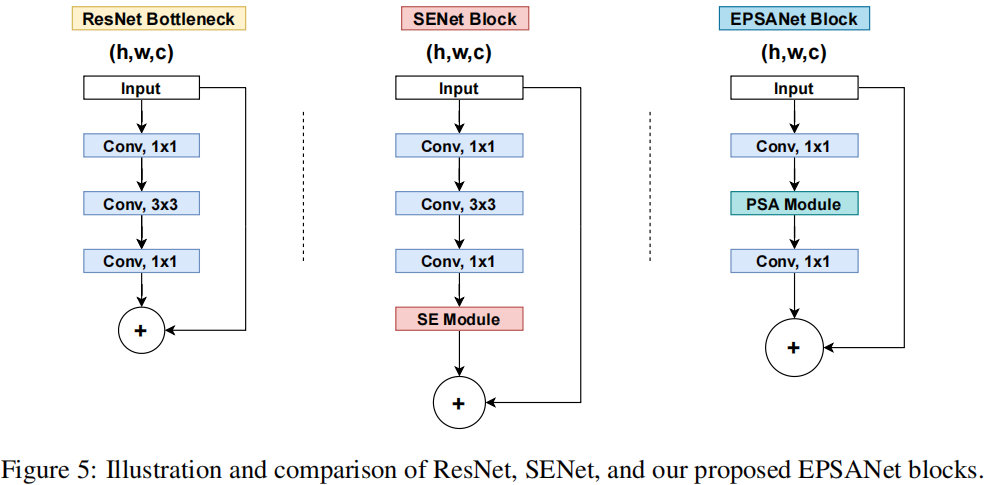
已有研究表明:将注意力模块嵌入到现有CNN中可以带来显著的性能提升。比如,SENet、BAM、CBAM、ECANet、GCNet、FcaNet等注意力机制均带来了可观的性能提升。但是,目前仍然存在两个具有挑战性的问题需要解决。一是如何有效地获取和利用不同尺度的特征图的空间信息,丰富特征空间。二是通道注意力或者或空间注意力只能有效捕获局部信息,而不能建立长期的依赖关系。最新的一些方法虽然能有效解决上述问题,但是他们同时会带来巨大的计算负担。基于此,本文首先提出了一种新颖的轻量且高效的PSA注意力模块。PSA模块可以处理多尺度的输入特征图的空间信息并且能够有效地建立多尺度通道注意力间的长期依赖关系。然后,我们将PSA 模块替换掉ResNet网络Bottleneck中的3x3x卷积,其余保持不变,最后得到了新的EPSA(efficient pyramid split attention) block.基于EPSA block我们构建了一个新的骨干网络称作:EPSANet。它既可以提供强有力的多尺度特征表示能力。与此同时,EPSANet不仅在图像识别任务中的Top-1 Acc大幅度优于现有技术,而且在计算参数量上有更加高效。具体效果:如下图所示,

论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.14447v1.pdf
代码地址:https://gitcode.com/mirrors/murufeng/epsanet/blob/master/models/epsanet.py
1.是什么?
Pyramid Split Attention (PSA)是一种基于注意力机制的模块,它可以用于图像分类、目标检测等任务中。PSA模块通过将不同大小的卷积核的卷积结果进行拼接,形成一个金字塔状的特征图,然后在这个特征图上应用注意力机制,以提取更加丰富的特征信息。与其他注意力模块相比,PSA模块具有轻量、简单高效等特点,可以与ResNet等主流网络结构结合使用,提高模型的性能。
2.为什么?
1. SE仅仅考虑了通道注意力,忽略了空间注意力。
2. BAM和CBAM考虑了通道注意力和空间注意力,但仍存在两个最重要的缺点:(1)没有捕获不同尺度的空间信息来丰富特征空间。(2)空间注意力仅仅考虑了局部区域的信息,而无法建立远距离的依赖。
3. 后续出现的PyConv,Res2Net和HS-ResNet都用于解决CBAM的这两个缺点,但计算量太大。
基于以上三点分析,提出了Pyramid Split Attention。
3.怎么样?
