类型特性
类型特性定义一个编译时基于模板的结构,以查询或修改类型的属性。
试图特化定义于 <type_traits> 头文件的模板导致未定义行为,除了 std::common_type 可依照其所描述特化。
定义于<type_traits>头文件的模板可以用不完整类型实例化,除非另外有指定,尽管通常禁止以不完整类型实例化标准库模板。
受支持操作
继承自 std::integral_constant
成员常量
| value [静态] | 若 T 可移动赋值则为 true ,否则为 false(公开静态成员常量) |
成员函数
| operator bool | 转换对象为 bool ,返回 value(公开成员函数) |
| operator() (C++14) | 返回 value(公开成员函数) |
成员类型
| 类型 | 定义 |
value_type | bool |
type | std::integral_constant<bool, value> |
检查类型是否有拥有移动赋值运算符
std::is_move_assignable,
std::is_trivially_move_assignable,
std::is_nothrow_move_assignable| template< class T > | (1) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class T > | (2) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class T > | (3) | (C++11 起) |
1) 若 T 不是可引用类型(即可为 cv 限定的 void 或带 cv-qualifier-seq 或 ref-qualifier 的函数类型),则提供等于 false 的成员常量 value 。否则,提供等于 std::is_assignable<T&, T&&>::value 的成员常量 value 。
2) 同 1) ,但使用 std::is_trivially_assignable<T&, T&&>
3) 同 1) ,但使用 std::is_nothrow_assignable<T&, T&&>
T 应为完整类型、(可为 cv 限定的) void ,或未知边界数组。否则行为未定义。
若上述模板的实例化直接或间接地依赖于不完整类型,并且如果假如使该类型完整,实例化就会产生不同的结果,则行为未定义。
辅助变量模板
| template< class T > | (C++17 起) | |
| template< class T > | (C++17 起) | |
| template< class T > | (C++17 起) |
可能的实现
template< class T>
struct is_move_assignable
: std::is_assignable< typename std::add_lvalue_reference<T>::type,
typename std::add_rvalue_reference<T>::type> {};
template< class T>
struct is_trivially_move_assignable
: std::is_trivially_assignable< typename std::add_lvalue_reference<T>::type,
typename std::add_rvalue_reference<T>::type> {};
template< class T>
struct is_nothrow_move_assignable
: std::is_nothrow_assignable< typename std::add_lvalue_reference<T>::type,
typename std::add_rvalue_reference<T>::type> {};注意
特性 std::is_move_assignable 不如可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 严格,因为它既不检查赋值的结果类型(对于可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 类型必须是 T& ),也不检查赋值后目标的值等于赋值前源的值的语义要求。
为满足此特性,类型不必实现移动赋值运算符,细节见可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <type_traits>
struct Foo
{
int n;
};
struct NoMove
{
// 避免默认的移动赋值运算符的隐式定义
// 然而,该类仍然可移动赋值,因为
// 其复制赋值运算符能绑定到右值参数
NoMove& operator=(const NoMove&)
{
return *this;
}
};
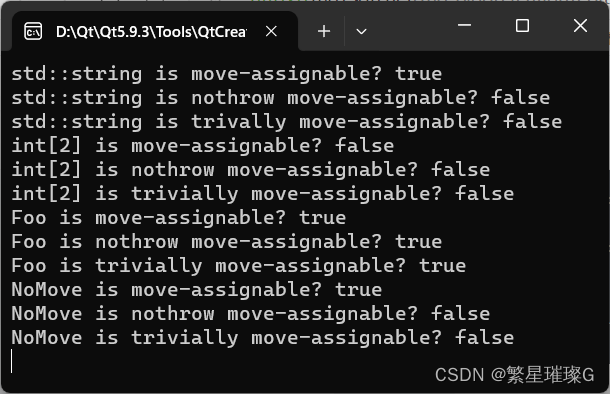
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "std::string is move-assignable? "
<< std::is_move_assignable<std::string>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::string is nothrow move-assignable? "
<< std::is_nothrow_move_assignable<std::string>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::string is trivially move-assignable? "
<< std::is_trivially_move_assignable<std::string>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "int[2] is move-assignable? "
<< std::is_move_assignable<int[2]>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "int[2] is nothrow move-assignable? "
<< std::is_nothrow_move_assignable<int[2]>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "int[2] is trivially move-assignable? "
<< std::is_trivially_move_assignable<int[2]>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "Foo is move-assignable? "
<< std::is_move_assignable<Foo>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "Foo is nothrow move-assignable? "
<< std::is_nothrow_move_assignable<Foo>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "Foo is trivially move-assignable? "
<< std::is_trivially_move_assignable<Foo>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << std::boolalpha
<< "NoMove is move-assignable? "
<< std::is_move_assignable<NoMove>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "NoMove is nothrow move-assignable? "
<< std::is_nothrow_move_assignable<NoMove>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "NoMove is trivially move-assignable? "
<< std::is_trivially_move_assignable<NoMove>::value << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出