目录
一. Redis整合ssm项目
1.1 pom配置
1.2 spring-redis.xml
①注册一个redis.properties
②配置数据源
③连接工厂
④配置序列化器
⑤配置redis的key生成策略
1.3 applicationContext.xml 中添加spring-redis.xml
二. Redis的注解式开发
2.1 @Cacheable
2.2 @CachePut
2.3 @CacheEvict
三. Redis的击穿,穿透,雪崩以及解决方案
3.1 击穿
产生原因
解决思路
3.2 穿透
解决思路
3.3 雪崩
解决思路
一. Redis整合ssm项目
1.1 pom配置
<redis.version>2.9.0</redis.version>
<redis.spring.version>1.7.1.RELEASE</redis.spring.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.spring.version}</version>
</dependency>注意:resources的配置必须要涵盖读取.properties结尾的文件
1.2 spring-redis.xml
①注册一个redis.properties
redis.properties
redis.hostName=localhost1
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
redis.timeout=10000
redis.maxIdle=300
redis.maxTotal=1000
redis.maxWaitMillis=1000
redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024
redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
redis.testOnBorrow=true
redis.testWhileIdle=true
redis.expiration=3600注意:当spring上下文中需要注册多个以.properties结尾的配置文件,不能在spring-*中添加注册
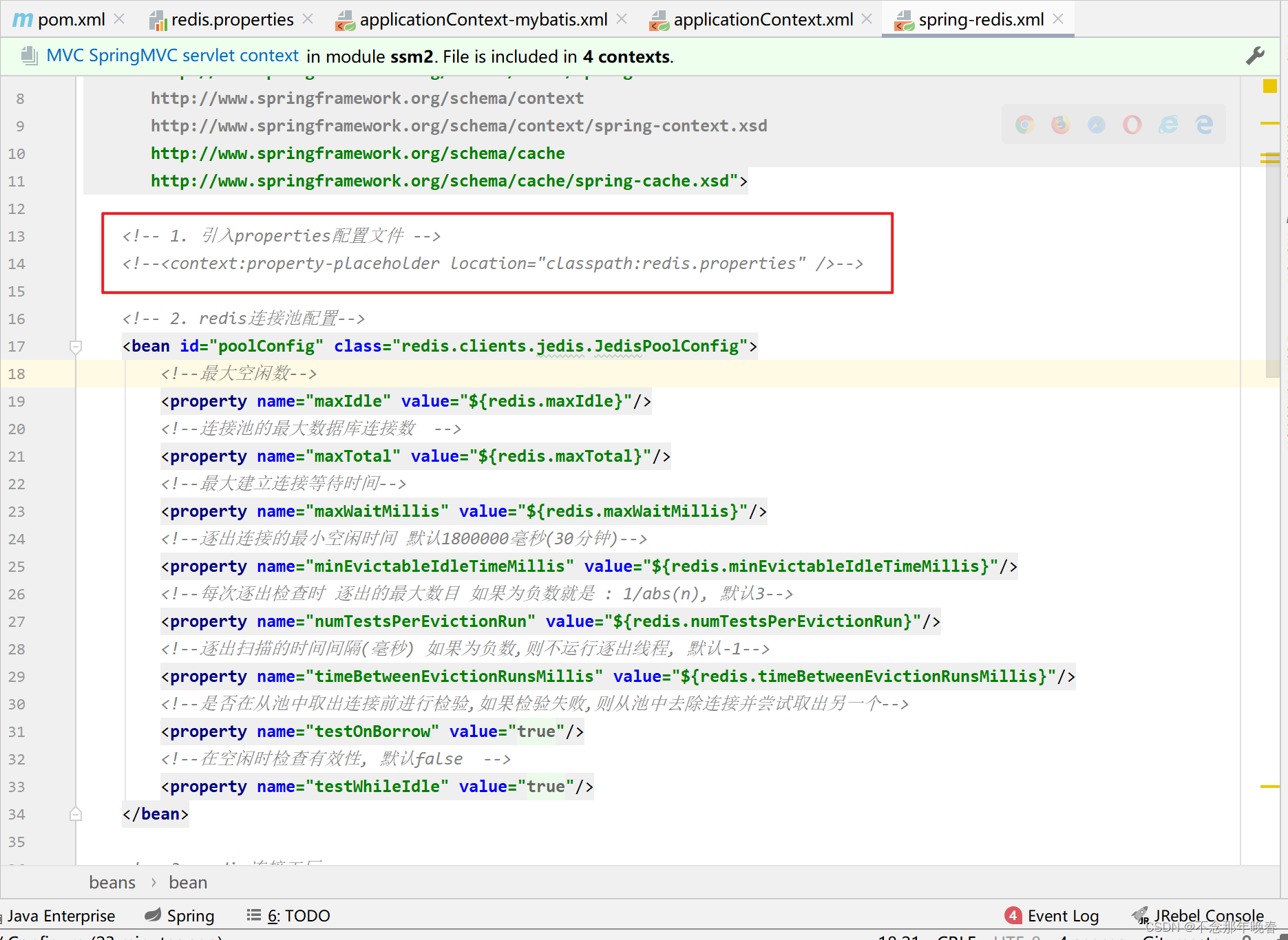
②配置数据源

③连接工厂
④配置序列化器
⑤配置redis的key生成策略
spring-redis.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!-- 1. 引入properties配置文件 -->
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:redis.properties" />-->
<!-- 2. redis连接池配置-->
<bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<!--最大空闲数-->
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"/>
<!--连接池的最大数据库连接数 -->
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/>
<!--最大建立连接等待时间-->
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/>
<!--逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)-->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/>
<!--每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3-->
<property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/>
<!--逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1-->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/>
<!--是否在从池中取出连接前进行检验,如果检验失败,则从池中去除连接并尝试取出另一个-->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/>
<!--在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false -->
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/>
</bean>
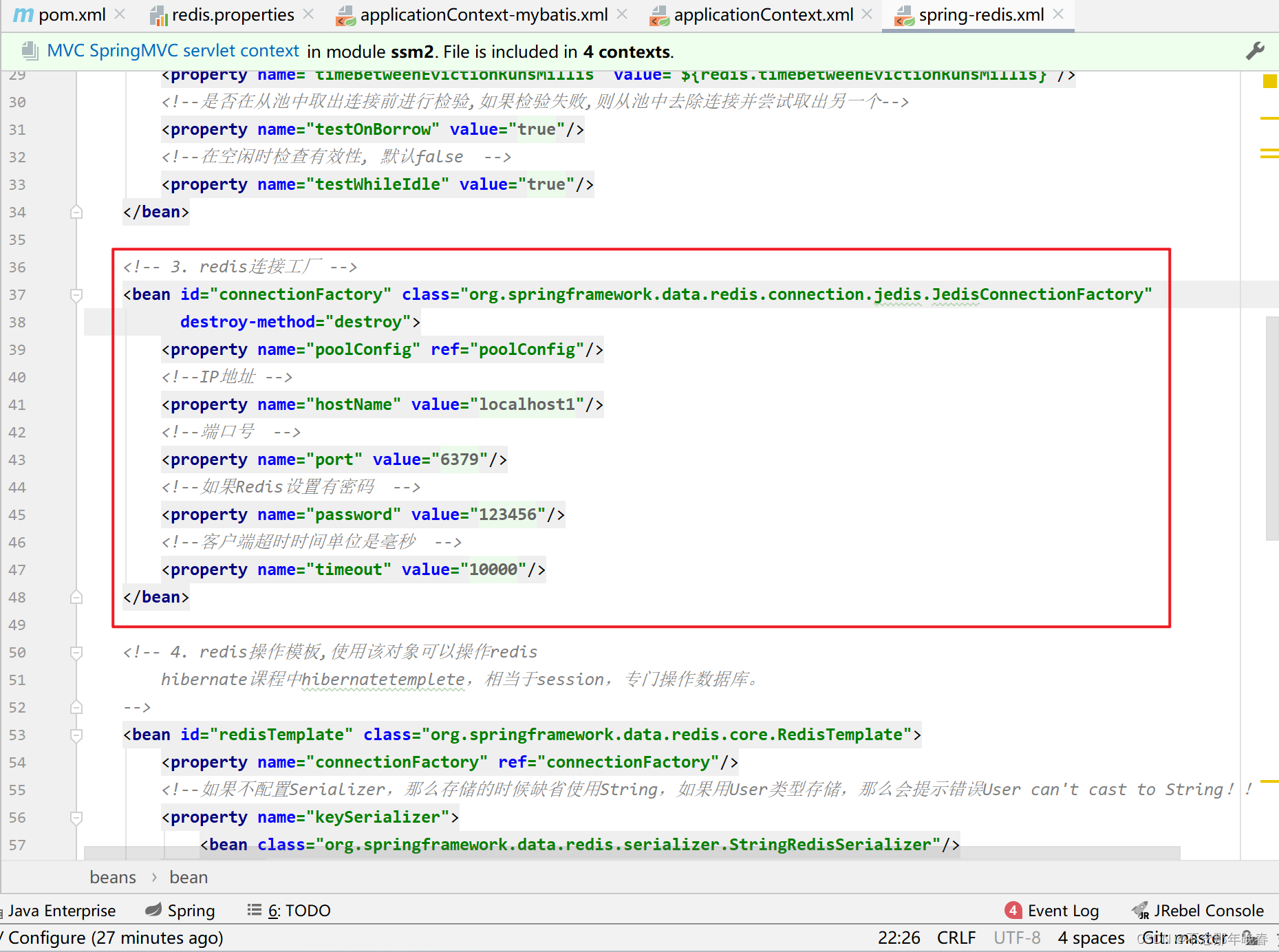
<!-- 3. redis连接工厂 -->
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"
destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/>
<!--IP地址 -->
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/>
<!--端口号 -->
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/>
<!--如果Redis设置有密码 -->
<property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/>
