文章目录
- Three common registration techniques
- Point-to-point technique
- Point-to-plane registration
- ICP registration
- Helper visualization function
- Input
- Global registration
- Extract geometric feature
- Input
- RANSAC
- Point-to-point ICP
- Point-to-plane ICP
- References
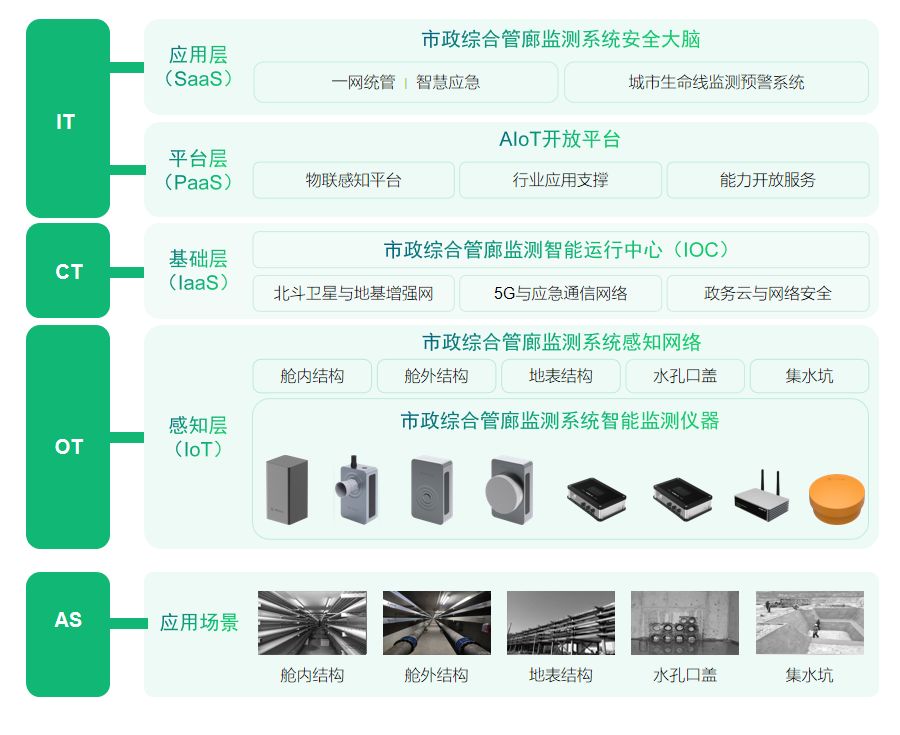
Three common registration techniques
假设有一个点集 P \boldsymbol{P} P 在源表面 S P \mathcal{S}_P SP,另一个点集 Q \boldsymbol{Q} Q 在目的表面 S Q \mathcal{S}_Q SQ。如果在每个表面都有 K K K 个点,那么配准问题可以看作一个刚体变换 T = [ R ∣ t ] \boldsymbol{T}=[\boldsymbol{R}|\boldsymbol{t}] T=[R∣t],最小化下面的对准误差: ϵ = ∑ k = 1 K ∥ Q k − ( R P k + t ) ∥ 2 \epsilon=\sum_{k=1}^K \| \boldsymbol{Q}_k-(\boldsymbol{R}\boldsymbol{P}_k+\boldsymbol{t})\|^2 ϵ=k=1∑K∥Qk−(RPk+t)∥2

Point-to-point technique
从源表面的一点 p \boldsymbol{p} p 出发,p2p 寻找目的表面上最近的点 q \boldsymbol{q} q。 d s d_s ds 代表两点之间的距离。为了找到最近点,通常会采用 kd-tree 来进行搜索。
Point-to-plane registration
从源点的法向量寻找目的表面的交叉点。如上图 (b) 所示,点 q ′ \boldsymbol{q}' q′ 是点 p \boldsymbol{p} p 在点 q \boldsymbol{q} q正切平面上的投影。
ICP registration
输入:两个点云及一个初始的可以大致对准两个点云的变换矩阵;
输出:可以准确对准两个点云的变换矩阵。
Helper visualization function
下面的函数可视化目标点云和经过变换后的源点云:
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4459,
front=[0.9288, -0.2951, -0.2242],
lookat=[1.6784, 2.0612, 1.4451],
up=[-0.3402, -0.9189, -0.1996])
因为函数
transform和paint_uniform_color会改变原始点云,因此这里用深拷贝copy.deepcopy来“保护”原始点云。
Input
下面的代码从两个文件中分别读入源点云和目标点云,并给出了一个初始变换矩阵。
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
threshold = 0.02
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.862, 0.011, -0.507, 0.5],
[-0.139, 0.967, -0.215, 0.7],
[0.487, 0.255, 0.835, -1.4], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
draw_registration_result(source, target, trans_init)
下面的函数 evaluate_registration 主要计算两个指标:
fitness:衡量重叠区域的大小(# of inlier correspondences / # of points in target),越大越好inlier_rmse:计算所有 inlier correspondences 的 RMSE,越小越好
初始的变换矩阵通常通过一个全局的配准算法得到。
Global registration
Extract geometric feature
下采样点云,估计法向量,然后对每个点计算 FPFH 特征。FPFH 特征是一个 33 维的向量,它可以描述一个点的局部几何性质。
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
Input
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: Load two point clouds and disturb initial pose.")
