本篇博文转载于https://www.cnblogs.com/1024incn/tag/CUDA/,仅用于学习。
Dynamic Parallelism
到目前为止,所有kernel都是在host端调用,CUDA Dynamic Parallelism允许GPU kernel在device端创建调用。Dynamic Parallelism使递归更容易实现和理解,由于启动的配置可以由device上的thread在运行时决定,这也减少了host和device之间传递数据和执行控制。我们接下来会分析理解使用Dynamic Parallelism。
Nested Execution
在host调用kernel和在device调用kernel的语法完全一样。kernel的执行则被分为两种类型:parent和child。一个parent thread,parent block或者parent grid可以启动一个新的grid,即child grid。child grid必须在parent 之前完成,也就是说,parent必须等待所有child完成。
当parent启动一个child grid时,在parent显式调用synchronize之前,child不保证会开始执行。parent和child共享同一个global和constant memory,但是有不同的shared 和local memory。不难理解的是,只有两个时刻可以保证child和parent见到的global memory完全一致:child刚开始和child完成。所有parent对global memory的操作对child都是可见的,而child对global memory的操作只有在parent进行synchronize操作后对parent才是可见的。

Nested Hello World on the GPU
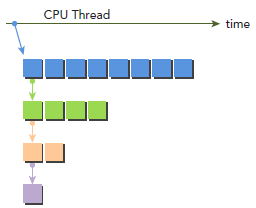
为了更清晰的讲解Dynamic Parallelism,我们改编最开始写的hello world程序。下图显示了使用Dynamic Parallelism的执行过程,host调用parent grid(每个block八个thread)。thread 0调用一个child grid(每个block四个thread),thread 0 的第一个thread又调用一个child grid(每个block两个thread),依次类推。
下面是具体的代码,每个thread会先打印出Hello World;然后,每个thread再检查自己是否该停止。
__global__ void nestedHelloWorld(int const iSize,int iDepth) {
int tid = threadIdx.x;
printf("Recursion=%d: Hello World from thread %d block %d\n",iDepth,tid,blockIdx.x);
// condition to stop recursive execution
if (iSize == 1) return;
// reduce block size to half
int nthreads = iSize>>1;
// thread 0 launches child grid recursively
if(tid == 0 && nthreads > 0) {
nestedHelloWorld<<<1, nthreads>>>(nthreads,++iDepth);
printf("-------> nested execution depth: %d\n",iDepth);
}
}
编译:
$ nvcc -arch=sm_35 -rdc=true nestedHelloWorld.cu -o nestedHelloWorld -lcudadevrt
-lcudadevrt是用来连接runtime库的,跟gcc连接库一样。-rdc=true使device代码可重入,这是DynamicParallelism所必须的,至于原因则将是一个比较大的话题,以后探讨。
代码的输出为:
./nestedHelloWorld Execution Configuration: grid 1 block 8 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 1 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 2 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 3 Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
这里的01234….输出顺序挺诡异的,太规整了,我们暂且认为CUDA对printf做过修改吧。还有就是,按照CPU递归程序的经验,这里的输出顺序就更怪了,当然,肯定不是编译器错误或者CUDA的bug,大家可以在调用kernel后边加上cudaDeviceSynchronize,就可以看到“正常”的顺序了,原因也就清楚了。
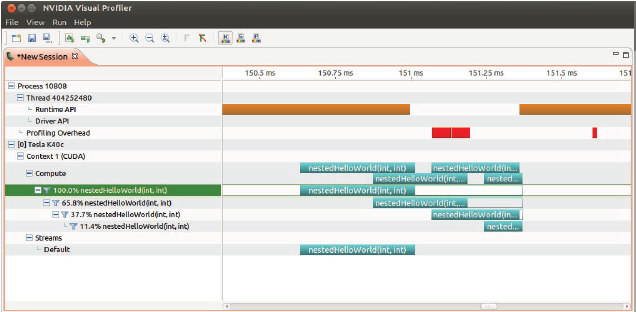
使用nvvp可以查看执行情况,空白说明parent在等待child执行结束:
$nvvp ./nesttedHelloWorld
接着,我们尝试使用两个block而不是一个:
$ ./nestedHelloWorld 2
输出是:
./nestedHelloWorld 2Execution Configuration: grid 2 block 8 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 1 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 0 Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 1 -------> nested execution depth: 1 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0 Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 2 -------> nested execution depth: 2 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0 -------> nested execution depth: 3 -------> nested execution depth: 3 Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0 Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
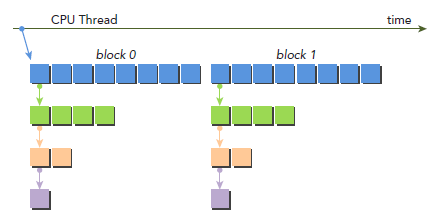
从上面结果来看,首先应该注意到,所有child的block的id都是0。下图是调用过程,parent有两个block了,但是所有child都只有一个blcok:
nestedHelloWorld<<<1, nthreads>>>(nthreads, ++iDepth);