<!--客户端超时时间单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 4. redis操作模板,使用该对象可以操作redis
hibernate课程中hibernatetemplete,相当于session,专门操作数据库。
-->
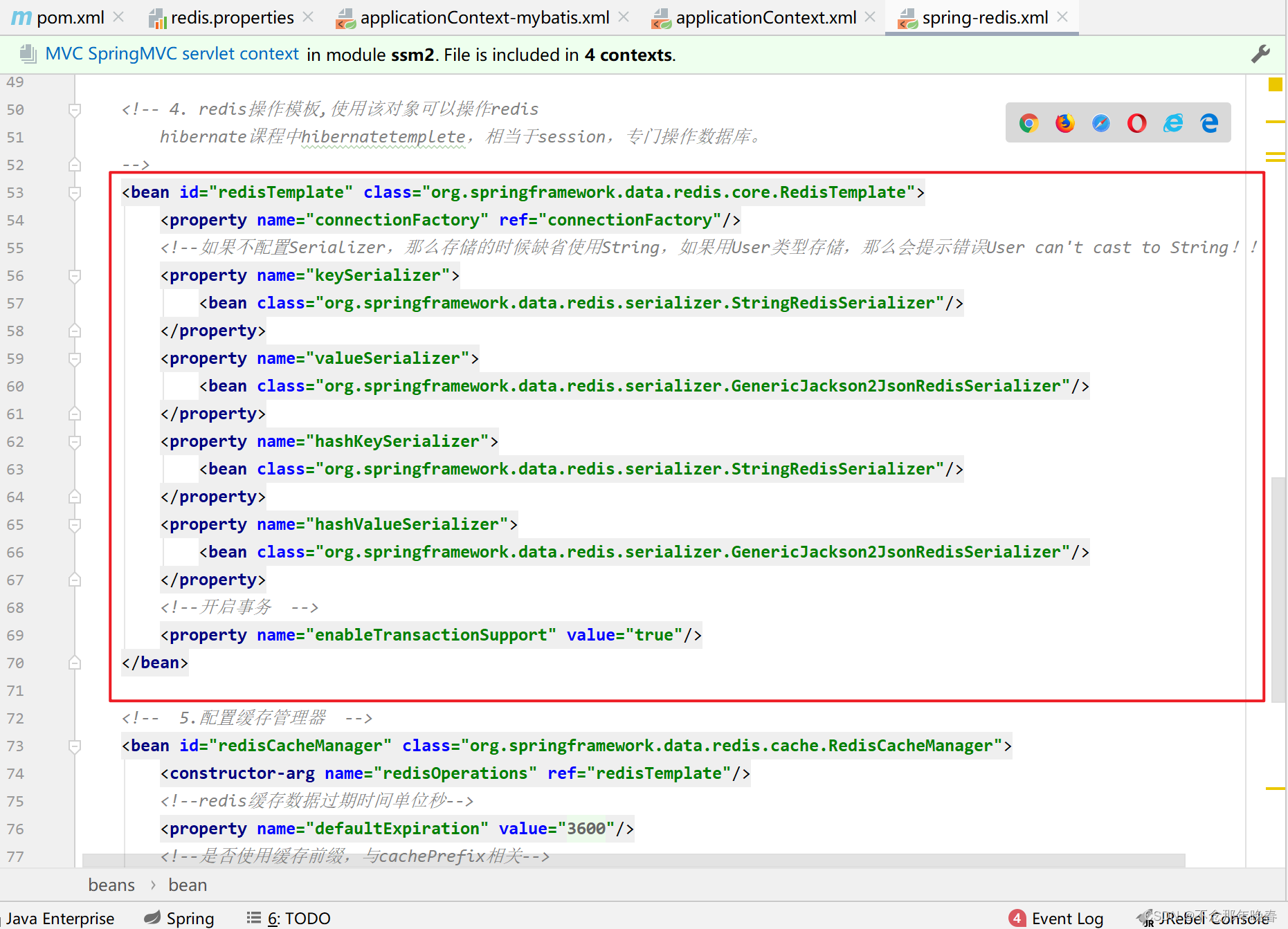
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/>
<!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! -->
<property name="keySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="valueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashKeySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashValueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<!--开启事务 -->
<property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/>
</bean>
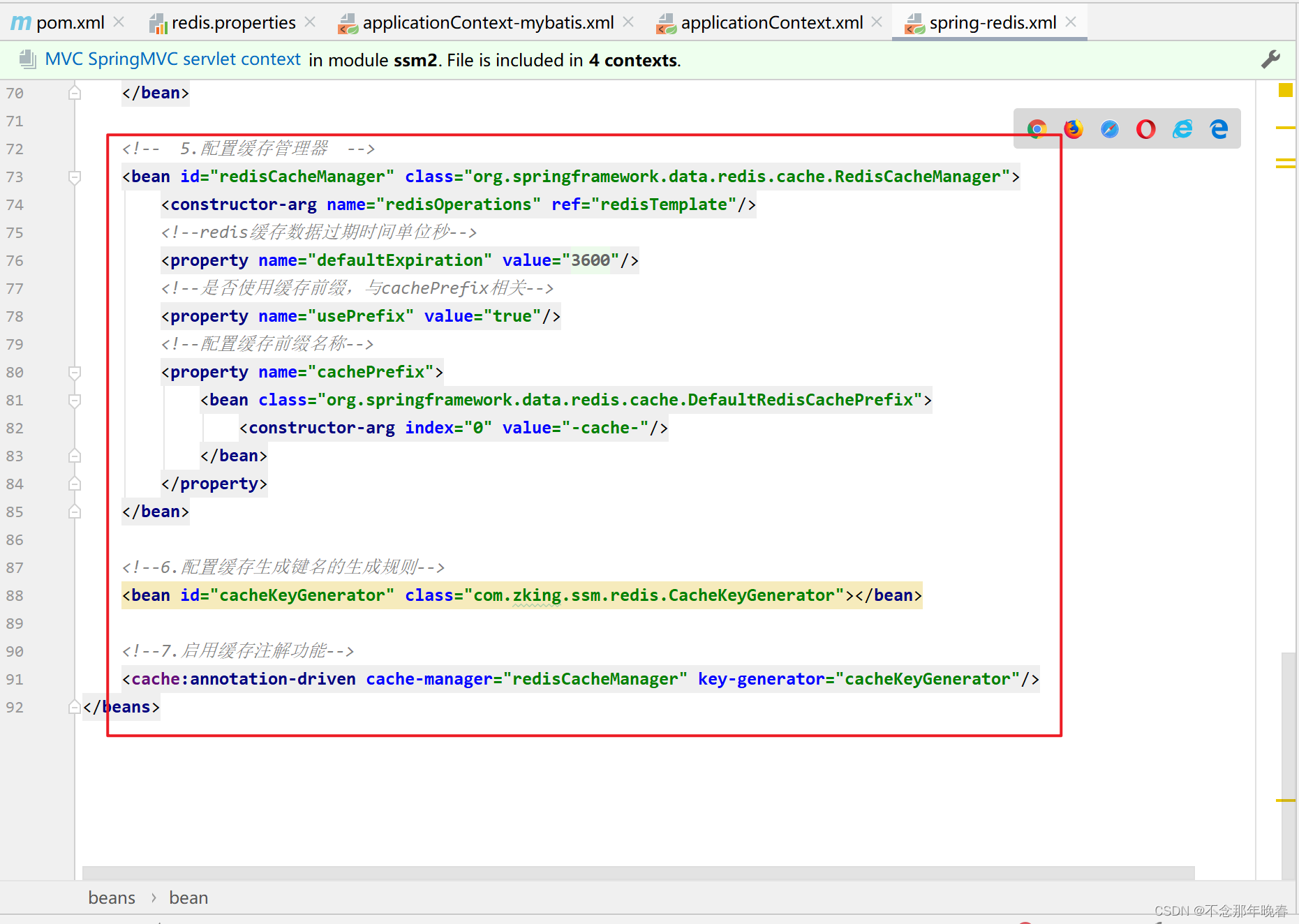
<!-- 5.配置缓存管理器 -->
<bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager">
<constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplate"/>
<!--redis缓存数据过期时间单位秒-->
<property name="defaultExpiration" value="${redis.expiration}"/>
<!--是否使用缓存前缀,与cachePrefix相关-->
<property name="usePrefix" value="true"/>
<!--配置缓存前缀名称-->
<property name="cachePrefix">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCachePrefix">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="-cache-"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!--6.配置缓存生成键名的生成规则-->
