目录
一、二叉搜索树的概念
二、二叉搜索树的结构
三、二叉搜索树的操作(非递归)
1.插入
2.查找
3.删除
4.遍历
四、二叉搜索树的操作(递归)
1.递归插入
2.递归查找
3.递归删除
4.递归遍历
五、二叉搜索树的默认成员函数
1.拷贝构造
2.赋值运算符重载
3.析构函数
4.默认构造函数
六、二叉搜索树的KV模型
一、二叉搜索树的概念
搜索二叉树结构上跟普通的二叉树一样,它要么是一棵空树,要么是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
如下图所示,这就是一颗二叉搜索树。我们可以发现这颗树的中序遍历就是有序的
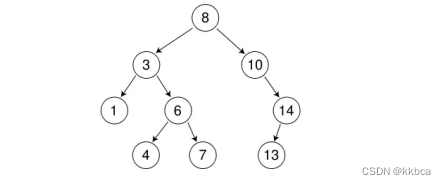
二、二叉搜索树的结构
首先我们肯定需要树节点,来帮助我们保持树的结构和存放数据。
如下代码我们就使用模板定义了树的结构,并添加了构造函数,方便我们创建结点
template<class T>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T>* _right;
T _key;
BSTreeNode(const T& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};二叉树的成员变量只有根结点
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
private:
Node* _root
}三、二叉搜索树的操作(非递归)
1.插入
我们定义了一个数组,现在要将这个数组的内容放到搜索二叉树里。
int a[] = {8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13};就会成为如下这棵树

依次插入0和16
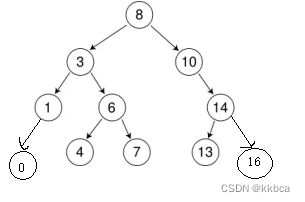
插入部分代码还算简单,首先就判断当前树是否为空,通过成员变量根结点来判断,根节点为空就直接new一个结点赋值给根结点返回true。
我们可以通过key值来比较往左走还是往右走,如果插入的key值比当前结点的值小,就往左走,如果比当前结点的值大,就往右走,如果相等,就证明你找到了结点,我们返回false,代表插入失败(二叉搜索树为了保持他的结构,是不能有相等的key的)。
- 目前我们已经找到了这个结点应该存放的位置,那么我们如何将他们链接起来呢?
这就需要一个父结点来帮助我们处理,让父结点一直跟随着当前结点走。直到找到应该存在的地方之后,再判断这个地方是父亲的左还是右(同样是用key来比较,key比父结点的值小,放在父结点的左边,大就放在父结点的右边,通过new一个结点来完成)最后返回true。
代码如下
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = new Node(key);
}
else
{
parent->_right = new Node(key);
}
return true;
}
2.查找
查找是插入的简洁版,依然用key来比较,找到了返回true,没找到就返回false
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}3.删除
删除部分是二叉搜索树较难的地方,因为我们得让这棵树删除之后依然保持原来的特性,也就是
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
因此我们得考虑很多种情况
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回, 否则要删除的结点可能分下面四种情 况:
a. 要删除的结点无孩子结点
b. 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
c. 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
d. 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
看起来有待删除节点有4中情况,实际情况a可以与情况b或者c合并起来,因此真正的删除过程 如下:
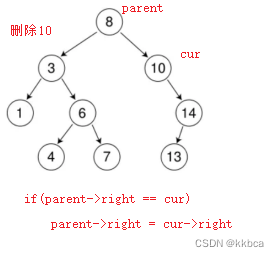
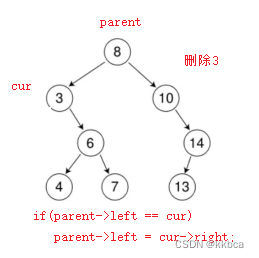
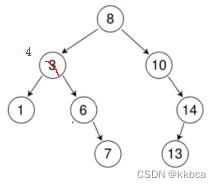
情况b:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点--直接删除
情况c:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点--直接删除
情况d:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点 中,再来处理该结点的删除问题--替换法删除
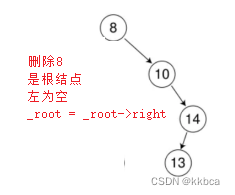
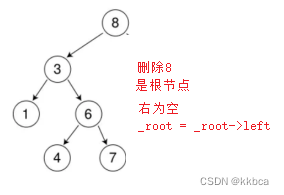
对于情况b和c,我们首先要判断找到的结点是否为根节点,如果是,根节点就会往相应方向走
左为空
右为空也是同理,我们就不多赘述了。
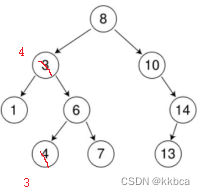
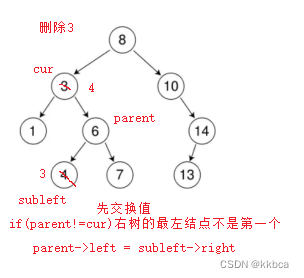
对于情况d我们使用替换法删除,比如删除4,我们可以拿4的右子树中的最小值(也就是3)和4交换,交换之后再去删除下面那个结点就行。这样也不会破坏数的结构,
当然你选择删除节点的左子树的最大值也是可行的
知道了先交换之后,我们也要分情况来看,判断右树的第一个节点是否为最左节点
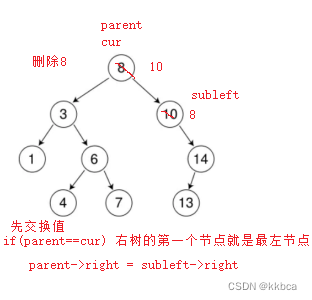
代码如下
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = _root;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//判断是否为根节点
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
//判断是父亲的左还是父亲的右
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
//判断是否为根节点
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
//判断是父亲的左还是父亲的右
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
parent = cur;
//定义右树的最左节点
Node* subleft = cur->_right;
//往最左走
while (subleft->_left)
{
parent = subleft;
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
//交换
swap(subleft->_key, cur->_key);
//右树第一个节点就是最左节点(没有进入循环)
if (parent == cur)
{
parent->_right = subleft->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = subleft->_right;
}
delete subleft;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}4.遍历
对于搜索二叉树,我们选择中序遍历,因为这样遍历出来的值是有序的。
这里我们先用非递归版本,递归版本在后面会写上。
使用stack来帮助我们操作,这里代码的重要点就是cur,对cur进行操作防止再次陷入循环。
