什么是决策阈值?
sklearn不允许我们直接设置决策阈值,但它允许我们访问用于进行预测的决策分数(决策函数o/p)。我们可以从决策函数输出中选择最佳得分并将其设置为决策阈值,并且将小于该决策阈值的所有那些决策得分值视为负类(0),并且将大于该决策阈值的所有那些决策得分值视为正类(1)。
对各种决策阈值使用精度-召回曲线,我们可以选择最佳的决策阈值,使它提供高精度(不影响召回很多)或高召回(不影响精度很多)的基础上,根据我们的项目是面向精度还是面向召回的。
这样做的主要目的是得到一个高精度ML模型,或高召回ML模型。
用于构建高精度ML模型的Python代码
# Import required modules.
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, recall_score, precision_score, accuracy_score
# Get the data.
data_set = datasets.load_breast_cancer()
# Get the data into an array form.
x = data_set.data # Input feature x.
y = data_set.target # Input target variable y.
# Get the names of the features.
feature_list = data_set.feature_names
# Convert the data into pandas data frame.
data_frame = pd.DataFrame(x, columns = feature_list)
# To insert an output column in data_frame.
data_frame.insert(30, 'Outcome', y) # Run this line only once for every new training.
# Data Frame.
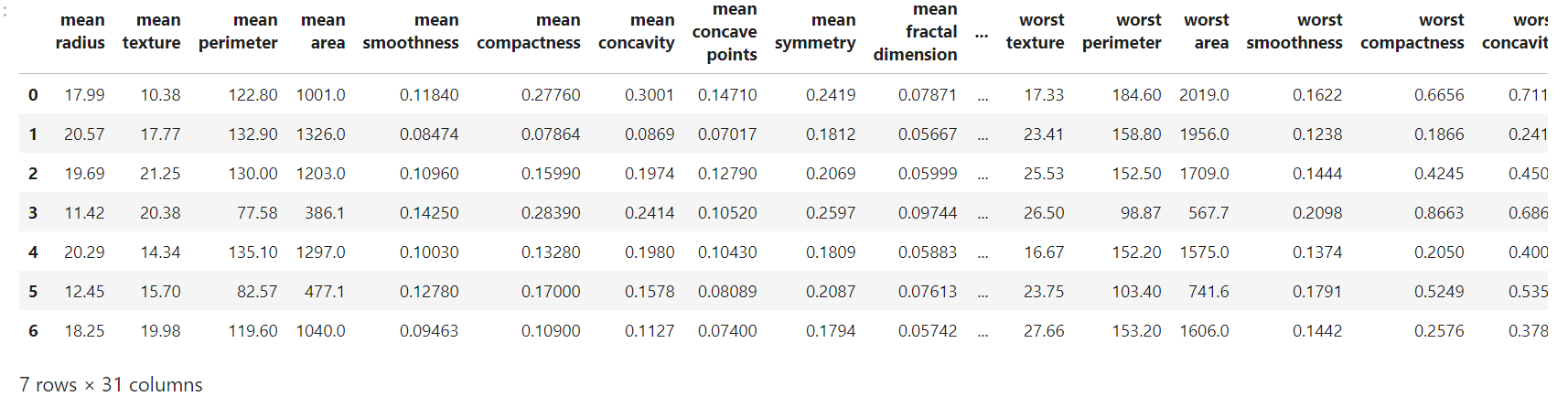
data_frame.head(7)
训练模型
# Train Test Split.
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 42)
# Create Classifier Object.
clf = SVC()
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Use decision_function method.
decision_function = clf.decision_function(x_test)
获得实际评分
# Actual obtained results without any manual setting of Decision Threshold.
predict_actual = clf.predict(x_test) # Predict using classifier.
