = findConcaveVertex();
if (srcVert == nullptr) {
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
auto tarVert = srcVert->next->next;
do {
if (!tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert) && !tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert->next) && !tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert->prev)) {
bool isInAngle = isLineInInnerAngle(srcVert, tarVert) && isLineInInnerAngle(tarVert, srcVert);
bool isNoIntersect = isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(srcVert, tarVert);
if (isInAngle && isNoIntersect) return make_pair(srcVert, tarVert);
}
tarVert = tarVert->next;
} while (!tarVert->isSameVert(srcVert->prev));
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
形成新的多边形
注意,在分割完所有凸多边形后,把之前连接孔洞的线也加入分割线,作为下一步合并多边形的判断
void NavMeshScene::clipPolygon() {
while (!_polygons.empty()) {
PolygonClass* polygon = _polygons.front();
_polygons.pop();
auto verts = polygon->findClipVert();
if (verts.first == nullptr || verts.second == nullptr) {
//凸边形
polygon->setConvexPolygonId(_convexPolygonId);
_convexPolygons.emplace(_convexPolygonId, polygon);
_convexPolygonId++;
}
else {
auto drawNode = DrawNode::create();
this->addChild(drawNode);
drawNode->drawSegment(verts.first->pos, verts.second->pos, 0.5, Color4F(0, 0, 0, 1));
float len = verts.first->pos.getDistance(verts.second->pos);
_clipLines.push(new Line(verts.first, verts.second, len, drawNode));
auto tarPrev = verts.second->prev;
auto srcNext = verts.first->next;
verts.first->next = verts.second;
verts.second->prev = verts.first;
polygon->setHead(verts.first);
PolygonClass* newPolygon = new PolygonClass();
Vertex* tail = new Vertex(verts.first->id, verts.first->pos);
tail->next = srcNext;
srcNext->prev = tail;
Vertex* head = new Vertex(verts.second->id, verts.second->pos);
head->prev = tarPrev;
head->next = tail;
tarPrev->next = head;
tail->prev = head;
newPolygon->setHead(head);
_polygons.push(polygon);
_polygons.push(newPolygon);
}
}
_isClipPolygon = true;
// 在分割完所有凸多边形后,把连接孔洞的线也加入分割线,作为合并多边形的判断
while (!_linkHoleLines.empty()) {
_clipLines.push(_linkHoleLines.front());
_linkHoleLines.pop();
}
}
合并多边形
前一步的分割,在寻找分割点的时候并没有做特殊处理,因此可能出现在一个凹点,分割了多条线才使凹点小于180°的情况。而其中的某些分割线在去掉后,新的顶点角仍是凸点。
合并分割边的顺序是根据线段长度来判断,长度最长的优先进行能否合并判断,以尽量减少狭长的多边形。
判断分割线能否去除
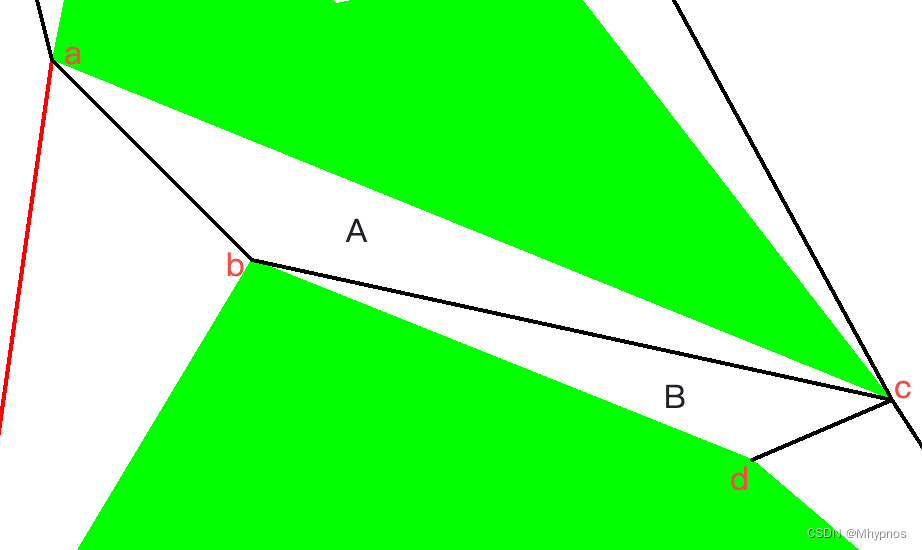
如图,根据分割边bc,找到相邻的两个多边形A和B,找到多边形A中分割点b的前一个顶点a,以及多边形B中分割点b的下一个顶点d,可判断若合并之后的∠abd是否小于180°。同理对另一个分割点c做相同判断
//获取分割边分割的凸多边形
tuple<PolygonClass*, PolygonClass*, Vertex*, Vertex*> NavMeshScene::getMergeInfo(Line* line) {
PolygonClass* firstPolygon = nullptr;
PolygonClass* secondPolygon = nullptr;
Vertex* vert1 = nullptr;
Vertex* vert2 = nullptr;
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
Vertex* linePrev = it.second->getLinePrevVert(line);
if (linePrev != nullptr) {
if (firstPolygon == nullptr) {
firstPolygon = it.second;
vert1 = linePrev;
}
else {
secondPolygon = it.second;
vert2 = linePrev;
break;
}
}
}
//能合并最大多边形判断
if (firstPolygon->getSize() + secondPolygon->getSize() - 2 > PolygonMaxVertex) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
if (!checkMergeLineAngle(vert1, vert2)) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
return make_tuple(firstPolygon, secondPolygon, vert1, vert2);
}
//判断分割边分割的两个凸多边形合并仍是凸多边形, 即分割边两个共享点在合并的凸多边形里是 凸点
bool NavMeshScene::checkMergeLineAngle(Vertex* linePrevVert1, Vertex* linePrevVert2) {
//求如果合并的新凸多边形, 公共边对应的两个角的顶点
Vec2 v1Prev = linePrevVert1->pos;
Vec2 v1 = linePrevVert1->next->pos;
Vec2 v1Next = linePrevVert2->next->next->next->pos;
Vec2 v2Prev = linePrevVert2->pos;
Vec2 v2 = linePrevVert2->next->pos;
Vec2 v2Next = linePrevVert1->next->next->next->pos;
if (GeometryMath::isInRight(v1Prev, v1, v1Next)) return false;
if (GeometryMath::isInRight(v2Prev, v2, v2Next)) return false;
return true;
}
合并成新多边形
void NavMeshScene::mergePolygon() {
while (!_clipLines.empty()) {
// 获取最长的分割边
auto line = _clipLines.top();
_clipLines.pop();
PolygonClass* firstPolygon;
PolygonClass* secondPolygon;
Vertex* vert1;
Vertex* vert2;
tie(firstPolygon, secondPolygon, vert1, vert2) = getMergeInfo(line);
if (firstPolygon == nullptr) {
_closeClipLines.push_back(line);
}
else {
_convexPolygons.erase(secondPolygon->getConvexPolygonId());
Vertex* cur = vert1->next;
Vertex* mergeEnd = vert1->next->next;
Vertex* next = vert2->next->next->next;
do {
Vertex* vNext = new Vertex(next->id, next->pos);
cur->next = vNext;
vNext->prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
next = next->next;
} while (!next->isSameVert(vert2->next));
cur->next = mergeEnd;
mergeEnd->prev = cur;
delete secondPolygon;
secondPolygon = nullptr;
line->drawNode->removeFromParent();
}
}
_isMergeTriangle = true;
}
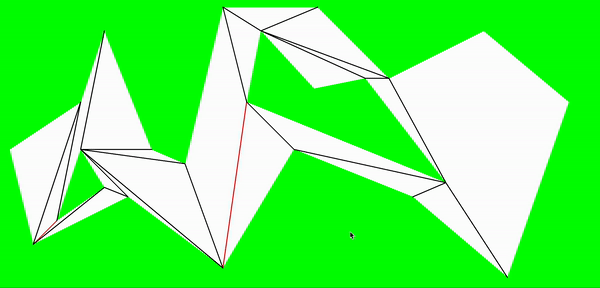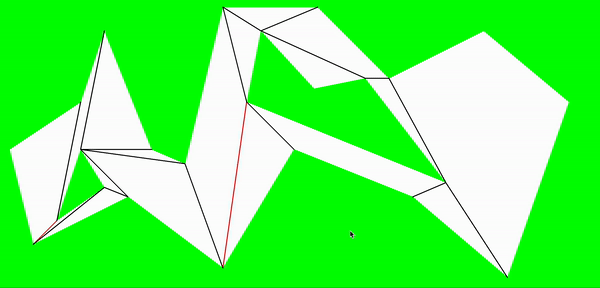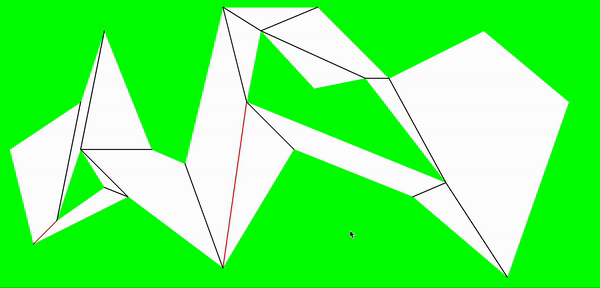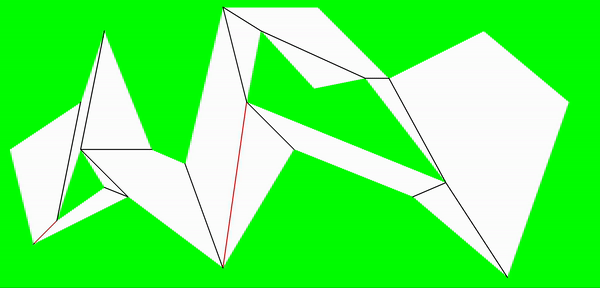
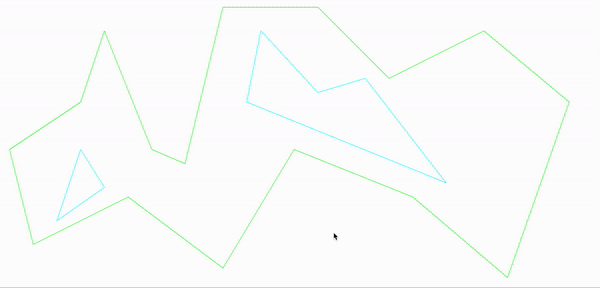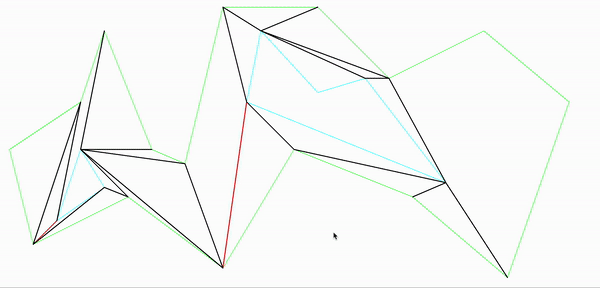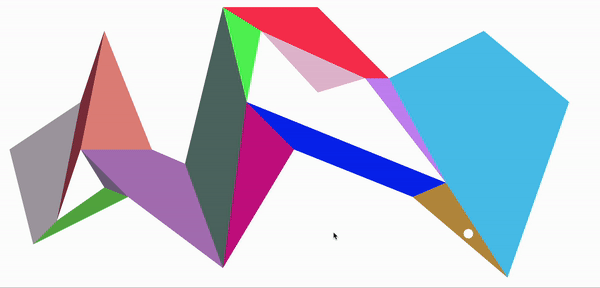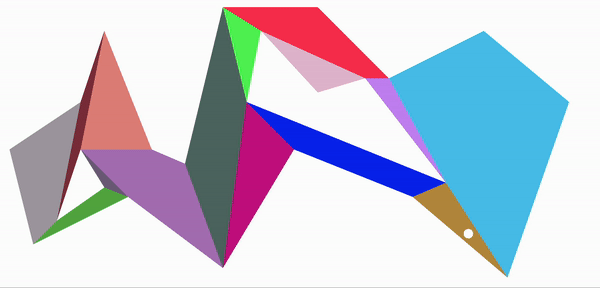
至此,把地图划分成了多个凸多边形,以据多边形以及分割边可以进行a*寻路处理
a*寻路
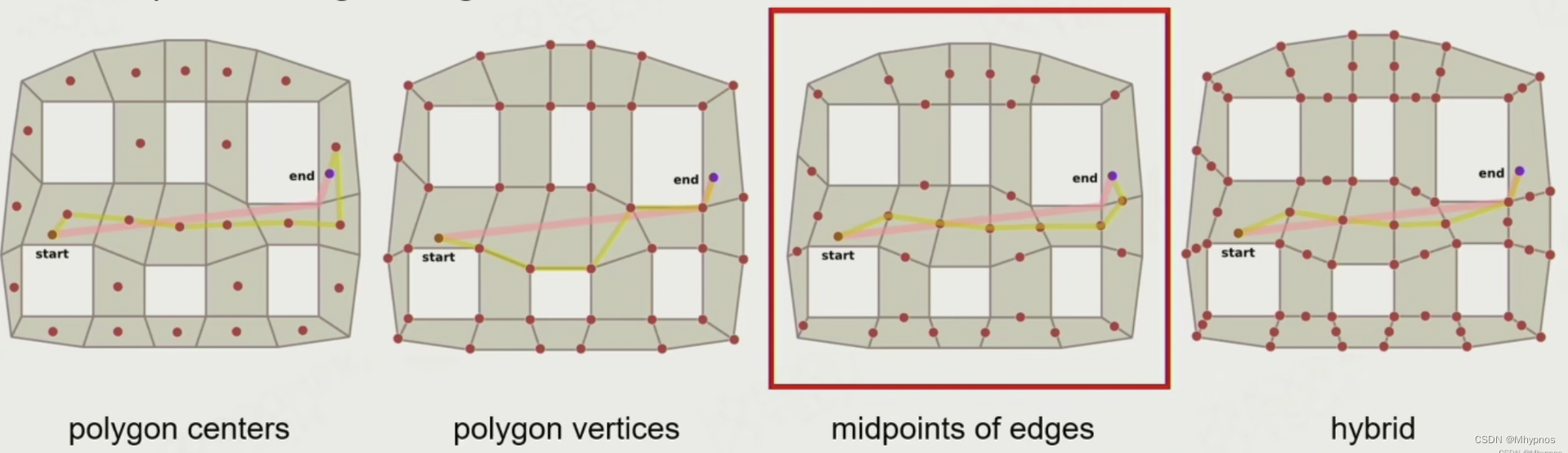
NavMesh进行a*寻路,有几种判断顶点的方式
1.以多边形的中心为寻路顶点
2.以分割边的两个端点为寻路顶点
3以分割边的中点为寻路顶点
4.以分割边的两个端点以及中点为寻路顶点
这里选择的是以分割边的中点作为寻路顶点
a*的思路
维护两个列表
openList:放的是当前可到达的顶点。最初的起点(起点所在多边形的边的中点)先放入这个表
closeList:放的是顶点数据被锁死不需要再修改的顶点,即已经求出最短路径的顶点
顶点数据包括:
route: 从起点到这个顶点移动的代价,或者说距离。
heuristicCost: 这个顶点到终点的估算代价/距离。这里直接用的是顶点与终点的距离做启发函数。
parentNode: 与route值的计算有关。route表示了从起点到这个顶点的路径消耗,parent指明了路径的方向,
srcPolygonIdx: 这里也记录了来源多边形,以便判断顶点的穿过方向
重复下面的步骤:
1.从openList中选中F值最小的顶点,作为探索顶点
2.把探索顶点换到closeList。因为探索顶点不会有新的更短的到起始位置的路径消耗。
3.以探索顶点寻找新的可到达的顶点,即探索顶点能到达的下一个凸多边形内其他边的中点。
对这些顶点进行判断:
*如果顶点不可通过或者已经在closeList忽略
*如果顶点不在openList中,以探索顶点作为父节点,计算顶点的route,heuristicCost等对应顶点数据,放入openList
*如果顶点已经在openList,顶点有旧的路径消耗(route),用探索顶点作为新的路径来计算route值,与旧的route值比较。如果新的route值小,则把顶点父节点设为当前探索顶点,route值刷新,来源多边形srcPolygonIdx也刷新。(也就是以当前探索顶点作为新路径和顶点记录的旧路径比较看哪个是这个顶点到起点的最短路径消耗。并记录下来)
重复上面三个步骤,直到:
1.到达了终点所在的凸多边形,寻路完成
2.openList已经空了,表示路径不存在,起点无法到达终点
注:如果终点和起点在同一多边形,可直接到达。凸多边形内任意两个可以直线到达
void NavMeshScene::moveToPath(Vec2 vec) {
int curPolygonIdx = -1;
int tarPolygonIdx = -1;
Vec2 srcVec = _player->getPosition();
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
if (it.second->isInnerVec2(srcVec)) {
curPolygonIdx = it.first;
}
if (it.second->isInnerVec2(vec)) {
