目录
1.新增
1.1单行数据 + 全列插入
2.2 多行数据 + 指定列插入
2.查询
2.1 全列查询
2.2 指定列查询
2.3查询字段为表达式
2.4 别名
2.5 去重:DISTINCT
2.6 排序:ORDER BY
2.7 条件查询:WHERE
2.8 分页查询:LIMIT
3.修改
4.删除
5. 内容重点总结
1.新增
创建学生表
create table if not exists student(
id int,
sn int,
name varchar(10),
qq_mail varchar(20)
);查看表结构
desc student; 
1.1单行数据 + 全列插入
插入两条记录, value_list 数量必须和定义表的列的数量及顺序一致
insert into student values (100, 10000, '唐三藏', NULL);
insert into student values (101, 10001, '孙悟空', '111111');2.2 多行数据 + 指定列插入
插入两条记录,value_list 数量必须和指定列数量及顺序一致
insert into student(id,sn,name) values
(102,20001,'曹孟德'),
(103,20002,'孙仲谋');2.查询
创建考试成绩表
create table exam_result(
id int,
name varchar(20),
chinese decimal(3,1),
math decimal(3,1),
english decimal(3,1)
);插入测试数据
insert into exam_result (id,name,chinese,math,english) values
(1,'唐三藏', 67, 98, 56),
(2,'孙悟空', 87.5, 78, 77),
(3,'猪悟能', 88, 98.5, 90),
(4,'曹孟德', 82, 84, 67),
(5,'刘玄德', 55.5, 85, 45),
(6,'孙权', 70, 73, 78.5),
(7,'宋公明', 75, 65, 30);2.1 全列查询
select * from exam_result; 
通常情况下不建议使用 * 进行全列查询
1.查询的列越多,意味着需要传输的数据量越大
2.可能会影响到索引的使用。(索引待后面课程讲解)
2.2 指定列查询
指定列的顺序不需要按定义表的顺序来
select id,name,english from exam_result;
2.3查询字段为表达式
表达式不包含字段
select id, name, 10 FROM exam_result;
表达式包含一个字段
select id, name, english + 10 FROM exam_result; 
表达式包含多个字段
select id, name, chinese + math + english FROM exam_result;
2.4 别名
为查询结果中的列指定别名,表示返回的结果集中,以别名作为该列的名称,语法:
select column [as] alinas_name from table_name;结果集中,表头的列名=别名
select id, name, chinese + math + english 总分 from exam_result; 
2.5 去重:DISTINCT
使用DISTINCT关键字对某列数据进行去重:
select distinct math from exam_result;2.6 排序:ORDER BY
语法:

1. 没有 ORDER BY 子句的查询,返回的顺序是未定义的,永远不要依赖这个顺序
2. NULL 数据排序,视为比任何值都小,升序出现在最上面,降序出现在最下面
查询同学姓名和 qq_mail,按 qq_mail 排序显示:
SELECT name, qq_mail FROM student ORDER BY qq_mail;
SELECT name, qq_mail FROM student ORDER BY qq_mail DESC;3. 使用表达式及别名排序
查询同学及总分,由高到低:
SELECT name, chinese + english + math FROM exam_result
ORDER BY chinese + english + math DESC;
SELECT name, chinese + english + math total FROM exam_result
ORDER BY total DESC;4. 可以对多个字段进行排序,排序优先级随书写顺序
查询同学各门成绩,依次按 数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
SELECT name, math, english, chinese FROM exam_result
ORDER BY math DESC, english, chinese;2.7 条件查询:WHERE
比较运算符:

逻辑运算符:
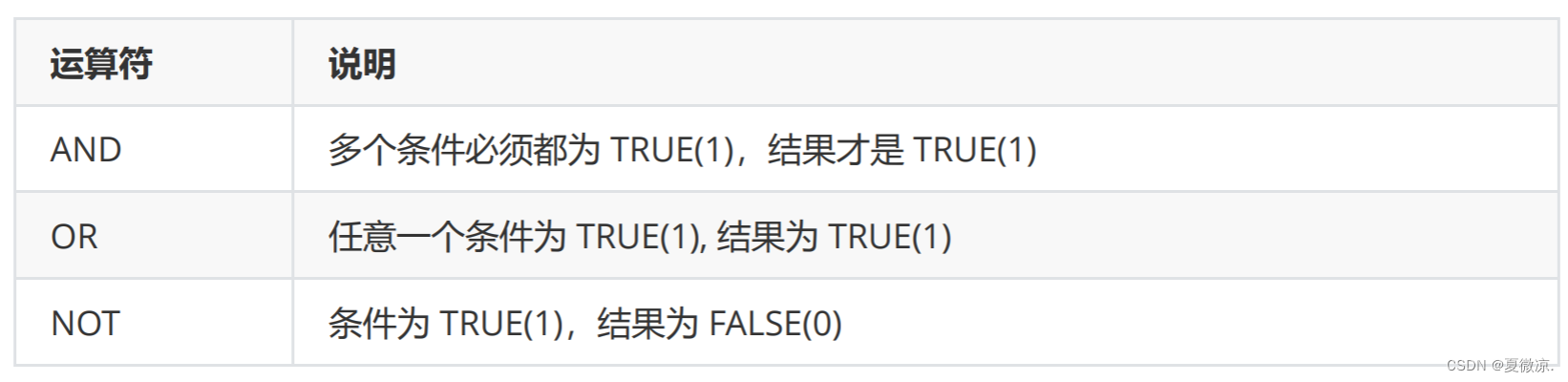
注:
1. WHERE条件可以使用表达式,但不能使用别名。
2. AND的优先级高于OR,在同时使用时,需要使用小括号()包裹优先执行的部分
案例:
基本查询:
-- 查询英语不及格的同学及英语成绩 ( < 60 )
SELECT name, english FROM exam_result WHERE english < 60;
-- 查询语文成绩好于英语成绩的同学
SELECT name, chinese, english FROM exam_result WHERE chinese > english;
-- 查询总分在 200 分以下的同学
SELECT name, chinese + math + english 总分 FROM exam_result
WHERE chinese + math + english < 200;AND与OR:
-- 查询语文成绩大于80分,且英语成绩大于80分的同学
SELECT * FROM exam_result WHERE chinese > 80 and english > 80;
