概述
基于深度学习的人脸表情识别,数据集采用公开数据集fer2013,可直接运行,效果良好,可根据需求修改训练代码,自己训练模型。
详细
一、概述
本项目以PyTorch为框架,搭建卷积神经网络模型,训练后可直接调用py文件进行人脸检测与表情识别,默认开启摄像头实时检测识别。效果良好,可根据个人需求加以修改。
二、演示效果:
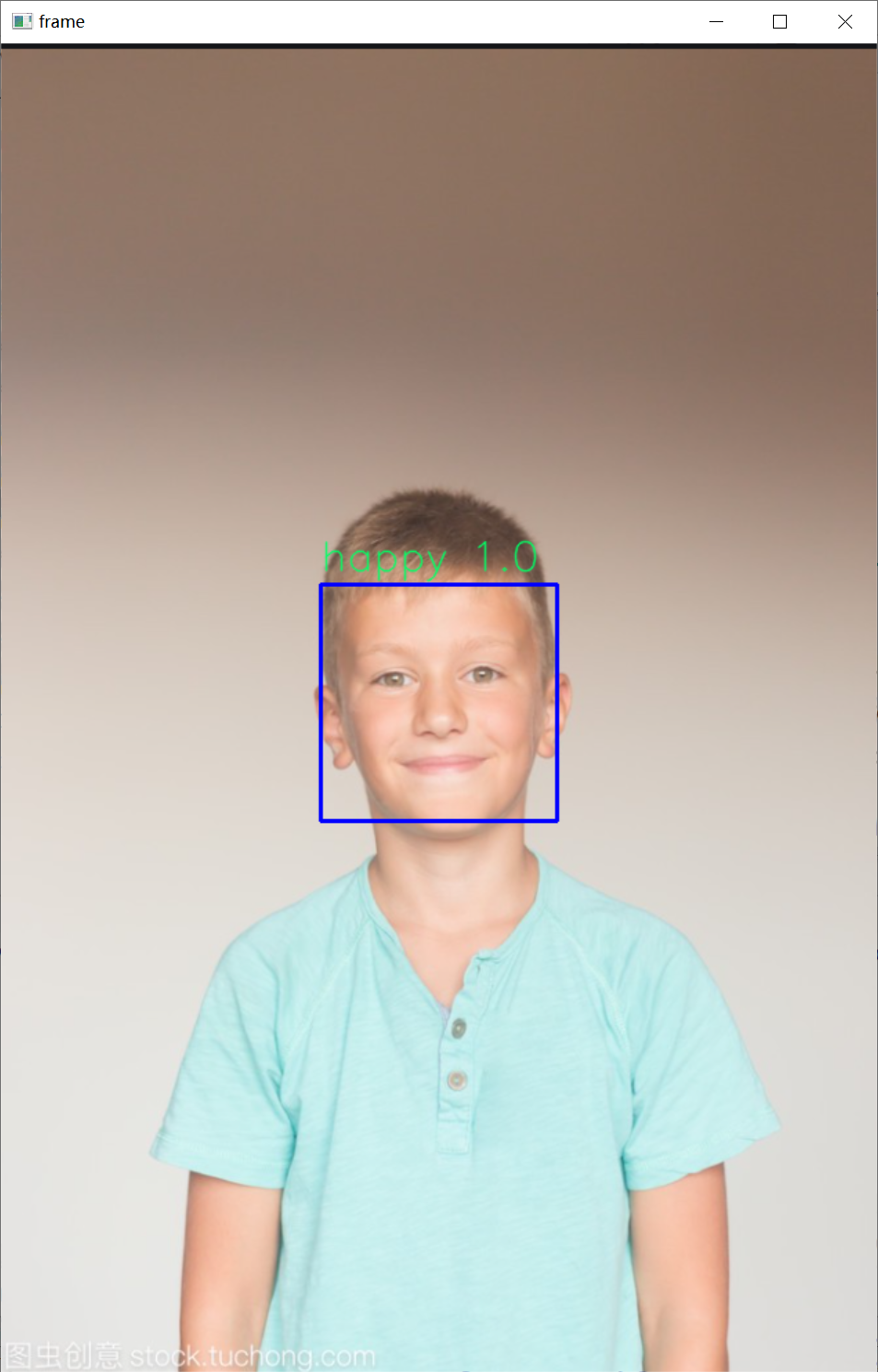
三、实现过程
1. 搭建网络
def __init__(self):
super(FaceCNN, self).__init__()
# 第一次卷积、池化
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), # 卷积层
# BatchNorm2d进行数据的归一化处理,这使得数据在进行Relu之前不会因为数据过大而导致网络性能的不稳定
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=64), # 归一化
nn.RReLU(inplace=True), # 激活函数
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 最大值池化
)
# 第二次卷积、池化
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=128),
nn.RReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
# 第三次卷积、池化
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=256),
nn.RReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
# 参数初始化
self.conv1.apply(gaussian_weights_init)
self.conv2.apply(gaussian_weights_init)
self.conv3.apply(gaussian_weights_init)
# 全连接层
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.2),
nn.Linear(in_features=256 * 6 * 6, out_features=4096),
nn.RReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024),
nn.RReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=256),
nn.RReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=256, out_features=7),
)2. 训练模型
# 载入数据并分割batch
train_loader = data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size)
# 损失函数
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 学习率衰减
# scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.8)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 构建模型
model = FaceCNN().to(device)
# 优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=wt_decay)
# 逐轮训练
for epoch in range(epochs):
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
learning_rate = learning_rate * 0.1
# 记录损失值
loss_rate = 0
# scheduler.step() # 学习率衰减
model.train() # 模型训练
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 梯度清零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播
output = model.forward(images)
# 误差计算
loss_rate = loss_function(output, labels)
# 误差的反向传播
loss_rate.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()3. 模型预测
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(face)
probability = torch.nn.functional.softmax(pred, dim=1)
probability = np.round(probability.cpu().detach().numpy(), 3)
max_prob = np.max(probability)
# print(max_prob)
predicted = classes[torch.argmax(pred[0])]
cv2.putText(img, predicted + " " + str(max_prob), (x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (100, 255, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imshow('frame', img)