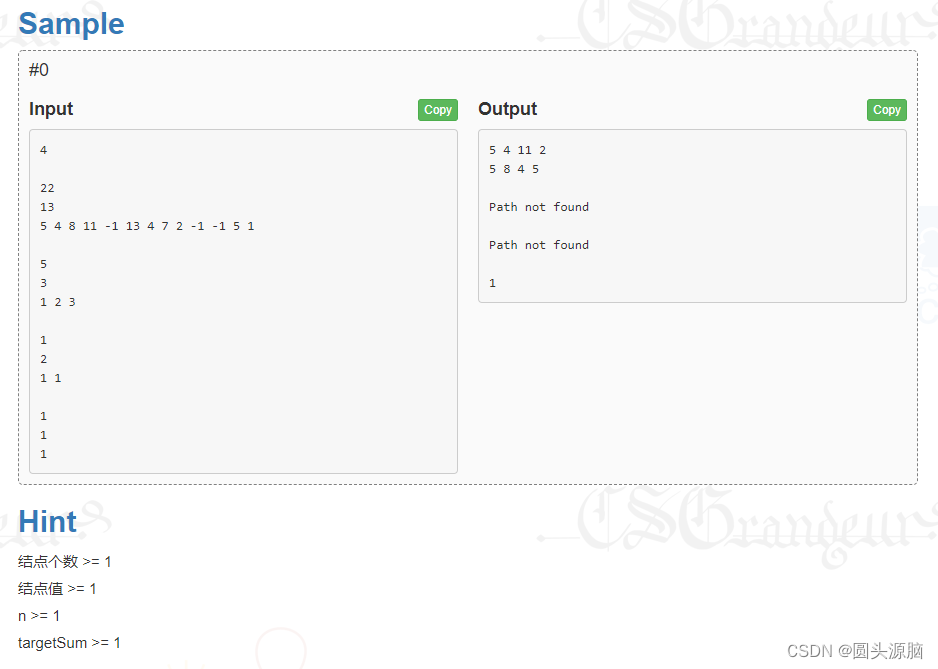
学生成绩预测是一个基于回归问题的流行数据科学案例研究。对于数据科学初学者来说,这是一个很好的回归问题,因为它很容易解决和理解。本文中,将带你通过使用Python的机器学习来完成学生成绩预测的任务。
学生成绩预测(案例研究)
您将获得有关学生的一些信息,例如:
- 他们选择的课程数目
- 学生每天平均学习时间
- 学生成绩
通过使用这些信息,你需要预测其他学生的分数。您可以从这里下载数据集。
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/yasserh/student-marks-dataset
基于Python的学生成绩预测
导入必要的Python库和数据集:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
data = pd.read_csv("Student_Marks.csv")
print(data.head(10))
输出
number_courses time_study Marks
0 3 4.508 19.202
1 4 0.096 7.734
2 4 3.133 13.811
3 6 7.909 53.018
4 8 7.811 55.299
5 6 3.211 17.822
6 3 6.063 29.889
7 5 3.413 17.264
8 4 4.410 20.348
9 3 6.173 30.862
数据集中只有三列。Marks列是目标列,因为我们需要预测学生的分数。
检查数据集是否包含任何null值:
print(data.isnull().sum())
输出
number_courses 0
time_study 0
Marks 0
dtype: int64
由于数据中没有空值,数据集可以使用,也不需要其他预处理。数据中有一列包含有关学生选择的课程数量的信息。让我们看看这一列所有值的数量:
data["number_courses"].value_counts()
输出
3 22
4 21
6 16
8 16
7 15
5 10
Name: number_courses, dtype: int64
从上可知,学生选择的课程最少三门,最多八门。让我们来绘制一个散点图,看看课程的数量是否会影响学生的分数:
figure = px.scatter(data_frame=data, x = "number_courses",
y = "Marks", size = "time_study",
title="Number of Courses and Marks Scored")
figure.show()
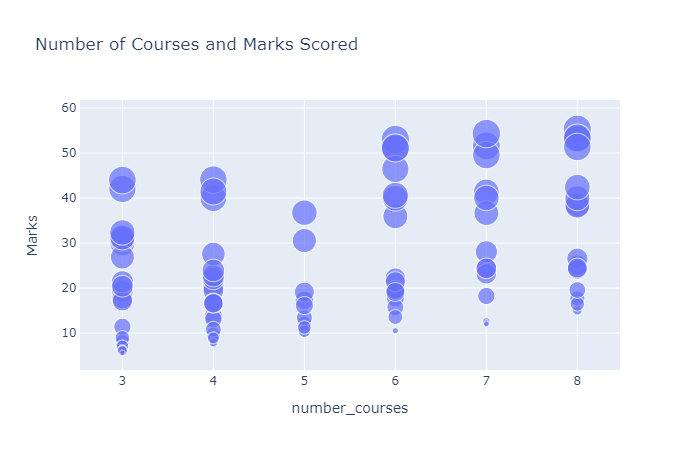
根据上述数据可视化,我们可以说,如果学生每天学习更多的时间,课程的数量可能不会影响学生的分数。那么让我们来看下每天学习的时间和学生得分之间的关系:
figure = px.scatter(data_frame=data, x = "time_study",
y = "Marks", size = "number_courses",
title="Time Spent and Marks Scored", trendline="ols")
figure.show()
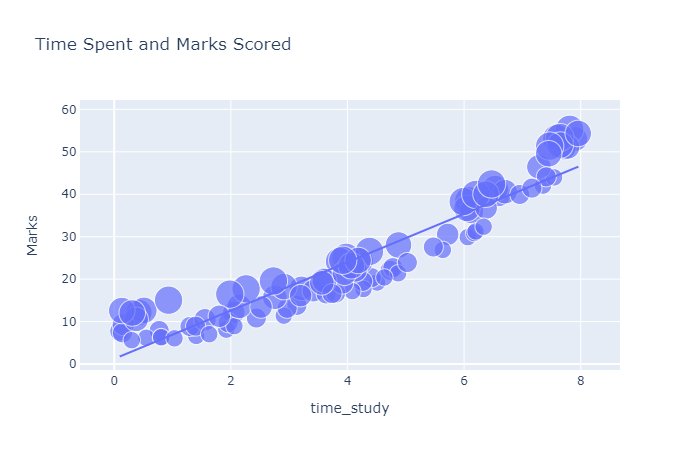
你可以看到,学习时间和分数之间存在线性关系。这意味着学生花在学习上的时间越多,他们的成绩就越好。
现在让我们来看看学生的分数与数据中其他两列之间的相关性:
correlation = data.corr()
print(correlation["Marks"].sort_values(ascending=False))
输出
Marks 1.000000
time_study 0.942254
number_courses 0.417335
Name: Marks, dtype: float64
因此,time_study列与Marks的相关性要高于number_courses列。
学生成绩预测模型
现在,让我们转向训练机器学习模型来预测学生的分数的任务。
在这里,首先将数据分为训练集和测试集:
x = np.array(data[["time_study", "number_courses"]])
y = np.array(data["Marks"])
xtrain, xtest, ytrain, ytest = train_test_split(x, y,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=42)
这里将使用最简单的线性回归算法训练机器学习模型:
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(xtrain, ytrain)
model.score(xtest, ytest)
输出
0.9459936100591212
现在,让我们测试这个机器学习模型的性能,根据我们用来训练模型和预测学生成绩的特征提供输入:
# Features = [["time_study", "number_courses"]]
features = np.array([[4.508, 3]])
model.predict(features)
输出
array([22.30738483])
以上,这就是如何使用Python通过机器学习来预测学生成绩的任务。