tarPolygonIdx = it.first;
}
if (curPolygonIdx >= 0 && tarPolygonIdx >= 0) break;
}
if (tarPolygonIdx < 0) {
CCLOG("=============>> cannot move !!!!!!! ");
return;
}
_moveLine->clear();
_openList.clear();
_closeList.clear();
if (curPolygonIdx == tarPolygonIdx) {
_moveVec.push(vec);
_moveLine->drawSegment(srcVec, vec, 0.5, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
}
else {
aStarSearch(curPolygonIdx, tarPolygonIdx, vec);
}
}
void NavMeshScene::aStarSearch(int curPolygonIdx, int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos) {
PolygonClass* curPolygon = _convexPolygons[curPolygonIdx];
vector<int> searchPointIdx = curPolygon->getSearchPointIdx();
for (auto idx : searchPointIdx) {
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[idx];
float route = _player->getPosition().getDistance(searchPoint->vecMid);
float heuristicCost = searchPoint->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos);
_openList.insert(new AStarNode(idx, route, heuristicCost, curPolygonIdx));
}
aStarAlgorithm(tarPolygonIdx, tarPos);
}
void NavMeshScene::aStarAlgorithm(int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos) {
if (_openList.empty()) return;
auto node = _openList.getExploredNode();
_closeList.insert(node);
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[node->searchPointIdx];
auto toPlygonIdx = searchPoint->getToPolygonIdx(node->srcPolygonIdx);
if (toPlygonIdx == tarPolygonIdx) {
_moveVec.push(tarPos);
if (PathSmoothing) createSmoothPath(node, tarPos);
else createPath(node, tarPos);
return;
}
auto toPolygon = _convexPolygons[toPlygonIdx];
vector<int> searchPointIdx = toPolygon->getSearchPointIdx();
for (auto idx : searchPointIdx) {
if (_closeList.getNode(idx) == nullptr) {
float route = node->route + searchPoint->vecMid.getDistance(_searchPoints[idx]->vecMid);
auto openNode = _openList.getNode(idx);
if (openNode == nullptr) {
_openList.insert(new AStarNode(idx, route, _searchPoints[idx]->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos), toPlygonIdx, node, node->passedLineNums + 1));
}
else if(route < openNode->route) {
openNode->route = route;
openNode->heuristicCost = _searchPoints[idx]->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos);
openNode->srcPolygonIdx = toPlygonIdx;
openNode->setParent(node);
openNode->setPassedLineNums(node->getPassedLineNums() + 1);
}
}
}
aStarAlgorithm(tarPolygonIdx, tarPos);
}
路径顺滑,拐点优化
navmesh如果分割都是完全的三角形的话,路径顺滑有一个Funnel算法。
凸多边形可以沿用这个思路进行路径的拐点优化
大噶思路是,以当前所在位置,以及下一个路径点所在边的两个端点作为当前可到达的端点,三点可形成一个扇形漏斗的视角范围,用此范围和下下一个路径点所在边的两个端点进行对比:
1.新的两个端点都在 漏斗左侧:则此时所能到达的左边端点作为路径拐点加了路径列表,并以此拐点进行新的漏斗视角对比,继续检测下一组端点。。
2.新的两个端点都在 漏斗右侧:与第1条类似,只是以所能到达的右边端点作为路径拐点
3.新的两个端点 都在 漏斗内测:则把新的两个端点更新为最新的所能到达端点,并更新漏洞视角范围,继续检测下一组端点。
4.新的左侧端点在漏斗内,右侧端点在漏斗右侧:则把新的左侧端点更新为当前能到达的左侧端点,继续检测下一组端点。
5.新的左侧端点在漏斗左侧, 右侧端点在漏斗内:与第4条类似,只是把新的右侧端点更新为当前所能到达的右侧端点。
6.新的两个端点形成的漏斗扇形大于当前所能到达的漏斗扇形范围:则不更新能到达的端点位置,直接继续检测下一组端点。
直到终点位置在所能到达的漏斗扇形范围内,则把终点位置直接加入路径列表。因为漏斗范围内的一切位置都可直接到达。
void NavMeshScene::createSmoothPath(AStarNode* node, Vec2 tarPos) {
vector<pair<Vec2, Vec2>> ret;
ret.resize(node->getPassedLineNums() + 1);
int idx = node->getPassedLineNums();
ret[idx] = make_pair(tarPos, tarPos);
do {
idx--;
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[node->searchPointIdx];
auto polygon = _convexPolygons[node->srcPolygonIdx];
//从出发的多边形角度看,由于多边形是逆时针,先出现的点在出发者的右边,下一个点即为出发者的左边
if (polygon->isV1BeforeV2(searchPoint->vec1, searchPoint->vec2)) {
ret[idx] = make_pair(searchPoint->vec2, searchPoint->vec1);
}
else {
ret[idx] = make_pair(searchPoint->vec1, searchPoint->vec2);
}
node = node->parentNode;
} while (node != nullptr);
Vec2 lastVec = _player->getPosition();
int canGoLeftIdx = 0;
int canGoRightIdx = 0;
int checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
int checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
stack<Vec2> temp;
while (checkLeftIdx < ret.size() && checkRightIdx < ret.size()) {
Vec2 canGoLeftPos = ret[canGoLeftIdx].first;
Vec2 canGoRightPos = ret[canGoRightIdx].second;
Vec2 checkLeftPos = ret[checkLeftIdx].first;
Vec2 checkRightPos = ret[checkRightIdx].second;
int LLVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, checkLeftPos);
int LRVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, checkRightPos);
int RLVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoRightPos, checkLeftPos);
int RRVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoRightPos, checkRightPos);
if (LRVCross < 0) {
// 新的两个端点都在 漏斗 leftPos 左侧
temp.push(canGoLeftPos);
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, 0.5, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
lastVec = canGoLeftPos;
canGoLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx;
canGoRightIdx = canGoLeftIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (RLVCross > 0) {
//新的两个端点都在 漏斗 rightPos 右侧
temp.push(canGoRightPos);
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, canGoRightPos, 0.5, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
lastVec = canGoRightPos;
canGoLeftIdx = canGoRightIdx;
canGoRightIdx = canGoRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross >= 0 && RRVCross <= 0) {
//新的两个端点 都在 漏斗内测
canGoLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx;
canGoRightIdx = checkRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross >= 0 && RRVCross > 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗内, 右侧端点 在漏斗 rightPos 右侧
canGoLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx;
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross < 0 && RRVCross <= 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗 leftPos 左侧, 右侧端点 在漏斗内
canGoRightIdx = checkRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross < 0 && RRVCross > 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗 leftPos 左侧, 右侧端点 在漏斗 rightPos 右侧
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
}
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, tarPos, 0.5, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
while (!temp.empty()) {
_moveVec.push(temp.top());
temp.pop();
}
}
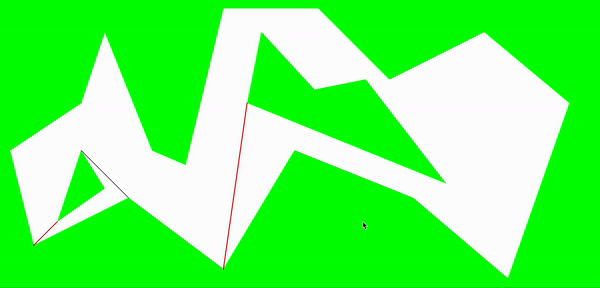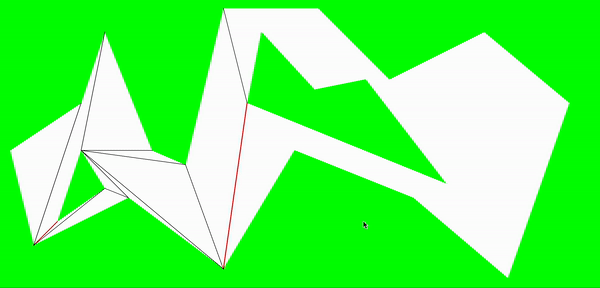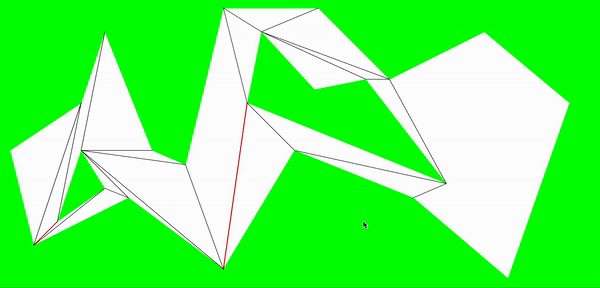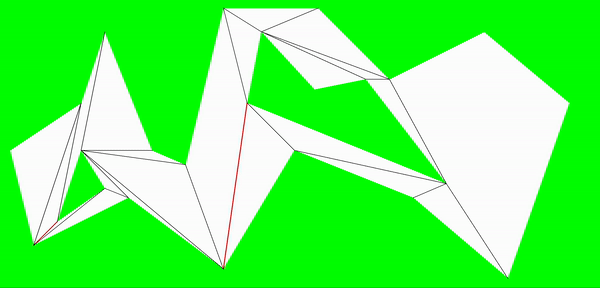
一些示例
一些改进的地方:
1.最终分割的多边形有很多狭长的凸多边形,包括减少合并的次数。主要是在从凹点寻找另一个分割顶点的时候,直接是从相邻顶点的下一个顶点依次判断下去,因此容易出现狭长的凸多边形。