accuracy_actual = clf.score(x_test, y_test)
classification_report_actual = classification_report(y_test, predict_actual)
print(predict_actual, accuracy_actual, classification_report_actual, sep ='\n')
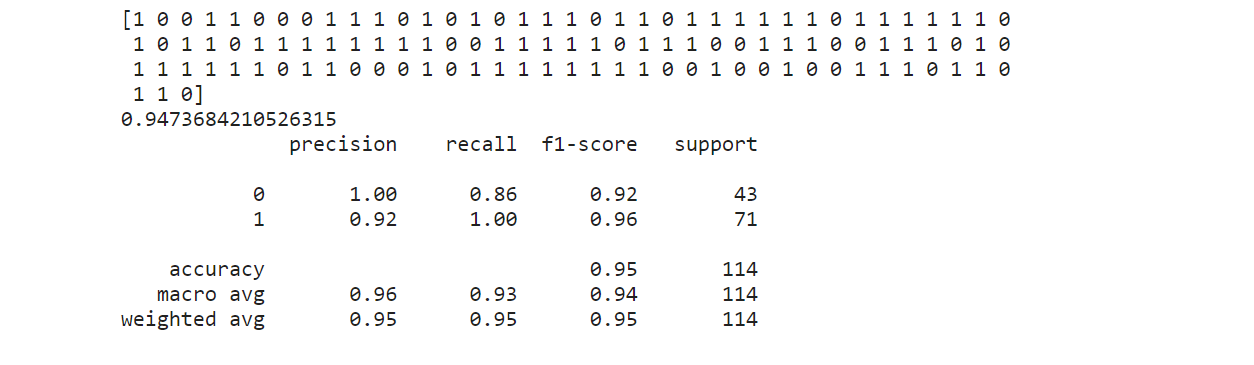
在上面的分类报告中,我们可以看到我们的模型精度值(1)是0.92,召回值(1)是1.00。由于本文中我们的目标是在预测(1)时构建一个高精度ML模型而不影响召回率,因此我们需要从下面的精确度-召回曲线中手动选择最佳的决策阈值值,以便我们可以提高该模型的精度。
# Plot Precision-Recall curve using sklearn.
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
precision, recall, threshold = precision_recall_curve(y_test, decision_function)
# Plot the output.
plt.plot(threshold, precision[:-1], c ='r', label ='PRECISION')
plt.plot(threshold, recall[:-1], c ='b', label ='RECALL')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.title('Precision-Recall Curve')
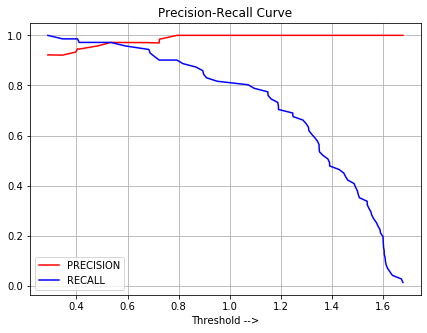
在上面的图中,我们可以看到,如果我们想要高精度值,那么我们需要增加决策阈值的值 (X轴),但这将降低召回值(这是不利的)。因此,我们需要选择决策阈值,它可以提高准确率,但召回率不会下降太多。形成上述曲线的一个这样的值是大约0.6决策阈值。
# Implementing main logic.
# Based on analysis of the Precision-Recall curve.
# Let Decision Threshold value be around 0.6... to get high Precision without affecting recall much.
# Desired results.
# Decision Function output for x_test.
df = clf.decision_function(x_test)
# Set the value of decision threshold.
decision_teshold = 0.5914643767268305
# Desired prediction to increase precision value.
desired_predict =[]
# Iterate through each value of decision function output
# and if decision score is > than Decision threshold then,
# append (1) to the empty list ( desired_prediction) else
# append (0).
for i in df:
if i<decision_teshold:
desired_predict.append(0)
else:
desired_predict.append(1)
新旧精度值的比较
# Comparison
# Old Precision Value
print("old precision value:", precision_score(y_test, predict_actual))
# New precision Value
print("new precision value:", precision_score(y_test, desired_predict))
输出
old precision value: 0.922077922077922
new precision value: 0.9714285714285714
结论
- 精度值从0.92增加到0.97。
- 召回值因精度-召回权重而减少。
注: 上面的代码没有经过数据预处理(数据清理),这只是一个在实践中如何使用决策阈值的想法。