文章目录
- 简介
- 插件实现
- 函数介绍
- 代码
- 调用原理
- 局限性
简介
在利用moveit_setup_assistant配置我们自己机械手后,当运行demo.launch.py时,会实例化一个moveit对象以及一个基于ros2_control的、虚拟的控制对象,从而可以实现一个完整的控制闭环。
此基于ros2_control的虚拟对象,包含了action(server)相关的实例化、关节状态的发布、虚拟伺服电机的驱动及读取。
我们也可以利用ros2_control,将我们自己的机械手与moveit连接起来,从而实现moveit对我们机械手的控制。但是这样做的话,会损失比较多的自由度。假如电机等伺服机构、传感器等硬件是直接接到ros系统所在板子上的话,用ros2_control是挺方便的,但是我的是接在下位机,然后通过串口通讯控制的,使用ros2_control貌似就不太合适了。
不过也简单尝试一下例程,说不定后面有机会用到。
插件实现
这里我还是用我之前的那个【机械手模型】,来进行演示。
关于ros2_control的介绍可以看这里:【ros2_control doc】,我们这里就不继续啰嗦了。
我们只需要知道一点够了:我们只需要对ros2_control的类hardware_interface::SystemInterface进行实例化,其余的moveit_setup_assistant/ros2_control已经帮我们做好了。
对该类进行重写实现时,根据官方文档【Writing a new hardware interface】,我们需要分别重写下面8个函数
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_init(
const hardware_interface::HardwareInfo & info) override;
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_configure(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
std::vector<hardware_interface::StateInterface> export_state_interfaces() override;
std::vector<hardware_interface::CommandInterface> export_command_interfaces() override;
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_activate(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_deactivate(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
hardware_interface::return_type read(
const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
hardware_interface::return_type write(
const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
函数介绍
分别介绍一下这几个函数的作用。
- hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_init( const hardware_interface::HardwareInfo & info) override;
在这个函数内要进行软件方面的初始化、检查等。主要是对将要用到的state、command的缓存空间进行申请、检查urdf规定的接口是不是符合我们的需求等。
- hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_configure( const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
在这个函数内,要进行硬件的连接,成功与其进行了通讯,并进行一些必要的配置(通讯频率、限制等?)
- std::vector<hardware_interface::StateInterface> export_state_interfaces() override;
这个函数主要是将在on_init里面申请好的state存储地址打包,返回给上层操作者
- std::vector<hardware_interface::CommandInterface> export_command_interfaces() override;
这个函数主要是将在on_init里面申请好的command内存地址打包,返回给上层操作者
- hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_activate(const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
在这个函数内,要让执行机构进行复位、清除异常等操作,准备好接收运动指令。
- hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_deactivate(const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
在这个函数内,要让执行机构进行断电、断气、解除负载等操作?
- hardware_interface::return_type read(const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
读取。从硬件读取此时位置,放到缓存中,再由上层来读取
- hardware_interface::return_type write(const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
写入。将从上层得到的指令(目标位置)发送给硬件
代码
myrobotinterface.h
#ifndef MYROBOTINTERFACE_H
#define MYROBOTINTERFACE_H
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "hardware_interface/handle.hpp"
#include "hardware_interface/hardware_info.hpp"
#include "hardware_interface/system_interface.hpp"
#include "hardware_interface/types/hardware_interface_return_values.hpp"
#include "hardware_interface/types/hardware_interface_type_values.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/macros.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_lifecycle/node_interfaces/lifecycle_node_interface.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_lifecycle/state.hpp"
class MyRobotInterface : public hardware_interface::SystemInterface
{
public:
// 这代码的作用是使此类能够直接使用 MyRobotInterface::sharedPtr
RCLCPP_SHARED_PTR_DEFINITIONS(MyRobotInterface);
MyRobotInterface();
// 初始化时的函数
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_init(
const hardware_interface::HardwareInfo & info) override;
// 配置时的函数
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_configure(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
// 导出状态数据的存储地址
std::vector<hardware_interface::StateInterface> export_state_interfaces() override;
// 导出命令数据的存储地址
std::vector<hardware_interface::CommandInterface> export_command_interfaces() override;
// 激活时的函数
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_activate(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
// 取消激活时的函数
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn on_deactivate(
const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & previous_state) override;
// 读取,从硬件读取此时位置
hardware_interface::return_type read(
const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
// 写入,将指令发送给硬件
hardware_interface::return_type write(
const rclcpp::Time & time, const rclcpp::Duration & period) override;
private:
// Parameters for the RRBot simulation
// 用于模拟的参数
double hw_start_sec_;
double hw_stop_sec_;
double hw_slowdown_;
// Store the command for the simulated robot
// 为此模拟机器人存储命令
std::vector<double> hw_commands_;
// 用于存储每个joint的状态。假如都是旋转关节,那么存储的就是当前的角度
std::vector<double> hw_states_;
};
#endif // MYROBOTINTERFACE_H
myrobotinterface.cpp
#include "myrobotinterface.h"
