文章目录
- 前言
- 一、回环测试代码
- 1.1 头文件 spidev.h
- 2.2 c代码 spidev_test.c
- 二、 编译验证
- 2.1 交叉编译
- 2.2 测试
前言
linux下做spi回环测试
一、回环测试代码
1.1 头文件 spidev.h
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0+ WITH Linux-syscall-note */
/*
* include/linux/spi/spidev.h
*
* Copyright (C) 2006 SWAPP
* Andrea Paterniani <a.paterniani@swapp-eng.it>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
*/
#ifndef SPIDEV_H
#define SPIDEV_H
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
/* User space versions of kernel symbols for SPI clocking modes,
* matching <linux/spi/spi.h>
*/
#define SPI_CPHA 0x01
#define SPI_CPOL 0x02
#define SPI_MODE_0 (0|0)
#define SPI_MODE_1 (0|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_MODE_2 (SPI_CPOL|0)
#define SPI_MODE_3 (SPI_CPOL|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_CS_HIGH 0x04
#define SPI_LSB_FIRST 0x08
#define SPI_3WIRE 0x10
#define SPI_LOOP 0x20
#define SPI_NO_CS 0x40
#define SPI_READY 0x80
#define SPI_TX_DUAL 0x100
#define SPI_TX_QUAD 0x200
#define SPI_RX_DUAL 0x400
#define SPI_RX_QUAD 0x800
#define SPI_CS_WORD 0x1000
#define SPI_TX_OCTAL 0x2000
#define SPI_RX_OCTAL 0x4000
#define SPI_3WIRE_HIZ 0x8000
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* IOCTL commands */
#define SPI_IOC_MAGIC 'k'
/**
* struct spi_ioc_transfer - describes a single SPI transfer
* @tx_buf: Holds pointer to userspace buffer with transmit data, or null.
* If no data is provided, zeroes are shifted out.
* @rx_buf: Holds pointer to userspace buffer for receive data, or null.
* @len: Length of tx and rx buffers, in bytes.
* @speed_hz: Temporary override of the device's bitrate.
* @bits_per_word: Temporary override of the device's wordsize.
* @delay_usecs: If nonzero, how long to delay after the last bit transfer
* before optionally deselecting the device before the next transfer.
* @cs_change: True to deselect device before starting the next transfer.
* @word_delay_usecs: If nonzero, how long to wait between words within one
* transfer. This property needs explicit support in the SPI controller,
* otherwise it is silently ignored.
*
* This structure is mapped directly to the kernel spi_transfer structure;
* the fields have the same meanings, except of course that the pointers
* are in a different address space (and may be of different sizes in some
* cases, such as 32-bit i386 userspace over a 64-bit x86_64 kernel).
* Zero-initialize the structure, including currently unused fields, to
* accommodate potential future updates.
*
* SPI_IOC_MESSAGE gives userspace the equivalent of kernel spi_sync().
* Pass it an array of related transfers, they'll execute together.
* Each transfer may be half duplex (either direction) or full duplex.
*
* struct spi_ioc_transfer mesg[4];
* ...
* status = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(4), mesg);
*
* So for example one transfer might send a nine bit command (right aligned
* in a 16-bit word), the next could read a block of 8-bit data before
* terminating that command by temporarily deselecting the chip; the next
* could send a different nine bit command (re-selecting the chip), and the
* last transfer might write some register values.
*/
struct spi_ioc_transfer {
__u64 tx_buf;
__u64 rx_buf;
__u32 len;
__u32 speed_hz;
__u16 delay_usecs;
__u8 bits_per_word;
__u8 cs_change;
__u8 tx_nbits;
__u8 rx_nbits;
__u8 word_delay_usecs;
__u8 pad;
/* If the contents of 'struct spi_ioc_transfer' ever change
* incompatibly, then the ioctl number (currently 0) must change;
* ioctls with constant size fields get a bit more in the way of
* error checking than ones (like this) where that field varies.
*
* NOTE: struct layout is the same in 64bit and 32bit userspace.
