这里写目录标题
- 递归的思想
- 序列求最大值
- 翻转字符串
- 斐波那契数列
- 数塔
- 回文字符串
- 上楼
- 汉诺塔
- 棋盘覆盖问题
- 数字螺旋矩阵
- 盒分形
递归的思想
子问题须与原始问题为同样的事,且更为简单。
不能无限制地调用本身,须有个出口,化简为非递归状况处理
序列求最大值
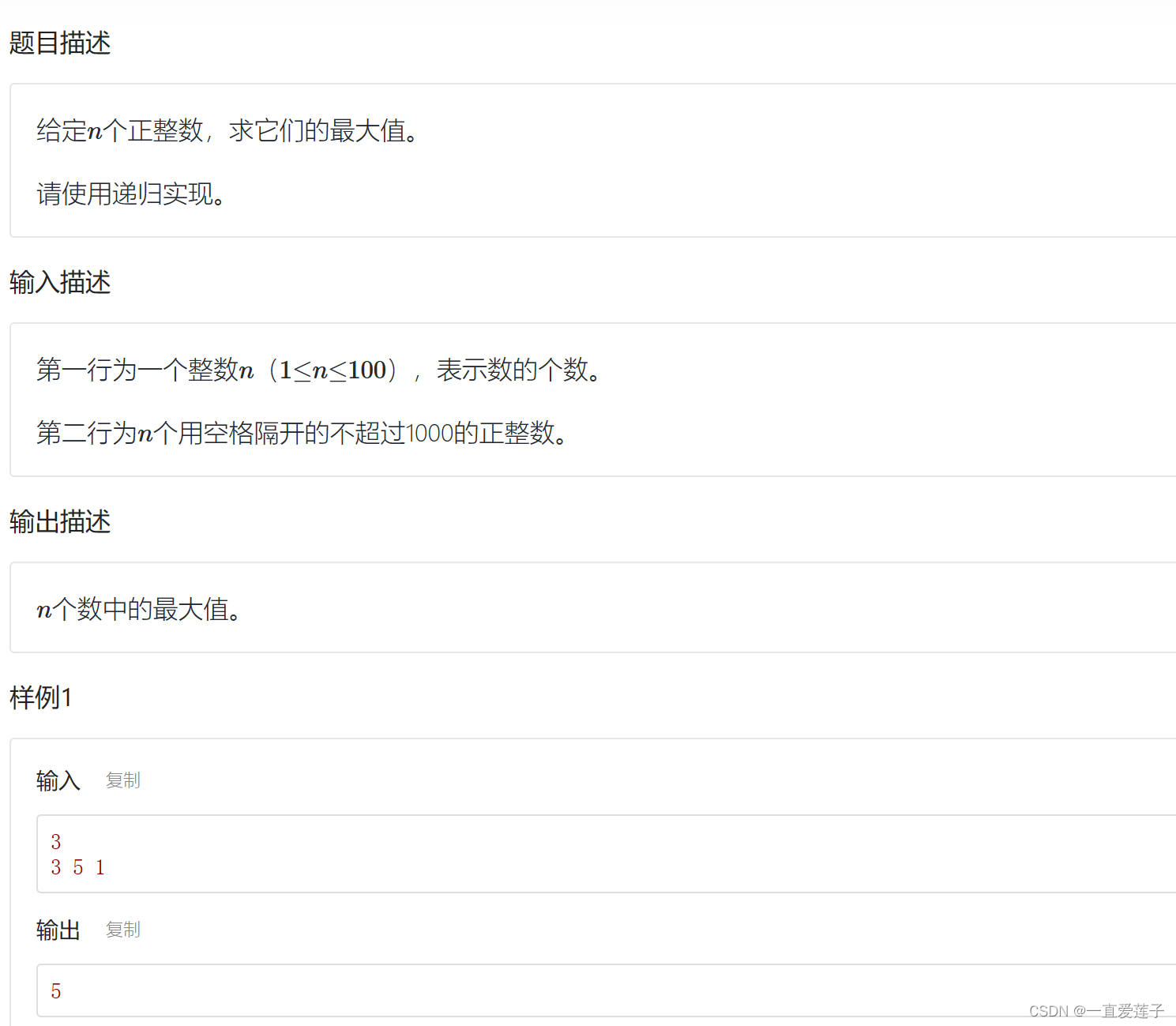
求出输出n个数据中的最大值
方法一:直接一边输出然后进行比较大小
方法二:利用数组然后用递归的思想进行
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
int a[N];//全局变量嘛,随意函数不需要再一次的定义了
int fin(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return a[1];
}
else
return max(fin(n - 1), a[n]);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
printf("%d", fin(n));
return 0;
}
翻转字符串
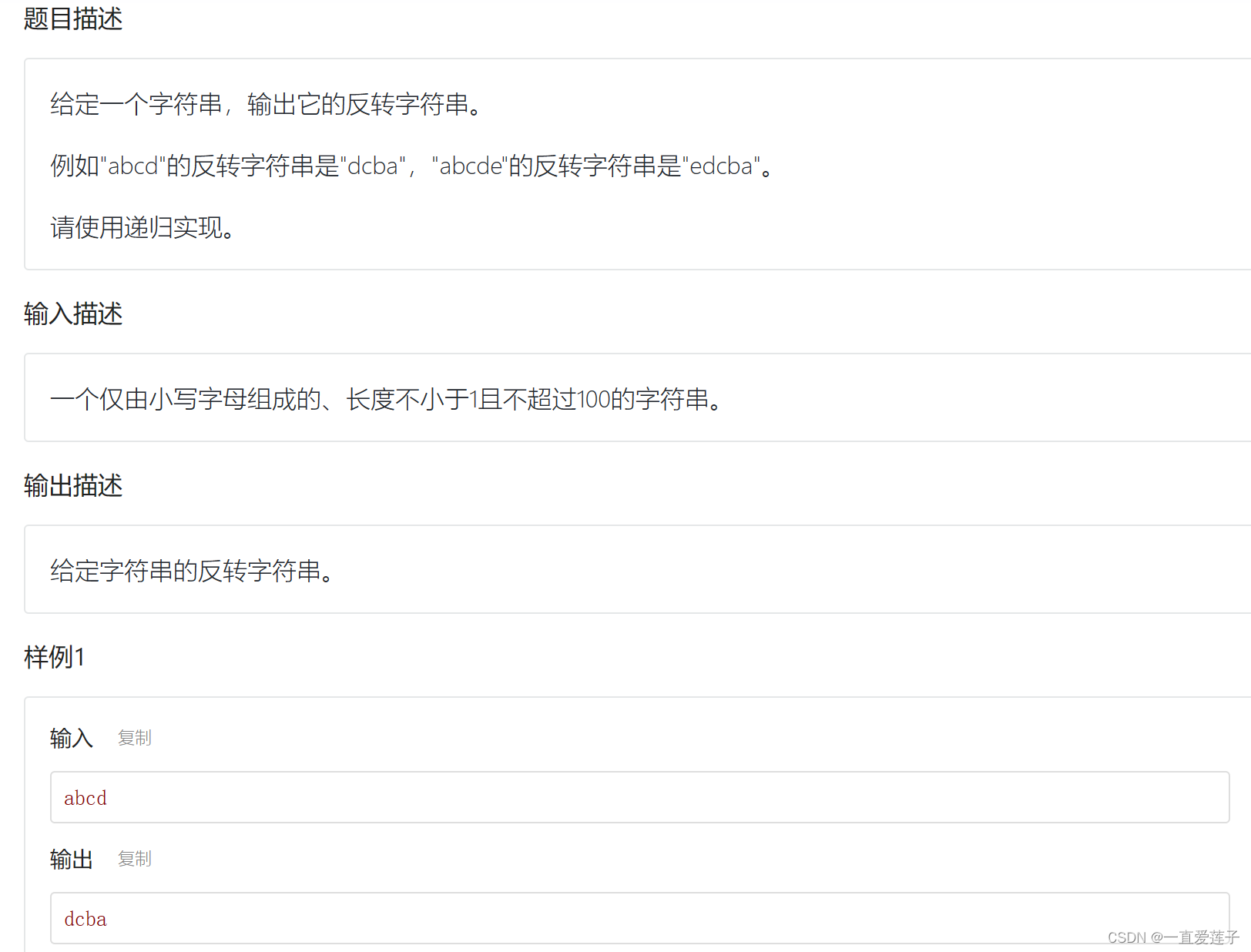
//其中考察的知识点有tring sub2 = s.substr(5, 3); //从下标为5开始截取长度为3位:sub2 = “567”
//需要知道的是在c++中string库中 字符相加是自动的链接的
//翻转字符串
//利用了一个函数s.substr()
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1001;
string s;