MyRobotInterface::MyRobotInterface()
{
}
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn MyRobotInterface::on_init(const hardware_interface::HardwareInfo &info)
{
// 这个是初始化,但是是偏向于软件方面的初始化;比如ros2_controllers.yaml里面描述的接口是否有问题,一些人为设定的其他参数等等
// 先让hardware_interface::HardwareInfo执行初始化(也就是赋值info_),它初始化成功了,我们自己再进行自己的初始化
if (
hardware_interface::SystemInterface::on_init(info) !=
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::SUCCESS)
{
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::ERROR;
}
// 上面经过 hardware_interface::SystemInterface::on_init 之后,info_已经被初始化了,可以直接用
// stod: string to double
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
hw_start_sec_ = stod(info_.hardware_parameters["example_param_hw_start_duration_sec"]);
hw_stop_sec_ = stod(info_.hardware_parameters["example_param_hw_stop_duration_sec"]);
hw_slowdown_ = stod(info_.hardware_parameters["example_param_hw_slowdown"]);
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
hw_states_.resize(info_.joints.size(), std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN());
hw_commands_.resize(info_.joints.size(), std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN());
// 遍历urdf文件所描述的所有joint,这里是和外面 ros2_controllers.yaml 里面的controller对应的
// command指的是moveit发送过来的指令,也就是本关节需要走到哪个角度;state指的是当前关节的状态
for (const hardware_interface::ComponentInfo & joint : info_.joints)
{
// 每个joint只接受1个指令
// RRBotSystemPositionOnly has exactly one state and command interface on each joint
if (joint.command_interfaces.size() != 1)
{
RCLCPP_FATAL(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"),
"Joint '%s' has %zu command interfaces found. 1 expected.", joint.name.c_str(),
joint.command_interfaces.size());
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::ERROR;
}
// 只接受 position类型的指令
if (joint.command_interfaces[0].name != hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION)
{
RCLCPP_FATAL(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"),
"Joint '%s' have %s command interfaces found. '%s' expected.", joint.name.c_str(),
joint.command_interfaces[0].name.c_str(), hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION);
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::ERROR;
}
// 只接受一种状态
if (joint.state_interfaces.size() != 1)
{
RCLCPP_FATAL(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"),
"Joint '%s' has %zu state interface. 1 expected.", joint.name.c_str(),
joint.state_interfaces.size());
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::ERROR;
}
// 只接受position状态
if (joint.state_interfaces[0].name != hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION)
{
RCLCPP_FATAL(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"),
"Joint '%s' have %s state interface. '%s' expected.", joint.name.c_str(),
joint.state_interfaces[0].name.c_str(), hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION);
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::ERROR;
}
}
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::SUCCESS;
}
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn MyRobotInterface::on_configure(const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & /*previous_state*/)
{
// 这里的函数是进行配置的,是经过init之后,再到这一步
// 这个也是初始化,但是这个会偏向硬件方面,主要是启动设备、检查设备等
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Configuring ...please wait...");
// 这里根据前面设定的启动时间,在模拟启动耗时
for (int i = 0; i < hw_start_sec_; i++)
{
rclcpp::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "%.1f seconds left...",
hw_start_sec_ - i);
}
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
// 对状态、命令等模拟参数进行初始化
// reset values always when configuring hardware
for (uint i = 0; i < hw_states_.size(); i++)
{
hw_states_[i] = 0;
hw_commands_[i] = 0;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Successfully configured!");
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::SUCCESS;
}
std::vector<hardware_interface::StateInterface> MyRobotInterface::export_state_interfaces()
{
// 这个是此机器人提供关节当前状态的数据存储地址,以供上层应用查询
// 上层查询时,直接通过此次获取到的地址读取数值即可,无需重复调用函数
std::vector<hardware_interface::StateInterface> state_interfaces;
for (uint i = 0; i < info_.joints.size(); i++)
{
state_interfaces.emplace_back(hardware_interface::StateInterface(
info_.joints[i].name, hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION, &hw_states_[i]));
}
return state_interfaces;
}
std::vector<hardware_interface::CommandInterface> MyRobotInterface::export_command_interfaces()
{
// 这个是此机器人提供关节当前正在执行的命令的存储地址,以供上层读写
std::vector<hardware_interface::CommandInterface> command_interfaces;
for (uint i = 0; i < info_.joints.size(); i++)
{
command_interfaces.emplace_back(hardware_interface::CommandInterface(
info_.joints[i].name, hardware_interface::HW_IF_POSITION, &hw_commands_[i]));
}
return command_interfaces;
}
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn MyRobotInterface::on_activate(const rclcpp_lifecycle::State &/*previous_state*/)
{
// 设备开始时执行此函数
// 这个activate。。。,怎么感觉和前面的 on_configure 一样的作用?