*/
};
/* not all platforms use <asm-generic/ioctl.h> or _IOC_TYPECHECK() ... */
#define SPI_MSGSIZE(N) \
((((N)*(sizeof (struct spi_ioc_transfer))) < (1 << _IOC_SIZEBITS)) \
? ((N)*(sizeof (struct spi_ioc_transfer))) : 0)
#define SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(N) _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 0, char[SPI_MSGSIZE(N)])
/* Read / Write of SPI mode (SPI_MODE_0..SPI_MODE_3) (limited to 8 bits) */
#define SPI_IOC_RD_MODE _IOR(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 1, __u8)
#define SPI_IOC_WR_MODE _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 1, __u8)
/* Read / Write SPI bit justification */
#define SPI_IOC_RD_LSB_FIRST _IOR(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 2, __u8)
#define SPI_IOC_WR_LSB_FIRST _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 2, __u8)
/* Read / Write SPI device word length (1..N) */
#define SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD _IOR(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 3, __u8)
#define SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 3, __u8)
/* Read / Write SPI device default max speed hz */
#define SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ _IOR(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 4, __u32)
#define SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 4, __u32)
/* Read / Write of the SPI mode field */
#define SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32 _IOR(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 5, __u32)
#define SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32 _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 5, __u32)
#endif /* SPIDEV_H */
2.2 c代码 spidev_test.c
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-only
/*
* SPI testing utility (using spidev driver)
*
* Copyright (c) 2007 MontaVista Software, Inc.
* Copyright (c) 2007 Anton Vorontsov <avorontsov@ru.mvista.com>
*
* Cross-compile with cross-gcc -I/path/to/cross-kernel/include
*/
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include "spidev.h"
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof((a)[0]))
static void pabort(const char *s)
{
if (errno != 0)
perror(s);
else
printf("%s\n", s);
abort();
}
static const char *device = "/dev/spidev1.1";
static uint32_t mode;
static uint8_t bits = 8;
static char *input_file;
static char *output_file;
static uint32_t speed = 500000;
static uint16_t delay;
static int verbose;
static int transfer_size;
static int iterations;
static int interval = 5; /* interval in seconds for showing transfer rate */
static uint8_t default_tx[] = {
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0x40, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x95,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
0xF0, 0x0D,
};
static uint8_t default_rx[ARRAY_SIZE(default_tx)] = {0, };
static char *input_tx;
static void hex_dump(const void *src, size_t length, size_t line_size,
char *prefix)
{
int i = 0;
const unsigned char *address = src;
const unsigned char *line = address;
unsigned char c;
printf("%s | ", prefix);
while (length-- > 0) {
printf("%02X ", *address++);
if (!(++i % line_size) || (length == 0 && i % line_size)) {
if (length == 0) {
while (i++ % line_size)
printf("__ ");
}
printf(" |");
while (line < address) {
c = *line++;
printf("%c", (c < 32 || c > 126) ? '.' : c);
}
printf("|\n");
if (length > 0)
printf("%s | ", prefix);
}
}
}
/*
* Unescape - process hexadecimal escape character
* converts shell input "\x23" -> 0x23
*/
static int unescape(char *_dst, char *_src, size_t len)
{
int ret = 0;
int match;
char *src = _src;
char *dst = _dst;
unsigned int ch;
while (*src) {
if (*src == '\\' && *(src+1) == 'x') {
match = sscanf(src + 2, "%2x", &ch);
if (!match)
pabort("malformed input string");
src += 4;
*dst++ = (unsigned char)ch;
