目录
一、前言
二、另一种下载数据集方式
三、MNIST的Pytorch源码
四、MNIST的Libtorch源码
一、前言
前面介绍过了MNIST的python的训练代码、和基于torchscript的模型序列化(导出模型)。今天看看,如何使用libtorch C++来实现手写数字训练。
二、另一种下载数据集方式
同时,我已经说过了,对你MNIST数据集该如何下载。有关数据集的下载,这种不重要的问题卡了很久,简直浪费时间,差评。这里再介绍一种下载方式,在官方仓库中,有个脚本可以直接下载https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/main/cpp/tools/download_mnist.py,直接在命令行窗口执行就可以下载,如下,可能网络会很卡,不过下载好了。
这里直接把download_mnist.py源码贴出来吧:
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import gzip
import os
import sys
import urllib
try:
from urllib.error import URLError
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
except ImportError:
from urllib2 import URLError
from urllib import urlretrieve
RESOURCES = [
'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
]
def report_download_progress(chunk_number, chunk_size, file_size):
if file_size != -1:
percent = min(1, (chunk_number * chunk_size) / file_size)
bar = '#' * int(64 * percent)
sys.stdout.write('\r0% |{:<64}| {}%'.format(bar, int(percent * 100)))
def download(destination_path, url, quiet):
if os.path.exists(destination_path):
if not quiet:
print('{} already exists, skipping ...'.format(destination_path))
else:
print('Downloading {} ...'.format(url))
try:
hook = None if quiet else report_download_progress
urlretrieve(url, destination_path, reporthook=hook)
except URLError:
raise RuntimeError('Error downloading resource!')
finally:
if not quiet:
# Just a newline.
print()
def unzip(zipped_path, quiet):
unzipped_path = os.path.splitext(zipped_path)[0]
if os.path.exists(unzipped_path):
if not quiet:
print('{} already exists, skipping ... '.format(unzipped_path))
return
with gzip.open(zipped_path, 'rb') as zipped_file:
with open(unzipped_path, 'wb') as unzipped_file:
unzipped_file.write(zipped_file.read())
if not quiet:
print('Unzipped {} ...'.format(zipped_path))
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Download the MNIST dataset from the internet')
parser.add_argument(
'-d', '--destination', default='.', help='Destination directory')
parser.add_argument(
'-q',
'--quiet',
action='store_true',
help="Don't report about progress")
options = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.exists(options.destination):
os.makedirs(options.destination)
try:
for resource in RESOURCES:
path = os.path.join(options.destination, resource)
url = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/{}'.format(resource)
download(path, url, options.quiet)
unzip(path, options.quiet)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('Interrupted')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()执行下载过程中,可能会很卡,下载信息如下:
(base) C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\examples-master_2\examples-master\cpp\tools>python download_mnist.py
.\train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz already exists, skipping ...
.\train-images-idx3-ubyte already exists, skipping ...
.\train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz already exists, skipping ...
.\train-labels-idx1-ubyte already exists, skipping ...
.\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz already exists, skipping ...
.\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte already exists, skipping ...
.\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz already exists, skipping ...
