题目
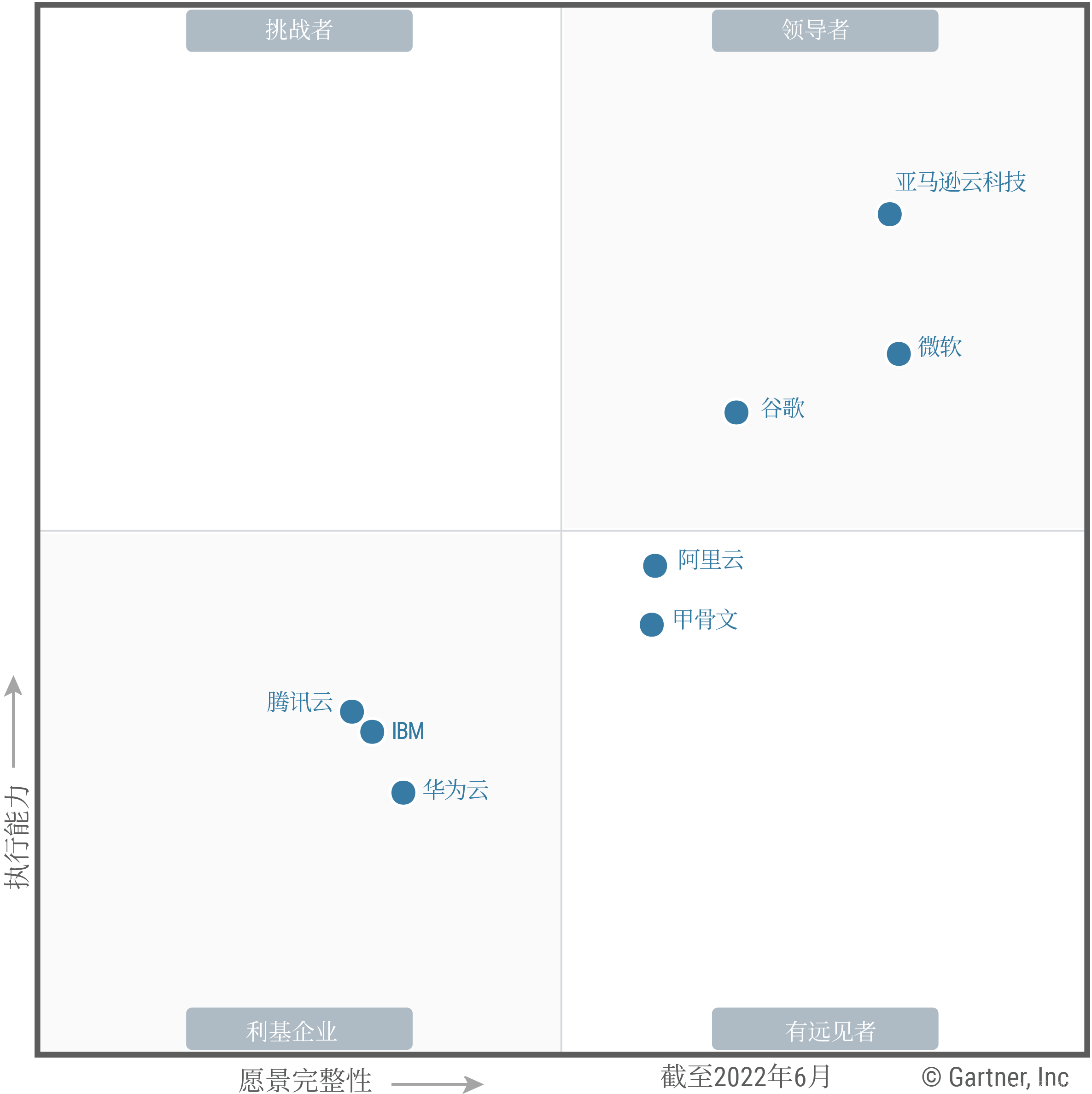
重庆城里有 n 个车站,m 条 双向 公路连接其中的某些车站。
每两个车站最多用一条公路连接,从任何一个车站出发都可以经过一条或者多条公路到达其他车站,但不同的路径需要花费的时间可能不同。
在一条路径上花费的时间等于路径上所有公路需要的时间之和。
佳佳的家在车站 1,他有五个亲戚,分别住在车站 a,b,c,d,e。
过年了,他需要从自己的家出发,拜访每个亲戚(顺序任意),给他们送去节日的祝福。
怎样走,才需要最少的时间?
