1.二分图的定义
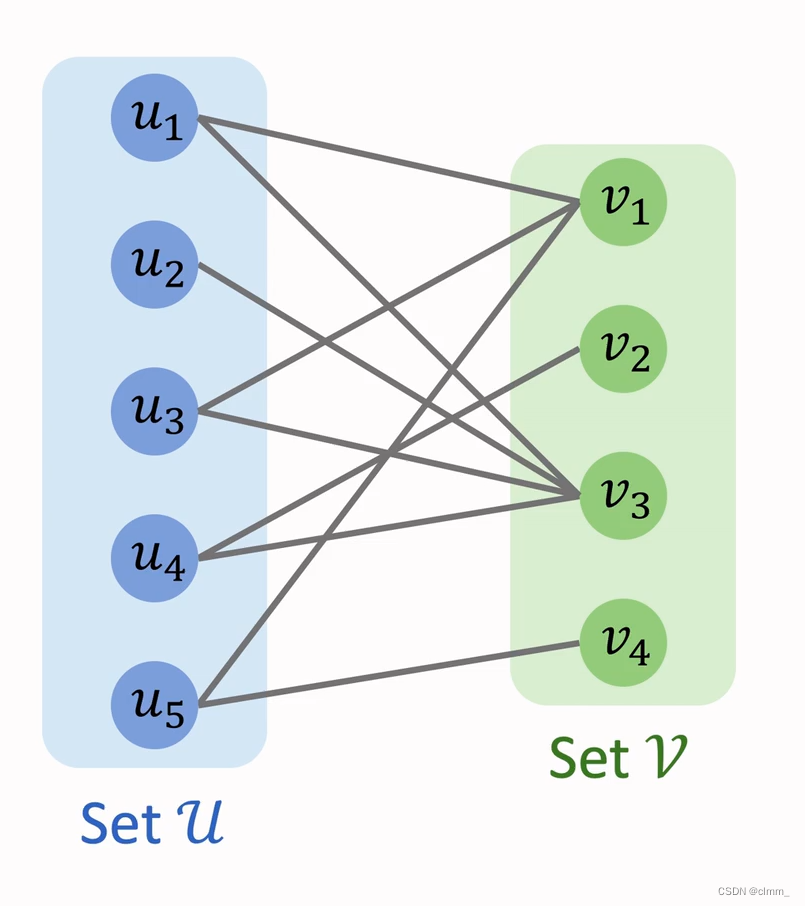
二分图是一种特殊的无向图,它的节点可以被划分为两个互不相交的集合,使得同一集合中的任意两个节点之间没有边相连,而不同集合中的节点之间都有边相连。
换句话说,如果一个无向图可以被划分为两个集合,并且所有边的两个端点都分别属于不同的集合,那么这个无向图就是一个二分图。
如图,有蓝色,绿色两个集合,集合内的点可以跟另一个集合内的点相互连接,但集合内部不能连接,这就叫二分图。
那么如何判定是否为二分图呢?这就要用到二分图的染色
2.二分图的染色

假设图中的颜色都还没标上,只有点和边,那么我们需要对各个点能直达的点染色(也就是不同集合的点的染不同颜色),如果能符合“相邻点的颜色不同”这个条件,就是一个二分图。
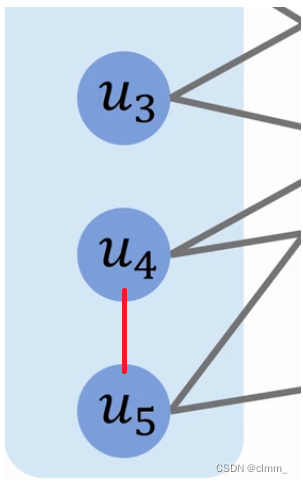
反之如下,两个蓝色的点之间有连线,可是他们颜色相同,就不能满足条件了
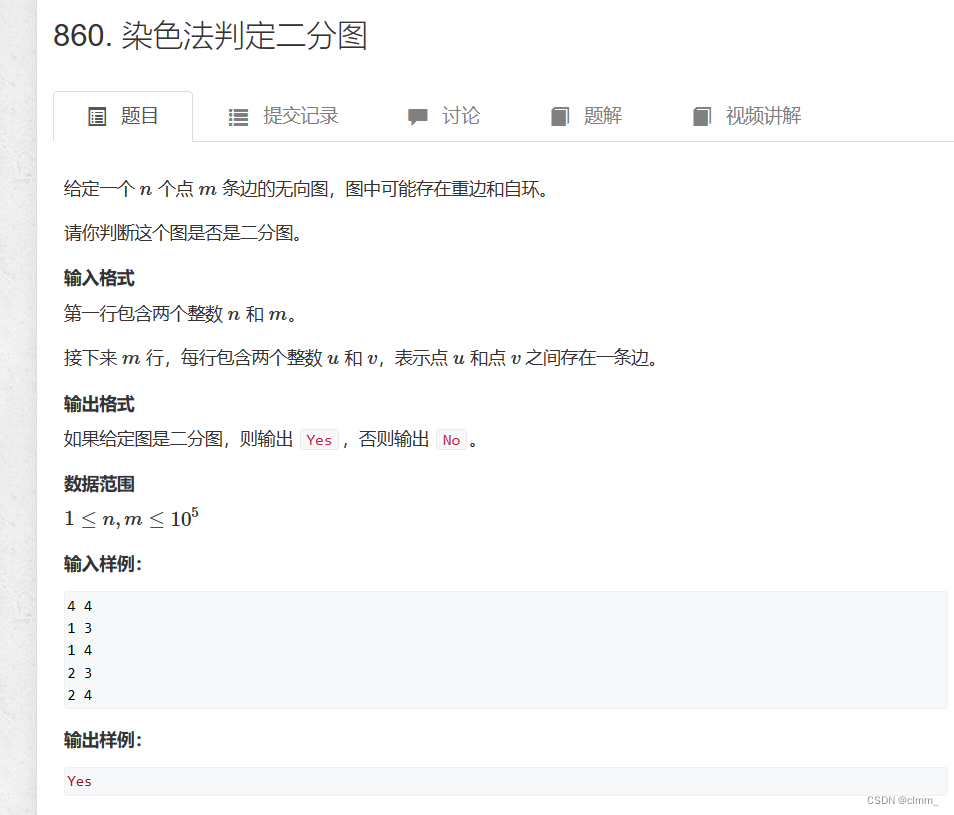
例题1
1.用vector建图,此时我们已经知道了各个点(记作点i)的所有邻接点(也就是只用走一条边就能到达的点),那么点i的邻接点j的颜色不能跟点i一样
2.如果点i是蓝色,点j就应该被染成绿色
3.我们要将以点i为起点,所有能到达的点都遍历,可以用dfs或者bfs
4.如果染的过程中,某点还没有染色,就将其染成相反色;
如果已经染了色,且颜色为相反色,则不用管;
如果已经染了色,且颜色相同,说明不满足条件,这不是一个二分图。
dfs写法
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<sstream>
#include<stack>
#include <utility>
#include<map>
#include <vector>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
//2147483647
#define int long long
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//long long MAX(long long a, long long b) { return a < b ? b : a; }
vector<int> edge[N];
int vis[N];//0为蓝色,1为绿色
bool ans = true;
void dfs(int cur, int c) {
//作用:遍历cur能到达的点,并且将这些点染色
vis[cur] = c;
for (auto x : edge[cur]) {
//遍历cur的邻接点
if (vis[x] == -1) {
//还未被染色
dfs(x, 1 - c);
//将x点染成跟cur不一样的颜色
//并且开始深搜
}
else if (vis[x] == vis[cur]) {
ans = false;
}
}
}
signed main() {
memset(vis, -1, sizeof vis);
