tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.UnknowError: Could not start
gRPC server
1. tf分布式
一台电脑=服务器=server是一个节点,包含了多个GPU。首先分布式的方式就是让多台电脑上的gpu共同干活。
分布式工作分为两个部分,parameter server(ps) 以及worker。眼熟ps与worker,因为这个是工作,每个server,都得干活,所以只能是从这两个工作里面选择。ps的工作类似于存储参数,而损失的计算,梯度的决定都是有worker进行的。这个对代码的影响就是,ps节点其实完全可以由cpu来做。worker必须由gpu做。
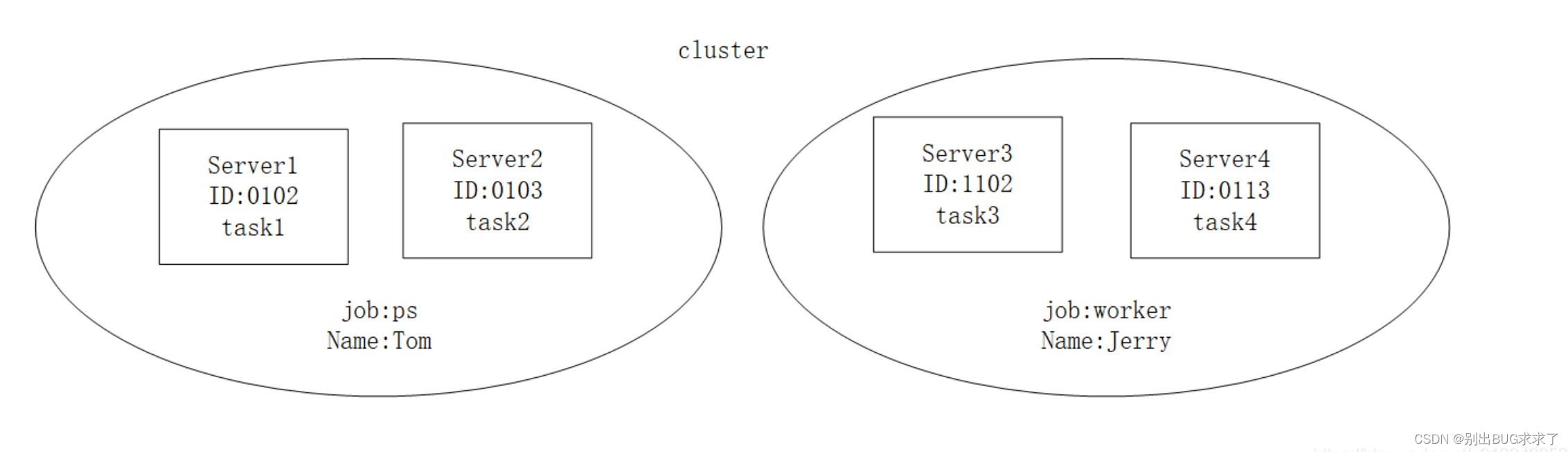
整体结构如图:一共四个sever,每个sever假设包含4个GPU,下图一共16个GPU。两个server工作是ps,两个sever的工作是worker,这个name其实没有在代码中配置,所以不用理会。server同做一个工作,也需要区分的,所以又引入了task,并且有task id。这里只是演示一下job(ps,worker)和server(节点)的关系。
2. 代码
代码的讲解是踩点来的。就是怎么用代码互相交流。
从理论上看,我们需要一些节点,并且给他们分配工作。
所以做一下程序入口接受参数(节点都是是谁,给什么工作了),我比较喜欢接收参数,不喜欢在代码里面写死。因为flags是tf基础,不想解释增加长度。
每个节点都得被单独通知,并且单独运行,这意味着如果你有一个ps,两个worker(一般用一个ps即可),你得在bash命令里:
python train.py --ps都谁(ps_hosts) --worker都谁(woker_hosts) --我被分配干啥(job_name) --我是第几个干这活的(task_index)
python train.py --ps都谁(ps_hosts) --worker都谁(woker_hosts) --我被分配干啥(job_name) --我是第几个干这活的(task_index)
python train.py --ps都谁(ps_hosts) --worker都谁(woker_hosts) --我被分配干啥(job_name) --我是第几个干这活的(task_index)
就是输入三次,跑三次,同时。ps和worker都会等你输完了在一起工作,毕竟要等同伴。
3. 示例
https://gist.github.com/yaroslavvb/1124bb02a9fd4abce3d86caf2f950cb2
"""Benchmark tensorflow distributed by adding vector of ones on worker2
to variable on worker1 as fast as possible.
