文章目录
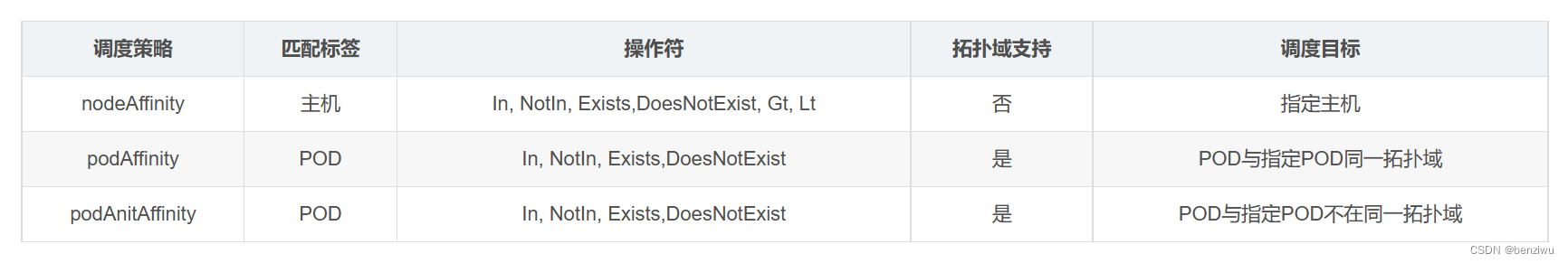
- 1.Environment作用
- 2.用法
- 2.1 systemEnvironment 和 systemProperties
- 2.2 MutablePropertySources
- 3.实际用法
- 4.总结
1.Environment作用
Environment:获取环境变量
2.用法
2.1 systemEnvironment 和 systemProperties
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//操作系统层面的环境变量
Map<String, Object> systemEnvironment = context.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment();
System.out.println(systemEnvironment);
System.out.println("==========Environment==========");
//java运行层面,通过-D指定的
Map<String, Object> systemProperties = context.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties();
System.out.println(systemProperties );