2.a寻路的时候有的时候会看起来像绕远路,主要是a的启发函数用的直接是顶点和终点的距离,如果有孔洞这种可能会找了更远的路。
3.一些数据结构的优化,包括寻找最长分割边,以及下一个探索顶点等。都要一些排序。同时也要顾及到索引
源码
怕上面没解释清楚,直接贴了源码供参考
NavMeshScene.h
#ifndef __NAVMESH_SCENE_H__
#define __NAVMESH_SCENE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
#include "Polygon.h"
#include "Line.h"
#include "SearchPoint.h"
#include "AStarQueue.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class NavMeshScene : public Scene
{
public:
static Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
virtual bool onTouchBegan(Touch* touch, Event* unused_event);
// implement the "static create()" method manually
CREATE_FUNC(NavMeshScene);
void update(float dt);
void linkHole();
void clipPolygon();
void mergePolygon();
void parseNavMeshData();
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> getLinkHoleVertex(PolygonClass* polygon, PolygonClass* hole);
tuple<PolygonClass*, PolygonClass*, Vertex*, Vertex*> getMergeInfo(Line* line);
bool checkMergeLineAngle(Vertex* linePrevVert1, Vertex* linePrevVert2);
void moveToPath(Vec2 vec);
void aStarSearch(int curPolygonIdx, int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos);
void aStarAlgorithm(int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos);
void createPath(AStarNode* aNode, Vec2 tarPos);
void createSmoothPath(AStarNode* aNode, Vec2 tarPos);
protected:
EventListenerTouchOneByOne* _touchListener;
Vec2 _touchBeganPosition;
DrawNode* _mapDrawNode;
DrawNode* _player;
DrawNode* _moveLine;
int _newPointId;
int _convexPolygonId;
vector<PolygonClass* > _holes;
queue<PolygonClass* > _polygons;
unordered_map<int, PolygonClass*> _convexPolygons;
queue<Line* > _linkHoleLines;
struct cmp {
bool operator () (Line* l1, Line* l2) const
{
return l1->len < l2->len;
};
};
priority_queue<Line*, vector<Line*>, cmp> _clipLines;
vector<Line*> _closeClipLines;
vector<SearchPoint*> _searchPoints;
stack<Vec2> _moveVec;
AStarQueue _openList;
AStarQueue _closeList;
bool _isLinkHole;
bool _isClipPolygon;
bool _isMergeTriangle;
bool _isParseNavMesh;
float _speed = 1000;
};
#endif
NavMeshScene.cpp
#include "NavMeshScene.h"
//vector<Vec2> VecArr = {
// Vec2(100,100),
// Vec2(800,100),
// Vec2(800,600),
// Vec2(100,600),
//
// Vec2(400, 300),
// Vec2(500, 300),
// Vec2(500, 400),
// Vec2(400, 400),
//
// Vec2(250, 200),
// Vec2(350, 200),
// Vec2(250, 300),
//
// Vec2(550, 200),
// Vec2(650, 200),
// Vec2(650, 300),
//
// Vec2(650, 500),
// Vec2(550, 500),
// Vec2(650, 400),
//
// Vec2(250, 400),
// Vec2(350, 500),
// Vec2(250, 500),
//
// Vec2(160, 140),
// Vec2(740, 140),
// Vec2(740, 180),
// Vec2(160, 180),
//
// Vec2(160, 560),
// Vec2(160, 520),
// Vec2(740, 520),
// Vec2(740, 560),
//};
//int polygonVertexNum = 4;
//vector<int> holeVertexNum = { 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4 };
vector<Vec2> VecArr = {
Vec2(100,100),
Vec2(130,70),
Vec2(170,110),
Vec2(210,100),
Vec2(240,250),
Vec2(300,50),
Vec2(330,170),
Vec2(400,300),
Vec2(420,30),
Vec2(490,50),
Vec2(600,20),
Vec2(650,100),
Vec2(680,120),
Vec2(720,130),
Vec2(730,115),
Vec2(765,170),
Vec2(800,150),
Vec2(820,160),
Vec2(855,200),
Vec2(900,175),
Vec2(930,165),
Vec2(990,230),
Vec2(1115,320),
Vec2(1115,620),
Vec2(100,620),
Vec2(150, 120),
Vec2(170, 120),
Vec2(170, 550),
Vec2(150, 550),
Vec2(380, 330),
Vec2(420, 320),
Vec2(450, 380),
Vec2(350, 420),
Vec2(365, 450),
Vec2(500, 500),
Vec2(330, 500),
Vec2(300, 550),
Vec2(700, 500),
Vec2(800, 600),
Vec2(300, 600),
Vec2(1000, 350),
Vec2(1050, 550),
Vec2(900, 600),
Vec2(800, 300),
Vec2(500, 300),
Vec2(600, 370),
Vec2(550, 350),
Vec2(480, 250),
Vec2(525, 240),
Vec2(585, 275),
Vec2(645, 240),
Vec2(605, 290),
Vec2(555, 310),
Vec2(450, 100),
Vec2(550, 100),
Vec2(700, 220),
Vec2(680, 220),
Vec2(210, 150),
Vec2(270, 450),
Vec2(290, 120),
Vec2(350, 300),
Vec2(340, 420),
Vec2(320, 480),
Vec2(300, 530),
Vec2(290, 500),
Vec2(270, 550),
Vec2(240, 535),
Vec2(235, 500),
Vec2(230, 470),
Vec2(220, 460),
Vec2(200, 445),
};
int polygonVertexNum = 25;
vector<int> holeVertexNum = {4,4,3,4,4,3,6,4,14};
//vector<Vec2> VecArr = {
// Vec2(100, 100),
// Vec2(300, 200),
// Vec2(500, 50),
// Vec2(650, 300),
// Vec2(900, 200),
// Vec2(1100, 30),
// Vec2(1230, 400),
// Vec2(1050, 550),
// Vec2(850, 450),
// Vec2(700, 600),
// Vec2(500, 600),
// Vec2(420, 270),
// Vec2(350, 300),
// Vec2(250, 550),
// Vec2(200, 400),
// Vec2(50, 300),
//
// Vec2(550, 400),
// Vec2(970, 230),
// Vec2(800, 450),
// Vec2(700, 420),
// Vec2(580, 550),
//
// Vec2(150, 150),
// Vec2(250, 220),
// Vec2(200, 300)
//};
//int polygonVertexNum = 16;
//vector<int> holeVertexNum = {5,3};
int PolygonMaxVertex = 10;
bool PathSmoothing = true;
Scene* NavMeshScene::createScene()
{
return NavMeshScene::create();
}
static void problemLoading(const char* filename)
{
printf("Error while loading: %s\n", filename);
printf("Depending on how you compiled you might have to add 'Resources/' in front of filenames in NavMeshScene.cpp\n");
}
// on "init" you need to initialize your instance
bool NavMeshScene::init()
{
//
// 1. super init first
if (!Scene::init())
{
return false;
}
auto visibleSize = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleSize();
Vec2 origin = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleOrigin();
_newPointId = VecArr.size();
_convexPolygonId = 1;
auto layer = LayerColor::create(Color4B(255,255,255,255));
layer:setContentSize(visibleSize);
this->addChild(layer);
_mapDrawNode = DrawNode::create();
this->addChild(_mapDrawNode);
PolygonClass *polygon = new PolygonClass();
for (int i = 0; i < polygonVertexNum; i++) {
Vec2 v1 = VecArr[i];
Vec2 v2;
if (i == polygonVertexNum - 1) {
v2 = VecArr[0];
}
else
{
v2 = VecArr[i + 1];
}
// _mapDrawNode->drawSegment(v1, v2, 0.5, Color4F(0, 1, 0, 1));
polygon->insert(i, v1);
}
// auto vecData = polygon->getVertVecData();
// Vec2* ptr = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(vecData.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr, vecData.size(), Color4F(1,1,1,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
//
// vector<Vec2> v1 = {Vec2(100, 100),Vec2(300, 200),Vec2(500, 50)};
// Vec2* ptr1 = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(v1.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr1, v1.size(), Color4F(0,1,0,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
// vector<Vec2> v2 = {Vec2(500, 50),Vec2(650, 300),Vec2(900, 200),Vec2(1100, 30)};