循环着先往最左子树走,边走边入栈,走到为空就结束循环,当前取出的栈顶元素就是最左结点,先打印,再将 cur = top->_right;往top结点的右边走,如此循环,便能中序遍历。
代码真的很巧妙,不理解的可以画递归图来帮助理解。
void InOrder()
{
stack<Node*> s;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur || !s.empty())
{
while (cur)
{
s.push(cur);
cur = cur->_left;
}
Node* top = s.top();
s.pop();
cout << top->_key << " ";
cur = top->_right;
}
cout << endl;
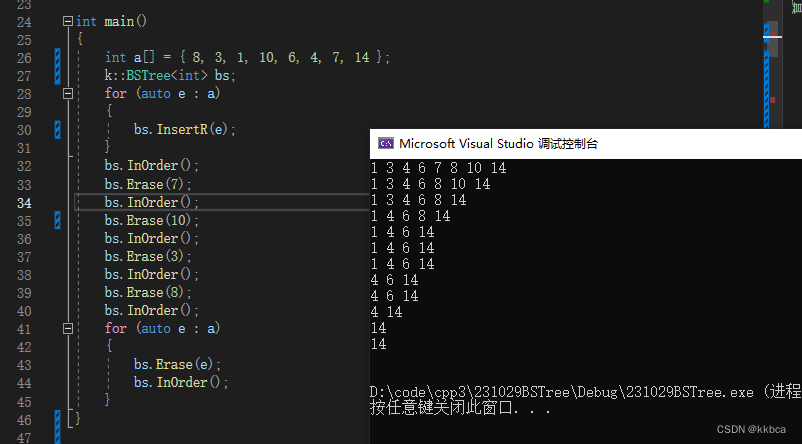
}我们测试一下,代码正常运行。
四、二叉搜索树的操作(递归)
1.递归插入
我们为了能够进行递归,需要再写一个函数,因为无法传入_root进行递归,这里我们将递归的函数用private修饰,防止类外调用。
代码逻辑跟普通的差不都,都是通过key来判断,key比当前结点的值大,就递归当前节点的右边,key比当前结点的值小,就递归当前节点的左边,相等就返回。
重要的点是我们无法找到父亲结点,因此可以选择引用传参,你给到的参数是root->left或者是 root->right,引用传参传递的就是root->left或者是root->right的别名,因此找到合适的位置可以直接 root = new Node(key);
public:
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}2.递归查找
依然是用两个函数,查找代码比插入更简单,不多赘述
public:
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root,key);
}
private:
bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if(root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}3.递归删除
删除也得使用引用,因为要让父亲结点指向空,因为传递的是别名,不需要让父亲跟随了,因此代码可以简洁不少,情况d(也就是左右都不为空),依然是用之前的交换,交换后再递归到右树去查找即可。
public:
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
return true;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* subleft = root->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
swap(subleft->_key, root->_key);
//到右子树再去递归删除
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
return false;
}4.递归遍历
更是小菜一碟,这是普通二叉树的操作,递归左,打印,递归右即可。
public:
void InOrderR()
{
_InOrderR(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrderR(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrderR(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrderR(root->_right);
}五、二叉搜索树的默认成员函数
1.拷贝构造
想要完成深拷贝,就需要将树的所有结点都拷贝一遍,这里用递归处理也是很方便的,因此我们定义了一个Copy函数,去进行先序遍历拷贝。
public:
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& bst)
{
_root = Copy(bst._root);
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = new Node(root->_key);
cur->_left = Copy(root->_left);
cur->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return cur;
}2.赋值运算符重载
这个很简单,不要传递 const 和 & 直接交换即可。
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> bst)
{
swap(bst._root, _root);
return *this;
}3.析构函数
调用后续递归函数进行析构
public:
~BSTree()
{
clear(_root);
}
private:
void clear(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
clear(root->_left);
clear(root->_right);
delete root;
}4.默认构造函数
因为我们重写了构造函数,因此编译器默认构造函数的就不提供了,我们随便写一份,这里使用了C++11的新特性,default代表默认生成
BSTree() = default;到目前为止,我们的二叉搜索树就算完成了,以下是代码
namespace k
{
template<class T>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T>* _right;
T _key;
BSTreeNode(const T& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& bst)
{
_root = Copy(bst._root);
}
~BSTree()
{
clear(_root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> bst)
{
swap(bst._root, _root);
return *this;
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = new Node(key);
}
else
{
parent->_right = new Node(key);
}
return true;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = _root;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//判断是否为根节点
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
//判断是父亲的左还是父亲的右
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
//判断是否为根节点
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
//判断是父亲的左还是父亲的右
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
parent = cur;
//定义右树的最左节点
Node* subleft = cur->_right;
//往最左走
while (subleft->_left)
{
parent = subleft;
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
