一:什么是 Promise
Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,其实是一个构造函数,自己身上有all、reject、resolve这几个方法,原型上有then、catch等方法。
Promise对象有以下两个特点。
(1)对象的状态不受外界影响。Promise对象代表一个异步操作,有三种状态:pending(进行中)、fulfilled(已成功)和rejected(已失败)。只有异步操作的结果,可以决定当前是哪一种状态,任何其他操作都无法改变这个状态。这也是Promise这个名字的由来,它的英语意思就是“承诺”,表示其他手段无法改变。
(2)一旦状态改变,就不会再变,任何时候都可以得到这个结果。Promise对象的状态改变,只有两种可能:从pending变为fulfilled和从pending变为rejected。只要这两种情况发生,状态就凝固了,不会再变了,会一直保持这个结果,这时就称为 resolved(已定型)。如果改变已经发生了,你再对Promise对象添加回调函数,也会立即得到这个结果。这与事件(Event)完全不同,事件的特点是,如果你错过了它,再去监听,是得不到结果的。
二:手写Promise
1、手写构造函数
设计思路
- 定义类
- 添加构造函数
- 定义resolve/reject
- 执行回调函数
代码实现
<script>
// 创建一个类
class wePromise{
// 实现构造器,并且实现resolve和reject两个方法
constructor(func) {
const reslove = (result) => {
console.log('reslove-执行啦:',result);
}
const reject = (result) => {
console.log('reject-执行啦:',result);
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove,reject)
}
}
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove,reject) => {
console.log('执行');
reslove('success')
reject('reject')
})
</script>运行效果

2、手写状态及原因
设计思路
- 添加状态
- 添加原因
- 调整resolve/reject
- 状态不可逆
代码实现
<script>
// 使用变量保存状态,便于后续使用,Ctrl + shift + p
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class wePromise {
state = PENDING // 状态
result = undefined // 原因
// 实现构造器,并且实现resolve和reject两个方法
constructor(func) {
// 改状态,pending => fulfilled
// 记录原因
const reslove = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) { // 锁定状态
this.state = FULFILLED
this.result = result
}
}
// 改状态,pending => rejected
// 记录原因
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) { // 锁定状态
this.state = REJECTED
this.result = result
}
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove, reject)
}
}
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove('success')
reject('reject')
})
</script>运行效果

3、then方法--成功和失败的回调
设计思路
- 添加实例方法
- 参数判断
- 执行成功/失败回调
代码实现
<script>
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class wePromise {
state = PENDING // 状态
result = undefined // 原因
// 构造函数
constructor(func) {
// 改状态,pending => fulfilled
const reslove = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.result = result
}
}
// 改状态,pending => rejected
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.result = result
}
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled,onReject){
// 判断传入的参数是不是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function'?onFulfilled : x=>x
onReject = typeof onReject === 'function'?onReject : x=>{throw x}
// 判断执行完成后的状态
if(this.state === FULFILLED){
onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
}else if(this.state === REJECTED){
onReject(this.result)
}
}
}
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove('success')
// reject('reject')
})
p.then(res => {
console.log('成功回调:',res);
},err => {
console.log('失败回调:',err);
})
</script>运行效果

4、then方法--异步和多次调用
设计思路
- 定义实例属性
- 保存回调函数
- 调用成功/失败回调函数
代码实现
<script>
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class wePromise {
state = PENDING // 状态
result = undefined // 原因
#handlers = [] // [{onFulfilled,onReject},......]
// 构造函数
constructor(func) {
// 改状态,pending => fulfilled
const reslove = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.result = result
// 下面这个是异步的时候,先保存,然后到这一步执行,就取出保存的函数并且执行
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled })=>{ // 解构
onFulfilled(this.result)
})
}
}
// 改状态,pending => rejected
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.result = result
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onReject })=>{
onReject(this.result)
})
}
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled, onReject) {
// 判断传入的参数是不是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : x => x
onReject = typeof onReject === 'function' ? onReject : x => { throw x }
// 判断执行完成后的状态
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
onReject(this.result)
} else if (this.state === PENDING){ // 还没有改变状态,说明是异步
// 保存回调函数
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled,onReject
})
}
}
}
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reslove('success')
// reject('reject')
}, 2000)
})
p.then(res => {
console.log('成功回调1:', res);
}, err => {
console.log('失败回调1:', err);
})
p.then(res => {
console.log('成功回调2:', res);
}, err => {
console.log('失败回调2:', err);
})
</script>运行效果