输入格式
第一行:包含两个整数 n,m,分别表示车站数目和公路数目。
第二行:包含五个整数 a,b,c,d,e,分别表示五个亲戚所在车站编号。
以下 m 行,每行三个整数 x,y,t,表示公路连接的两个车站编号和时间。
输出格式
输出仅一行,包含一个整数 T,表示最少的总时间。
数据范围
1 ≤ n ≤ 50000
1 ≤ m ≤ 10^5
1 < a,b,c,d,e ≤ n
1 ≤ x , y ≤ n
1 ≤ t ≤ 100
思路
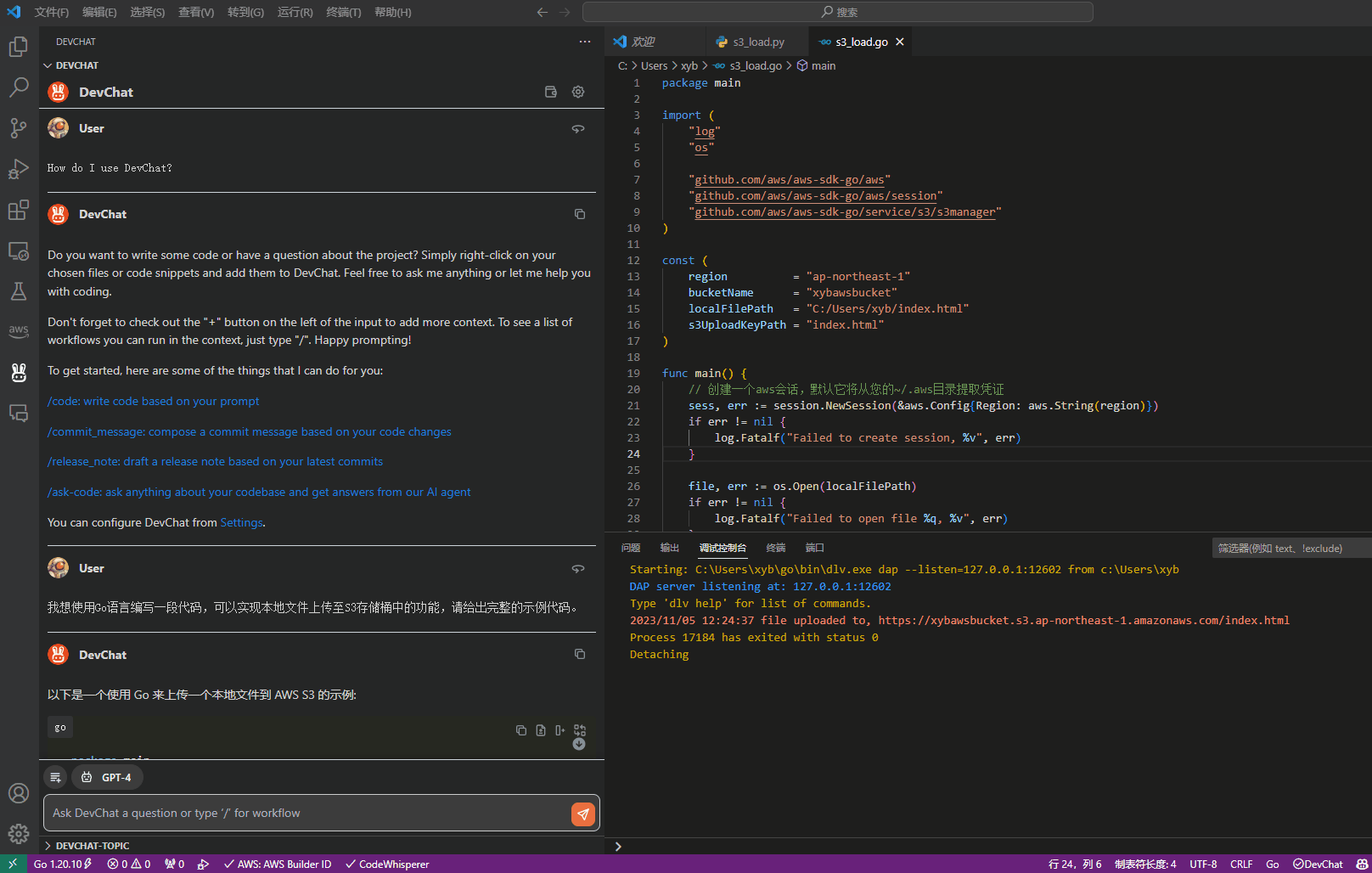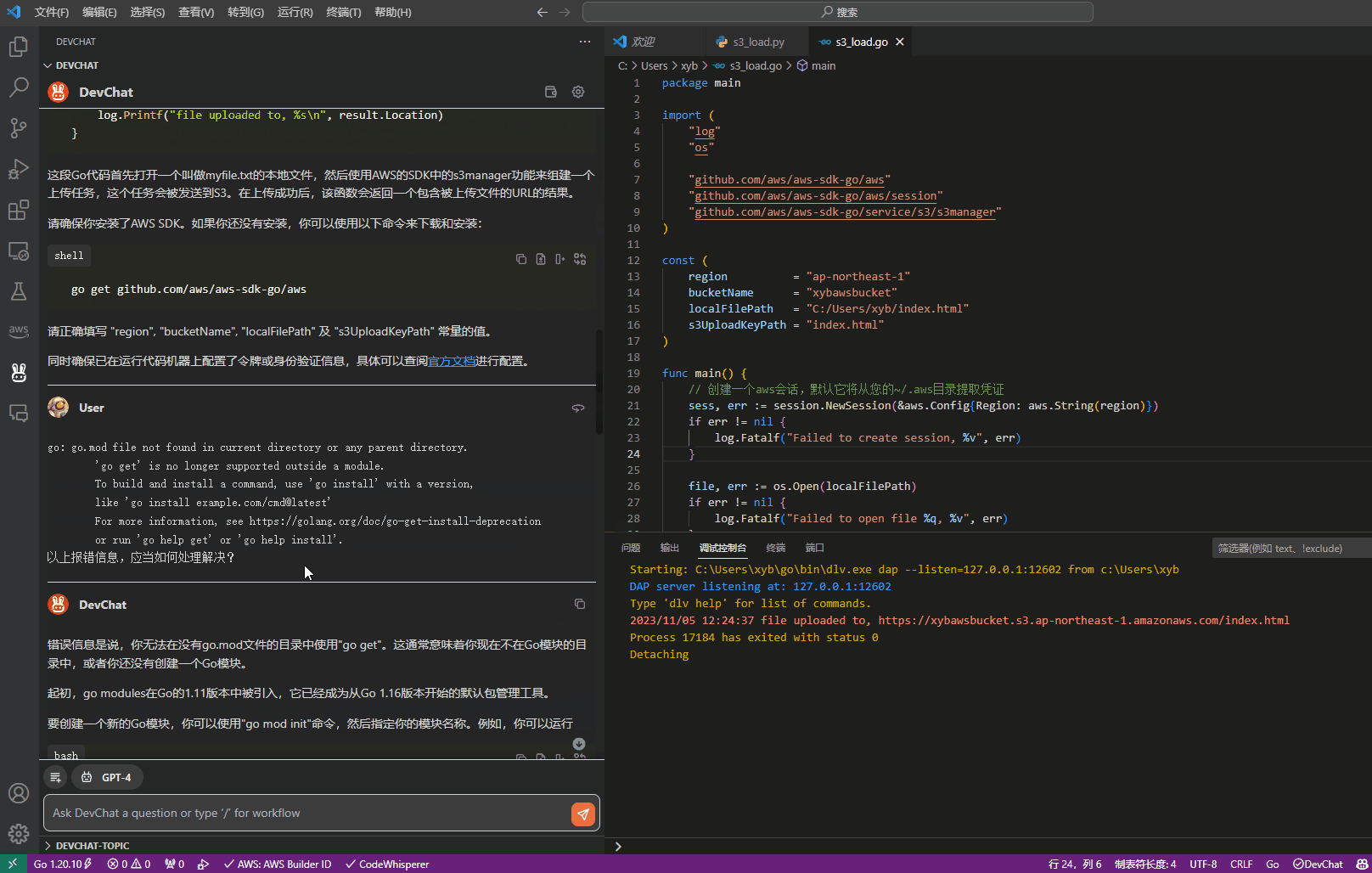