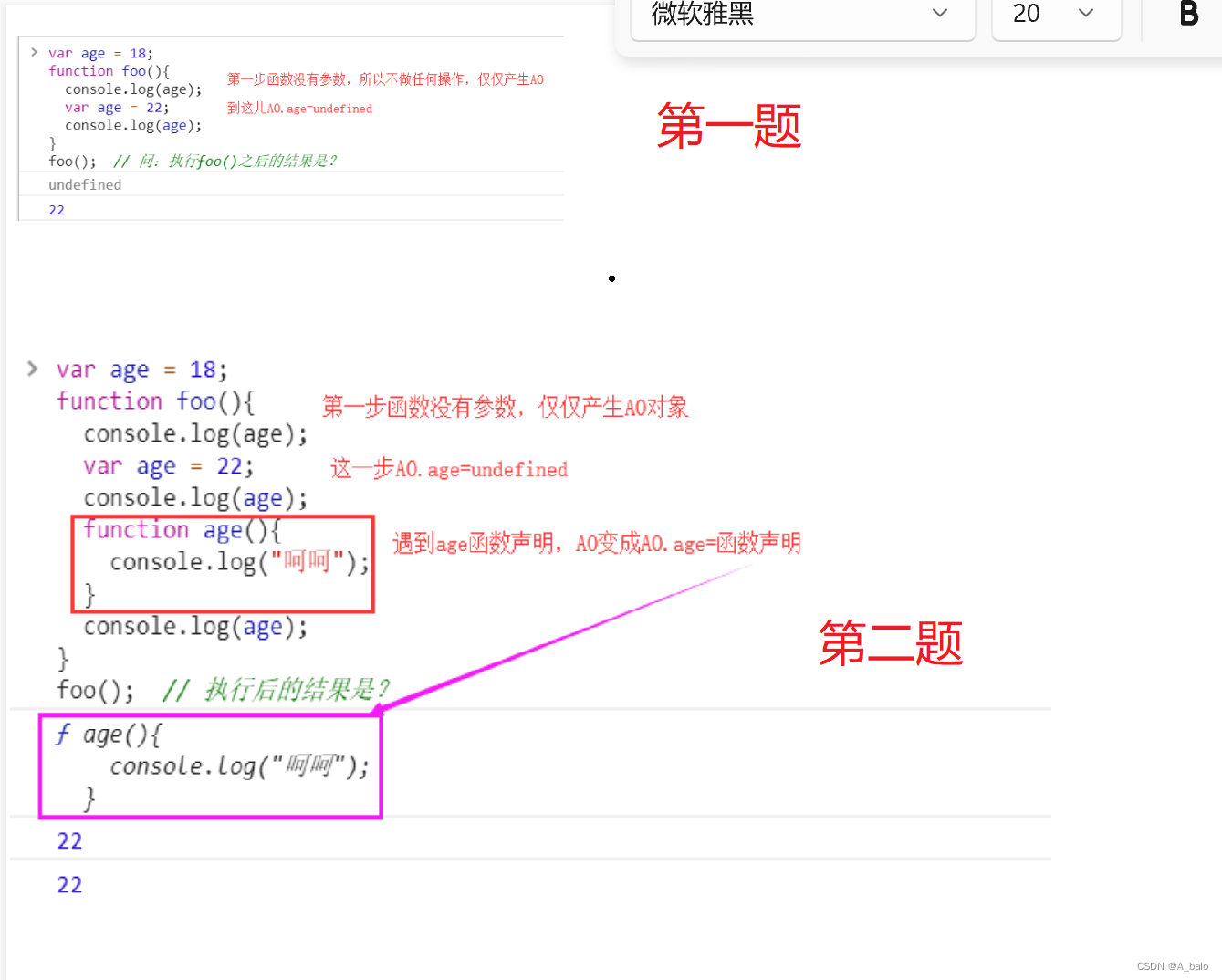
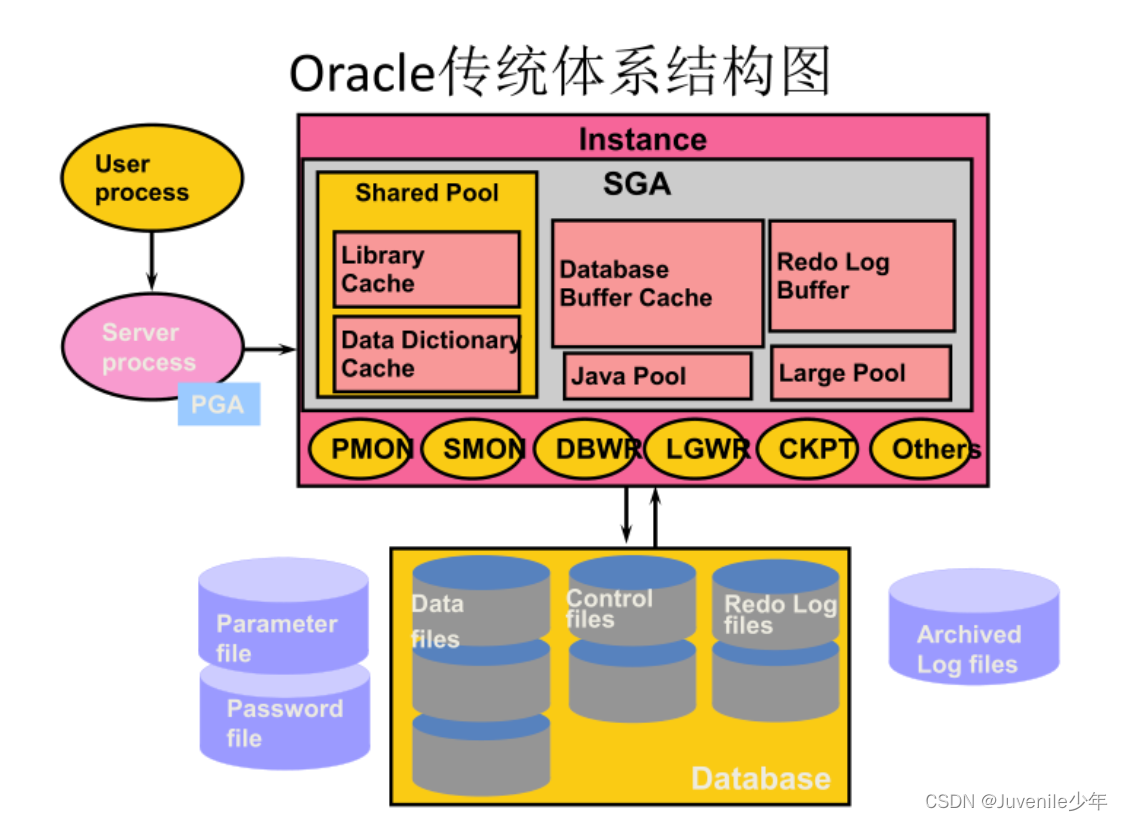
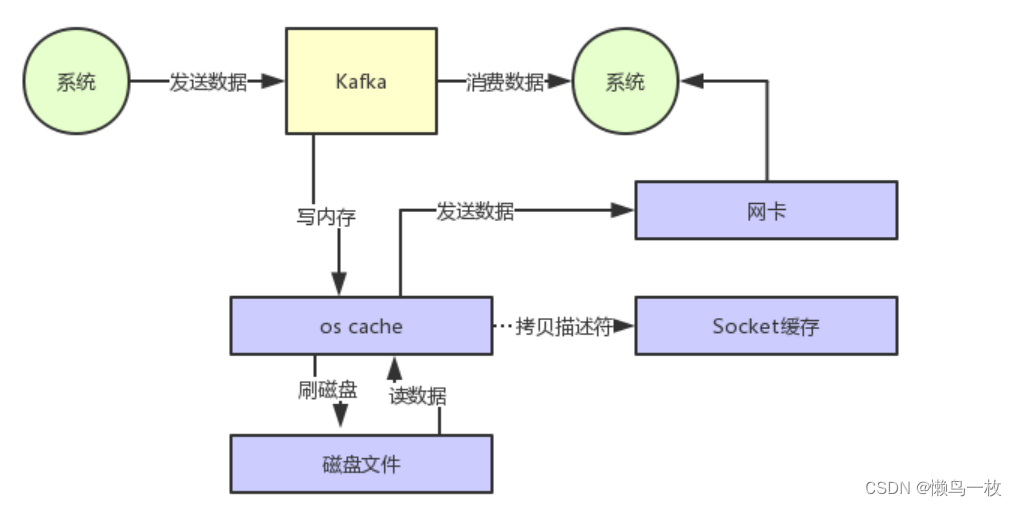
进程是由CPU给分配的执行单元,比较消耗空间和内存

创建、使用线程
import threading
# 进程
# 线程
from time import sleep
def download():
list1 = ["girl.png", "boy.png", "child.png"]
for l in list1:
print(l)
sleep(1.5)
print("下载{}成功!".format(l), end='\n')
def listen():
list1 = ["爱情买卖", "大风吹", "小米"]
for l in list1:
print("正在听{}成功!".format(l), end='\n')
sleep(1.5)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = threading.Thread(target=download)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=listen)
t1.start()
t2.start()
n = 1
while True:
if n == 100:
break
sleep(1.5)
print(n)
n += 1
线程的状态

线程共享全局变量
import threading
from multiprocessing import Process