string reverse(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return s.substr(0, 1);
}
else
return s.substr(n - 1, 1) + reverse(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
cin >> s;
cout << reverse(s.length()) << endl;
return 0;
}
斐波那契数列

雯波那契数列
给定一个正整数n,求结果第n项f[n]
当n=1时,f[n]=1 n=2时 f[n]=1
n>2时 f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)
#include <cstdio>
int f(int n) {
if (n <= 2) {
return 1;
} else {
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", f(n));
return 0;
}
数塔
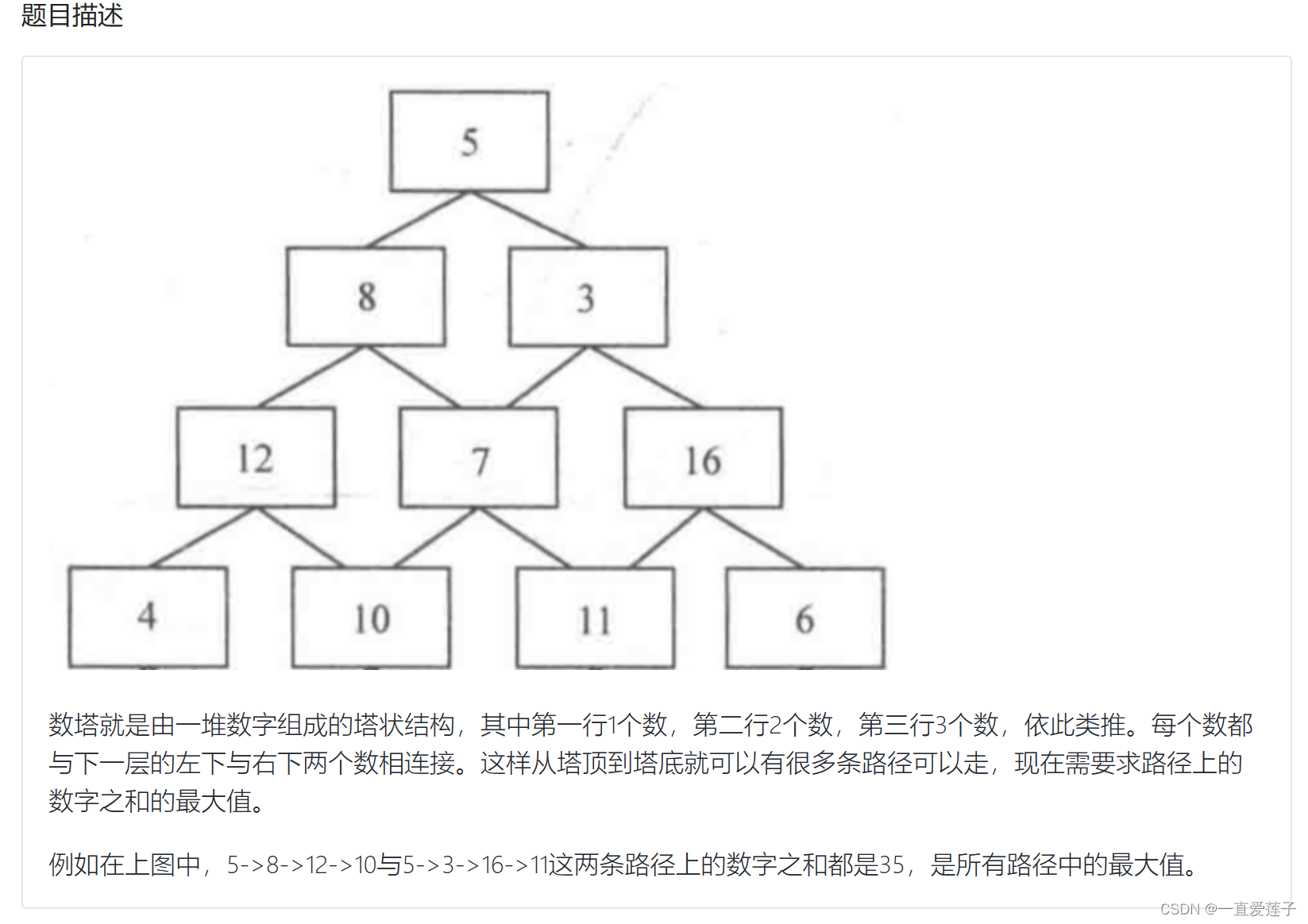
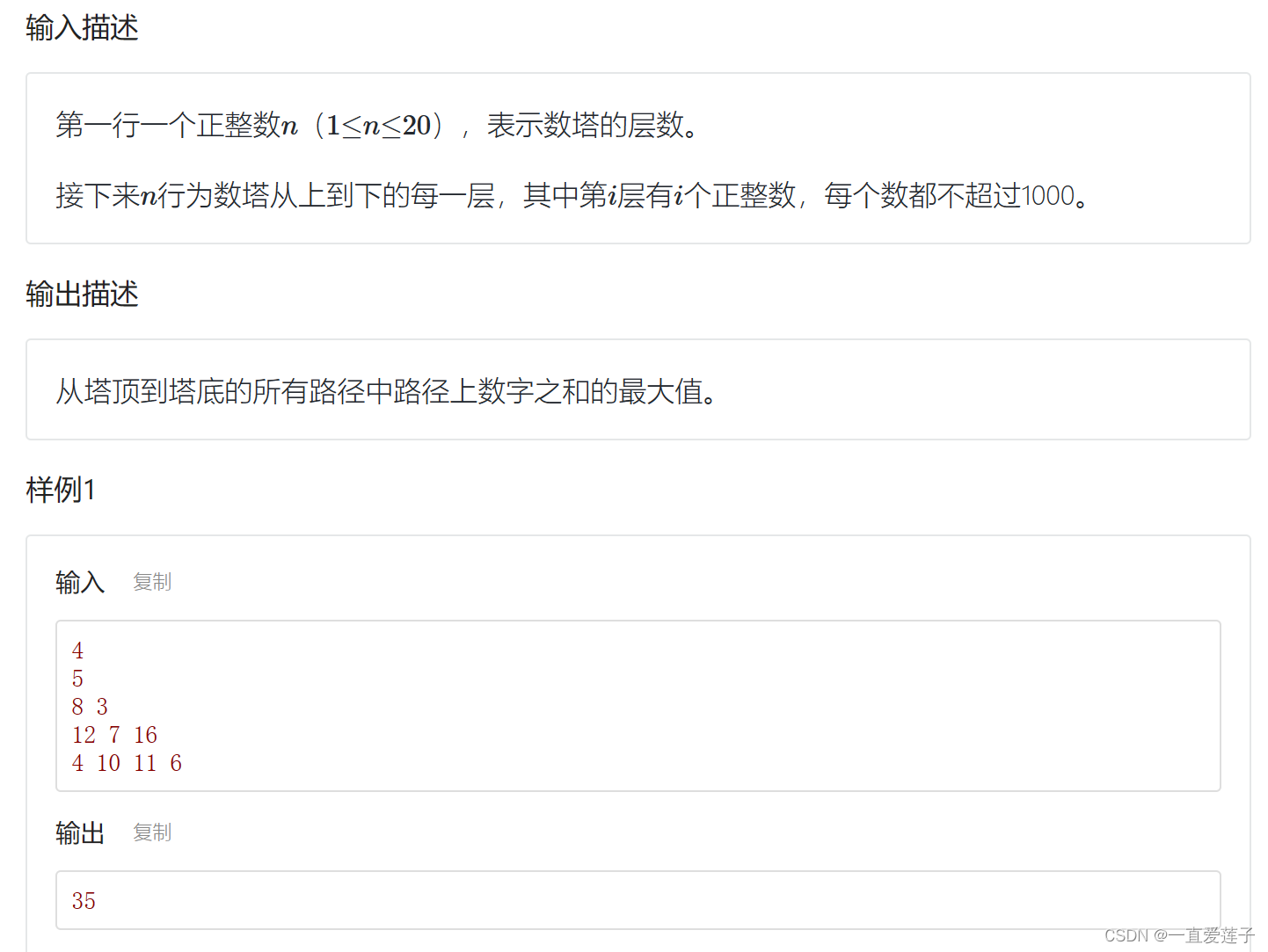
//#include<iostream>
//#include<algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1001;
//int a[N][N], n;
//int getmax(int i, int j)//从左边和右边分别求出最大值的路径,递归的方式
//{
// if (n == i)//这个是到n层是的条件,进行反向的输出数据
// {
// return a[n][j];
