目录
输入流和输出流
File文件增删
常用IO流类及其分类
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream
BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream
FileReader/FileWriter
BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
InputStreamReader/InputStreamWriter
Properties读取配置文件
输入流和输出流
在学习IO编程之前,需要先清楚输入流和输出流之间的关系:输入流和输出流是相对于程序来讲的,如下图所示:
File文件增删
File新建文件构建文件对象有三种常用方式:
- public File(String filePath)
- public File(File parent,String child)
- public File(String parent,String child)
任选其中一种在指定的路径下通过createNewFile方法创建文件,通过mkDir(创建单层目录)、mkDirs(创建多层目录)创建目录:@Test public void createFile() throws IOException { String filePath = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\hello.txt"; String filePathOfDir = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\helloDir"; File file = new File(filePath); File fileDir = new File(filePathOfDir); try { if(file.createNewFile()) { //返回值boolean类型 System.out.println("创建成功"); } else { System.out.println("创建失败"); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (fileDir.mkdir()) { System.out.println("目录创建成功"); } else { System.out.println("目录创建失败"); } }
Delete删除空目录或者文件
删除上面创建的文件以及目录:
@Test
public void deleteFile() {
String filePath = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\hello.txt";
String pathOfDir = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\helloDir";
File file = new File(filePath);
File fileDir = new File(pathOfDir);
if(file.delete()) { //删除文件
System.out.println(file.getName() + "文件删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(file.getName() + "文件删除失败");
}
if(fileDir.delete()) { //删除目录
System.out.println(fileDir.getName() + "目录删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(fileDir.getName() + "目录删除失败");
}
}常用IO流类及其分类
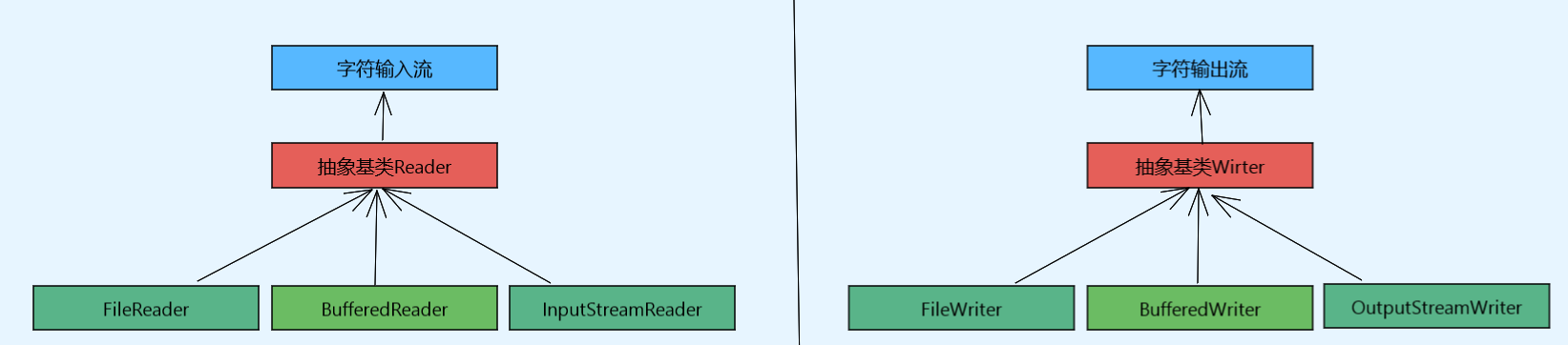
在Java程序中,输入流和输出流分为字节输入/输出流以及字符输入/输出流。字节输入输出流以InputStream和OutputStream作为其抽象基类;字符输入输出流以Reader和Writer作为其抽象基类。常见的IO流类及其继承关系如下:
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
使用字节输入流FileInputStream读取文件
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public void readFile() {
String filePath = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
/*使用read一次读取单个字节
try {
int byte_ = 0;
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while ((byte_ = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) byte_);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}*/
//使用字节数组方式一次读取byte.length个字节
try {
byte[] byte_ = new byte[4];
int readLength = 0;
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while ((readLength = fileInputStream.read(byte_)) != -1) { //read(byte)返回读取到的字节个数
System.out.println(new String(byte_, 0, readLength));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}使用字节输出流FileOutputStream写文件
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 使用FileOutputStream写文件
* 创建FileOutputStream时,如果没有这个文件会自动创建,如果有且append属性为false时会清空该文件
* 在写入文件后没有关闭继续写时,会继续将内容追加文件末尾
*/
@Test
public void writeFile() {
String filePath = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\hello.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, false);//true代表再次写入数据时追加原数据