.\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte already exists, skipping ... python代码训练5个epoch结果。
Test set: Average loss: 0.0287, Accuracy: 9907/10000 (99%)三、MNIST的Pytorch源码
MNIST 的python源码:
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # self指的是类实例对象本身(注意:不是类本身)。
# self不是关键词
# super 用于继承,https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-super.html
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# input:28*28
x = self.conv1(x) # -> (28 - 3 + 1 = 26),26*26*32
x = F.relu(x)
# input:26*26*32
x = self.conv2(x) # -> (26 - 3 + 1 = 24),24*24*64
# input:24*24*64
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)# -> 12*12*64 = 9216
x = self.dropout1(x) #不改变维度
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # 9216*1
# w = 128*9216
x = self.fc1(x) # -> 128*1
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
# w = 10*128
x = self.fc2(x) # -> 10*1
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) # softmax归一化
return output
def train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
# 在使用pytorch构建神经网络的时候,训练过程中会在程序上方添加一句model.train(),
# 作用是启用batch normalization和drop out。
# 测试过程中会使用model.eval(),这时神经网络会沿用batch normalization的值,并不使用drop out。
model.train()
# 可以查看下卷积核的参数尺寸
#model.conv1.weight.shape torch.Size([32, 1, 3, 3]
#model.conv2.weight.shape torch.Size([64, 32, 3, 3])
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
# train_loader.dataset.data.shape
# Out[9]: torch.Size([60000, 28, 28])
# batch_size:64
# data:64个样本输入,torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
# target: 64个label,torch.Size([64])
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# output:torch.Size([64, 10])
output = model(data)
# 类似于交叉熵
# reference: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22210253/article/details/85229988
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 我们打印一个卷积核参数看看
# print(model.conv2._parameters)
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
if args.dry_run:
break
def test(model, device, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
def main():
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Example')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=5, metavar='N',
help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.7, metavar='M',
help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.7)')
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables CUDA training')
parser.add_argument('--dry-run', action='store_true', default=False,
help='quickly check a single pass')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
help='random seed (default: 1)')
parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=True,
help='For Saving the current Model')
args = parser.parse_args()
use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
train_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.batch_size}
test_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.test_batch_size}
if use_cuda:
cuda_kwargs = {'num_workers': 1,
'pin_memory': True, # 锁页内存,可以加快内存到显存的速度
'shuffle': True}
train_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
test_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
# torchvision.transforms是pytorch中的图像预处理包。一般用Compose把多个步骤整合到一起
#
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(), # (H x W x C)、[0, 255] -> (C x H x W)、[0.0, 1.0]
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # 数据的归一化
])
dataset1 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transform)
dataset2 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=False,
transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset1,**train_kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset2, **test_kwargs)
model = Net().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adadelta(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
# 固定步长衰减
# reference: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/93624972
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=args.gamma)
for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test(model, device, test_loader)
scheduler.step()
if args.save_model:
#torch.save(model.state_dict(), "pytorch_mnist.pt")
torch.save(model, "pytorch_mnist.pth")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()四、MNIST的Libtorch源码
以下是C++代码(官方的C++代码的网络结果似乎和python代码不能完全对应上,所以我作了修改,其实就是改了网络模型,请看struct Net : torch::nn::Module):可以对一下struct Net : torch::nn::Module和上述python代码中的 class Net(nn.Module):