3.1网络结构

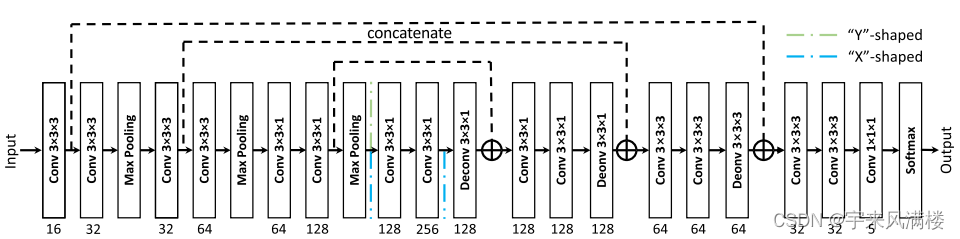
PSA模块主要通过四个步骤实现
- 首先,利用SPC模块来对通道进行切分,然后针对每个通道特征图上的空间信息进行多尺度特征提取;
- 其次,利用SEWeight模块提取不同尺度特征图的通道注意力,得到每个不同尺度上的通道注意力向量;
- 第三,利用Softmax对多尺度通道注意力向量进行特征重新标定,得到新的多尺度通道交互之后的注意力权重。
- 第四,对重新校准的权重和相应的特征图按元素进行点乘操作,输出得到一个多尺度特征信息注意力加权之后的特征图。该特征图多尺度信息表示能力更丰富。
3.2 SPC module
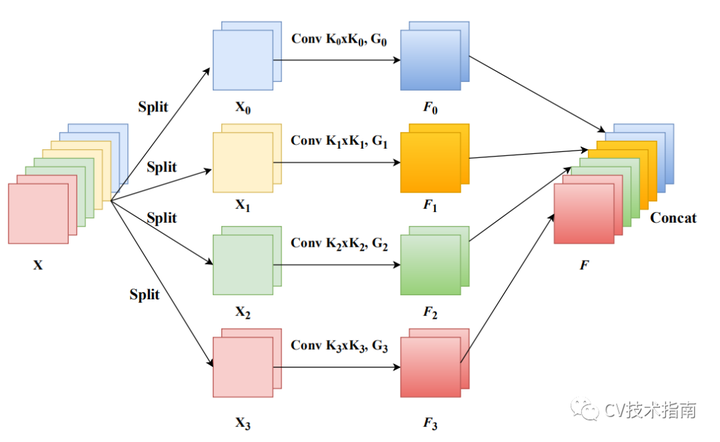
从前面我们了解到:PSA的关键在于多尺度特征提取,即SPC模块。假设输入为X,我们先将其拆分为S部分,然后对不同部分提取不同尺度特征,最后将所提取的多尺度特征通过Concat进行拼接。上述过程可以简单描述如下:
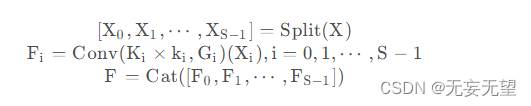
在上述特征基础上,我们对不同部分特征提取注意力权值,公式如下:
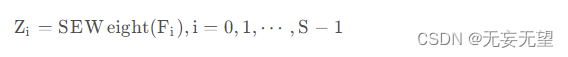
为更好的实现注意力信息交互并融合跨维度信息,我们将上述所得注意力向量进行拼接,即.然后,我们再对所得注意力权值进行归一化,定义如下:
![]()
最后,我们即可得到校正后的特征:Y = F ⊙ att
3.3 框图
3.4 代码实现
SEWeightModule
import torch.nn as nn
class SEWeightModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, reduction=16):
super(SEWeightModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels//reduction, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(channels//reduction, channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
out = self.avg_pool(x)
out = self.fc1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
weight = self.sigmoid(out)
return weightPSAModule
def conv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1):
"""standard convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class PSAModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplans, planes, conv_kernels=[3, 5, 7, 9], stride=1, conv_groups=[1, 4, 8, 16]):
super(PSAModule, self).__init__()
self.conv_1 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[0], padding=conv_kernels[0]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[0])
self.conv_2 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[1], padding=conv_kernels[1]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[1])
self.conv_3 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[2], padding=conv_kernels[2]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[2])
self.conv_4 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[3], padding=conv_kernels[3]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[3])
self.se = SEWeightModule(planes // 4)
self.split_channel = planes // 4
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.shape[0]
x1 = self.conv_1(x)
x2 = self.conv_2(x)
x3 = self.conv_3(x)
x4 = self.conv_4(x)
feats = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4), dim=1)
feats = feats.view(batch_size, 4, self.split_channel, feats.shape[2], feats.shape[3])
x1_se = self.se(x1)
x2_se = self.se(x2)
x3_se = self.se(x3)
x4_se = self.se(x4)
x_se = torch.cat((x1_se, x2_se, x3_se, x4_se), dim=1)
attention_vectors = x_se.view(batch_size, 4, self.split_channel, 1, 1)
attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors)
feats_weight = feats * attention_vectors
for i in range(4):
x_se_weight_fp = feats_weight[:, i, :, :]
if i == 0:
out = x_se_weight_fp
else:
out = torch.cat((x_se_weight_fp, out), 1)
return outEPSANET
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