On 2014 macbook, TensorFlow 0.10 this shows
Local rate: 2175.28 MB per second
Distributed rate: 107.13 MB per second
"""
import subprocess
import tensorflow as tf
import time
import sys
flags = tf.flags
flags.DEFINE_integer("iters", 10, "Maximum number of additions")
flags.DEFINE_integer("data_mb", 100, "size of vector in MBs")
flags.DEFINE_string("port1", "12222", "port of worker1")
flags.DEFINE_string("port2", "12223", "port of worker2")
flags.DEFINE_string("task", "", "internal use")
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# setup local cluster from flags
host = "127.0.0.1:"
cluster = {"worker": [host+FLAGS.port1, host+FLAGS.port2]}
clusterspec = tf.train.ClusterSpec(cluster).as_cluster_def()
def default_config():
optimizer_options = tf.OptimizerOptions(opt_level=tf.OptimizerOptions.L0)
config = tf.ConfigProto(
graph_options=tf.GraphOptions(optimizer_options=optimizer_options))
config.log_device_placement = False
config.allow_soft_placement = False
return config
def create_graph(device1, device2):
"""Create graph that keeps variable on device1 and
vector of ones/addition op on device2"""
tf.reset_default_graph()
dtype=tf.int32
params_size = 250*1000*FLAGS.data_mb # 1MB is 250k integers
with tf.device(device1):
params = tf.get_variable("params", [params_size], dtype,
initializer=tf.zeros_initializer)
with tf.device(device2):
# constant node gets placed on device1 because of simple_placer
# update = tf.constant(1, shape=[params_size], dtype=dtype)
update = tf.get_variable("update", [params_size], dtype,
initializer=tf.ones_initializer)
add_op = params.assign_add(update)
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
return init_op, add_op
def run_benchmark(sess, init_op, add_op):
"""Returns MB/s rate of addition."""
sess.run(init_op)
sess.run(add_op.op) # warm-up
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(FLAGS.iters):
# change to add_op.op to make faster
sess.run(add_op)
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
return float(FLAGS.iters)*FLAGS.data_mb/elapsed_time
def run_benchmark_local():
ops = create_graph(None, None)
sess = tf.Session(config=default_config())
return run_benchmark(sess, *ops)
def run_benchmark_distributed():
ops = create_graph("/job:worker/task:0", "/job:worker/task:1")
# launch distributed service
def runcmd(cmd): subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT)
runcmd("python %s --task=0"%(sys.argv[0]))
runcmd("python %s --task=1"%(sys.argv[0]))
time.sleep(1)
sess = tf.Session("grpc://"+host+FLAGS.port1, config=default_config())
return run_benchmark(sess, *ops)
if __name__=='__main__':
if not FLAGS.task:
rate1 = run_benchmark_local()
rate2 = run_benchmark_distributed()
print("Adding data in %d MB chunks" %(FLAGS.data_mb))
print("Local rate: %.2f MB per second" %(rate1,))
print("Distributed rate: %.2f MB per second" %(rate2,))
else: # Launch TensorFlow server
server = tf.train.Server(clusterspec, config=default_config(),
job_name="worker",
task_index=int(FLAGS.task))
server.join()
4. 单个节点上运行 2 个分布式worker工作线程
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40877246/distributed-tensorflow-not-working-with-simple-example
https://github.com/ischlag/distributed-tensorflow-example/blob/master/example.py
'''
Distributed Tensorflow 1.2.0 example of using data parallelism and share model parameters.
Trains a simple sigmoid neural network on mnist for 20 epochs on three machines using one parameter server.
Change the hardcoded host urls below with your own hosts.