// }
// else
// {
// return max(getmax(i + 1, j), getmax(i + 1, j + 1));//求出的是左右边值的最大值
// }
//
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)//纵坐标是根据衡坐标来的,但是本质上还是二维数组
// {
// cin >> a[i][j];
// }
// }
// printf("%d", getmax(1, 1));//调用二维数组衡坐标和纵坐标
// return 0;
//}
回文字符串
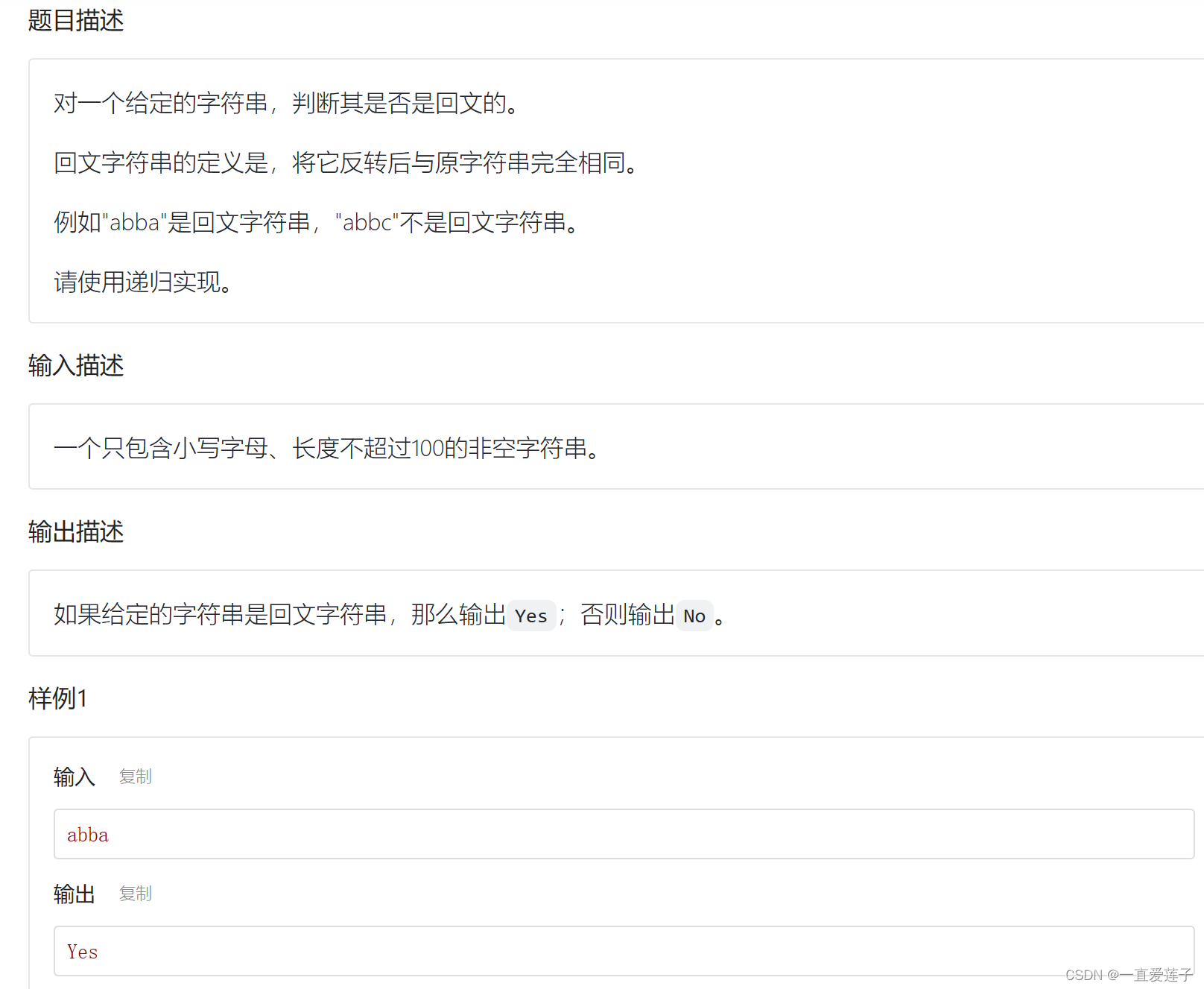
//运用的是true进行判断的,实际的效果真的很好
//注意的点:
//求字符串的长度的时候,用s.length()本身自带的函数
//利用布尔函数进行
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
string s;
bool personer(int i, int j)
{
if (i >= j)
{
return true;
}
else
return (personer(i + 1, j - 1) && s[i] == s[j]);
}
int main()
{
cin >> s;
//判断是不是回文,'YES'是true,’NO‘是false
cout << personer(0, s.length() - 1) ? "YES" : "NO" << endl;
return 0;
}
上楼
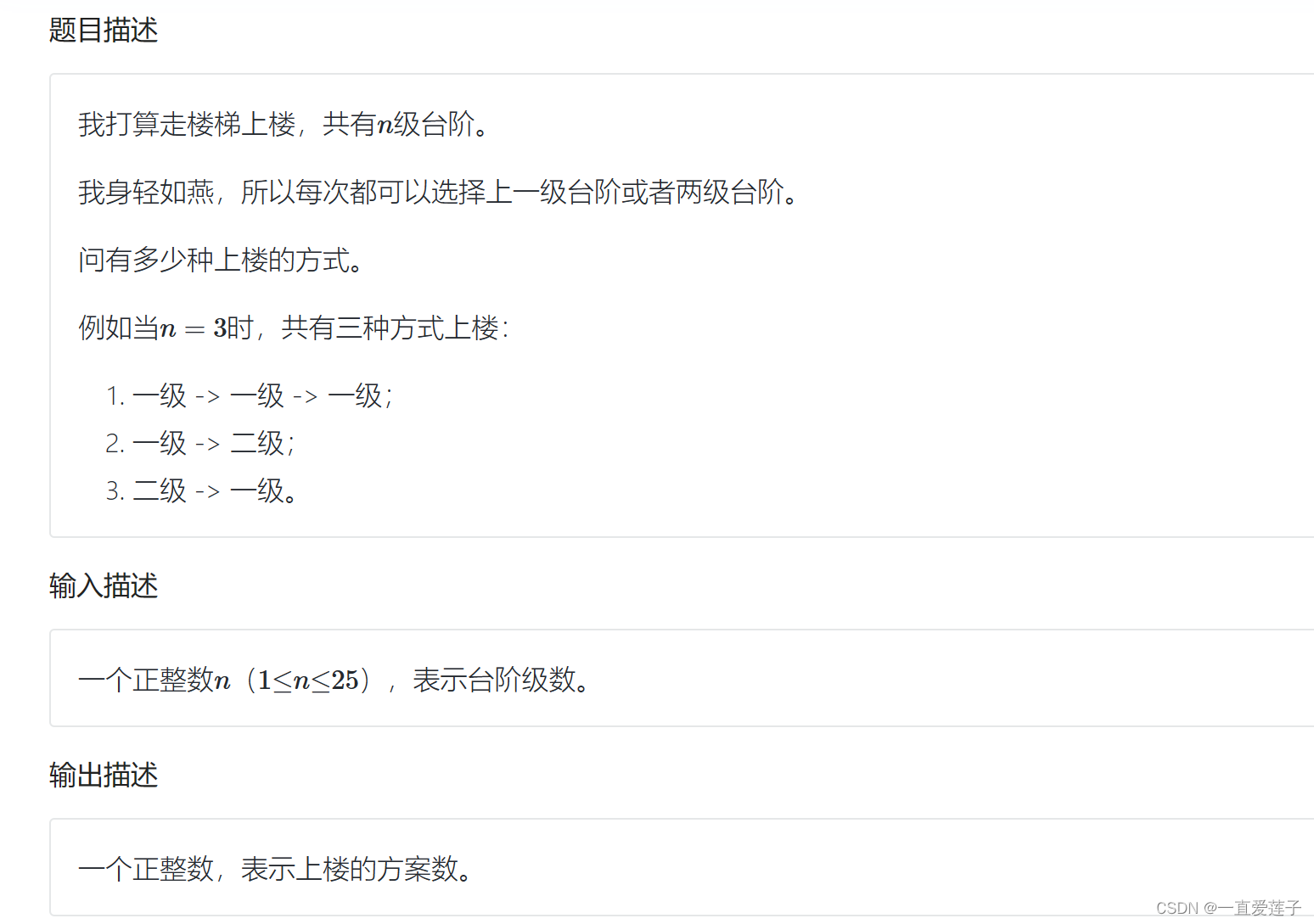

上楼问题,一共有n级台阶,每次选择上一级或者两级
例如当 n=3时,共有三种方式上楼:
一级->一级->一级;
一级->二级;
二级->一级。
因为就只有两种方式,所以
#include <cstdio>
int f(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", f(n));
return 0;
}
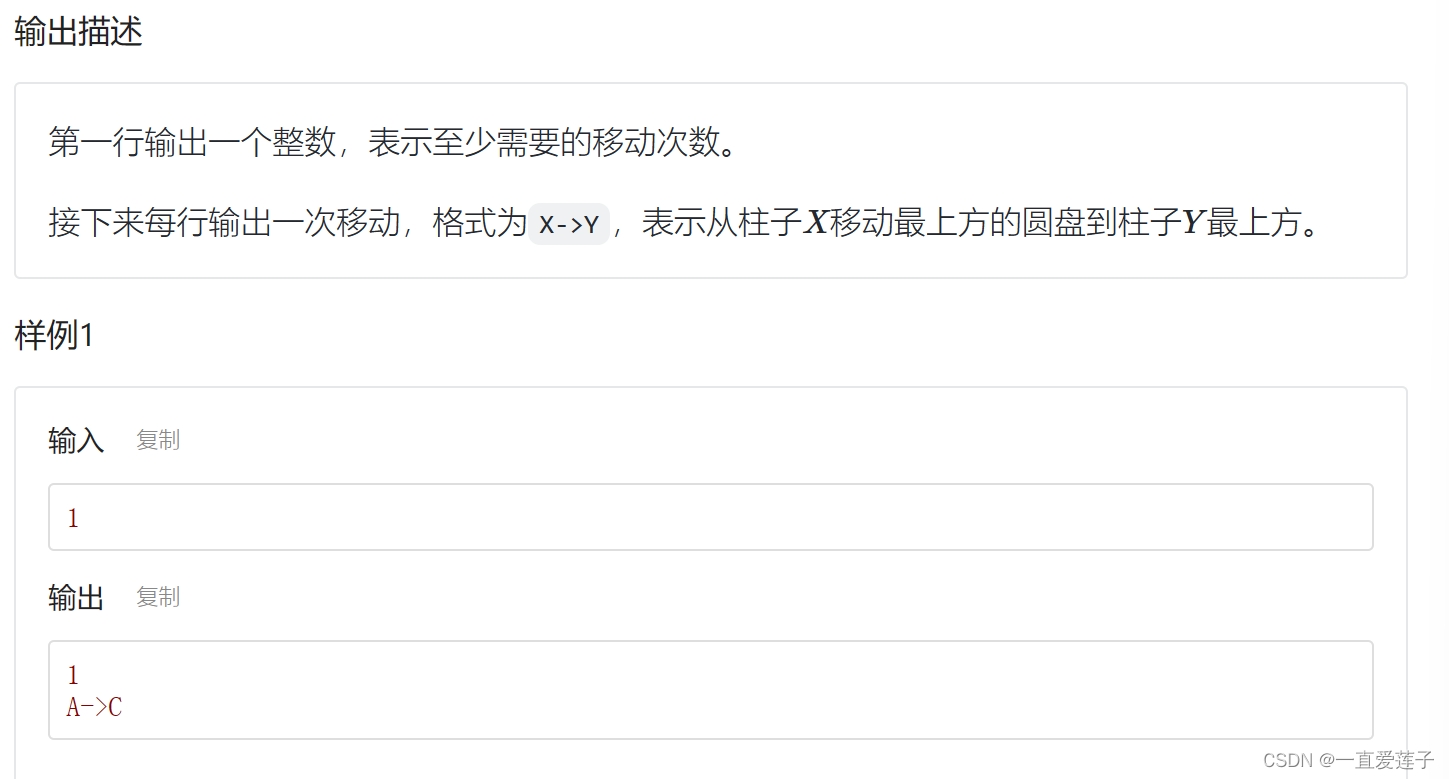
汉诺塔


//#include <cstdio>
//#include <cmath>
//void moveHanoi(int n, char from, char to, char mid)
//{
// if (n == 0)
// {
// return;
// }
// else
// {
// moveHanoi(n - 1, from, mid, to);
// printf("%c->%c\n", from, to);
// moveHanoi(n - 1, mid, to, from);
// }
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// int n;
// scanf("%d", &n);
// printf("%d\n", (int)pow(2.0, 1.0 * n) - 1);
// moveHanoi(n, 'A', 'C', 'B');
// return 0;
//}
//步骤,将n-1个圆盘移动到辅助柱上面,最后一个移动到目标柱,然后将辅助柱上的所有移动到目标柱子上面
//void hanoi(int num,char sou, char tar, char aux)//圆盘的个数,起始点,目标点,辅助点
//{
// static int count = 1;
// if (num == 1)
// {