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
RANSAC
在每个 RANSAC 的迭代中,ransac_n 个随机点从源点云中被选出。它们在目标点云中的对应点通过查询 33 维的 FPFH 特征空间得到。
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: RANSAC registration on downsampled point clouds.")
print(" Since the downsampling voxel size is %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" we use a liberal distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True,
distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False),
3, [
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(
0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(
distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)
之后我们就需要用点到点的 ICP 或者点到面的 ICP 来进一步提升配准精度。
Point-to-point ICP
从以下两步骤中进行迭代:
- 从目标点云 P \boldsymbol{P} P 中寻找对应点集 K = { ( p , q ) } \mathcal{K}=\{(\boldsymbol{p},\boldsymbol{q})\} K={(p,q)},源点云通过现有的变换矩阵 T \boldsymbol{T} T 进行变换;
- 通过最小化目标函数 E ( T ) E(\boldsymbol{T}) E(T) 来更新变换矩阵 T \boldsymbol{T} T。不同的 ICP 变体会采用不同的目标函数 E ( T ) E(\boldsymbol{T}) E(T),这里使用如下的目标函数 E ( T ) = ∑ ( p , q ) ∈ K ∥ p − T q ∥ 2 E(\boldsymbol{T})=\sum_{(\boldsymbol{p},\boldsymbol{q})\in \mathcal{K}} \|\boldsymbol{p}-\boldsymbol{T}\boldsymbol{q} \|^2 E(T)=(p,q)∈K∑∥p−Tq∥2
print("Apply point-to-point ICP")
reg_p2p = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, threshold, trans_init,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint())
print(reg_p2p)
print("Transformation is:")
print(reg_p2p.transformation)
draw_registration_result(source, target, reg_p2p.transformation)
默认情况下,registration_icp 会运行直到收敛或者达到了默认最大迭代次数(30)。 也可以指定最大的迭代次数:
reg_p2p = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, threshold, trans_init,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(),
o3d.pipelines.registration.ICPConvergenceCriteria(max_iteration=2000))
print(reg_p2p)
print("Transformation is:")
print(reg_p2p.transformation)
draw_registration_result(source, target, reg_p2p.transformation)
Point-to-plane ICP
点到面的 ICP 采用下面的目标函数:
E
(
T
)
=
∑
(
p
,
q
)
∈
K
(
(
p
−
T
q
)
⋅
n
p
)
2
E(\boldsymbol{T})=\sum_{(\boldsymbol{p},\boldsymbol{q})\in \mathcal{K}} ((\boldsymbol{p}-\boldsymbol{T}\boldsymbol{q})\cdot \boldsymbol{n}_p)^2
E(T)=(p,q)∈K∑((p−Tq)⋅np)2
n
p
\boldsymbol{n}_p
np 代表每个点
p
\boldsymbol{p}
p 的法向量。点到面 ICP 比点到点 ICP 有更快的收敛速度。
print("Apply point-to-plane ICP")
reg_p2l = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, threshold, trans_init,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
print(reg_p2l)
print("Transformation is:")
print(reg_p2l.transformation)
draw_registration_result(source, target, reg_p2l.transformation)
References
[1] open3d 官方文档,http://www.open3d.org/docs/release/tutorial/pipelines/icp_registration.html
[2] Park, S.-Y & Subbarao, M… (2003). A fast Point-to-Tangent Plane technique for multi-view registration. Fourth IEEE International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling. 500. 276- 283. 10.1109/IM.2003.1240260.