#include<torch/torch.h>
#include<cstddef>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
// 继承自Module模块
struct Net : torch::nn::Module
{
// 构造函数
Net() :
conv1(torch::nn::Conv2dOptions(1, 32, 3)), // kernel_size = 5
conv2(torch::nn::Conv2dOptions(32, 64, 3)),
fc1(9216, 128),
fc2(128, 10)
{
register_module("conv1", conv1);
register_module("conv2", conv2);
register_module("conv2_drop", conv2_drop);
register_module("fc1", fc1);
register_module("fc2", fc2);
}
// 成员函数:前向传播
torch::Tensor forward(torch::Tensor x)
{
// input:1*28*28
x = torch::relu(conv1->forward(x)); //conv1:(28 - 3 + 1 = 26), 26*26*32
// input:26*26*32
x = torch::max_pool2d(torch::relu(conv2->forward(x)), 2);//conv2:(26 - 3 + 1 = 24),24*24*64; max_poolded:12*12*64 = 9216
x = torch::dropout(x, 0.25, is_training());
x = x.view({ -1, 9216 });// 9216*1
// w:128*9216
x = torch::relu(fc1->forward(x)); //fc1:w = 128*9216,w * x ->128*1
x = torch::dropout(x, 0.5, is_training());
// w:10*128
x = fc2->forward(x);//fc2:w = 10*128,w * x -> 10*1
x = torch::log_softmax(x, 1);
return x;
}
// 模块成员
torch::nn::Conv2d conv1;
torch::nn::Conv2d conv2;
torch::nn::Dropout2d conv2_drop;
torch::nn::Linear fc1;
torch::nn::Linear fc2;
};
//train
template<typename DataLoader>
void train(size_t epoch, Net& model, torch::Device device, DataLoader& data_loader, torch::optim::Optimizer& optimizer, size_t dataset_size)
{
//set "train" mode
model.train();
size_t batch_idx = 0;
for (auto& batch: data_loader)
{
auto data = batch.data.to(device);
auto targets = batch.target.to(device);
optimizer.zero_grad();
auto output = model.forward(data);
auto loss = torch::nll_loss(output, targets);
AT_ASSERT(!std::isnan(loss.template item<float>()));
loss.backward();
optimizer.step();
// 每10个batch_size打印一次loss
if (batch_idx++ % 10 == 0)
{
std::printf("\rTrain Epoch: %ld [%5ld/%5ld] Loss: %.4f",
epoch,
batch_idx * batch.data.size(0),
dataset_size,
loss.template item<float>());
}
}
}
template<typename DataLoader>
void test(Net& model, torch::Device device, DataLoader& data_loader, size_t dataset_size)
{
torch::NoGradGuard no_grad;
// set "test" mode
model.eval();
double test_loss = 0;
int32_t correct = 0;
for (const auto& batch: data_loader)
{
auto data = batch.data.to(device);
auto targets = batch.target.to(device);
auto output = model.forward(data);
test_loss += torch::nll_loss(output, targets, /*weight=*/{}, torch::Reduction::Sum).template item<float>();
auto pred = output.argmax(1);
// eq = equal 判断prediction 是否等于label
correct += pred.eq(targets).sum().template item<int64_t>();
}
test_loss /= dataset_size;
std::printf(
"\nTest set: Average loss: %.4f | Accuracy: %.3f\n",
test_loss,
static_cast<double>(correct) / dataset_size);
}
int main()
{
torch::manual_seed(1);
torch::DeviceType device_type;
if (torch::cuda::is_available())
{
std::cout << "CUDA available! Training on GPU." << std::endl;
device_type = torch::kCUDA;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Training on CPU." << std::endl;
device_type = torch::kCPU;
}
torch::Device device(device_type);
Net model;
model.to(device);
// load train data
auto train_dataset = torch::data::datasets::MNIST("D://MNIST//")
.map(torch::data::transforms::Normalize<>(0.1307, 0.3081))
.map(torch::data::transforms::Stack<>());
const size_t train_dataset_size = train_dataset.size().value();
std::cout << train_dataset_size << std::endl;
auto train_loader = torch::data::make_data_loader<torch::data::samplers::SequentialSampler>(
std::move(train_dataset), 64);
// load test data
auto test_dataset = torch::data::datasets::MNIST(
"D://MNIST//", torch::data::datasets::MNIST::Mode::kTest)
.map(torch::data::transforms::Normalize<>(0.1307, 0.3081))
.map(torch::data::transforms::Stack<>());
const size_t test_dataset_size = test_dataset.size().value();
auto test_loader =
torch::data::make_data_loader(std::move(test_dataset), 1000);
// optimizer
torch::optim::SGD optimizer(model.parameters(), torch::optim::SGDOptions(0.01).momentum(0.5));
//train
for (size_t epoch = 0; epoch < 5; epoch++)
{
train(epoch, model, device, *train_loader, optimizer, train_dataset_size);
test(model, device, *test_loader, test_dataset_size);
}
// save
return 1;
}C++代码训练结果如图:
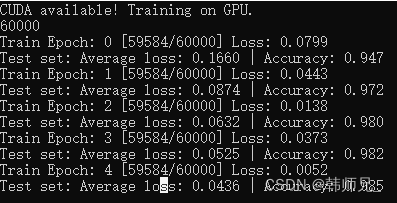
可以看到C++版本的 MNIST代码能够正常训练模型