// Vec2* ptr2 = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(v2.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr2, v2.size(), Color4F(0,1,0,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
// vector<Vec2> v3 = {Vec2(500, 600),Vec2(420, 270),Vec2(350, 300),Vec2(250, 550)};
// Vec2* ptr3 = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(v3.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr3, v3.size(), Color4F(0,1,0,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
// vector<Vec2> v4 = {Vec2(1050, 550),Vec2(850, 450),Vec2(700, 600)};
// Vec2* ptr4 = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(v4.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr4, v4.size(), Color4F(0,1,0,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
for (int i = 0; i < polygonVertexNum; i++) {
Vec2 v1 = VecArr[i];
Vec2 v2;
if (i == polygonVertexNum - 1) {
v2 = VecArr[0];
}
else
{
v2 = VecArr[i + 1];
}
_mapDrawNode->drawSegment(v1, v2, 0.5, Color4F(0, 1, 0, 1));
}
_polygons.push(polygon);
int posOffsetIdx = 0;
for (int num : holeVertexNum) {
PolygonClass* hole = new PolygonClass();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
Vec2 v1 = VecArr[polygonVertexNum + posOffsetIdx];
Vec2 v2;
if (i == num - 1) {
v2 = VecArr[polygonVertexNum + posOffsetIdx - num + 1];
}
else {
v2 = VecArr[polygonVertexNum + posOffsetIdx + 1];
}
_mapDrawNode->drawSegment(v1, v2, 0.5, Color4F(0, 1, 1, 1));
hole->insert(polygonVertexNum + posOffsetIdx, v1);
posOffsetIdx = posOffsetIdx + 1;
}
_holes.push_back(hole);
// auto vecData = hole->getVertVecData();
// Vec2* ptr = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(vecData.data());
// _mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr, vecData.size(), Color4F(0,1,0,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
}
_moveLine = DrawNode::create();
this->addChild(_moveLine);
// auto node = DrawNode::create();
// this->addChild(node);
// node->drawSegment(Vec2(1200,400), Vec2(1400,400), 0.5, Color4F(0,0,0,1));
_touchListener = EventListenerTouchOneByOne::create();
_touchListener->setSwallowTouches(true);
_touchListener->onTouchBegan = CC_CALLBACK_2(NavMeshScene::onTouchBegan, this);
this->getEventDispatcher()->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(_touchListener, layer);
this->scheduleUpdate();
return true;
}
bool NavMeshScene::onTouchBegan(Touch* touch, Event* event)
{
_touchBeganPosition = touch->getLocation();
CCLOG("==========》 %f, %f", _touchBeganPosition.x, _touchBeganPosition.y);
if (!_isLinkHole) {
linkHole();
return true;
}
if (!_isClipPolygon) {
clipPolygon();
return true;
}
if (!_isMergeTriangle) {
mergePolygon();
return true;
}
if (!_isParseNavMesh) {
parseNavMeshData();
return true;
}
moveToPath(_touchBeganPosition);
return true;
}
void NavMeshScene::update(float dt)
{
if (!_moveVec.empty()) {
Vec2 tarPos = _moveVec.top();
float speed = _speed * dt;
Vec2 srcPos = _player->getPosition();
Vec2 velocity = tarPos - srcPos;
velocity.normalize();
velocity *= speed;
if (tarPos.x == srcPos.x) {
if (velocity.y >= abs(tarPos.y - srcPos.y)) {
_player->setPosition(tarPos);
_moveVec.pop();
}
else {
_player->setPosition(srcPos + velocity);
}
}
else {
if(abs(velocity.x) >= abs(tarPos.x - srcPos.x)){
_player->setPosition(tarPos);
_moveVec.pop();
}
else {
_player->setPosition(srcPos + velocity);
}
}
}
}
void NavMeshScene::linkHole() {
while (!_holes.empty()) {
PolygonClass* hole = _holes[0];
_holes.erase(_holes.begin());
if (_polygons.front()->isInnerHole(hole)) {
auto verts = getLinkHoleVertex(_polygons.front(), hole);
if (verts.second == nullptr || verts.first == nullptr) _holes.push_back(hole);
else {
auto drawNode = DrawNode::create();
drawNode->drawSegment(verts.first->pos, verts.second->pos, 1, Color4F(1, 0, 0, 1));
this->addChild(drawNode);
Vertex* vPolygon = verts.first;
Vertex* vertPolygonNext = vPolygon->next;
//hole的顶点需要顺时针插入polygon
Vertex* vHole = verts.second;
do {
Vertex* vert = new Vertex(vHole->id, vHole->pos);
vPolygon->next = vert;
vert->prev = vPolygon;
vPolygon = vert;
vHole = vHole->prev;
} while (!vHole->isSameVert(verts.second));
_newPointId++;
Vertex* newVHole = new Vertex(_newPointId, verts.second->pos);
newVHole->prev = vPolygon;
vPolygon->next = newVHole;
_newPointId++;
Vertex* newVPolygon = new Vertex(_newPointId, verts.first->pos);
newVHole->next = newVPolygon;
newVPolygon->prev = newVHole;
newVPolygon->next = vertPolygonNext;
vertPolygonNext->prev = newVPolygon;
float len = verts.first->pos.getDistance(verts.second->pos);
_linkHoleLines.emplace(new Line(verts.first, verts.second, len, drawNode));
delete hole;
hole = nullptr;
}
}
}
_isLinkHole = true;
return;
}
// 从hole 选择一个顶点pA
// 从polygon选择一个顶点pB,保证与pA连线不与polygon以及hole上的任意非相邻边相交
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> NavMeshScene::getLinkHoleVertex(PolygonClass* polygon, PolygonClass* hole) {
Vertex* vertHole = hole->getHead();
do {
Vertex* vertPolygon = polygon->getHead();
do {
bool isInAngle = polygon->isLineInInnerAngle(vertHole, vertPolygon) && !hole->isLineInInnerAngle(vertPolygon, vertHole);
if (isInAngle) {
bool noIntersect = polygon->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole) && hole->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole);
for (auto hole = _holes.begin(); hole != _holes.end(); hole++) {
if (!(*hole)->isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(vertPolygon, vertHole)) {
noIntersect = false;
break;
}
}
if (noIntersect) return make_pair(vertPolygon, vertHole);
}
vertPolygon = vertPolygon->next;
} while (!vertPolygon->isSameVert(polygon->getHead()));
vertHole = vertHole->next;
} while (!vertHole->isSameVert(hole->getHead()));
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
void NavMeshScene::clipPolygon() {
while (!_polygons.empty()) {
PolygonClass* polygon = _polygons.front();
_polygons.pop();
auto verts = polygon->findClipVert();
if (verts.first == nullptr || verts.second == nullptr) {
//凸边形
polygon->setConvexPolygonId(_convexPolygonId);
_convexPolygons.emplace(_convexPolygonId, polygon);
_convexPolygonId++;
}
else {
auto drawNode = DrawNode::create();
this->addChild(drawNode);
drawNode->drawSegment(verts.first->pos, verts.second->pos, 1, Color4F(0, 0, 0, 1));
float len = verts.first->pos.getDistance(verts.second->pos);