-- 查询语文成绩大于80分,或英语成绩大于80分的同学
SELECT * FROM exam_result WHERE chinese > 80 or english > 80;
-- 观察AND 和 OR 的优先级:
SELECT * FROM exam_result WHERE chinese > 80 or math>70 and english > 70;
SELECT * FROM exam_result WHERE (chinese > 80 or math>70) and english > 70;
范围查询:
1. BETWEEN ... AND...
--查询语文成绩在 [80, 90] 分的同学及语文成绩
SELECT name, chinese FROM exam_result WHERE chinese BETWEEN 80 AND 90;
--使用 AND 也可以实现
SELECT name, chinese FROM exam_result WHERE chinese >= 80 AND chinese <= 90;2. IN
-- 查询数学成绩是 58 或者 59 或者 98 或者 99 分的同学及数学成绩
SELECT name, math FROM exam_result WHERE math IN (58, 59, 98, 99);
-- 使用 OR 也可以实现
SELECT name, math FROM exam_result WHERE math = 58 OR math = 59 OR math
= 98 OR math = 99;
2.8 分页查询:LIMIT
语法:
-- 起始下标为 0
-- 从 0 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT s, n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果,比第二种用法更明确,建议使用
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT n OFFSET s;案例:按 id 进行分页,每页 3 条记录,分别显示 第 1、2、3 页
-- 第一页
select id, name , math, english, chinese from exam_result order by id limit 3 offset 0;
-- 第二页
select id, name , math, english, chinese from exam_result order by id limit 3 offset 3;
-- 第三页, 如果结果不足3个, 不会有影响
select id, name , math, english, chinese from exam_result order by id limit 3 offset 6;3.修改
语法:
UPDATE table_name SET column = expr [, column = expr ...]
[WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...]案例:
-- 将孙悟空同学的数学成绩变更为 80 分
UPDATE exam_result SET math = 80 WHERE name = '孙悟空';
-- 将曹孟德同学的数学成绩变更为 60 分,语文成绩变更为 70 分
UPDATE exam_result SET math = 60, chinese = 70 WHERE name = '曹孟德';
-- 将总成绩倒数前三的 3 位同学的数学成绩加上 30 分
UPDATE exam_result SET math = math + 30 ORDER BY chinese + math + english LIMIT 3;
-- 将所有同学的语文成绩更新为原来的 2 倍
UPDATE exam_result SET chinese = chinese * 2;
4.删除
语法:
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...]案例:
-- 删除孙悟空同学的考试成绩
DELETE FROM exam_result WHERE name = '孙悟空';
-- 删除整张表数据
-- 准备测试表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS for_delete;
CREATE TABLE for_delete (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO for_delete (name) VALUES ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
-- 删除整表数据
DELETE FROM for_delete;5. 内容重点总结
新增:
-- 新增
insert into 表(字段1, ..., 字段N) values (value1, ..., value N);
-- 多行插入
insert into 表(字段1, ..., 字段N) values
(value1, ...),
(value2, ...),
(value3, ...);
查询:
-- 全列查询
select * from 表
-- 指定列查询
select 字段1,字段2... from 表
-- 查询表达式字段
select 字段1+100,字段2+字段3 from 表
-- 别名
select 字段1 别名1, 字段2 别名2 from 表
-- 去重DISTINCT
select distinct 字段 from 表
-- 排序ORDER BY
select * from 表 order by 排序字段
-- 条件查询WHERE:
-- (1)比较运算符 (2)BETWEEN ... AND ... (3)IN (4)IS NULL (5)LIKE (6)AND (7)OR (8)NOT
select * from 表 where 条件
修改:
update 表 set 字段1=value1, 字段2=value2... where 条件删除:
delete from 表 where 条件