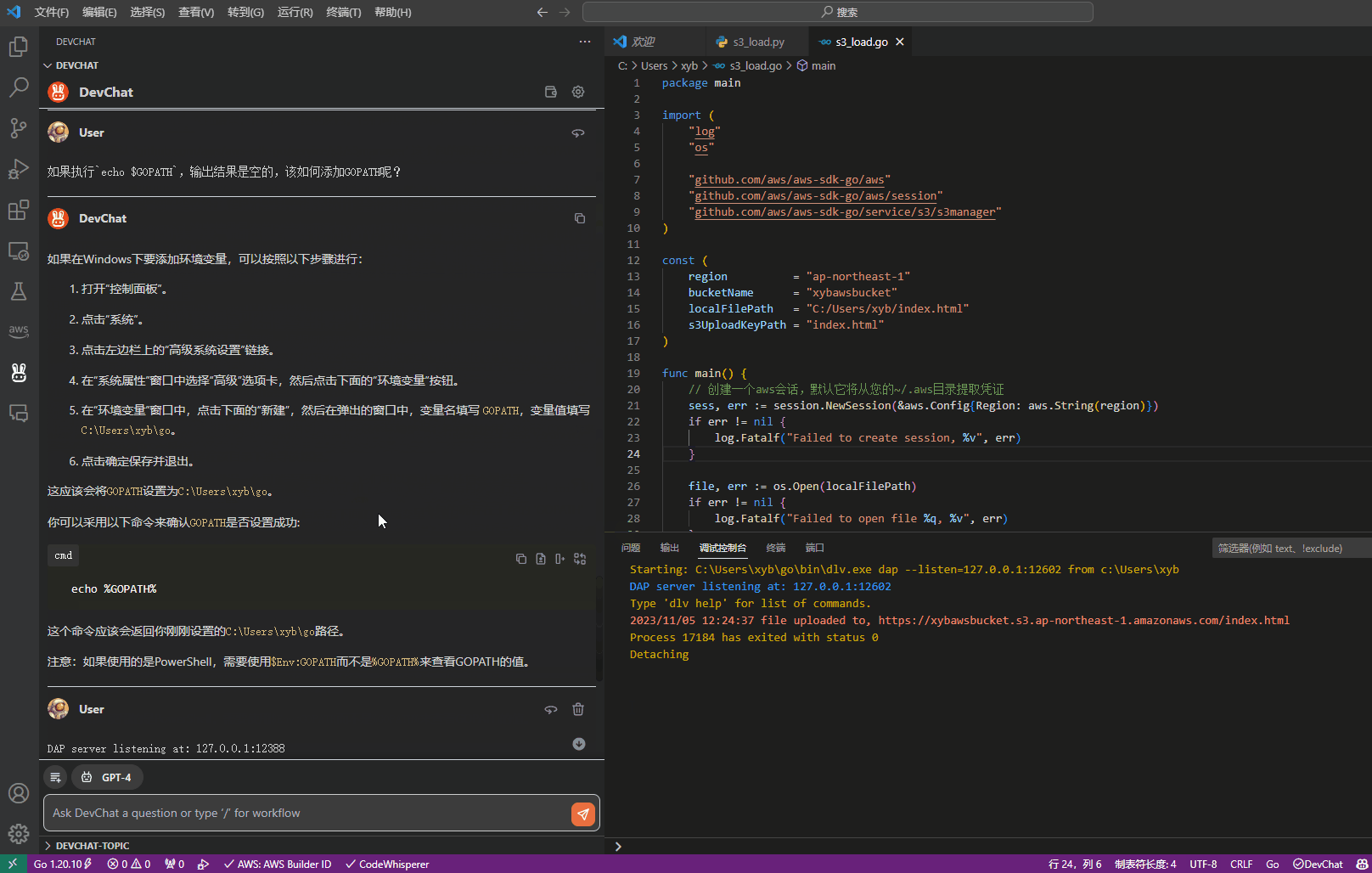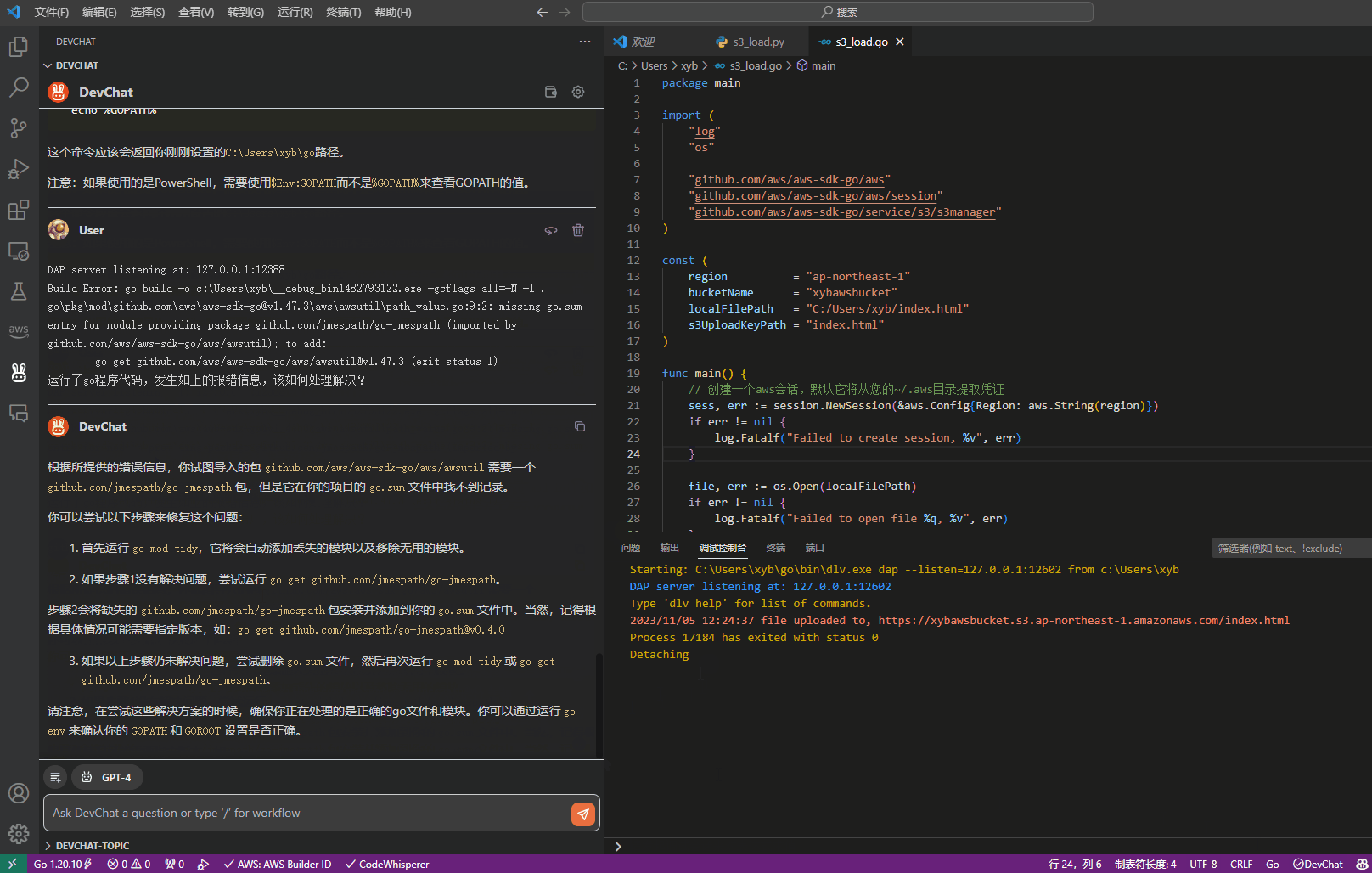
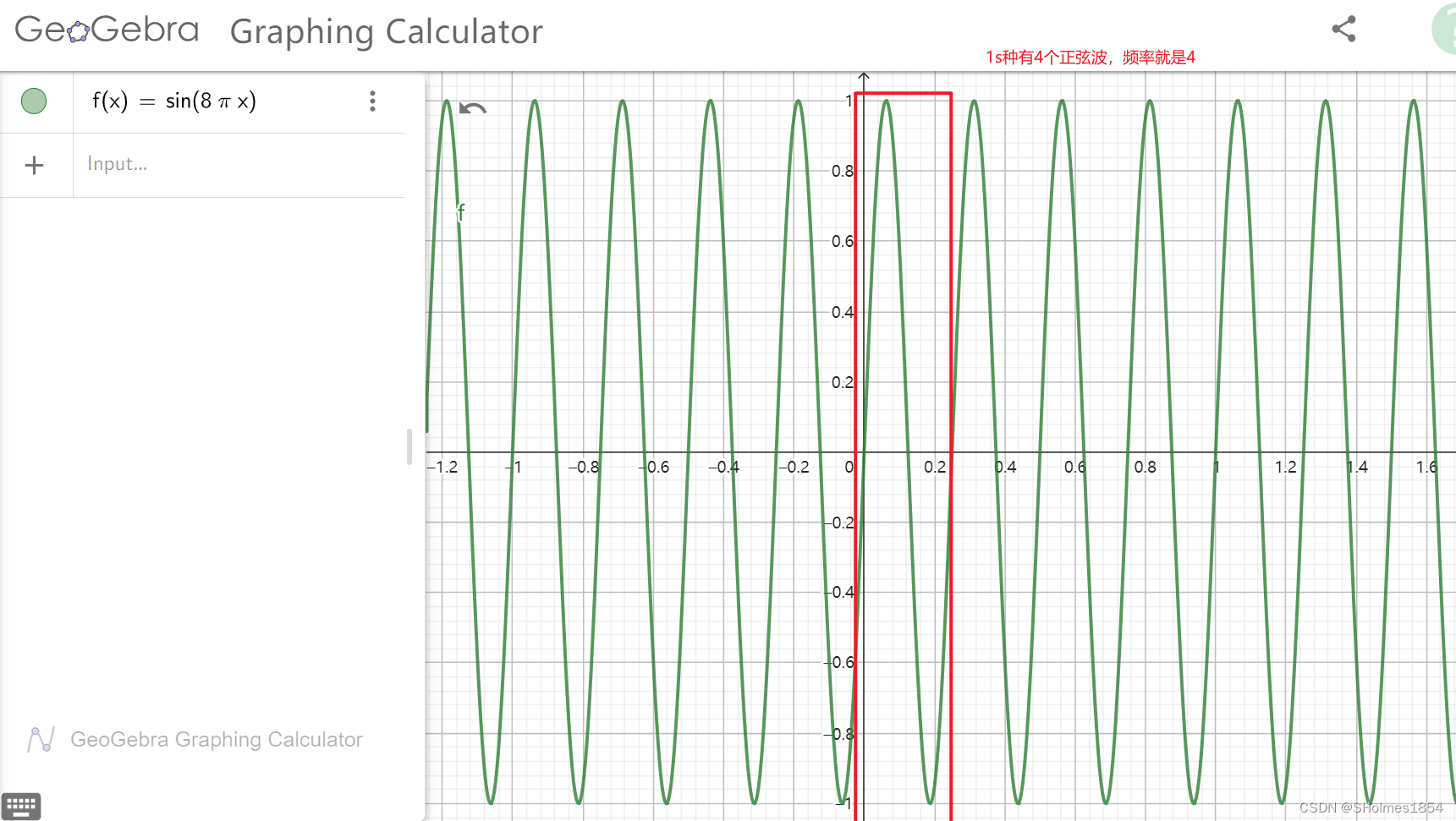
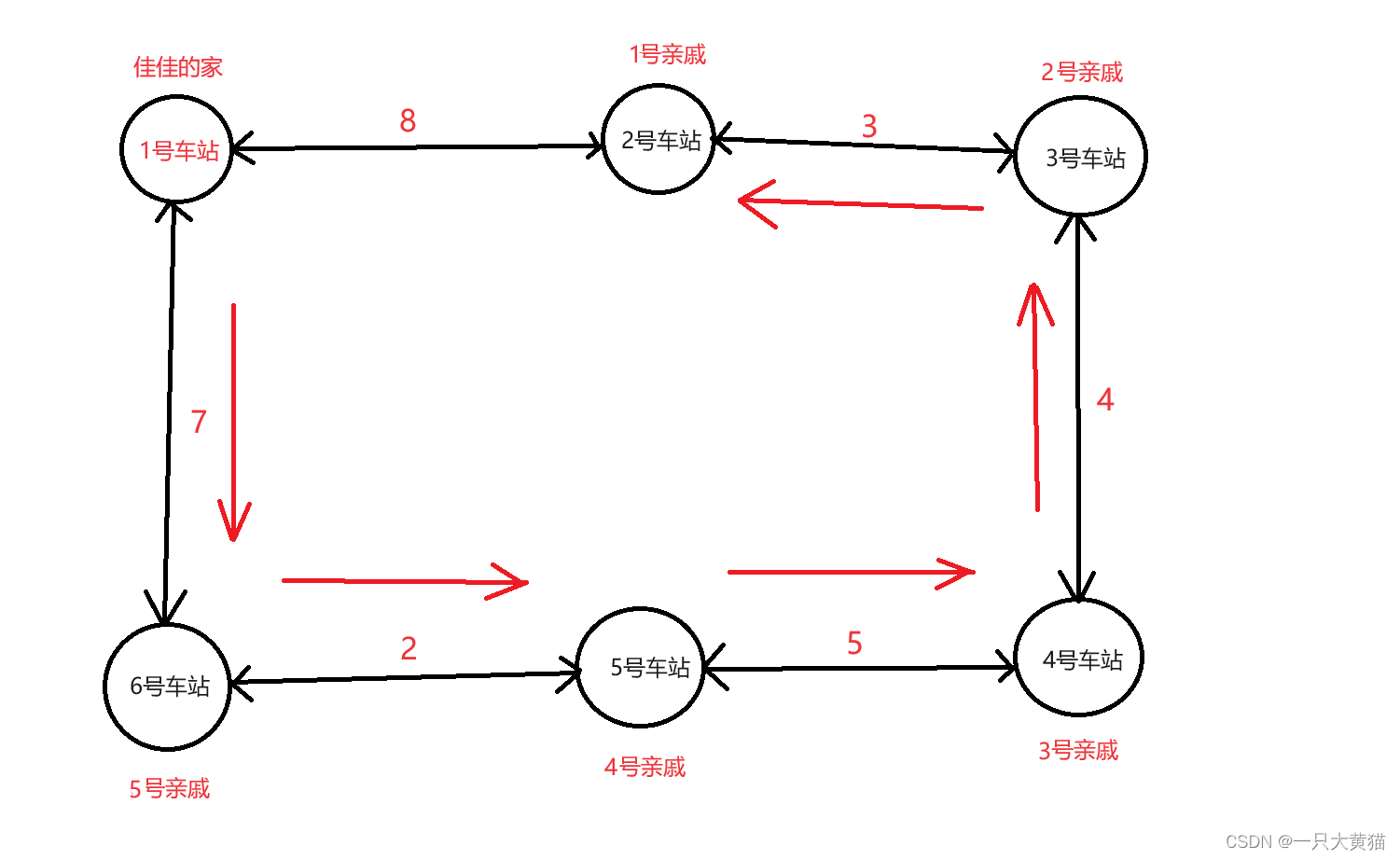
样例:
6 6
2 3 4 5 6
1 2 8
2 3 3
3 4 4
4 5 5
5 6 2
1 6 7根据样例,我们可以得到一张图:
因为数据范围:
1 ≤ n ≤ 50000
1 ≤ m ≤ 10^5
我们可知这是一张稀疏图,我们可以使用邻接矩阵进行存储。