_clipLines.push(new Line(verts.first, verts.second, len, drawNode));
auto tarPrev = verts.second->prev;
auto srcNext = verts.first->next;
verts.first->next = verts.second;
verts.second->prev = verts.first;
polygon->setHead(verts.first);
PolygonClass* newPolygon = new PolygonClass();
Vertex* tail = new Vertex(verts.first->id, verts.first->pos);
tail->next = srcNext;
srcNext->prev = tail;
Vertex* head = new Vertex(verts.second->id, verts.second->pos);
head->prev = tarPrev;
head->next = tail;
tarPrev->next = head;
tail->prev = head;
newPolygon->setHead(head);
_polygons.push(polygon);
_polygons.push(newPolygon);
}
}
_isClipPolygon = true;
// 在分割完所有凸多边形后,把连接孔洞的线也加入分割线,作为合并多边形的判断
while (!_linkHoleLines.empty()) {
_clipLines.push(_linkHoleLines.front());
_linkHoleLines.pop();
}
}
//判断分割边分割的两个凸多边形合并仍是凸多边形, 即分割边两个共享点在合并的凸多边形里是 凸点
bool NavMeshScene::checkMergeLineAngle(Vertex* linePrevVert1, Vertex* linePrevVert2) {
//求如果合并的新凸多边形, 公共边对应的两个角的顶点
Vec2 v1Prev = linePrevVert1->pos;
Vec2 v1 = linePrevVert1->next->pos;
Vec2 v1Next = linePrevVert2->next->next->next->pos;
Vec2 v2Prev = linePrevVert2->pos;
Vec2 v2 = linePrevVert2->next->pos;
Vec2 v2Next = linePrevVert1->next->next->next->pos;
if (GeometryMath::isInRight(v1Prev, v1, v1Next)) return false;
if (GeometryMath::isInRight(v2Prev, v2, v2Next)) return false;
return true;
}
//获取分割边分割的凸多边形
tuple<PolygonClass*, PolygonClass*, Vertex*, Vertex*> NavMeshScene::getMergeInfo(Line* line) {
PolygonClass* firstPolygon = nullptr;
PolygonClass* secondPolygon = nullptr;
Vertex* vert1 = nullptr;
Vertex* vert2 = nullptr;
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
Vertex* linePrev = it.second->getLinePrevVert(line);
if (linePrev != nullptr) {
if (firstPolygon == nullptr) {
firstPolygon = it.second;
vert1 = linePrev;
}
else {
secondPolygon = it.second;
vert2 = linePrev;
break;
}
}
}
//能合并最大多边形判断
if (firstPolygon->getSize() + secondPolygon->getSize() - 2 > PolygonMaxVertex) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
if (!checkMergeLineAngle(vert1, vert2)) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
return make_tuple(firstPolygon, secondPolygon, vert1, vert2);
}
void NavMeshScene::mergePolygon() {
while (!_clipLines.empty()) {
// 获取最长的分割边
auto line = _clipLines.top();
_clipLines.pop();
PolygonClass* firstPolygon;
PolygonClass* secondPolygon;
Vertex* vert1;
Vertex* vert2;
tie(firstPolygon, secondPolygon, vert1, vert2) = getMergeInfo(line);
if (firstPolygon == nullptr) {
_closeClipLines.push_back(line);
}
else {
_convexPolygons.erase(secondPolygon->getConvexPolygonId());
Vertex* cur = vert1->next;
Vertex* mergeEnd = vert1->next->next;
Vertex* next = vert2->next->next->next;
do {
Vertex* vNext = new Vertex(next->id, next->pos);
cur->next = vNext;
vNext->prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
next = next->next;
} while (!next->isSameVert(vert2->next));
cur->next = mergeEnd;
mergeEnd->prev = cur;
delete secondPolygon;
secondPolygon = nullptr;
line->drawNode->removeFromParent();
}
}
_isMergeTriangle = true;
}
void NavMeshScene::parseNavMeshData() {
_mapDrawNode->clear();
float i = 1;
float nums = _convexPolygons.size() + i;
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
auto vecData = it.second->getVertVecData();
// int t = RandomHelper::random_real<float>(200, 1200);;
float r = RandomHelper::random_real<float>(0, 1);
float g = RandomHelper::random_real<float>(0, 1);
float b = RandomHelper::random_real<float>(0, 1);
Vec2* ptr = reinterpret_cast<Vec2*>(vecData.data());
_mapDrawNode->drawPolygon(ptr, vecData.size(), Color4F(r,g,b,1), 0, Color4F(0,0,0,0));
i++;
/*auto num = Label::create();
this->addChild(num);
num->setString(to_string(it.second->getConvexPolygonId()));
num->setPosition(it.second->getInnerVec2());*/
}
for (int i = 0; i < _closeClipLines.size(); i++) {
auto line = _closeClipLines[i];
line->drawNode->removeFromParent();
PolygonClass* firstPolygon = nullptr;
PolygonClass* secondPolygon = nullptr;
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
if (it.second->hasLine(line)) {
if (firstPolygon == nullptr) firstPolygon = it.second;
else if (secondPolygon == nullptr) {
secondPolygon = it.second;
break;
}
}
}
firstPolygon->insertSearchPointIdx(i);
secondPolygon->insertSearchPointIdx(i);
_searchPoints.push_back(new SearchPoint(line->vert1->pos, line->vert2->pos, firstPolygon->getConvexPolygonId(), secondPolygon->getConvexPolygonId()));
}
_player = DrawNode::create();
this->addChild(_player);
_player->drawDot(Vec2(0, 0), 10, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 1));
auto polygon = (*_convexPolygons.begin()).second;
_player->setPosition(polygon->getInnerVec2());
_isParseNavMesh = true;
}
void NavMeshScene::moveToPath(Vec2 vec) {
int curPolygonIdx = -1;
int tarPolygonIdx = -1;
Vec2 srcVec = _player->getPosition();
for (auto it : _convexPolygons) {
if (it.second->isInnerVec2(srcVec)) {
curPolygonIdx = it.first;
}
if (it.second->isInnerVec2(vec)) {
tarPolygonIdx = it.first;
}
if (curPolygonIdx >= 0 && tarPolygonIdx >= 0) break;
}
if (tarPolygonIdx < 0) {
CCLOG("=============>> cannot move !!!!!!! ");
return;
}
_moveLine->clear();
_openList.clear();
_closeList.clear();
if (curPolygonIdx == tarPolygonIdx) {
_moveVec.push(vec);
_moveLine->drawSegment(srcVec, vec, 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
}
else {
aStarSearch(curPolygonIdx, tarPolygonIdx, vec);
}
}
void NavMeshScene::aStarSearch(int curPolygonIdx, int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos) {
PolygonClass* curPolygon = _convexPolygons[curPolygonIdx];
vector<int> searchPointIdx = curPolygon->getSearchPointIdx();
for (auto idx : searchPointIdx) {
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[idx];
float route = _player->getPosition().getDistance(searchPoint->vecMid);
float heuristicCost = searchPoint->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos);
_openList.insert(new AStarNode(idx, route, heuristicCost, curPolygonIdx));
}
aStarAlgorithm(tarPolygonIdx, tarPos);
}
void NavMeshScene::aStarAlgorithm(int tarPolygonIdx, Vec2 tarPos) {
if (_openList.empty()) return;
auto node = _openList.getExploredNode();
_closeList.insert(node);
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[node->searchPointIdx];
auto toPlygonIdx = searchPoint->getToPolygonIdx(node->srcPolygonIdx);
