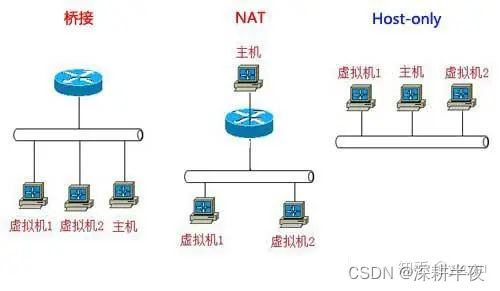
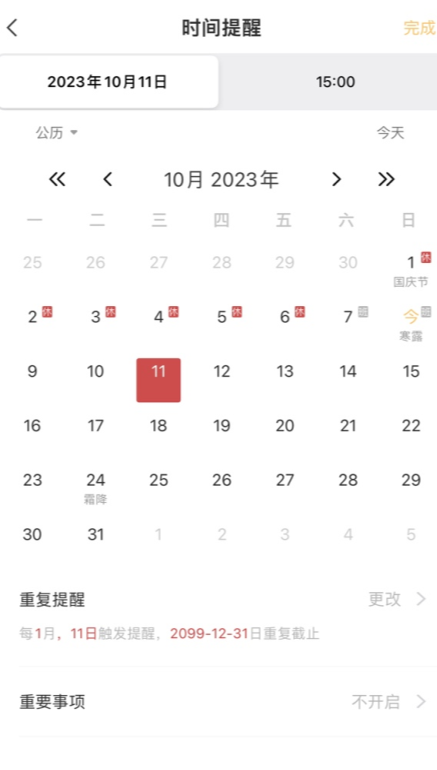
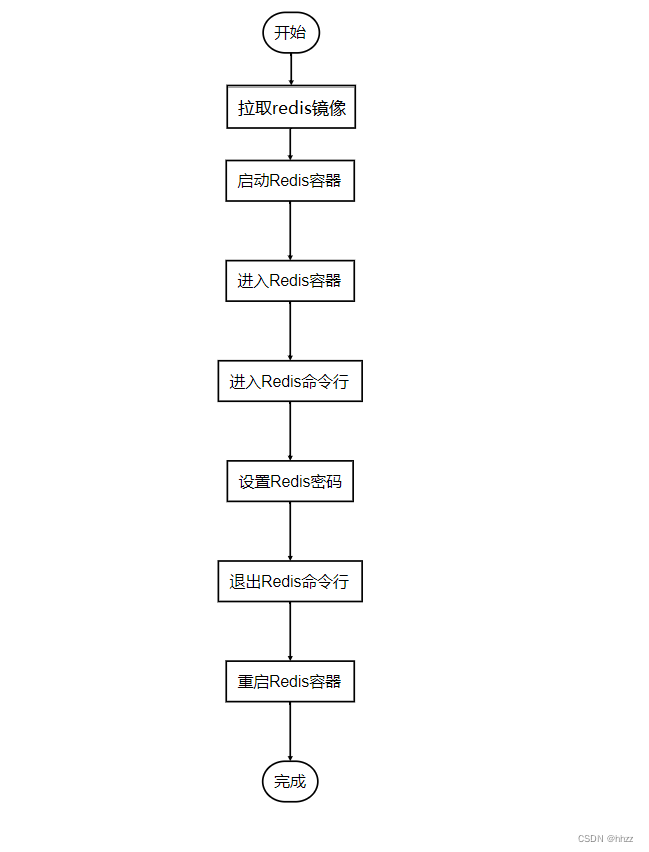
图:由点的集合和边的集合组成。
常用的表示图的方法有两种:
1、邻接表法
将一个点的邻居都列出来。有向图只列出从这个点出发向外发散的点

2、邻接矩阵法
将点集列出一列行,列出一列列,在矩阵中填两点之间的权值(距离)

【精选】数据结构:图(Graph)【详解】_数据结构图_UniqueUnit的博客-CSDN博客
解图有关的题目的思路:
图有很多表达方式,我们通常都是 先将图转化为熟悉的表达方式,再实现算法
图结构模板
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;//点集:编号、点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;//边集:边
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
class Node {
public int value;//数据
public int in;//入度
public int out;//出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts;//对有向图,从当前这个点出发发散的直接邻居的点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;//对有向图,发散出去的边属于这个点,指向进来的边则不属于这个点
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
class Edge {
public int weight;//权值
public Node from;//边的起点
public Node to;//边的终点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
其他图的方式转化为此结构示例
原来的表达方式
| 权值weight | 始节点from | 末节点to |
| 5 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 7 | 0 | 2 |
package graph;
public class Transmit {
//matrix矩阵,n*3,[weight,from,to]
public static Graph creatGraph(Integer[][] matrix) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {//遍历每组数据
Integer weight = matrix[i][0];
Integer from = matrix[i][1];
Integer to = matrix[i][2];
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)) {//没有from节点
graph.nodes.put(from, new Node(from));//创建from节点,加入到图的点集之中
}
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)) {//没有to节点
graph.nodes.put(to, new Node(to));//创建to节点,加入到图的点集之中
}
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to);
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);//加入到from的nexts集合中
fromNode.out++;//fromNode出度++
toNode.in++;//toNode入度++
Edge edge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode);//创建边
graph.edges.add(edge);//加入到图的边集
fromNode.edges.add(edge);//加入到fromNode点的边集中
}
return graph;
}
}

图的遍历的注意点:二叉树无环、图有环(避免图的环导致代码死循环)
宽度遍历:一层一层向下遍历,先遍历距离A最近的点,再遍历距离A隔了一层的节点
深度遍历:一条路走到死,再返回去看还有哪条路可以走

图的宽度遍历
如果确定节点的类型为数字,可以将哈希表写成数组结构用索引查找,可以节省时间
package graph;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Traversal {
public static void widthTraversal(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
HashSet<Node> hashSet = new HashSet();//放一个set防止重复把节点丢到队列里造成死循环
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
hashSet.add(node);
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node0 = queue.poll();//从队列中弹出
System.out.println(node0.value);//打印or执行操作
for (Node node1 : node.nexts) {//遍历node的nexts的点集中的所有的点
if(!hashSet.contains(node1)){//判断是否在set里面,是否出现过,防止环形结构死循环
hashSet.add(node1);//如果没有,就放入set和队列中
queue.add(node1);
}
}
}
}
}
图的深度遍历

public static void deepTraversal(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
HashSet<Node> hashSet = new HashSet();//放一个set防止重复把节点丢到队列里造成死循环
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack();
hashSet.add(node);
stack.add(node);
System.out.println(node.value);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node0 = stack.pop();
for (Node node1 : node0.nexts) {
if(!node0.nexts.contains(node1)){
stack.push(node0);//node再重新入栈
stack.push(node1);//邻居入栈
hashSet.add(node1);//入set集合
System.out.println(node1.value);
break;
}
}
}
}