from .SE_weight_module import SEWeightModule
def conv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1):
"""standard convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class PSAModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplans, planes, conv_kernels=[3, 5, 7, 9], stride=1, conv_groups=[1, 4, 8, 16]):
super(PSAModule, self).__init__()
self.conv_1 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[0], padding=conv_kernels[0]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[0])
self.conv_2 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[1], padding=conv_kernels[1]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[1])
self.conv_3 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[2], padding=conv_kernels[2]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[2])
self.conv_4 = conv(inplans, planes//4, kernel_size=conv_kernels[3], padding=conv_kernels[3]//2,
stride=stride, groups=conv_groups[3])
self.se = SEWeightModule(planes // 4)
self.split_channel = planes // 4
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.shape[0]
x1 = self.conv_1(x)
x2 = self.conv_2(x)
x3 = self.conv_3(x)
x4 = self.conv_4(x)
feats = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4), dim=1)
feats = feats.view(batch_size, 4, self.split_channel, feats.shape[2], feats.shape[3])
x1_se = self.se(x1)
x2_se = self.se(x2)
x3_se = self.se(x3)
x4_se = self.se(x4)
x_se = torch.cat((x1_se, x2_se, x3_se, x4_se), dim=1)
attention_vectors = x_se.view(batch_size, 4, self.split_channel, 1, 1)
attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors)
feats_weight = feats * attention_vectors
for i in range(4):
x_se_weight_fp = feats_weight[:, i, :, :]
if i == 0:
out = x_se_weight_fp
else:
out = torch.cat((x_se_weight_fp, out), 1)
return out
class EPSABlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, norm_layer=None, conv_kernels=[3, 5, 7, 9],
conv_groups=[1, 4, 8, 16]):
super(EPSABlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.conv2 = PSAModule(planes, planes, stride=stride, conv_kernels=conv_kernels, conv_groups=conv_groups)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class EPSANet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,block, layers, num_classes=1000):
super(EPSANet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layers(block, 64, layers[0], stride=1)
self.layer2 = self._make_layers(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layers(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layers(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def _make_layers(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, num_blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def epsanet50():
model = EPSANet(EPSABlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=1000)
return model
def epsanet101():
model = EPSANet(EPSABlock, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=1000)
return model
参考:
EPSANet: 一种高效的多尺度通道注意力机制,主要提出了金字塔注意力模块,即插即用,效果显著,已开源!
EPSANet:金字塔拆分注意力模块