if (toPlygonIdx == tarPolygonIdx) {
_moveVec.push(tarPos);
if (PathSmoothing) createSmoothPath(node, tarPos);
else createPath(node, tarPos);
return;
}
auto toPolygon = _convexPolygons[toPlygonIdx];
vector<int> searchPointIdx = toPolygon->getSearchPointIdx();
for (auto idx : searchPointIdx) {
if (_closeList.getNode(idx) == nullptr) {
float route = node->route + searchPoint->vecMid.getDistance(_searchPoints[idx]->vecMid);
auto openNode = _openList.getNode(idx);
if (openNode == nullptr) {
_openList.insert(new AStarNode(idx, route, _searchPoints[idx]->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos), toPlygonIdx, node, node->passedLineNums + 1));
}
else if(route < openNode->route) {
openNode->route = route;
openNode->heuristicCost = _searchPoints[idx]->vecMid.getDistance(tarPos);
openNode->srcPolygonIdx = toPlygonIdx;
openNode->setParent(node);
openNode->setPassedLineNums(node->getPassedLineNums() + 1);
}
}
}
aStarAlgorithm(tarPolygonIdx, tarPos);
}
void NavMeshScene::createPath(AStarNode* node, Vec2 tarPos) {
Vec2 last, next;
last = tarPos;
do {
next = _searchPoints[node->searchPointIdx]->vecMid;
_moveVec.push(next);
_moveLine->drawSegment(last, next, 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
last = next;
node = node->parentNode;
} while (node != nullptr);
_moveLine->drawSegment(last, _player->getPosition(), 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
}
void NavMeshScene::createSmoothPath(AStarNode* node, Vec2 tarPos) {
vector<pair<Vec2, Vec2>> ret;
ret.resize(node->getPassedLineNums() + 1);
int idx = node->getPassedLineNums();
ret[idx] = make_pair(tarPos, tarPos);
do {
idx--;
auto searchPoint = _searchPoints[node->searchPointIdx];
auto polygon = _convexPolygons[node->srcPolygonIdx];
//从出发的多边形角度看,由于多边形是逆时针,先出现的点在出发者的右边,下一个点即为出发者的左边
if (polygon->isV1BeforeV2(searchPoint->vec1, searchPoint->vec2)) {
ret[idx] = make_pair(searchPoint->vec2, searchPoint->vec1);
}
else {
ret[idx] = make_pair(searchPoint->vec1, searchPoint->vec2);
}
node = node->parentNode;
} while (node != nullptr);
Vec2 lastVec = _player->getPosition();
int canGoLeftIdx = 0;
int canGoRightIdx = 0;
int checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
int checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
stack<Vec2> temp;
while (checkLeftIdx < ret.size() && checkRightIdx < ret.size()) {
Vec2 canGoLeftPos = ret[canGoLeftIdx].first;
Vec2 canGoRightPos = ret[canGoRightIdx].second;
Vec2 checkLeftPos = ret[checkLeftIdx].first;
Vec2 checkRightPos = ret[checkRightIdx].second;
int LLVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, checkLeftPos);
int LRVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, checkRightPos);
int RLVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoRightPos, checkLeftPos);
int RRVCross = GeometryMath::getVectorCross(lastVec, canGoRightPos, checkRightPos);
if (LRVCross < 0) {
// 新的两个端点都在 漏斗 leftPos 左侧
temp.push(canGoLeftPos);
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, canGoLeftPos, 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
lastVec = canGoLeftPos;
canGoLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx;
canGoRightIdx = canGoLeftIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (RLVCross > 0) {
//新的两个端点都在 漏斗 rightPos 右侧
temp.push(canGoRightPos);
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, canGoRightPos, 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
lastVec = canGoRightPos;
canGoLeftIdx = canGoRightIdx;
canGoRightIdx = canGoRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross >= 0 && RRVCross <= 0) {
//新的两个端点 都在 漏斗内测
canGoLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx;
canGoRightIdx = checkRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = canGoLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = canGoRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross >= 0 && RRVCross > 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗内, 右侧端点 在漏斗 rightPos 右侧
canGoLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx;
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross < 0 && RRVCross <= 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗 leftPos 左侧, 右侧端点 在漏斗内
canGoRightIdx = checkRightIdx;
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
else if (LLVCross < 0 && RRVCross > 0) {
//新的左侧端点 在漏斗 leftPos 左侧, 右侧端点 在漏斗 rightPos 右侧
checkLeftIdx = checkLeftIdx + 1;
checkRightIdx = checkRightIdx + 1;
}
}
_moveLine->drawSegment(lastVec, tarPos, 1, Color4F(1, 1, 1, 0.7));
while (!temp.empty()) {
_moveVec.push(temp.top());
temp.pop();
}
}
Polygon.h
#ifndef __POLYGON_H__
#define __POLYGON_H__
#include "Vertex.h"
#include "GeometryMath.h"
#include "cocos2d.h"
#include "Line.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class PolygonClass
{
public:
PolygonClass(): _head(nullptr) {};
void insert(int id, Vec2 pos);
bool isInnerHole(PolygonClass* hole);
bool isInnerVert(Vertex* vert);
bool isInnerVec2(Vec2 vec);
Vertex* getHead() { return _head; };
bool isLineInInnerAngle(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2);
bool isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2);
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> findClipVert();
Vertex* findConcaveVertex();
void setHead(Vertex* head);
Vertex* getLinePrevVert(Line* line);
bool hasLine(Line* line);
int getSize();
void setConvexPolygonId(int id) { _convexPolygonId = id; };
int getConvexPolygonId() { return _convexPolygonId; };
vector<Vec2> getVertVecData();
Vec2 getInnerVec2();
void display();
void insertSearchPointIdx(int searchPointIdx) { _searchPointIdx.push_back(searchPointIdx); };
vector<int> getSearchPointIdx() { return _searchPointIdx; };
bool isV1BeforeV2(Vec2 v1, Vec2 v2);
~PolygonClass();
private:
Vertex* _head;
int _convexPolygonId;
vector<int> _searchPointIdx;
};
#endif
Polygon.cpp
#include "Polygon.h"
void PolygonClass::insert(int id, Vec2 pos) {
Vertex* vert = new Vertex(id, pos);
if (_head == nullptr) {
_head = vert;
_head->next = vert;
_head->prev = vert;
}else {
Vertex* tail = _head->prev;
tail->next = vert;
vert->next = _head;
vert->prev = tail;
_head->prev = vert;
}
}
PolygonClass::~PolygonClass() {
if (_head == nullptr) return;
auto cur = _head->next;
while (!cur->isSameVert(_head)) {
auto temp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete temp;