5、异步任务
api介绍:
- 使用api:queueMicrotask、MutationObserve、setTimeout
- queueMicrotask:内置的全局函数,直接queueMicrotask() 就可以调用
- MutationObserve:内置的全局函数,比较麻烦,需要创建节点,具体看代码
- setTimeout:内置的全局函数,定时器
设计思路
- 定义函数
- 调用核心api
- 调用函数
代码实现
<script>
// 定义函数
function runAsynctask(callback) {// callback 是一个回调函数
// 调用核心api
if (typeof queueMicrotask === 'function') { // 调用三个函数是为了解决浏览器不兼容问题,先判断是不是函数
queueMicrotask(callback)
} else if (typeof MutationObserver === "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback)
const divNode = document.createElement('div')
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true })
divNode.innerHTML = '打酱油改变以下内容'
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0)
}
}
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class wePromise {
state = PENDING // 状态
result = undefined // 原因
#handlers = [] // [{onFulfilled,onReject},......]
// 构造函数
constructor(func) {
// 改状态,pending => fulfilled
const reslove = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.result = result
// 下面这个是异步的时候,先保存,然后到这一步执行,就取出保存的函数并且执行
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => { // 解构
onFulfilled(this.result)
})
}
}
// 改状态,pending => rejected
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.result = result
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onReject }) => {
onReject(this.result)
})
}
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled, onReject) {
// 判断传入的参数是不是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : x => x
onReject = typeof onReject === 'function' ? onReject : x => { throw x }
// 判断执行完成后的状态
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsynctask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
})
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsynctask(() => {
onReject(this.result)
})
} else if (this.state === PENDING) { // 还没有改变状态,说明是异步
// 保存回调函数
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsynctask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
})
},
onReject: () => {
runAsynctask(() => {
onReject(this.result)
})
}
})
}
}
}
console.log('top');
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove('success')
// reject('reject')
})
p.then(res => {
console.log('成功回调:', res);
}, err => {
console.log('失败回调:', err);
})
console.log('bottom');
</script>运行效果

6、链式编程
设计思路
- 返回Promise实例
- 获取返回值
- 处理返回值
- 处理异常
- 处理返回Promise(调用then方法)
- 处理重复引用(抛出异常)
代码实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>7.处理返回Promise</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 定义函数
function runAsynctask(callback) {// callback 是一个回调函数
// 调用核心api
if (typeof queueMicrotask === 'function') { // 调用三个函数是为了解决浏览器不兼容问题,先判断是不是函数
queueMicrotask(callback)
} else if (typeof MutationObserver === "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback)
const divNode = document.createElement('div')
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true })
divNode.innerHTML = '打酱油改变以下内容'
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0)
}
}
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class wePromise {
state = PENDING // 状态
result = undefined // 原因
#handlers = [] // [{onFulfilled,onReject},......]
// 构造函数
constructor(func) {
// 改状态,pending => fulfilled
const reslove = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.result = result
// 下面这个是异步的时候,先保存,然后到这一步执行,就取出保存的函数并且执行
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => { // 解构
onFulfilled(this.result)
})
}
}
// 改状态,pending => rejected
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.result = result
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onReject }) => {
onReject(this.result)
})
}
}
// 执行回调函数
func(reslove, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled, onReject) {
// 判断传入的参数是不是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : x => x
onReject = typeof onReject === 'function' ? onReject : x => { throw x }
const p2 = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
// 判断执行完成后的状态
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsynctask(() => {
try {
// 获取返回值
const x = onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
reslovePromise(p2, x, reslove, reject)
} catch (error) {
// 处理异常
reject(error)
}
})
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsynctask(() => {
try {
const x = onReject(this.result)
reslovePromise(p2, x, reslove, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
} else if (this.state === PENDING) { // 还没有改变状态,说明是异步
// 保存回调函数
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsynctask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.result) // 返回结果
reslovePromise(p2, x, reslove, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
},
onReject: () => {
runAsynctask(() => {
try {
const x = onReject(this.result) // 返回结果
reslovePromise(p2, x, reslove, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
})
}
})
return p2
}
}
function reslovePromise(p2, x, reslove, reject) {
// 处理重复引用
if (x === p2) {
// 抛出错误
throw new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>')
}
// 处理返回的Promise
if (x instanceof wePromise) {
// 调用then方法
x.then(res => reslove(res), err => reject(err))
} else {
// 处理返回值
reslove(x)
}
}
// 创建对象,调用两个方法
const p = new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove('success')
// reject('reject')
})
p.then(res => {
return new wePromise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove(2)
})
// console.log('成功回调1:', res);
// throw 'throw-error'
// return 2
}, err => {
console.log('失败回调1:', err);
}).then(res => {
console.log('成功回调2:', res);
}, err => {
console.log('失败回调2:', err);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>运行效果
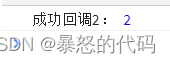
这个运行效果是只测了一个,有兴趣的小伙伴可以吧代码复制下来自己测。
三:总结
截止到目前为止已经将 Promise 的核心功能实现了,还有实例方法和静态方法这些没有实现。由于篇幅过长,因此会拆分成两篇文章来完成,感觉本文还不错的小伙伴可以继续看下一篇哦!
![[SQL开发笔记]WHERE子句 : 用于提取满足指定条件的记录](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/112a932af7774594b42ad28bf2a85e78.png)