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
while (m--) {
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
edge[a].push_back(b);
edge[b].push_back(a);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (vis[i] == -1) dfs(i, 1);
}
if (ans) cout << "Yes";
else cout << "No";
return 0;
}bfs写法
#include<assert.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<sstream>
#include<stack>
#include <utility>
#include<map>
#include <vector>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
//2147483647
#define int long long
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//long long MAX(long long a, long long b) { return a < b ? b : a; }
vector<int> edge[N];
int vis[N];//0为蓝色,1为绿色
bool ans = true;
void bfs(int cur) {
//作用:遍历cur能到达的点,并且将这些点染色
queue<int> q;
q.push(cur);
vis[cur] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto x : edge[t]) {
if (vis[x] == -1) {
q.push(x);
vis[x] = 1 - vis[t];
}
else if (vis[x] == vis[t]) {
ans = false;
return;
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
memset(vis, -1, sizeof vis);
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
while (m--) {
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
edge[a].push_back(b);
edge[b].push_back(a);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (vis[i] == -1) bfs(i);
}
if (ans) cout << "Yes";
else cout << "No";
return 0;
}例题2
D - Good Tuple Problem
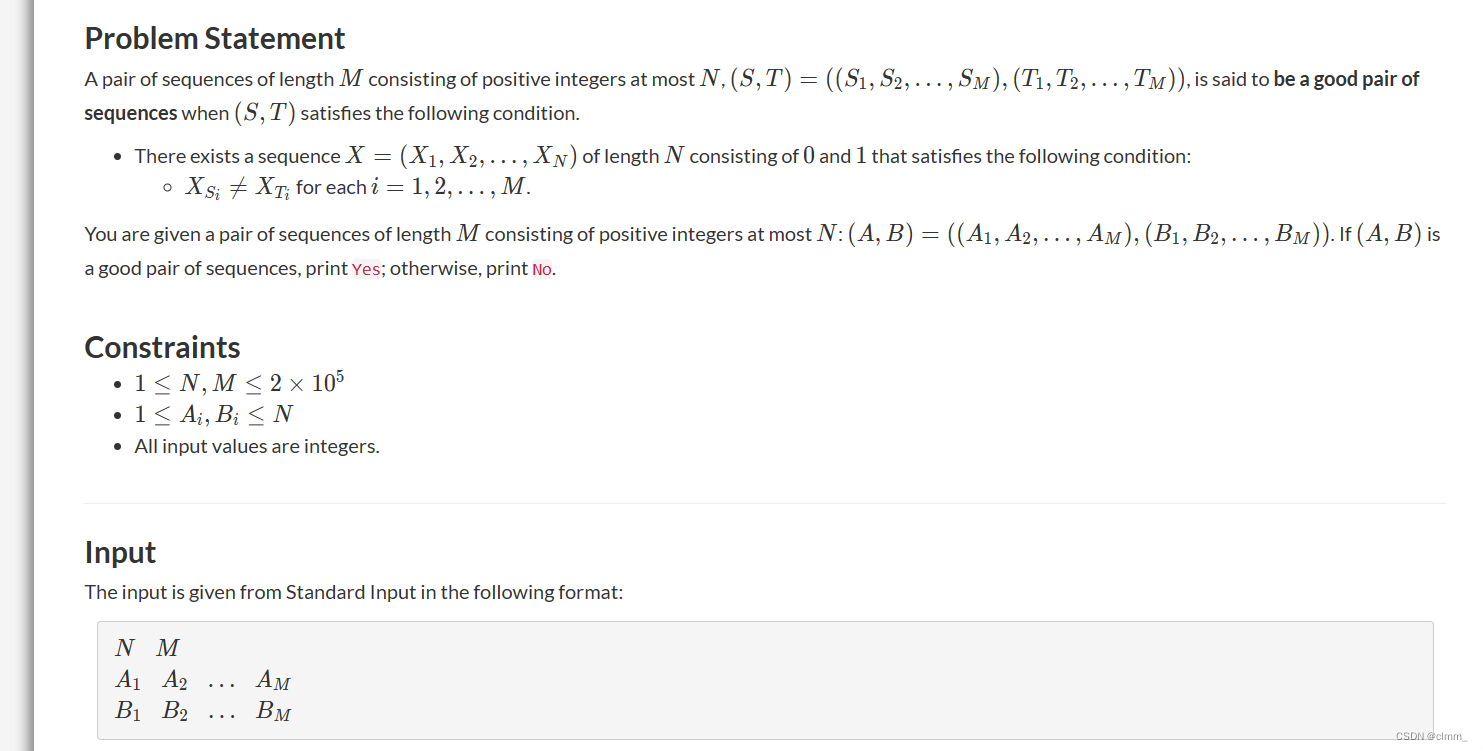

分析:atcoder周赛,基本就是模板题了
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<sstream>
#include<stack>
#include <utility>
#include<map>
#include <vector>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
//2147483647
#define int long long
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//long long MAX(long long a, long long b) { return a < b ? b : a; }
vector<int> dif[N];//dif[i]存的是,需要跟i结点不同的结点
int a[N], b[N], x[N];
bool ans = true;
void dfs(int i, int s) {
x[i] = s;
for (int j = 0; j < dif[i].size(); j++) {
if (x[dif[i][j]] == -1) {
dfs(dif[i][j], 1 - s);
}
else if (x[dif[i][j]] == x[i]) ans = false;
}
}
signed main() {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dif[a[i]].push_back(b[i]);
dif[b[i]].push_back(a[i]);
}
memset(x, -1, sizeof x);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(x[i]==-1) dfs(i, 0);
}
if (ans) cout << "Yes";
else cout << "No";
return 0;
}3.匈牙利算法
匈牙利算法是用来求二分图的最大匹配数,注意!是最大匹配数,是无权的

假设有这些男生和女生,男生对一些女生中意,问怎么匹配才能让匹配出来的情侣数量最多
答:我们把下面的行为看成一个“追”的动作
男生i一个个访问自己中意的女生,如果该女生j还没有对象,则直接匹配成功。
如果女生j有对象,即match[j]这个男生,那么去找找看match[j]这个男生能不能换一个女朋友(即女生j有调整空间),然后把女生j让给男生i。如果可以,则男生i也匹配成功。
如果男生i遍历完所有中意的女生还是找不到,就匹配失败。
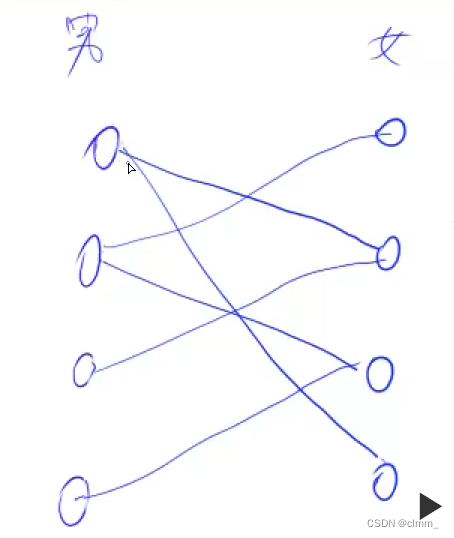
着重解释一下st[]。作用是不重复访问同一个女生,导致递归陷入死循环。
我们可以把st[]的作用看成一个“预定”的行为,当女生j还没被预定,则使其被预定,即st[j] = true,看看这个女朋友能不能追到手(也就是我上面“答”的部分)。不行的话去看看其他中意的女生。