}
delete _head;
}
// 判断多边形hole是否被polygon完全包含
bool PolygonClass::isInnerHole(PolygonClass* hole) {
// hole的所有点都被polygon包含
Vertex* cur = hole->getHead();
if (_head == nullptr) return false;
do {
if (!this->isInnerVert(cur)) return false;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(hole->getHead()));
return true;
}
// 判断点是否在多边形中
bool PolygonClass::isInnerVert(Vertex* vert) {
return isInnerVec2(vert->pos);
}
bool PolygonClass::isInnerVec2(Vec2 vec) {
//从 顶点 向右 发射一条向右水平射线, 水平射线与所有边的交点数目,为奇数,则在内部, 为偶数,则在外部
Vertex* cur = _head;
int intersectLines = 0;
do {
if (GeometryMath::isRayIntersectLine(vec, cur->pos, cur->next->pos)) intersectLines++;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return intersectLines % 2 == 1;
}
bool PolygonClass::isLineInInnerAngle(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2) {
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2)) return false;
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2->prev)) return false;
if (vertL1->isSamePos(vertL2->next)) return false;
Vec2 vecL2Prev = vertL2->prev->pos;
Vec2 vecL2= vertL2->pos;
Vec2 vecL2Next = vertL2->next->pos;
Vec2 vecL1 = vertL1->pos;
if (GeometryMath::isInLeft(vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next)) return GeometryMath::checkVectorInConvexAngle(vecL1, vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next);
/*else if (GeometryMath::isInRight(vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next)) return GeometryMath::checkVectorInConcaveAngle(vecL1, vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next);
else return GeometryMath::isInRight(vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL1);*/
return GeometryMath::checkVectorInConcaveAngle(vecL1, vecL2Prev, vecL2, vecL2Next);
}
bool PolygonClass::isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(Vertex* vertL1, Vertex* vertL2) {
Vertex* cur = _head;
do {
// 防止 连接点的相邻边 与 新增线 重合
/*if (GeometryMath::isVertexInLine(v1, v2, curPos) && GeometryMath::isVertexInLine(v1, v2, nextPos)) return false;*/
if (!vertL1->isSamePos(cur) && !vertL1->isSamePos(cur->next) && !vertL2->isSamePos(cur) && !vertL2->isSamePos(cur->next)) {
if (GeometryMath::checkTwoVectorIntersect(vertL1->pos, vertL2->pos, cur->pos, cur->next->pos)) return false;
}
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return true;
}
Vertex* PolygonClass::findConcaveVertex() {
Vertex* cur = _head;
do {
if(!GeometryMath::isInLeft(cur->prev->pos,cur->pos,cur->next->pos)) return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return nullptr;
}
//找到一个凹角顶点a
//从点a 找到一个 不相邻点b 且能连接成完全在内部的对角线,
//因为a为凹角,所以从a出发一定在∠a内, 则需要对角线在目标点的∠B内,且不与任何非相邻边相交
pair<Vertex*, Vertex*> PolygonClass::findClipVert() {
auto srcVert = findConcaveVertex();
if (srcVert == nullptr) {
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
auto tarVert = srcVert->next->next;
do {
if (!tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert) && !tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert->next) && !tarVert->isSamePos(srcVert->prev)) {
bool isInAngle = isLineInInnerAngle(srcVert, tarVert) && isLineInInnerAngle(tarVert, srcVert);
bool isNoIntersect = isVectorNoIntersectWithAdjacentEdge(srcVert, tarVert);
if (isInAngle && isNoIntersect) return make_pair(srcVert, tarVert);
}
tarVert = tarVert->next;
} while (!tarVert->isSameVert(srcVert->prev));
return make_pair(nullptr, nullptr);
}
void PolygonClass::setHead(Vertex* head) {
_head = head;
}
Vertex* PolygonClass::getLinePrevVert(Line* line) {
auto vert1 = line->vert1;
auto vert2 = line->vert2;
auto cur = _head;
do {
if (cur->isSamePos(vert1) && cur->next->isSamePos(vert2)) return cur->prev;
if (cur->isSamePos(vert2) && cur->next->isSamePos(vert1)) return cur->prev;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return nullptr;
}
bool PolygonClass::hasLine(Line* line) {
return getLinePrevVert(line) != nullptr;
}
int PolygonClass::getSize() {
int num = 0;
auto cur = _head;
do {
num++;
cur = cur->next;
}while(!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return num;
}
vector<Vec2> PolygonClass::getVertVecData() {
vector<Vec2> data;
auto cur = _head;
do {
data.push_back(cur->pos);
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return data;
}
Vec2 PolygonClass::getInnerVec2() {
Vec2 v1 = _head->pos.getMidpoint(_head->next->pos);
Vec2 v2 = _head->pos.getMidpoint(_head->prev->pos);
return v1.getMidpoint(v2);
}
bool PolygonClass::isV1BeforeV2(Vec2 v1, Vec2 v2) {
auto cur = _head;
do {
if (cur->pos == v1 && cur->next->pos == v2) return true;
else if (cur->pos == v2 && cur->next->pos == v1) return false;
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
return false;
}
void PolygonClass::display()
{
Vertex* cur = _head;
do {
CCLOG("==========》 %d, %f, %f", cur->id, cur->pos.x, cur->pos.y);
cur = cur->next;
} while (!cur->isSameVert(_head));
}
Vertex.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __VERTEX_H__
#define __VERTEX_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class Vertex
{
public:
Vertex(int id, Vec2 pos) {
this->id = id;
this->pos = pos;
}
bool isSameVert(Vertex* vert) {
return vert->id == id && vert->pos == pos;
}
bool isSamePos(Vertex* vert) {
return vert->pos == pos;
}
int id;
Vec2 pos;
Vertex* next;
Vertex* prev;
};
#endif
SearchPoint.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __SEARCH_POINT_H__
#define __SEARCH_POINT_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class SearchPoint
{
public:
SearchPoint(Vec2 vec1, Vec2 vec2, int polygonId1, int polygonId2)
:
vec1(vec1),
vec2(vec2),
polygonId1(polygonId1),
polygonId2(polygonId2)
{
vecMid = vec1.getMidpoint(vec2);
}
int getToPolygonIdx(int fromPolygonIdx) { return fromPolygonIdx == polygonId1 ? polygonId2 : polygonId1; }
Vec2 vecMid;
Vec2 vec1;
Vec2 vec2;
int polygonId1;
int polygonId2;
};
#endif
Line.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __LINE_H__
#define __LINE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
#include "Vertex.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
Line(Vertex* vert1, Vertex* vert2, float len, DrawNode* drawNode) {
this->vert1 = new Vertex(vert1->id, vert1->pos);
this->vert2 = new Vertex(vert2->id, vert2->pos);
this->len = len;
this->drawNode = drawNode;
}
Vertex* vert1;
Vertex* vert2;
float len;
DrawNode* drawNode;
};
#endif