Run like this:
pc-01$ python example.py --job_name="ps" --task_index=0
pc-02$ python example.py --job_name="worker" --task_index=0
pc-03$ python example.py --job_name="worker" --task_index=1
pc-04$ python example.py --job_name="worker" --task_index=2
More details here: ischlag.github.io
'''
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import sys
import time
# cluster specification
parameter_servers = ["pc-01:2222"]
workers = [ "pc-02:2222",
"pc-03:2222",
"pc-04:2222"]
cluster = tf.train.ClusterSpec({"ps":parameter_servers, "worker":workers})
# input flags
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string("job_name", "", "Either 'ps' or 'worker'")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("task_index", 0, "Index of task within the job")
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# start a server for a specific task
server = tf.train.Server(
cluster,
job_name=FLAGS.job_name,
task_index=FLAGS.task_index)
# config
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.0005
training_epochs = 20
logs_path = "/tmp/mnist/1"
# load mnist data set
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
if FLAGS.job_name == "ps":
server.join()
elif FLAGS.job_name == "worker":
# Between-graph replication
with tf.device(tf.train.replica_device_setter(
worker_device="/job:worker/task:%d" % FLAGS.task_index,
cluster=cluster)):
# count the number of updates
global_step = tf.get_variable(
'global_step',
[],
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0),
trainable = False)
# input images
with tf.name_scope('input'):
# None -> batch size can be any size, 784 -> flattened mnist image
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 784], name="x-input")
# target 10 output classes
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10], name="y-input")
# model parameters will change during training so we use tf.Variable
tf.set_random_seed(1)
with tf.name_scope("weights"):
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 100]))
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100, 10]))
# bias
with tf.name_scope("biases"):
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([100]))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
# implement model
with tf.name_scope("softmax"):
# y is our prediction
z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(x,W1),b1)
a2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(z2)
z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(a2,W2),b2)
y = tf.nn.softmax(z3)
# specify cost function
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
# this is our cost
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
# specify optimizer
with tf.name_scope('train'):
# optimizer is an "operation" which we can execute in a session
grad_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
'''
rep_op = tf.train.SyncReplicasOptimizer(
grad_op,
replicas_to_aggregate=len(workers),
replica_id=FLAGS.task_index,
total_num_replicas=len(workers),
use_locking=True)
train_op = rep_op.minimize(cross_entropy, global_step=global_step)
'''
train_op = grad_op.minimize(cross_entropy, global_step=global_step)
'''
init_token_op = rep_op.get_init_tokens_op()
chief_queue_runner = rep_op.get_chief_queue_runner()
'''
with tf.name_scope('Accuracy'):
# accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# create a summary for our cost and accuracy
tf.summary.scalar("cost", cross_entropy)
tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", accuracy)
# merge all summaries into a single "operation" which we can execute in a session
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
print("Variables initialized ...")
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(is_chief=(FLAGS.task_index == 0),
global_step=global_step,
init_op=init_op)
begin_time = time.time()
frequency = 100
with sv.prepare_or_wait_for_session(server.target) as sess:
'''
# is chief
if FLAGS.task_index == 0:
sv.start_queue_runners(sess, [chief_queue_runner])
sess.run(init_token_op)
'''
# create log writer object (this will log on every machine)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_path, graph=tf.get_default_graph())
# perform training cycles
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
# number of batches in one epoch
batch_count = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
count = 0
for i in range(batch_count):
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# perform the operations we defined earlier on batch
_, cost, summary, step = sess.run(
[train_op, cross_entropy, summary_op, global_step],
feed_dict={x: batch_x, y_: batch_y})
writer.add_summary(summary, step)
count += 1
if count % frequency == 0 or i+1 == batch_count:
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
start_time = time.time()
print("Step: %d," % (step+1),
" Epoch: %2d," % (epoch+1),
" Batch: %3d of %3d," % (i+1, batch_count),
" Cost: %.4f," % cost,
" AvgTime: %3.2fms" % float(elapsed_time*1000/frequency))
count = 0
print("Test-Accuracy: %2.2f" % sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels}))
print("Total Time: %3.2fs" % float(time.time() - begin_time))
print("Final Cost: %.4f" % cost)
sv.stop()
print("done")