文章目录
- 1. 定义
- 2. 实现保护性暂停模式
- 3. Join原理
- 4. 保护性暂停模式的扩展
1. 定义
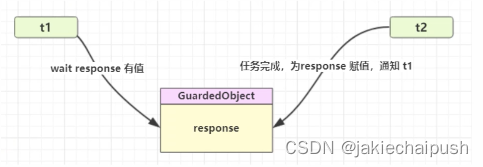
即Guarded Suspension,用在一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果。
- 有一个结果需要从一个线程传递给另一个线程,让他们关联到同一个GuarderObject(这就是保护性暂停模式,是两个线程之间交换结果的模式)
- 如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程可以使用消息队列(这个是生产者-消费者模式)
- JDK中,Join实现,Futrue的实现,采用的就是此模式
- 因为要等待另一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式
2. 实现保护性暂停模式
实现这个模式的关键是GuardedObject,response属性是用来保存中间结果。所以我们使用wait-notify来实现保护性暂停模式。
实现保护对象
class GuardedObject{
private Object response;
//获取结果
public Object get() {
synchronized (this){
while(response==null){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
}
public void complete(Object response){
synchronized (this){
this.response=response;
this.notify();
}
}
}
案例场景,线程1等待线程二的下载结果
public class jvm {
public static List<String> downLoad() throws IOException {
HttpURLConnection connection= (HttpURLConnection) new URL("https://www.baidu.com/").openConnection();
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
try(BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))){
String line;
while((line= reader.readLine())!=null){
list.add(line);
}
}
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GuardedObject guardedObject=new GuardedObject();
new Thread(()->{
log.debug("等待结果");
List<String> list= (List<String>) guardedObject.get();
log.debug("结果大小,[{}]",list.size());
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
log.debug("执行下载");
try {
List<String> list=downLoad();
guardedObject.complete(list);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"线程2").start();
}
}

3. Join原理
Join底层原理就是基于这种保护性暂停的模式,首先我们来看看Join的底层源码
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
//获得系统当前的时间戳
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
//定义当前时间戳为0
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
//如果传入的等待时间为0
if (millis == 0) {
//如果线程是存活的就一直等待,调用wait(0)
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
join(millis);
}
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
从源码可以看出,join的底层就是使用wait机制实现的。
4. 保护性暂停模式的扩展
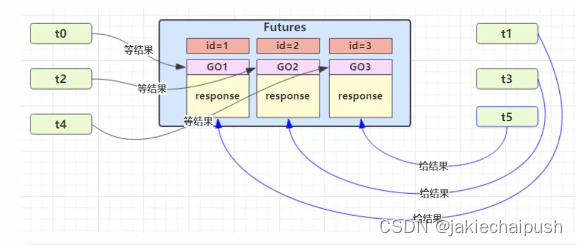
途中Futures就好比居民楼的一层信箱(每个信箱都有自己的编号),左侧的t0,t2,t4就好比等待邮件的居民(等待结果的线程),右侧t1,t3,t5就好比邮递员。如果需要在多个类之间使用GuardedObject对象,作为参数传递不是很方便,因此设计一个用来解耦的中间类,这样不仅仅能够解藕结果等待者和结果生产者,还能支持多个任务的管理。
改造GuardedObject类
class GuardedObject{
private Object response;
private int id;
public GuardedObject(){
}
public GuardedObject(int id){
this.id=id;
}
public int getId(){
return id;
}
//获取结果
public Object get() {
synchronized (this){
while(response==null){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
}
public void complete(Object response){
synchronized (this){
this.response=response;
this.notify();
}
}
}
构造解耦类
class Boxes{
private static Map<Integer,GuardedObject> box=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//产生一个唯一的id
public static int id=1;
private static synchronized int increment(){
return id++;
}
public static GuardedObject getGuardedObject(int id){
return box.remove(id);
}
public static GuardedObject creatGuardedObject(){
GuardedObject guardedObject=new GuardedObject(increment());
box.put(guardedObject.getId(),guardedObject);
return guardedObject;
}
public static Set<Integer> getIds(){
return box.keySet();
}
}
创造等待线程和生产线程
@Slf4j
class PostMan extends Thread{
private int id;
private String mail_contex;
//邮递员创建信件
public PostMan(int id,String mail_contex){
this.id=id;
this.mail_contex=mail_contex;
}
@Override
public void run(){
GuardedObject guardedObject=Boxes.getGuardedObject(id);
log.debug("送信-{},内容-{}",id,mail_contex);
guardedObject.complete(mail_contex);
}
}
class Boxes{
private static Map<Integer,GuardedObject> box=new Hashtable<>();
//产生一个唯一的id
public static int id=1;
private static synchronized int increment(){
return id++;
}
public static GuardedObject getGuardedObject(int id){
return box.remove(id);
}
public static GuardedObject creatGuardedObject(){
GuardedObject guardedObject=new GuardedObject(increment());
box.put(guardedObject.getId(),guardedObject);
return guardedObject;
}
public static Set<Integer> getIds(){
return box.keySet();
}
}
测试
public class jvm {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Poeple().start();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
for (Integer id : Boxes.getIds()) {
new PostMan(id, "内容" + id).start();
}
}
}