} else {
*dst++ = *src++;
}
ret++;
}
return ret;
}
static void transfer(int fd, uint8_t const *tx, uint8_t const *rx, size_t len)
{
int ret;
int out_fd;
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
.len = len,
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
if (mode & SPI_TX_OCTAL)
tr.tx_nbits = 8;
else if (mode & SPI_TX_QUAD)
tr.tx_nbits = 4;
else if (mode & SPI_TX_DUAL)
tr.tx_nbits = 2;
if (mode & SPI_RX_OCTAL)
tr.rx_nbits = 8;
else if (mode & SPI_RX_QUAD)
tr.rx_nbits = 4;
else if (mode & SPI_RX_DUAL)
tr.rx_nbits = 2;
if (!(mode & SPI_LOOP)) {
if (mode & (SPI_TX_OCTAL | SPI_TX_QUAD | SPI_TX_DUAL))
tr.rx_buf = 0;
else if (mode & (SPI_RX_OCTAL | SPI_RX_QUAD | SPI_RX_DUAL))
tr.tx_buf = 0;
}
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1)
pabort("can't send spi message");
if (verbose)
hex_dump(tx, len, 32, "TX");
if (output_file) {
out_fd = open(output_file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (out_fd < 0)
pabort("could not open output file");
ret = write(out_fd, rx, len);
if (ret != len)
pabort("not all bytes written to output file");
close(out_fd);
}
if (verbose)
hex_dump(rx, len, 32, "RX");
}
static void print_usage(const char *prog)
{
printf("Usage: %s [-DsbdlHOLC3vpNR24SI]\n", prog);
puts(" -D --device device to use (default /dev/spidev1.1)\n"
" -s --speed max speed (Hz)\n"
" -d --delay delay (usec)\n"
" -b --bpw bits per word\n"
" -i --input input data from a file (e.g. \"test.bin\")\n"
" -o --output output data to a file (e.g. \"results.bin\")\n"
" -l --loop loopback\n"
" -H --cpha clock phase\n"
" -O --cpol clock polarity\n"
" -L --lsb least significant bit first\n"
" -C --cs-high chip select active high\n"
" -3 --3wire SI/SO signals shared\n"
" -v --verbose Verbose (show tx buffer)\n"
" -p Send data (e.g. \"1234\\xde\\xad\")\n"
" -N --no-cs no chip select\n"
" -R --ready slave pulls low to pause\n"
" -2 --dual dual transfer\n"
" -4 --quad quad transfer\n"
" -8 --octal octal transfer\n"
" -S --size transfer size\n"
" -I --iter iterations\n");
exit(1);
}
static void parse_opts(int argc, char *argv[])
{
while (1) {
static const struct option lopts[] = {
{ "device", 1, 0, 'D' },
{ "speed", 1, 0, 's' },
{ "delay", 1, 0, 'd' },
{ "bpw", 1, 0, 'b' },
{ "input", 1, 0, 'i' },
{ "output", 1, 0, 'o' },
{ "loop", 0, 0, 'l' },
{ "cpha", 0, 0, 'H' },
{ "cpol", 0, 0, 'O' },
{ "lsb", 0, 0, 'L' },
{ "cs-high", 0, 0, 'C' },
{ "3wire", 0, 0, '3' },
{ "no-cs", 0, 0, 'N' },
{ "ready", 0, 0, 'R' },
{ "dual", 0, 0, '2' },
{ "verbose", 0, 0, 'v' },
{ "quad", 0, 0, '4' },
{ "octal", 0, 0, '8' },
{ "size", 1, 0, 'S' },
{ "iter", 1, 0, 'I' },
{ NULL, 0, 0, 0 },
};
int c;
c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "D:s:d:b:i:o:lHOLC3NR248p:vS:I:",
lopts, NULL);
if (c == -1)
break;
switch (c) {
case 'D':
device = optarg;
break;
case 's':
speed = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'd':
delay = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
bits = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'i':
input_file = optarg;
break;
case 'o':
output_file = optarg;
break;
case 'l':
mode |= SPI_LOOP;
break;
case 'H':
mode |= SPI_CPHA;
break;
case 'O':
mode |= SPI_CPOL;
break;
case 'L':
mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
break;
case 'C':
mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
break;
case '3':
mode |= SPI_3WIRE;
break;
case 'N':
mode |= SPI_NO_CS;
break;
case 'v':
verbose = 1;
break;
case 'R':
mode |= SPI_READY;
break;
case 'p':
input_tx = optarg;
break;
case '2':
mode |= SPI_TX_DUAL;
break;
case '4':
mode |= SPI_TX_QUAD;
break;
case '8':
mode |= SPI_TX_OCTAL;
break;
case 'S':
transfer_size = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'I':
iterations = atoi(optarg);
break;
default:
print_usage(argv[0]);
}
}
if (mode & SPI_LOOP) {
if (mode & SPI_TX_DUAL)