注意!不论女生j追没追到手,她都已经是被”预定“过了,后续不能再访问。
那到底是怎么陷入死循环的呢?
如果没有st数组的情况如下。
当男生i访问到了女生j,女生j已经有男生k当男朋友了,那么此时就要看看男生k能不能换别的女朋友。所以男生k就会遍历所有自己中意的女生,看看有没有未被选的女生,或者有调整空间的女生。
问题就出在这里!这样的话男生k可能又会访问到女生j,然后看女生j有没有调整空间,也就是自己有没有调整空间,陷入递归死循环!
因此,st[]的存在是必要的。
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<sstream>
#include<stack>
#include <utility>
#include<map>
#include <vector>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
//2147483647
#define int long long
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//long long MAX(long long a, long long b) { return a < b ? b : a; }
int cnt = 0;
int head[N], e[N], ne[N];
int match[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int u, int v) {
e[cnt] = v, ne[cnt] = head[u], head[u] = cnt++;
}
bool find(int x) {
//找x能不能配对到女朋友
//遍历x所中意的女生
for (int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j]) {
st[j] = true;
if (match[j]==0 || find(match[j])) {
//如果女生j没有男朋友,或者女生当前的男朋友可以选择其他女生
//那么就让那个男生去找别的女生,男生x跟女生j匹配
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int a, b, n;
signed main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof head);
cin >> a >> b >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v;
add(u, v);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
memset(st, false, sizeof st);
if (find(i)) ans++;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}