我们可以进行6次堆优化版的dijkstra算法,依次求出佳佳与五个亲戚到其他点的最小距离。
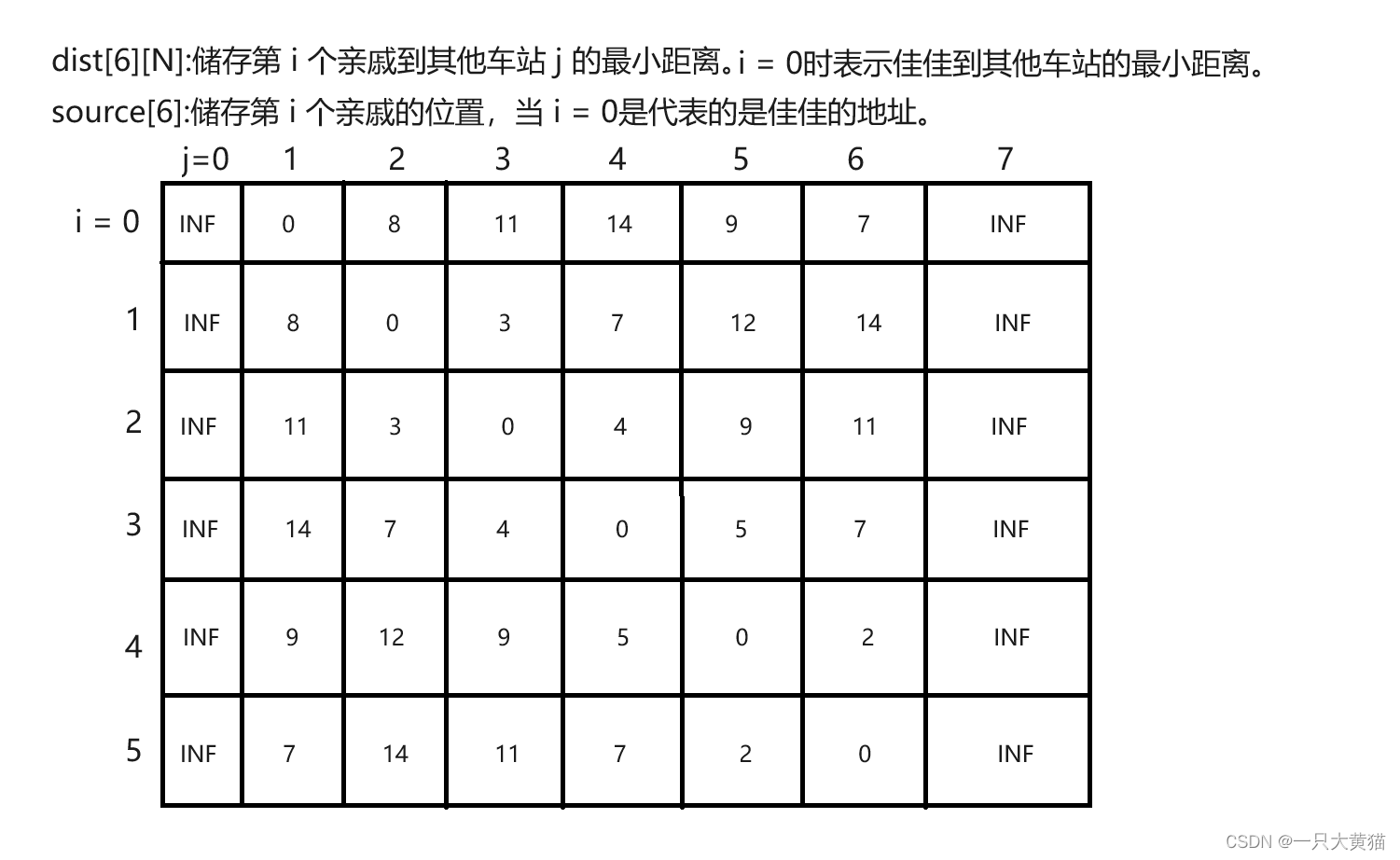
当我们得到佳佳与五个亲戚到其余点的最小距离之后,我们可以考虑使用深度搜索去搜索佳佳拜访五位亲戚的顺序,并保留这些顺序中的最小值。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50010,M = 200010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
int n,m;
int source[6];
int h[N],e[M],w[M],ne[M],idx;
int q[N],dist[6][N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx] = b,w[idx] = c,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx ++;
}
void spfa(int start,int dist[])
{
memset(dist,0x3f,N * 4);
dist[start] = 0;
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII>> heap;
heap.emplace(0,start);
while(!heap.empty())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int x = t.second;
for(int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[x] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[x] + w[i];
heap.emplace(dist[j],j);
}
}
}
}
int dfs(int u,int start,int distance)
{
if(u == 6) return distance;
int res = INF;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
if(!st[i])
{
int next = source[i];
st[i] = true;
res = min(res,dfs(u + 1,i,distance + dist[start][next]));
st[i] = false;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
source[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i<= 5; i ++) scanf("%d",&source[i]);
memset(h,-1,sizeof(h));
while(m --)
{
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
add(a,b,c),add(b,a,c);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i ++) spfa(source[i],dist[i]);
cout << dfs(1,0,0) << endl;
return 0;
}