from time import sleep
money = 1000
def run1():
global money
for i in range(100):
money -= 1
def run2():
global money
for i in range(100):
money -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
p1 = threading.Thread(target=run1)
p2 = threading.Thread(target=run2)
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join()
p2.join()
print(money)
线程同步(加锁/lock/rlock/GIL)
python解释器会在创建线程的时候默认加锁(GIL全局解释器锁)
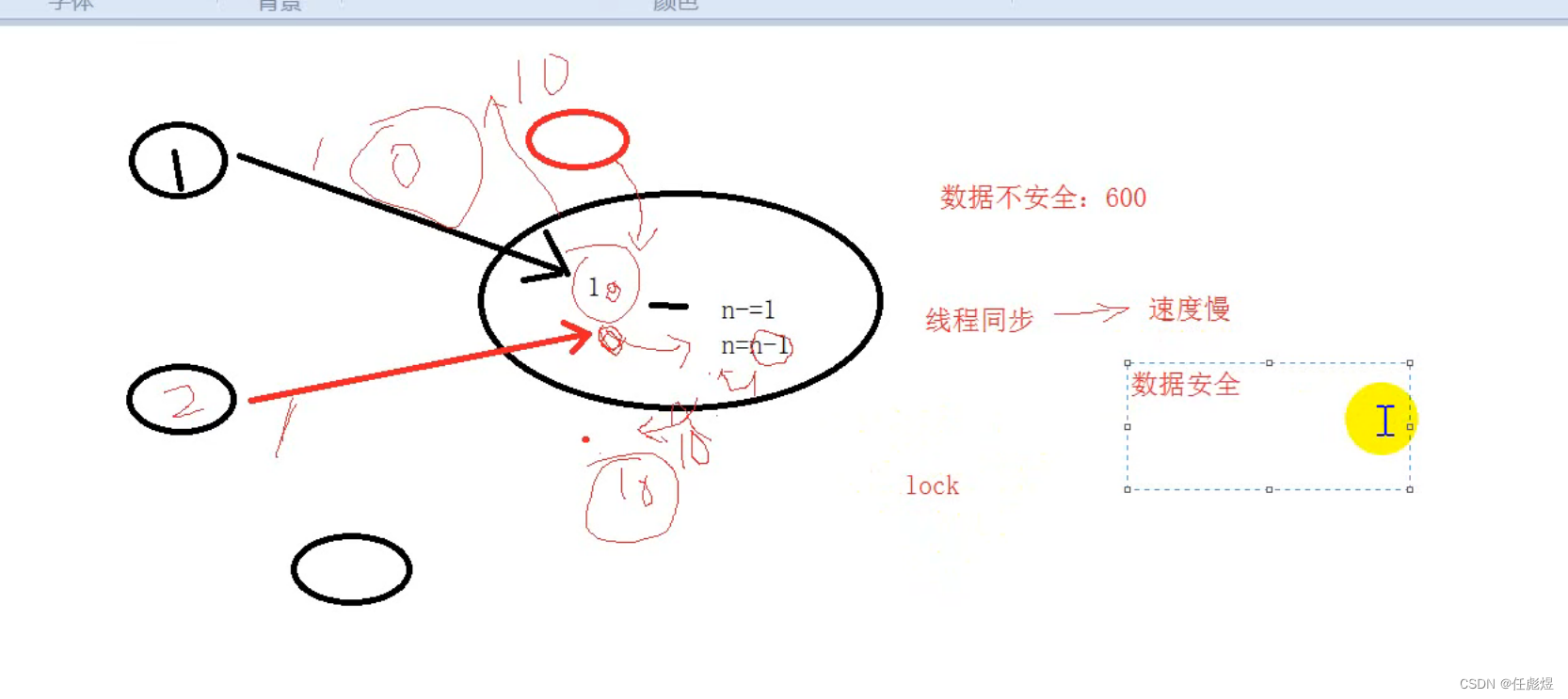
import threading
import random
import time
lock = threading.Lock()
list1 = [0] * 10
def task1():
lock.acquire()
for i in range(len(list1)):
list1[i] = i
time.sleep(0.5)
lock.release()
def task2():
lock.acquire()
for i in range(len(list1)):
print(list1[i])
time.sleep(0.5)
lock.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = threading.Thread(target=task1)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=task2)
t2.start()
t1.start()
print("over~~~~~")
t1.join()
t2.join()
print(list1)
死锁
import threading
import random
import time
lock1 = threading.Lock()
lock2 = threading.Lock()
def task1():
print("任务一")
if lock1.acquire():
print("Lock1--->任务1")
time.sleep(2.5)
if lock2.acquire(timeout=2):
print("Lock2--->任务1")
time.sleep(2.5)
lock1.release()
def task2():
print("任务二")
if lock2.acquire():
print("Lock2--->任务2")
time.sleep(2.5)
if lock1.acquire(timeout=2):
print("Lock1--->任务2")
time.sleep(2.5)
lock2.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = threading.Thread(target=task1)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=task2)
t2.start()
t1.start()