System.out.println("=========Properties===========");
}
getSystemProperties获取的是java运行层面,通过-D指定的变量:
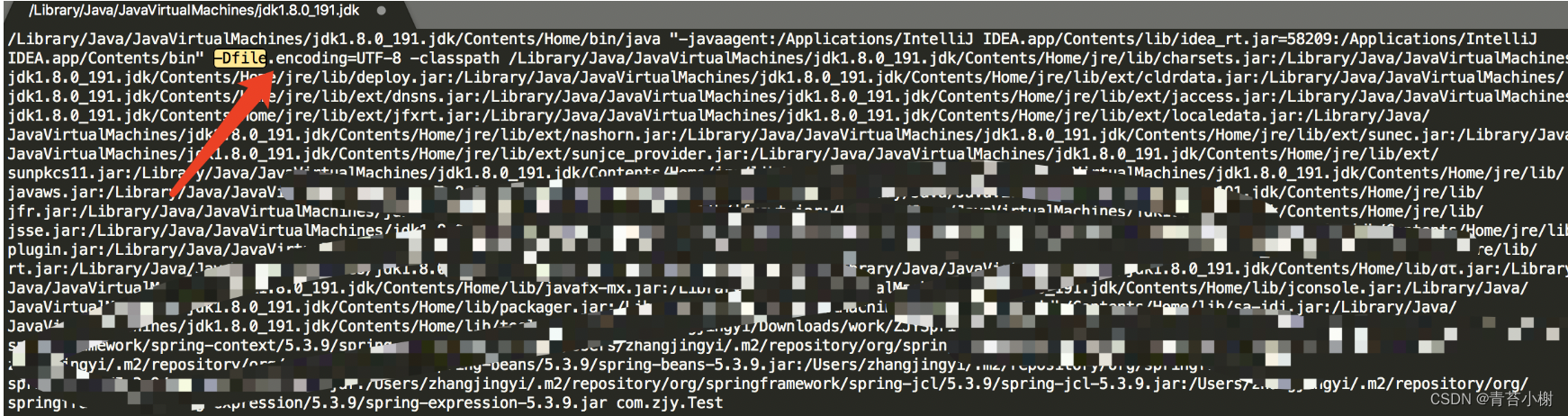
我们运行打印之后,如图,把第一行的数据复制出来放到其他文件里
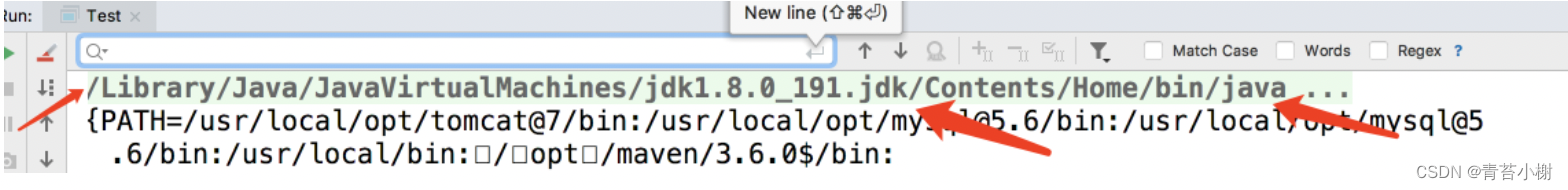
搜索 Dfile , 可以看到定义的UTF-8 编码格式
再看
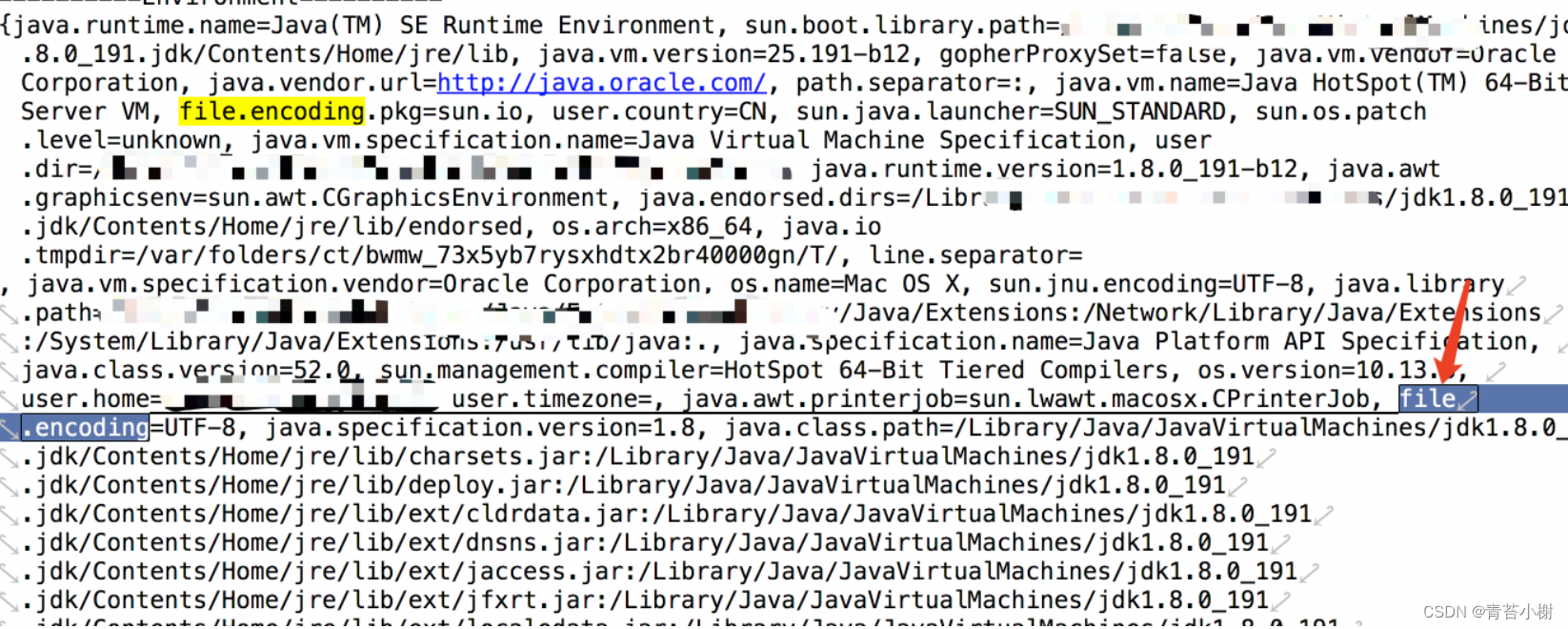
Map<String, Object> systemProperties = context.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties();
打印出的数据,如图红箭头处可以找到指定的 UTF-8
2.2 MutablePropertySources
MutablePropertySources sources = context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
System.out.println(sources);
System.out.println("=========MutablePropertySources===========");
打印结果:
[PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'}, SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}, ResourcePropertySource {name='class path resource [spring.properties]'}]
MutablePropertySources 包括了systemProperties 和systemEnvironment 和配置文件,是最强大的,但一般并不会这样用。
3.实际用法
//操作系统层面
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("JAVA_HOME"));
//指定环境变量
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("sun.jnu.encoding"));
//配置文件
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("zjy"));
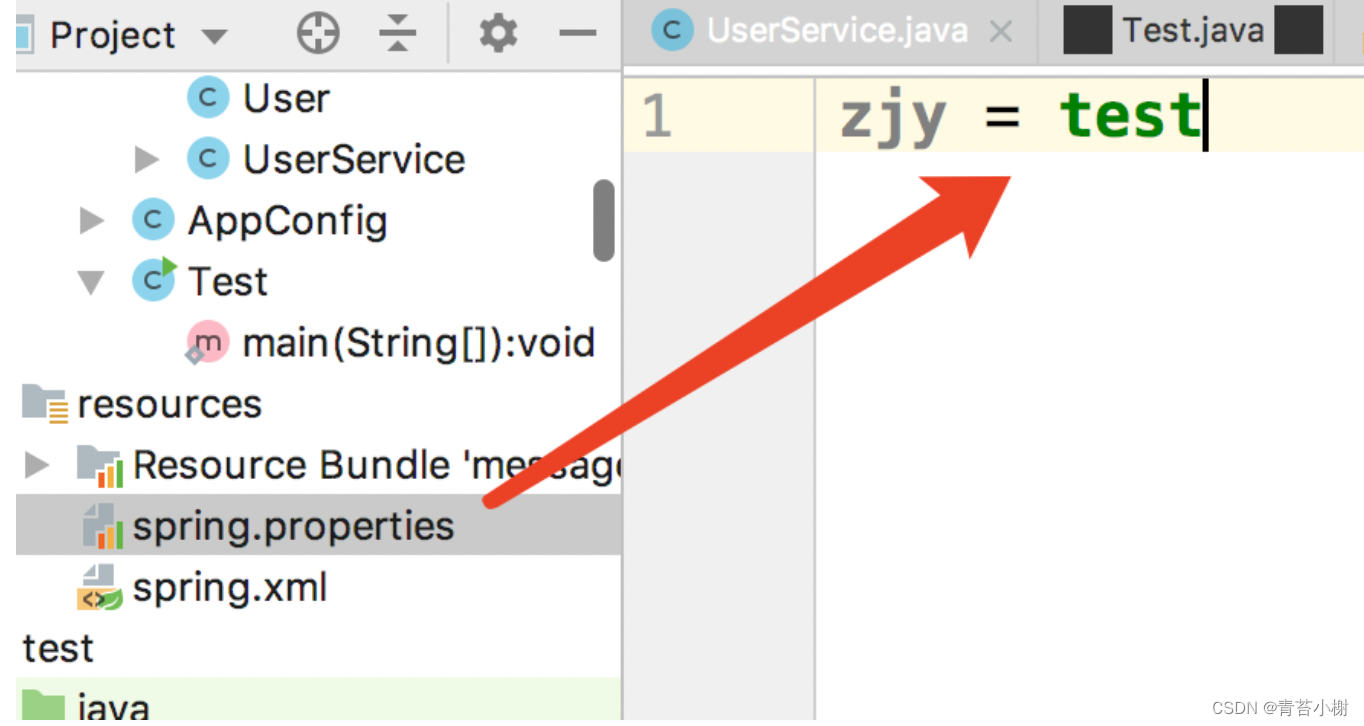
(spring.properties文件配置如下)
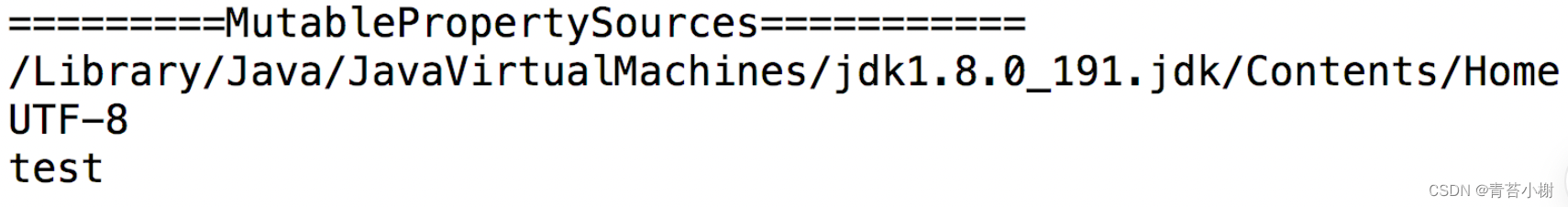
打印结果:
4.总结
好记性不如烂笔头,知道不如做到。




![[ 代码审计篇 ] 代码审计案例详解(一) SQL注入代码审计案例](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3890237a1d4040bc8b83fd4879b1be28.png)