//交换
swap(subleft->_key, cur->_key);
//右树第一个节点就是最左节点(没有进入循环)
if (parent == cur)
{
parent->_right = subleft->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = subleft->_right;
}
delete subleft;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
stack<Node*> s;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur||!s.empty())
{
while (cur)
{
s.push(cur);
cur = cur->_left;
}
Node* top = s.top();
s.pop();
cout << top->_key << " ";
cur = top->_right;
}
cout << endl;
}
void InOrderR()
{
_InOrderR(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root,key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
void clear(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
clear(root->_left);
clear(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = new Node(root->_key);
cur->_left = Copy(root->_left);
cur->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return cur;
}
void _InOrderR(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrderR(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrderR(root->_right);
}
bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if(root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
return true;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* subleft = root->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
swap(subleft->_key, root->_key);
//到右子树再去递归删除
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
return false;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}六、二叉搜索树的KV模型
二叉搜索树不仅仅有K模型,还有KV模型,我们只需要给结点多添加上一个value即可
template<class T, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _right;
T _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const T& key,const V&value)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
,_value(value)
{}
};代码逻辑部分都是没问题的,只有少部分地方需要略做修改,大家直接看代码吧
namespace kv
{
template<class T, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _right;
T _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const T& key,const V&value)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
,_value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key,const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = new Node(key,value);
}
else
{
parent->_right = new Node(key, value);
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = _root;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
parent = cur;
Node* subleft = cur->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
parent = subleft;
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
swap(subleft->_key, cur->_key);
if (parent == cur)
{
parent->_right = subleft->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = subleft->_right;
}
delete subleft;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key,const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key,value);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " " << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return root;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key,const V& value)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key,value);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
return true;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* subleft = root->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
swap(subleft->_key, root->_key);
//到右子树再去递归删除
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
return false;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}KV模型测试
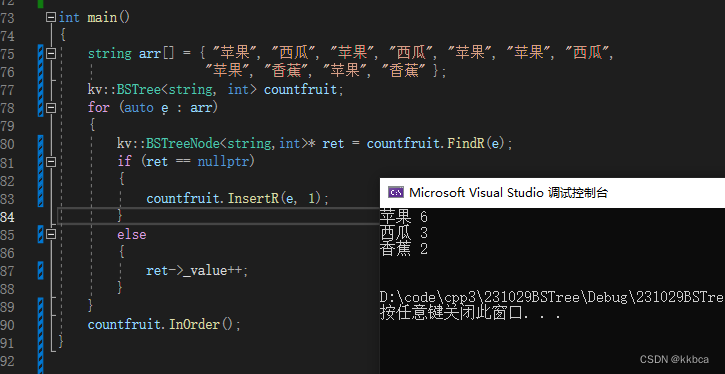
如此一来我们就算大功告成了。
谢谢大家观看!!!