AStarQueue.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __ASTAR_QUEUE_H__
#define __ASTAR_QUEUE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
#include "AStarNode.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class AStarQueue
{
public:
AStarQueue(){
}
void insert(AStarNode* aNode) { _map.emplace(aNode->searchPointIdx, aNode); };
AStarNode* getExploredNode() {
if (_map.empty()) return nullptr;
AStarNode* aNode = (*_map.begin()).second;
for (auto it : _map) {
if (it.second->getAStarCost() < aNode->getAStarCost()){
aNode = it.second;
}
}
_map.erase(aNode->searchPointIdx);
return aNode;
};
bool empty() { return _map.empty(); };
AStarNode* getNode(int searchPointIdx) {
auto it = _map.find(searchPointIdx);
if (it == _map.end()) {
return nullptr;
}
else {
return (*it).second;
}
};
void clear() {
for (auto it : _map) {
delete it.second;
it.second = nullptr;
}
_map.clear();
}
map<int, AStarNode*> _map;
};
#endif
AStarNode.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __ASTAR_NODE_H__
#define __ASTAR_NODE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class AStarNode
{
public:
AStarNode(int searchPointIdx, float route, float heuristicCost, int srcPolygonIdx)
:
searchPointIdx(searchPointIdx),
route(route),
heuristicCost(heuristicCost),
srcPolygonIdx(srcPolygonIdx),
parentNode(nullptr),
passedLineNums(1)
{}
AStarNode(int searchPointIdx, float route, float heuristicCost, int srcPolygonIdx, AStarNode* aNode, int passedLineNums)
:
searchPointIdx(searchPointIdx),
route(route),
heuristicCost(heuristicCost),
srcPolygonIdx(srcPolygonIdx),
parentNode(aNode),
passedLineNums(passedLineNums)
{}
void setParent(AStarNode* aNode) {
parentNode = aNode;
}
void setPassedLineNums(int num) {
passedLineNums = num;
}
int getPassedLineNums(){
return passedLineNums;
}
float getAStarCost() { return route + heuristicCost; };
int searchPointIdx;
AStarNode* parentNode;
float route;
float heuristicCost;
int srcPolygonIdx;
int passedLineNums;
};
#endif
GeometryMath.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __GEOMETRY_MATH_H__
#define __GEOMETRY_MATH_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
class GeometryMath
{
public:
static bool isRayIntersectLine(Vec2 vR, Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2);
static bool isInLeft(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static bool isInRight(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static bool isCollineation(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static int getVectorCross(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static bool checkVectorInConvexAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static bool checkVectorInConcaveAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c);
static bool checkTwoVectorIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd);
static bool isVertexInLine(Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2, Vec2 vert);
static bool isStrictlyIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd);
private:
};
#endif
GeometryMath.cpp
#include "GeometryMath.h"
bool GeometryMath::isRayIntersectLine(Vec2 vR, Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2) {
//线段水平,与射线重合或平行
if (vL1.y == vL2.y) return false;
//线段在 水平射线上方
if (vL1.y > vR.y && vL2.y > vR.y) return false;
//线段在 水平射线下方
if (vL1.y < vR.y && vL2.y < vR.y) return false;
float minY = min(vL1.y, vL2.y);
float maxY = min(vL1.y, vL2.y);
/*线段下方端点在线上, 与 线段上方端点的在线上的情况,只能选择一种作为相交,另一种作为不相交
否则射线穿过的顶点的相交判断会有问题
即maxY 或者 minY 只选择一种做判断*/
if (maxY == vR.y) return false;
//线段两个端点分别在 射线的上下, 求线段在 射线的水平线上的x点,判断x点与 射线起点x轴坐标(射线方向向右)
float offsetY = vL2.y - vR.y;
float offsetX = offsetY / (vL2.y - vL1.y) * (vL2.x - vL1.x);
float x = vL2.x - offsetX;
return x >= vR.x;
}
// 点 c 在a到b向量的左边, 即∠abc 小于180°
bool GeometryMath::isInLeft(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
float e = getVectorCross(a, b, c);
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) < 0;
}
// 点 c 在a到b向量的右边, 即∠abc 大于180°
bool GeometryMath::isInRight(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) > 0;
}
// 点 c 与a到b向量共线, 即∠abc 等于180°
bool GeometryMath::isCollineation(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return getVectorCross(a, b, c) == 0;
}
int GeometryMath::getVectorCross(Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
Vec2 vectorBA = a - b;
Vec2 vectorBC = c - b;
return vectorBA.cross(vectorBC);
}
// 小于180°的角 ∠abc,点a,点b,点c是逆时针,判定线vb在角内, 线需在ab的左边,并且在bc的左边
bool GeometryMath::checkVectorInConvexAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return isInLeft(a, b, v) && isInLeft(b, c, v);
}
//大于180°的角 ∠abc,点a,点b,点c是逆时针,判定线vb在角内,即线不在∠abc的外侧,即线不在∠cba里
bool GeometryMath::checkVectorInConcaveAngle(Vec2 v, Vec2 a, Vec2 b, Vec2 c) {
return !checkVectorInConvexAngle(v, c, b, a);
}
// vert 在 vectorL12 线段之间
bool GeometryMath::isVertexInLine(Vec2 vL1, Vec2 vL2, Vec2 vert) {
if (!isCollineation(vL1, vL2, vert)) return false;
if (vL1.x == vL2.x) return (vert.y >= min(vL1.y, vL2.y)) && (vert.y <= max(vL1.y, vL2.y));
else return (vert.x >= min(vL1.x, vL2.x)) && (vert.x <= max(vL1.x, vL2.x));
}
// 检查 vectorAB 与 vectorCD 相交
bool GeometryMath::checkTwoVectorIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd) {
if (isStrictlyIntersect(va, vb, vc, vd)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(va, vb, vc)) {
return true; }
if (isVertexInLine(va, vb, vd)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(vc, vd, va)) {
return true;
}
if (isVertexInLine(vc, vd, vb)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 检查 vectorAB 与 vectorCD 严格相交, 点va,点vb在 线vectorCD 两侧, 且点vc,点vd 在线vectorAB 两侧
bool GeometryMath::isStrictlyIntersect(Vec2 va, Vec2 vb, Vec2 vc, Vec2 vd) {
if (isCollineation(va, vb, vc)) return false;
if (isCollineation(va, vb, vd)) return false;
if (isCollineation(vc, vd, va)) return false;
if (isCollineation(vc, vd, vb)) return false;
if (isInLeft(va, vb, vc) == isInLeft(va, vb, vd)) return false;
if (isInLeft(vc, vd, va) == isInLeft(vc, vd, vb)) return false;
return true;
}

![[开源]Web端的P2P文件传输工具,简单安全高效的P2P文件传输服务](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/ab1d163717ab9238deb71913ab8e2788.png)

![[Unity+OpenAI TTS] 集成openAI官方提供的语音合成服务,构建海王暖男数字人](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a006eaca336d496a986ed7ea9d2a2c32.png)