// cout << "第" << count << "次:从<<sou<<"移动到" <<tar<<endl;
// count++
// }
// else
// {
// hanoi(num - 1, sou, aux, tar);
// cout << "第" << count << "次:从" << sou << "移动到" << tar << endl;
// count++;
// hanoi(num - 1, aux, tar, sou);
// }
//}
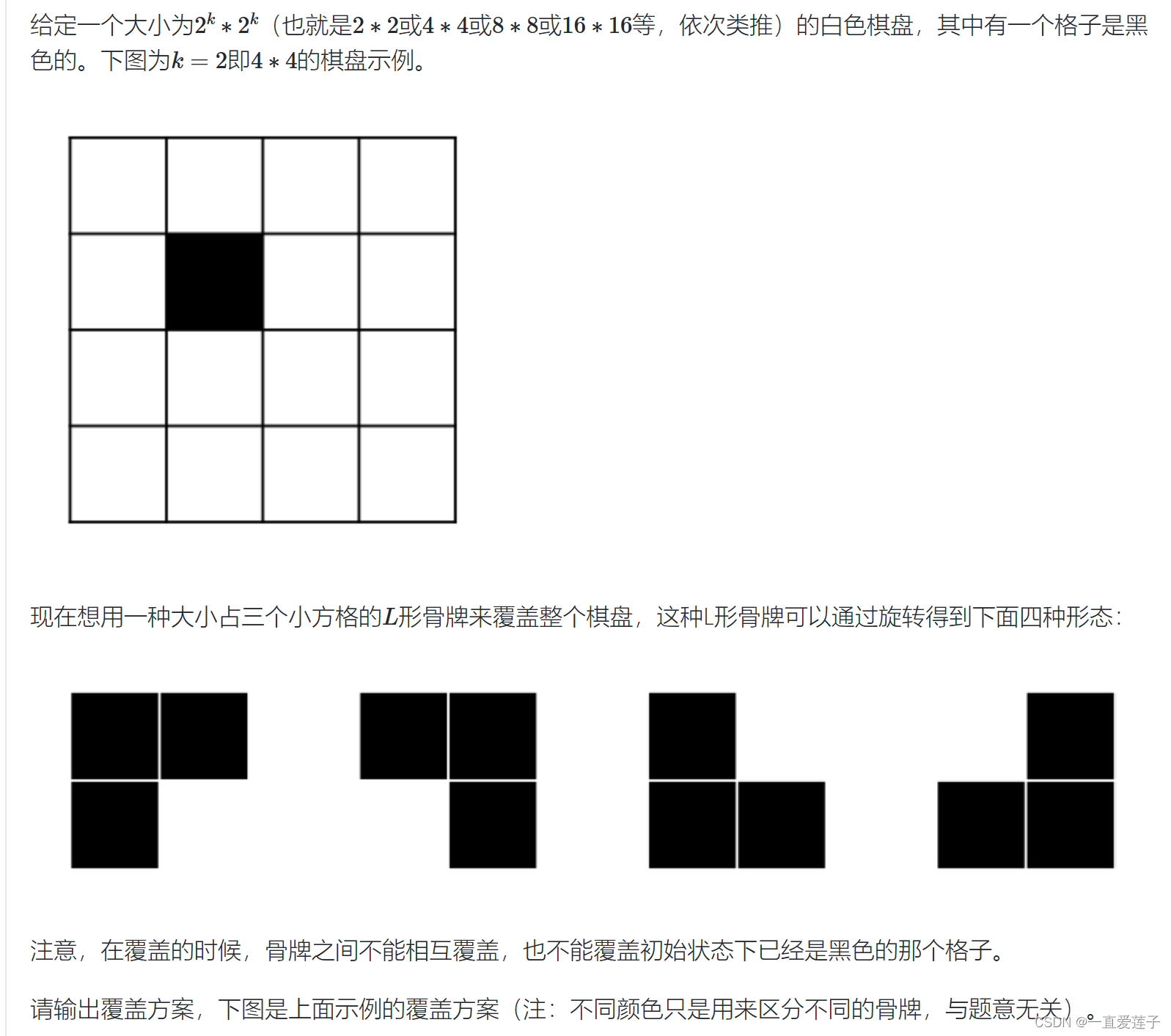
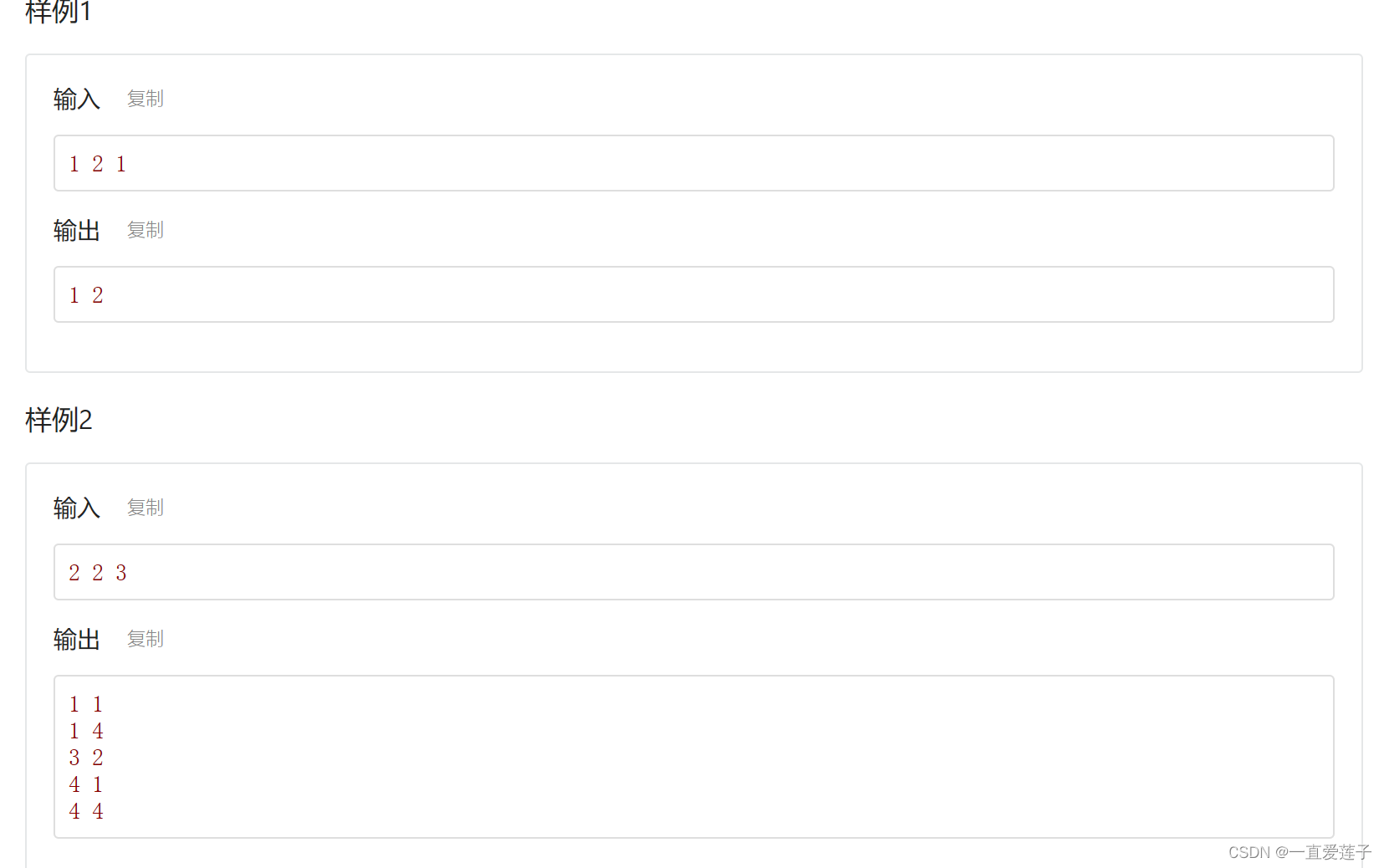
棋盘覆盖问题


#include <iostream>
int tile = 1; // 骨牌序号
int board[128][128]; // 二维数组模拟棋盘
// (tr,tc)表示棋盘的左上角坐标(即确定棋盘位置), (dr,dc)表示特殊方块的位置, size=2^k确定棋盘大小
void chessBoard(int tr, int tc, int dr, int dc, int size)
{
// 递归出口
if (size == 1)
return;
int s = size / 2; //分割棋盘
int t = tile++; //t记录本层骨牌序号
// 判断特殊方格在不在左上棋盘
if (dr < tr + s && dc < tc + s)
{
chessBoard(tr, tc, dr, dc, s); //特殊方格在左上棋盘的递归处理方法
}
else
{
board[tr + s - 1][tc + s - 1] = t; // 用t号的L型骨牌覆盖右下角
chessBoard(tr, tc, tr + s - 1, tc + s - 1, s); // 递归覆盖其余方格