mode |= SPI_RX_DUAL;
if (mode & SPI_TX_QUAD)
mode |= SPI_RX_QUAD;
if (mode & SPI_TX_OCTAL)
mode |= SPI_RX_OCTAL;
}
}
static void transfer_escaped_string(int fd, char *str)
{
size_t size = strlen(str);
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
tx = malloc(size);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
rx = malloc(size);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
size = unescape((char *)tx, str, size);
transfer(fd, tx, rx, size);
free(rx);
free(tx);
}
static void transfer_file(int fd, char *filename)
{
ssize_t bytes;
struct stat sb;
int tx_fd;
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
if (stat(filename, &sb) == -1)
pabort("can't stat input file");
tx_fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (tx_fd < 0)
pabort("can't open input file");
tx = malloc(sb.st_size);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
rx = malloc(sb.st_size);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
bytes = read(tx_fd, tx, sb.st_size);
if (bytes != sb.st_size)
pabort("failed to read input file");
transfer(fd, tx, rx, sb.st_size);
free(rx);
free(tx);
close(tx_fd);
}
static uint64_t _read_count;
static uint64_t _write_count;
static void show_transfer_rate(void)
{
static uint64_t prev_read_count, prev_write_count;
double rx_rate, tx_rate;
rx_rate = ((_read_count - prev_read_count) * 8) / (interval*1000.0);
tx_rate = ((_write_count - prev_write_count) * 8) / (interval*1000.0);
printf("rate: tx %.1fkbps, rx %.1fkbps\n", rx_rate, tx_rate);
prev_read_count = _read_count;
prev_write_count = _write_count;
}
static void transfer_buf(int fd, int len)
{
uint8_t *tx;
uint8_t *rx;
int i;
tx = malloc(len);
if (!tx)
pabort("can't allocate tx buffer");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
tx[i] = random();
rx = malloc(len);
if (!rx)
pabort("can't allocate rx buffer");
transfer(fd, tx, rx, len);
_write_count += len;
_read_count += len;
if (mode & SPI_LOOP) {
if (memcmp(tx, rx, len)) {
fprintf(stderr, "transfer error !\n");
hex_dump(tx, len, 32, "TX");
hex_dump(rx, len, 32, "RX");
exit(1);
}
}
free(rx);
free(tx);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
int fd;
parse_opts(argc, argv);
if (input_tx && input_file)
pabort("only one of -p and --input may be selected");
fd = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
pabort("can't open device");
/*
* spi mode
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set spi mode");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get spi mode");
/*
* bits per word
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set bits per word");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get bits per word");
/*
* max speed hz
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set max speed hz");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get max speed hz");
printf("spi mode: 0x%x\n", mode);
printf("bits per word: %u\n", bits);
printf("max speed: %u Hz (%u kHz)\n", speed, speed/1000);
if (input_tx)
transfer_escaped_string(fd, input_tx);
else if (input_file)
transfer_file(fd, input_file);
else if (transfer_size) {
struct timespec last_stat;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &last_stat);
while (iterations-- > 0) {
struct timespec current;
transfer_buf(fd, transfer_size);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, ¤t);
if (current.tv_sec - last_stat.tv_sec > interval) {
show_transfer_rate();
last_stat = current;
}
}
printf("total: tx %.1fKB, rx %.1fKB\n",
_write_count/1024.0, _read_count/1024.0);
} else
transfer(fd, default_tx, default_rx, sizeof(default_tx));
close(fd);
return ret;
}
二、 编译验证
2.1 交叉编译
arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc spidev_test.c -o spidev_test -static
2.2 测试
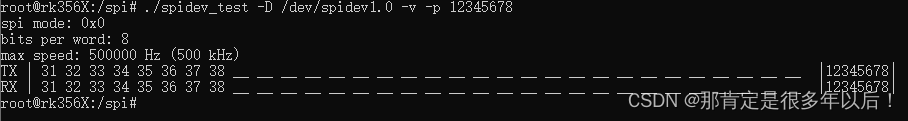
./spidev_test -D /dev/spidev1.0 -v -p 12345678
没短接rx,tx,数据接收异常

短接rx,tx,数据收发正常