<bean id="cacheKeyGenerator" class="com.zking.ssm.redis.CacheKeyGenerator"></bean>
<!--7.启用缓存注解功能-->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager" key-generator="cacheKeyGenerator"/>
</beans>1.3 applicationContext.xml 中添加spring-redis.xml
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--1. 引入外部多文件方式 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
<property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
<value>classpath:redis.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 随着后续学习,框架会越学越多,不能将所有的框架配置,放到同一个配制间,否者不便于管理 -->
<import resource="applicationContext-mybatis.xml"></import>
<import resource="spring-redis.xml"></import>
<import resource="applicationContext-shiro.xml"></import>
</beans>
二. Redis的注解式开发
2.1 @Cacheable
配置在方法或类上.
作用:本方法执行后,先去缓存看有没有数据,如果没有,从数据库中查找出来,给缓存中存一份,返回结果。 下次本方法执行,在缓存未过期情况下,先在缓存中查找,有的话直接返回,没有的话从数据库查找。
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
测试代码:
@Cacheable(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ClazzBizTest {
@Autowired
private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
}
}测试结果:redis中有数据,则访问redis;如果没有数据,则访问MySQL;
2.2 @CachePut
类似于更新操作,即每次不管缓存中有没有结果,都从数据库查找结果,并将结果更新到缓存,并返回结果。
value:缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个
key:缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合
condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存
测试代码:
@CachePut(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ClazzBizTest {
@Autowired
private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
}
}测试结果:只存不取
2.3 @CacheEvict
用来清除用在本方法或者类上的缓存数据(用在哪里清除哪里)
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
allEntries:true表示清除value中的全部缓存,默认为false
测试代码:
@CacheEvict(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",allEntries = true)
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ClazzBizTest {
@Autowired
private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
@Test
public void test2(){
clazzBiz.deleteByPrimaryKey(10);
}
}测试结果:可以配置删除指定缓存数据,也可以删除符合规则的所有缓存数据;
三. Redis的击穿,穿透,雪崩以及解决方案
3.1 击穿
缓存击穿就是在处于集中式高并发访问的情况下,当某个热点 key 在失效的瞬间,大量的请求在缓存中获取不到。瞬间击穿了缓存,所有请求直接打到数据库,就像是在一道屏障上击穿了一个洞。
产生原因
- Key 过期
在 Redis 中,key 有过期时间。如果某一时刻(淘宝秒杀,双十一零点开始)key 失效,那么零点之后对某个 key 失效的商品的所有请求将会直接打到数据库上,很有可能倒是数据库崩掉,仅而造成整个服务的不可用。
- Key 被内存淘汰机制淘汰
因为内存是有限的,时时刻刻都有新的缓存数据被放到内存中,而旧的数据被淘汰移除内存。如果开启了 Redis 的内存淘汰机制,Key 会存在被所设置的内存淘汰机制所淘汰的情况。
解决思路
由于 key 过期在所难免(注意:非必要情况下不要设置缓存时间永不过期),根据 Redis 的单线程特性,可认为任务是在队列中依次执行的。当请求到达 Redis 发现 key 已经过期时,进行一个操作:设置锁。
具体流程大概如下:
- 获取 Redis 锁,如果没有获取到,则回到任务队列继续排队
- 获取到锁,从数据库拉取数据并放入缓存中
- 释放锁,其他请求从缓存中拿到数据
限流:请求redis之前做流量削峰