}
// 判断特殊方格在不在右上棋盘
if (dr < tr + s && dc >= tc + s)
{
chessBoard(tr, tc + s, dr, dc, s);
}
else
{
board[tr + s - 1][tc + s] = t;
chessBoard(tr, tc + s, tr + s - 1, tc + s, s);
}
// 判断特殊方格在不在左下棋盘
if (dr >= tr + s && dc < tc + s)
{
chessBoard(tr + s, tc, dr, dc, s);
}
else
{
board[tr + s][tc + s - 1] = t;
chessBoard(tr + s, tc, tr + s, tc + s - 1, s);
}
// 判断特殊方格在不在右下棋盘
if (dr >= tr + s && dc >= tc + s)
{
chessBoard(tr + s, tc + s, dr, dc, s);
}
else
{
board[tr + s][tc + s] = t;
chessBoard(tr + s, tc + s, tr + s, tc + s, s);
}
}
int main()
{
int boardSize = 8; // 棋盘边长
chessBoard(0, 0, 3, 3, boardSize); // (0, 0)为顶点,大小为boardSize的棋盘; 特殊方块位于(3, 3)
// 打印棋盘
int i, j;
printf("\n\n\n");
for (i = 0; i < boardSize; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < boardSize; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", board[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\n\n");
}
return 0;
}
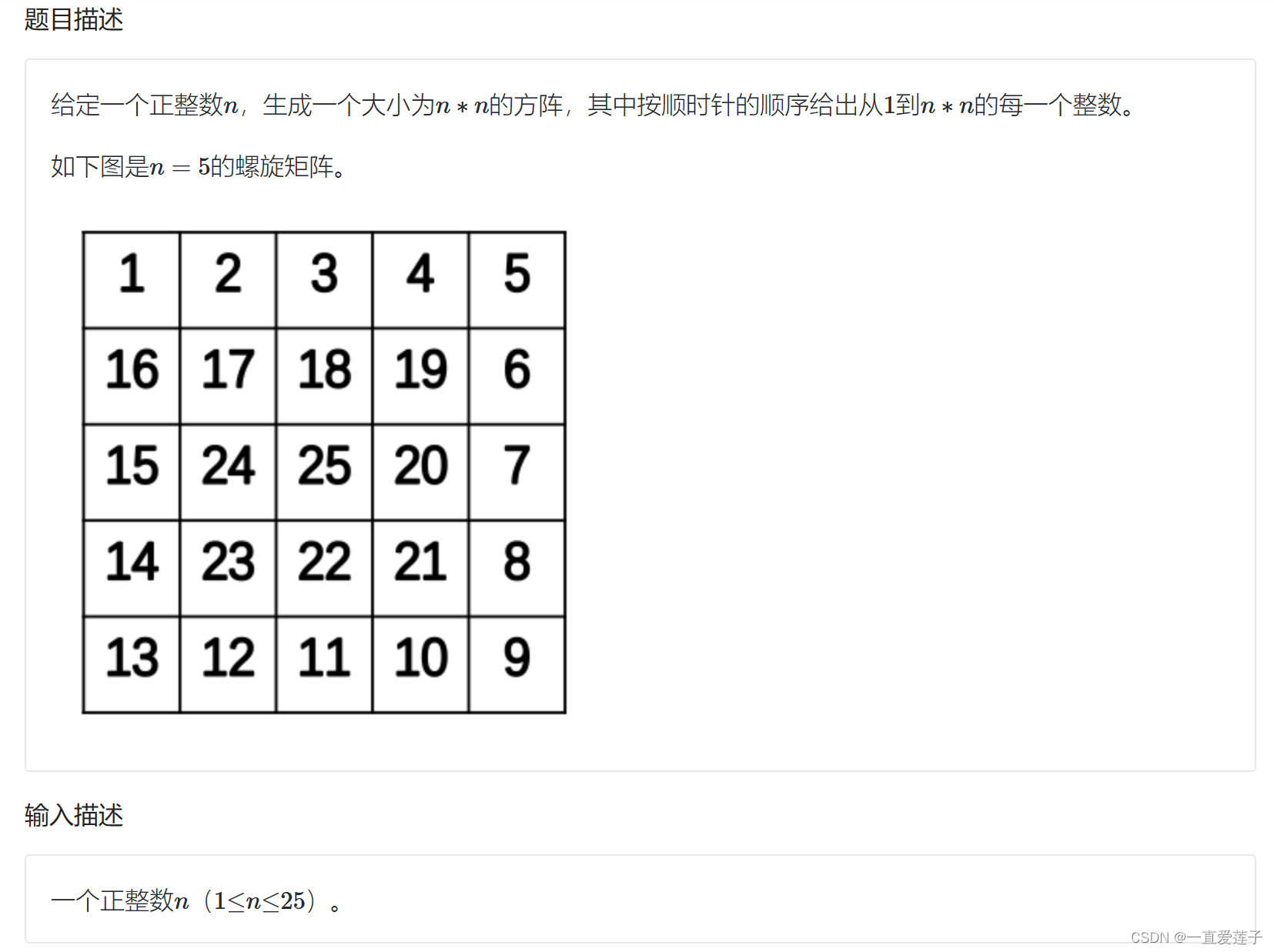
数字螺旋矩阵
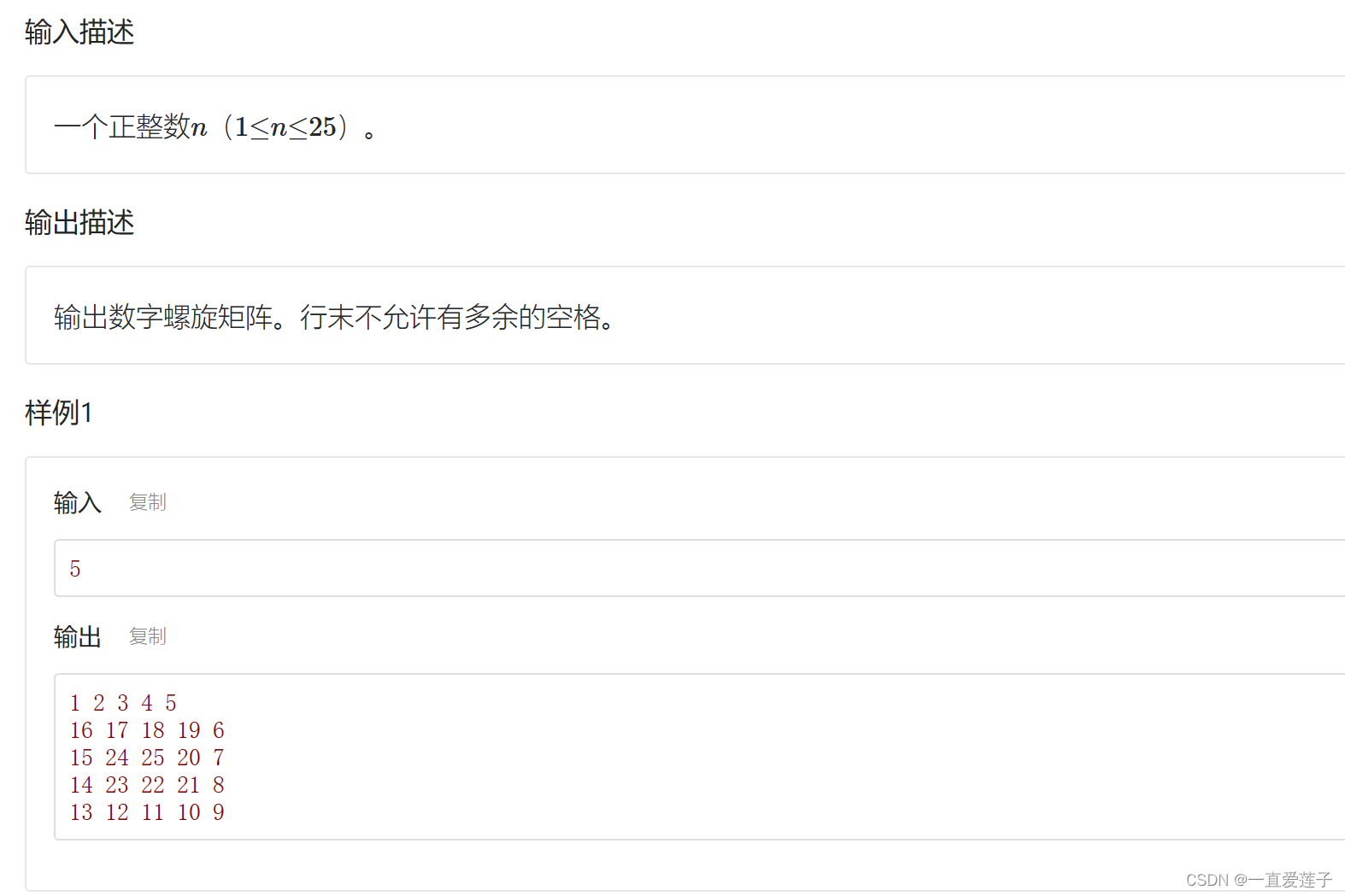
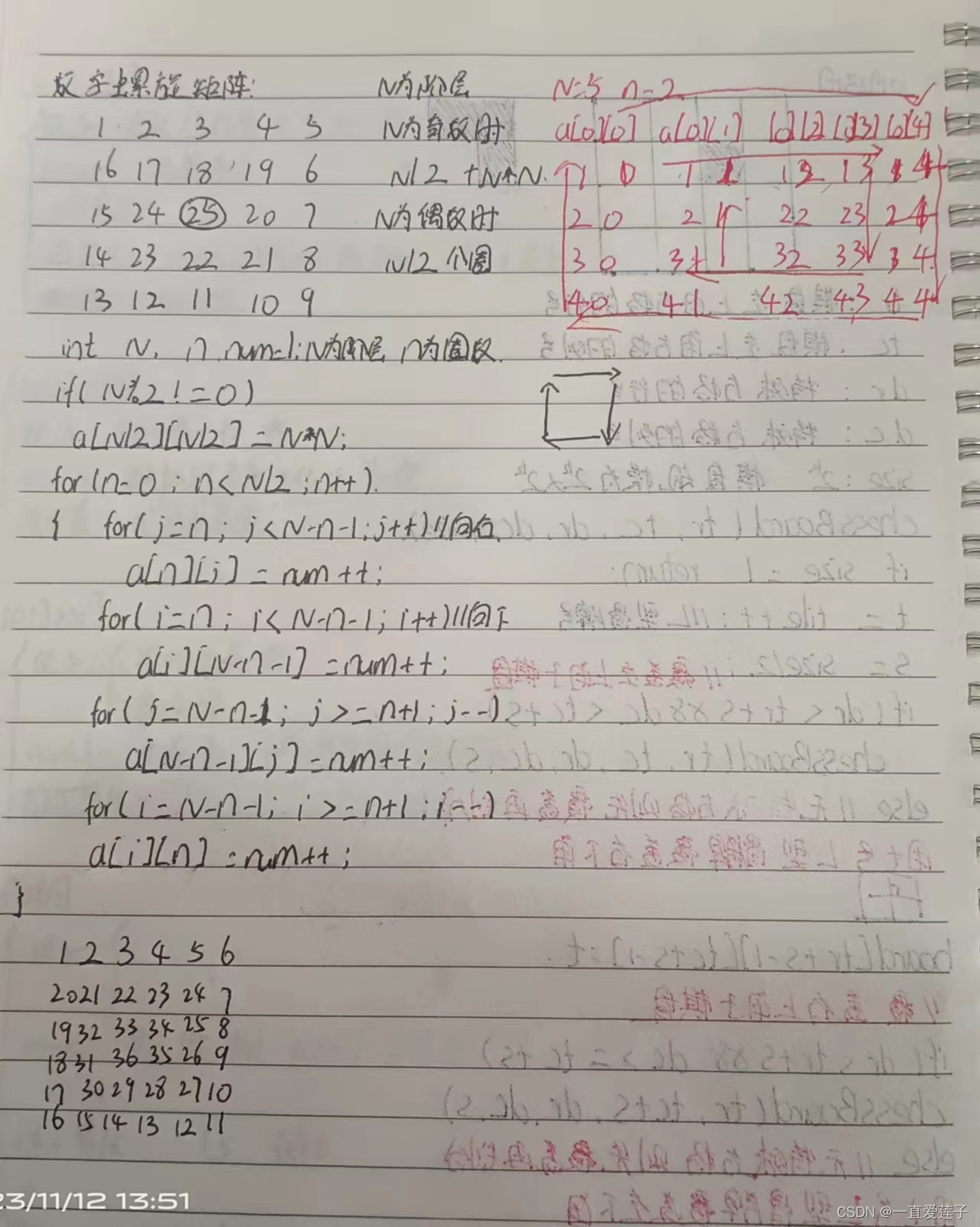
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 25;
int a[MAXN][MAXN], idx = 1;
void genMatrix(int n, int x, int y) {
if (n == 0) {
return;
} else if (n == 1) {
a[x][y] = idx++;
} else {
for (int j = y; j < y + n - 1; j++) {
a[x][j] = idx++;
}
for (int i = x; i < x + n - 1; i++) {
a[i][y + n - 1] = idx++;
}
for (int j = y + n - 1; j > y; j--) {
a[x + n - 1][j] = idx++;
}
for (int i = x + n - 1; i > x; i--) {
a[i][y] = idx++;
}
genMatrix(n - 2, x + 1, y + 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