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Activating ...please wait...");
for (int i = 0; i < hw_start_sec_; i++)
{
rclcpp::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "%.1f seconds left...",
hw_start_sec_ - i);
}
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
// 在激活时,目标位置和当前位置应该要一样?
// command and state should be equal when starting
for (uint i = 0; i < hw_states_.size(); i++)
{
hw_commands_[i] = hw_states_[i];
}
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Successfully activated!");
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::SUCCESS;
}
hardware_interface::CallbackReturn MyRobotInterface::on_deactivate(const rclcpp_lifecycle::State &/*previous_state*/)
{
// 设备停止时执行此函数
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Deactivating ...please wait...");
for (int i = 0; i < hw_stop_sec_; i++)
{
rclcpp::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "%.1f seconds left...",
hw_stop_sec_ - i);
}
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Successfully deactivated!");
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
return hardware_interface::CallbackReturn::SUCCESS;
}
hardware_interface::return_type MyRobotInterface::read(const rclcpp::Time &time, const rclcpp::Duration &period)
{
// 这个是进行执行器关节状态的读取,将读取到的值存放在hw_states_上面。相当于从硬件同步数据
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Reading...");
for (uint i = 0; i < hw_states_.size(); i++)
{
// Simulate RRBot's movement
hw_states_[i] = hw_states_[i] + (hw_commands_[i] - hw_states_[i]) / hw_slowdown_;
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Got state %.5f for joint %d!",
hw_states_[i], i);
}
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Joints successfully read!");
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