3.2 穿透
穿透主要原因是很多请求都在访问数据库一定不存在的数据,造成请求将缓存和数据库都穿透的情况。
例如一个卖书的商城一直被请求查询茶叶产品,由于 Redis 缓存主要是用来缓存热点数据,此数据是在数据库上存在的。对于数据库都不存在的数据,是没法缓存的。这种异常流量就会直接到达数据库并且返回“NULL”的查询结果。
解决思路
- 规则排除
可以增加一些参数检验。例如数据库数据 id 一般都是递增的,如果请求 id = -10 这种参数,势必绕过Redis。避免这种情况,可以对用户真实性检验等操作。
null值填充
当缓存穿透时,redis存入一个类似null的值,下次访问则直接缓存返回空,当数据库中存在该数据的值则需要把redis存在的null值清除并载入新值,此方案不能解决频繁随机不规则的key请求。
3.3 雪崩
雪崩和击穿类似,不同的是击穿是一个热点 Key 某时刻失效,而雪崩是大量的热点 Key 在一瞬间失效。当大量缓存的过期时间相同时,缓存到达过期时间集体失效或者未加载到内存中,大量请求绕过缓存层直接访问数据库 load 数据,导致数据库频繁 IO,性能下降乃至宕机崩溃。
例如:双十一零点,很快就会迎来一波抢购,这波商品时间比较集中的放入了缓存,假设缓存30分钟。那么到了凌晨零点半的时候,这批商品的缓存就都过期了。而对这批商品的访问查询,都落到了数据库上,对于数据库而言,就会产生周期性的压力波峰。
解决思路
- 随机过期时间策略,尽量让缓存失效的时间均匀分布。
可以采取不同分类商品,缓存不同周期。在同一分类中的商品,加上一个随机因子。这样能尽可能分散缓存过期时间,而且,热门类目的商品缓存时间长一些,冷门类目的商品缓存时间短一些,也能节省缓存服务的资源。
注意:但是随机过期时间策略在有时点性的情况下是有问题的方案。举个例子:银行做活动,之前这个利息系数为2%,过了零点系数改为3%,这种情况能将用户的对应的 key 改为随机过期吗?明显不可以,同样存钱,你存到年底利息300万,隔壁老王才200万,银行经理不被天天打才怪。
- 触发批量更新
正确的思路是:首先要看看这个 Key 过期是不是时点性有关,时点性无关的话,可以随机过期时间解决。如果是时点性有关,例如上述的银行利率调整,那么就要利用强依赖击穿方案,策略是先过去的线程更新一下所有 key。这样带来的问题是一次对要对批量更新操作加上锁,防止重复更新,也要保证批量更新的时间不会对用户体验带来影响。
- 缓存标记
给每一个缓存数据增加相应的缓存标记,记录缓存的是否失效,如果缓存标记失效,则更新数据缓存。
缓存标记:记录缓存数据是否过期,如果过期会触发通知另外的线程在后台去更新实际key的缓存;
缓存数据:它的过期时间比缓存标记的时间延长 1 倍。例:标记缓存时间 30 分钟,数据缓存设置为 60 分钟。 这样,当缓存标记 key 过期后,实际缓存还能把旧数据返回给调用端,直到另外的线程在后台更新完成后,才会返回新缓存。R