// fileOutputStream.write('ad');//向hello.txt中写入单个字节
String str = "hello,world";
//getBytes将字符转换成一个字节数组
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
System.out.println("写入成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}应用:拷贝文件
/**
* 使用输入输出流完成文件的拷贝,在读/写文件时使用字节数组提高读取和写入效率
*/
@Test
public void copy() {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\Copy.txt");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\copyFinish.txt");
int temp = 0;
int readLength = 0;
//创建字符数组,提高文件的读取效率
byte[] byte_ = new byte[1024];
while ((readLength = fileInputStream.read(byte_)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(byte_, 0, readLength);
}
System.out.println("复制完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if(fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream
与FileReader和FileWriter类似,对象输入/输出流ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream也为处理流。用于保存数据的类型和值,并且能够按照特定的序列恢复出元数据类型和值。
序列化和反序列化:
- 序列化是指在保存数据时,保存数据的值和数据类型
- 反序列化是指在恢复数据时,恢复数据的值和数据类型
使用对象输入输出流进行文件的读写:
//Dog类
package objectstream;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Dog类实现了Serializable接口,表明其可以被序列化
*/
public class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;//String类默认实现了Serializable接口
private int age;
public Dog(String name,int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + this.name + " " + this.age +"]";
}
}
//ObjectOutputStream_类
public class ObjectOutputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\IOStream\\objectStream\\object.dat"));
//序列化对应的数据时,要求该数据的数据类型是可序列化的,即实现了Serializable或Externalizable接口
oos.writeInt(7);
oos.writeUTF("hello");
oos.writeObject(new Dog("小黑",7));
System.out.println("序列化完成(文件写入完成)");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (oos != null) {
try { //序列化结束后关闭流
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
//ObjectInputStream_类
import java.io.*;
public class ObjectInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\IOStream\\objectStream\\object.dat"));
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (ois != null) { //结束后记得关闭流
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}对象输入输出流使用的注意事项:
- 序列化的文件是以(.dat)的方式进行存储的
- 数据的序列化和反序列化的顺序要一致,否则会抛出java.io.OptionalDataException异常
- 序列化或者反序列化的对象,都需要实现Serializable或者Externalizable接口
- 序列化的类中建议添加SerialVersionUID,提高版本的兼容性
- 序列化类中的成员属性时,除了static和transient修饰的属性,其他属性都会被序列化
- 序列化自定义对象在取出时,如果要调用自定义对象中的自定义方法,需要进行向下转型并且确保自定义对象是能够被访问的
BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream
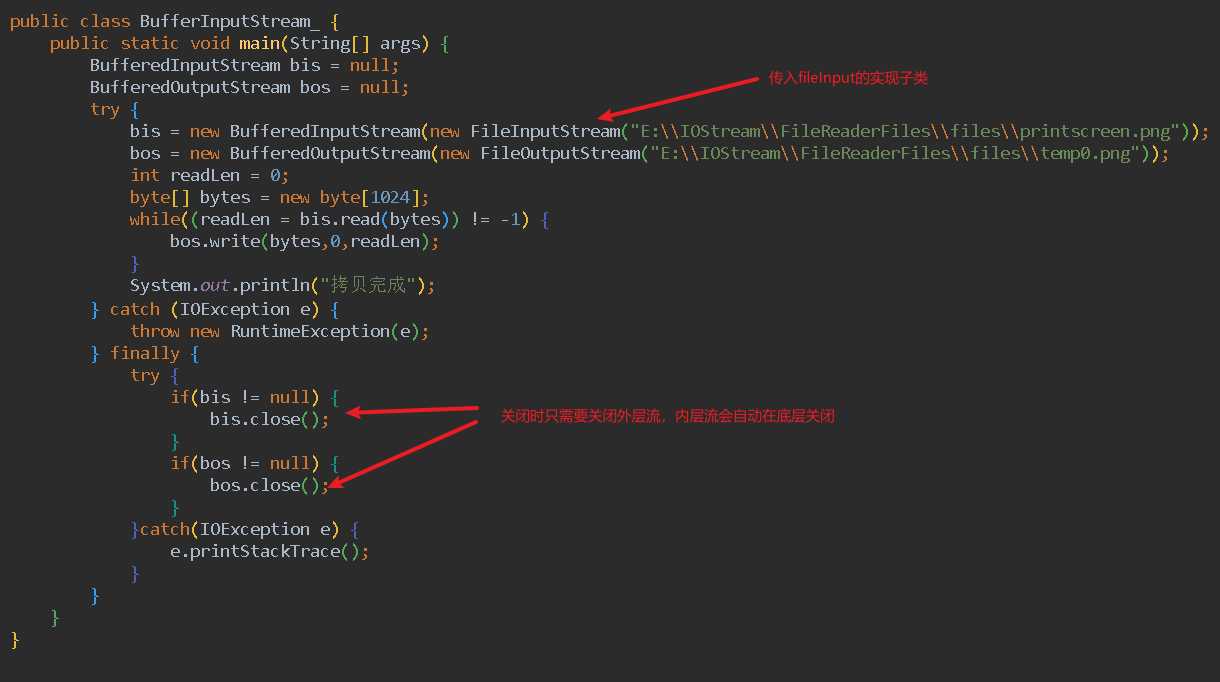
注意事项:
使用BufferedOutputStream处理流进行文件内容的输出结束后,应当关闭文件,否则内容不能在写入成功。
FileReader/FileWriter
使用字符输入流FileReader读取文件:
import java.io.fileReader;
public class BufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\temp.txt");
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while((readLen = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(chars,0,readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}使用字符输出流FileWriter写文件:
- 注意事项:
使用FileWriter进行文件的写入时,只有在写入完成后关闭文件才能成功将内容写入。当在创建FileWriter对象时,如果不指定append属性为false,那么当文件打开进行写入时将以覆写的方式覆盖原文件的数据。
import org.juint.jupiter.api.test;
@Test
public void writeFile() {
FileWriter fileWrtier = null;
String path = "E:\\IOStream\\FileInputStreamFiles\\temp.txt";
try {
fileWrtier = new FileWriter(path);
fileWrtier.write("你好,川藏318");
//fileWrtier.write(int c);
//fileWrtier.write(str,start,end);
//fileWrtier.write(char[] chars,start,end);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileWrtier.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
节点流和处理流:
- 节点流可以从一个特定的数据源进行数据的读取,如FileReader,FIleWriter
- 处理流也成包装流,连接已存在的流之上,为程序提供更为强大的读写功能吗,如BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter处理流进行文件的写入:
- 注意事项:
使用BufferedReader进行文件的写入时,只有在写入完成后关闭文件才能成功将内容写入。当在创建BufferedReader对象时,如果不指定append属性为false,那么当文件打开进行写入时将以覆写的方式覆盖原文件的数据。
使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter进行文件的拷贝时,避免拷贝二进制文件(声音,图像,视频,word,pdf),拷贝结束打开时会发生异常。
public class BufferedWriter__ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
//设置append属性:在传入BufferedWriter对象中封装的Writer对象中指定
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\\IOStream\\FileReaderFiles\\files\\temp.java",true));
bufferedWriter.write("hello");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行
if(bufferedWriter != null) {
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
}InputStreamReader/InputStreamWriter
InputStreamReader和InputStreamWriter又称为转换流,能够将字节处理流转换为字符处理流并且指定特定的编码格式。
引出:使用字节处理流读取gbk编码文件出现中文乱码,为了解决这种问题,可以使用InputStreamReader将对应的字节处理流包装成字符处理流,并且指定特定的编码格式在进行读取。
public class BufferedReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("E:\\java代码\\IO_Stream_21\\io\\read.txt"),"GBK"));//在进行转换时指定待读取文件的编码格式,防止出现乱码问题
String str = null;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}public class OutputStreamWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("E:\\java代码\\IO_Stream_21\\io\\read.txt",true),"gbk");//指定的编码格式进行内容的写入
osw.write(" hello世界 ");
System.out.println("文件写入成功");
osw.close();
}
}注意事项:
转换流InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter可以解决乱码问题,但在使用时应当注意编码格式的对应。
Properties读取配置文件
后缀.properties的文件通常作为Java的配置文件,文件内的数据格式以键值对的方式进行存放。使用properties配置文件提高了程序的灵活性。
使用Properties操作文件的相关操作:
public class Properties_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("username"));
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("ip"));
System.out.println(pro.get("username"));
pro.setProperty("active", "good");
pro.setProperty("state", "stable");
pro.setProperty("active", "silence");
pro.setProperty("uio", "玛利亚");
pro.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql.properties"), "good");
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("uio"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
注意事项:
在idea中保存信息到配置文件,如果信息含有中文,会存储为对应的unicode编码。


![[Python图像识别] 五十一.水书图像识别之利用数据增强扩充图像数据集](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/22b1dae5ef244d4f9ff86a826cf69ff2.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBARWFzdG1vdW50,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16#pic_center)