文章目录
- 1. 单向环形链表应用场景
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 3.1. 实现单向环形链表
- 3.2. 产生出队编号序列
- 3.2.1. 思路分析
- 3.2.2. 代码实现
1. 单向环形链表应用场景
Josephu(约瑟夫、约瑟夫环) 问题:
设编号为 1,2,… n 的 n 个人围坐一圈,约定编号为 k(1 ≤ k ≤ n)的人从 1 开始报数,数到 m 的那个人出列,它的下一位又从 1 开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列,依次类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列。

提示:
用一个不带头结点的循环链表来处理 Josephu 问题:先构成一个有 n个结点的单循环链表,然后由 k 结点起从 1 开始计数,计到 m 时,对应结点从链表中删除,然后再从被删除结点的下一个结点又从 1开始计数,直到最后一个结点从链表中删除算法结束。
假设:n=5,即有5人;k=1,从第一个人开始报数;m=2,数到2出列。
单向环形链表完成约瑟夫问题

出圈顺序为:2–>4–>1–>5–>3
2. 思路分析
构建一个单向环形链表的思路:
①先创建第一个节点(如下图的节点1), 让 first 指向该节点,并形成环形

②后面当我们每创建一个新的节点(如下图的节点2),就把该节点加入到已有的环形链表中即可
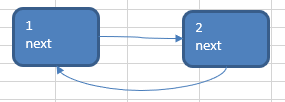
③重复步骤2(假设重复两次,形成如下4个节点的单向环形链表)
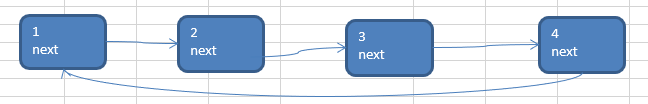
遍历环形链表
- 先让一个**辅助指针(**变量) curBoy,指向first节点
- 然后通过一个while循环遍历 该环形链表即可
curBoy.next == first结束
3. 代码实现
3.1. 实现单向环形链表
package Linkedlist;
public class Josepfu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(5);//加入5个小孩节点
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
}
}
//创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
//创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = new Boy(-1);
//添加小孩,构建成一个环形的链表
public void addBoy(int nums) {
//对 nums 做一个数据校验(不能小于1)
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确,不能小于1");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null;//辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
//使用for来创建环形链表
for(int i = 1; i <= nums; i++){
//根据编号,创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
//如果是第一个小孩
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);//构成环状
curBoy = first;//让curBoy指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);//
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
//遍历当前环形链表
public void showBoy() {
//判断链表是否为空
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,没有任何小孩");
return;
}
//因为first不能动,因此使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
Boy curBoy = first;
while (true) {
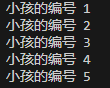
System.out.printf("小孩的编号 %d \n", curBoy.getNo());
if (curBoy.getNext() == first) {//说明已经遍历完毕
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();//curBoy后移
}
}
}
//创建一个Boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy{
private int no;//编号
private Boy next;//指向下一个节点,默认null
public Boy(int no){
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return this.no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return this.next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
运行结果:
3.2. 产生出队编号序列
3.2.1. 思路分析
①需求创建一个辅助指针(变量) helper , 事先应该指向环形链表的最后这个节点(小孩报数前,先让 first 和 helper 移动 k - 1次)
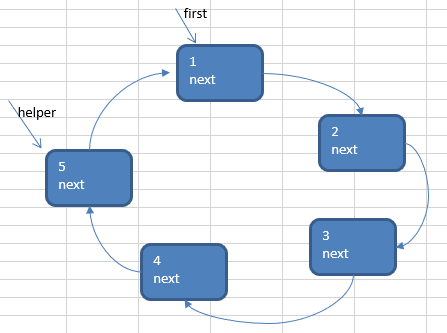
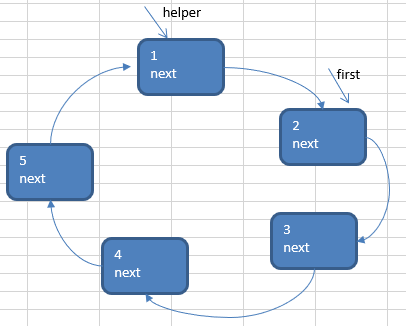
②当小孩报数时,让first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 m - 1 次
(本题m=2,故移动m-1=1次)
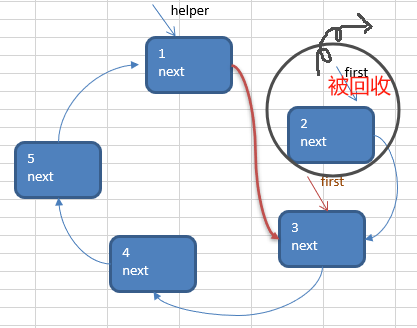
③这时就可以将first指向的小孩节点 出圈
first = first .next
helper.next = first
(原来first 指向的节点就没有任何引用,就会被回收)
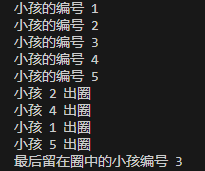
出圈的顺序: 2->4->1->5->3
3.2.2. 代码实现
package Linkedlist;
public class Josepfu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(5);// 加入5个小孩节点
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
// 出圈
circleSingleLinkedList.countBoy(1, 2, 5);// 2->4->1->5->3
}
}
// 创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
// 创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = new Boy(-1);
// 添加小孩,构建成一个环形的链表
public void addBoy(int nums) {
// 对 nums 做一个数据校验(不能小于1)
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确,不能小于1");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null;// 辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
// 使用for来创建环形链表
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
// 根据编号,创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
// 如果是第一个小孩
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);// 构成环状
curBoy = first;// 让curBoy指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);//
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
// 遍历当前环形链表
public void showBoy() {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,没有任何小孩");
return;
}
// 因为first不能动,因此使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
Boy curBoy = first;
while (true) {
System.out.printf("小孩的编号 %d \n", curBoy.getNo());
if (curBoy.getNext() == first) {// 说明已经遍历完毕
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();// curBoy后移
}
}
// 根据输入,计算出小孩出圈的顺序
/**
*
* @param startNo 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum 表示数几下
* @param nums 表示多少个小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
// 先对数据进行校验
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误,请重新输入");
return;
}
// 创建一个辅助指针 helper 帮助完成小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
// 创建一个辅助指针(变量)helper,事先应该指向环形链表的最后这个节点
while (true) {
if (helper.getNext() == first) {
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
// 小孩报数前,先让first和helper移动k-1次
for (int j = 0; j < startNo - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
// 当小孩报数时,让first和helper指针同时移动m-1次,然后出圈
// 这里是一个循环操作,直到圈中只有一个节点
while (true) {
if (helper == first) {// 说明圈中只有一个节点
break;
}
// 让first和helper指针同时移动countNum-1
for (int j = 0; j < countNum - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
// 这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的节点
System.out.printf("小孩 %d 出圈\n", first.getNo());
// 这时将first指向的小孩出圈
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号 %d \n", first.getNo());
}
}
// 创建一个Boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy {
private int no;// 编号
private Boy next;// 指向下一个节点,默认null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return this.no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return this.next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
运行结果:



![[Kettle] 生成记录](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1e271ac5647c4a33ad5aac86387692c8.png)