genMatrix(n, 0, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
printf("%d", a[i][j]);
printf(j < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
盒分形
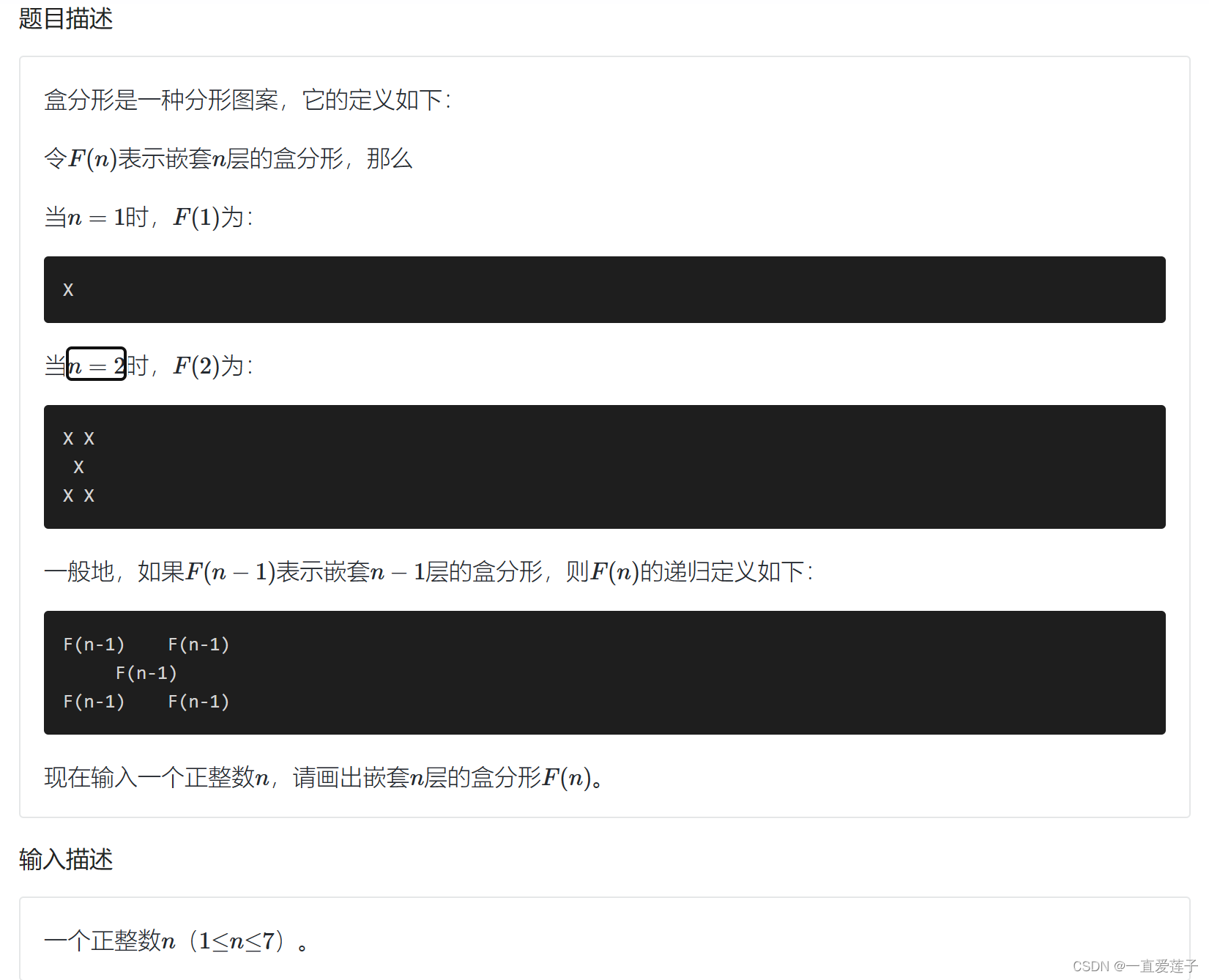

#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
const int MAXN = 3 * 3 * 3 * 3 * 3 * 3;
char mp[MAXN][MAXN];
void f(int n, int x, int y) {
if (n == 1) {
mp[x][y] = 'X';
} else {
int unit = (int)pow(3.0, n - 2);
f(n - 1, x, y);
f(n - 1, x, y + 2 * unit);
f(n - 1, x + unit, y + unit);
f(n - 1, x + 2 * unit, y);
f(n - 1, x + 2 * unit, y + 2 * unit);
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(mp, ' ', sizeof(mp));
f(n, 0, 0);
int edge = (int)pow(3.0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < edge; j++) {
printf("%c", mp[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}