return hardware_interface::return_type::OK;
}
hardware_interface::return_type MyRobotInterface::write(const rclcpp::Time &time, const rclcpp::Duration &period)
{
// 这个是将需要发送的目标位置写到执行器。
// 需要写入(执行)的值已经被上层写到 hw_commands_ 了,所以在此处传入进来的参数中,并没看到具体关节的值
// BEGIN: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Writing...");
for (uint i = 0; i < hw_commands_.size(); i++)
{
// Simulate sending commands to the hardware
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Got command %.5f for joint %d!",
hw_commands_[i], i);
}
RCLCPP_INFO(
rclcpp::get_logger("RRBotSystemPositionOnlyHardware"), "Joints successfully written!");
// END: This part here is for exemplary purposes - Please do not copy to your production code
return hardware_interface::return_type::OK;
}
调用原理
需要注意的是,此实例化的类是以插件的形式被ros2_control来调用的(In ros2_control hardware system components are libraries, dynamically loaded by the controller manager using the pluginlib interface. ),也就是我们urdf文件中的ros2_control–》hardware–》plugin节点中指定的插件。
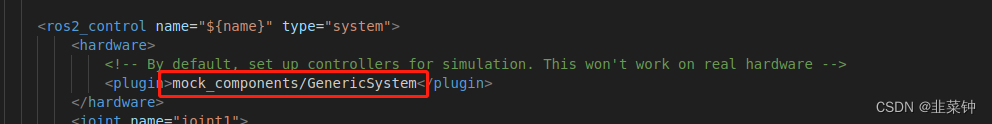 比如说上面的 mock_components/GenericSystem,我们可以在/opt/ros/humble/share/hardware_interface、/opt/ros/humble/include/mock_components找到他们的踪迹。
比如说上面的 mock_components/GenericSystem,我们可以在/opt/ros/humble/share/hardware_interface、/opt/ros/humble/include/mock_components找到他们的踪迹。
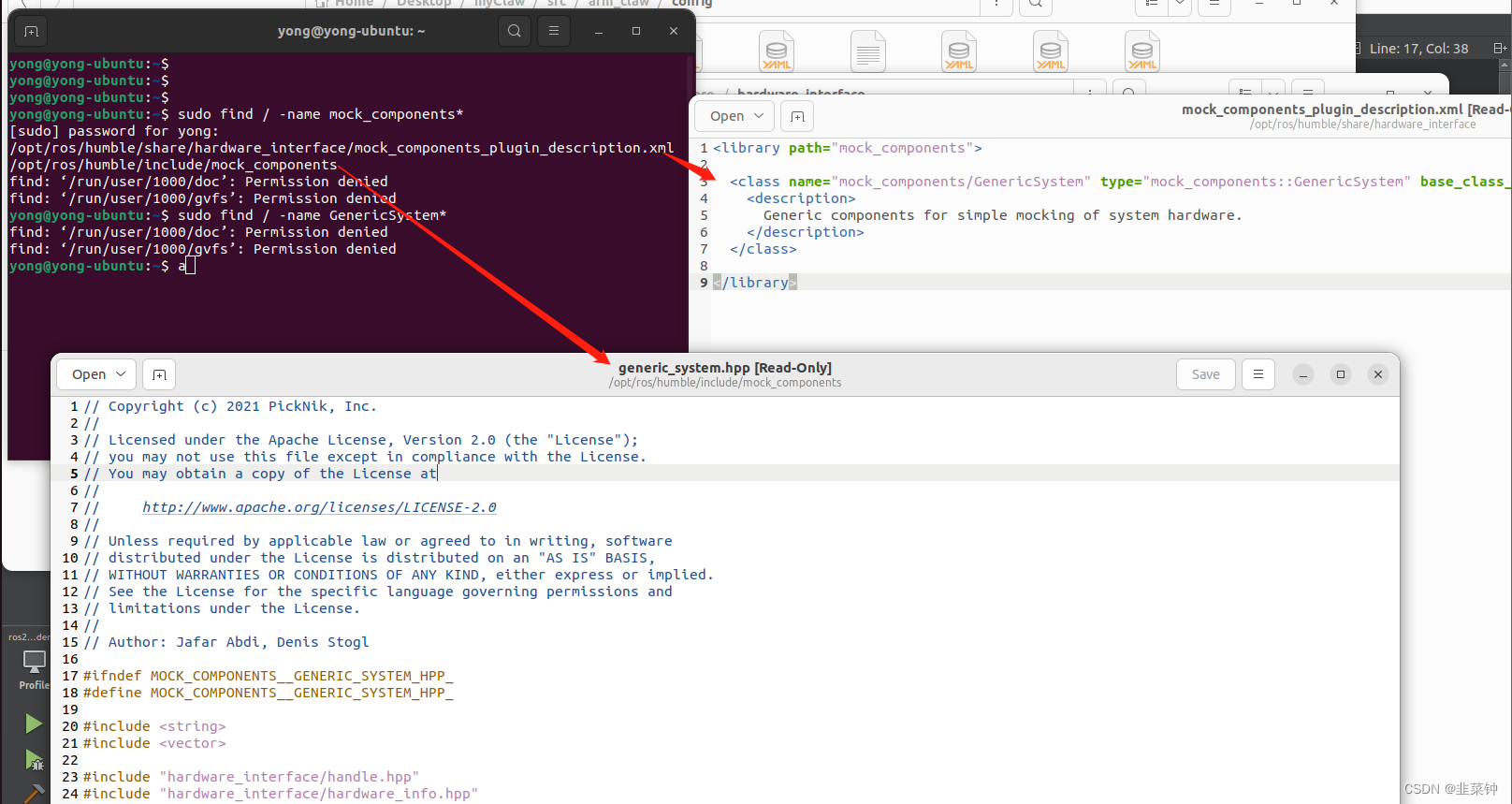 因此,我们需要把我们的硬件接口编译成动态库,然后填写一个插件描述文件放在文件夹中,然后ros2_control通过名字来找到此插件。
因此,我们需要把我们的硬件接口编译成动态库,然后填写一个插件描述文件放在文件夹中,然后ros2_control通过名字来找到此插件。
局限性
这样一来有个问题,我希望Action的Server接口是由我们的Qt程序来实现,与我们的Qt程序处于同一个进程,而不是一个插件、动态库的形式,因为我需要取得路径点进行调试、与其他类操作进行交互等,这该如何处理?
可能这个ros2_control,是比较适合组件化、黑盒子的设计吧,而不是我目前需要弄的一体化设计。
暂时不研究这个了。
参考:
【 ros-controls/ros2_control_demos】



![[CANN训练营]UART通信笔记](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/56f8c29731854dc89400f5d27db07133.png)