注意:Dynamic Parallelism只有在CC3.5以上才被支持。通过Dynamic Parallelism调用的kernel不能执行于不同的device(物理上实际存在的)上。调用的最大深度是24,但实际情况是,kernel要受限于memory资源,其中包括为了同步parent和child而需要的额外的memory资源。
Nested Reduction
学过算法导论之类的算法书应该知道,因为递归比较消耗资源的,所以如果可以的话最好是展开,而这里要讲的恰恰相反,我们要实现递归,这部分主要就是再次证明DynamicParallelism的好处,有了它就可以实现像C那样写递归代码了。
下面的代码就是一份实现,和之前一样,每个child的有一个block,block中第一个thread调用kernel,不同的是,parent的grid有很多的block。第一步还是讲global memory的地址g_idata转化为每个block本地地址。然后,if判断是否该退出,退出的话,就将结果拷贝回global memory。如果不该退出,就进行本地reduction,一般的线程执行in-place(就地)reduction,然后,同步block来保证所有部分和的计算。thread0再次产生一个只有一个block和当前一半数量thread的child grid。
__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduce (int *g_idata, int *g_odata,
unsigned int isize) {
// set thread ID
unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x;
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
int *odata = &g_odata[blockIdx.x];
// stop condition
if (isize == 2 && tid == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]+idata[1];
return;
}
// nested invocation
int istride = isize>>1;
if(istride > 1 && tid < istride) {
// in place reduction
idata[tid] += idata[tid + istride];
}
// sync at block level
__syncthreads();
// nested invocation to generate child grids
if(tid==0) {
gpuRecursiveReduce <<<1, istride>>>(idata,odata,istride);
// sync all child grids launched in this block
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
// sync at block level again
__syncthreads();
}
编译运行,下面结果是运行在Kepler K40上面:
$ nvcc -arch=sm_35 -rdc=true nestedReduce.cu -o nestedReduce -lcudadevrt ./nestedReduce starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512 cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576 gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
相较于neighbored,nested的结果是非常差的。
从上面结果看,2048个block被初始化了。每个block执行了8个recursion,16384个child block被创建,__syncthreads也被调用了16384次。这都是导致效率很低的原因。
当一个child grid被调用后,他看到的memory是和parent完全一样的,因为child只需要parent的一部分数据,block在每个child grid的启动前的同步操作是不必要的,修改后:
__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduceNosync (int *g_idata, int *g_odata,unsigned int isize) {
// set thread ID
unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x;
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int *odata = &g_odata[blockIdx.x];
// stop condition
if (isize == 2 && tid == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0] + idata[1];
return;
}
// nested invoke
int istride = isize>>1;
if(istride > 1 && tid < istride) {
idata[tid] += idata[tid + istride];
if(tid==0) {
gpuRecursiveReduceNosync<<<1, istride>>>(idata,odata,istride);
}
}
}
运行输出,时间减少到原来的三分之一:
./nestedReduceNoSync starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512 cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576 gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nestedNosyn elapsed 0.059125 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
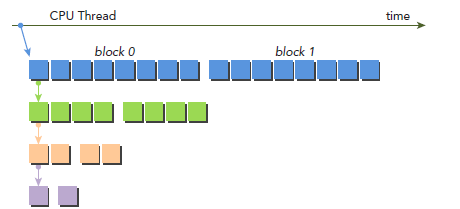
不过,性能还是比neighbour-paired要慢。接下来在做点改动,主要想法如下图所示,kernel的调用增加了一个参数iDim,这是因为每次递归调用,child block的大小就减半,parent 的blockDim必须传递给child grid,从而使每个thread都能计算正确的global memory偏移地址。注意,所有空闲的thread都被移除了。相较于之前的实现,每次都会有一半的thread空闲下来而被移除,也就释放了一半的计算资源。
__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduce2(int *g_idata, int *g_odata, int iStride,int const iDim) {
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*iDim;
// stop condition
if (iStride == 1 && threadIdx.x == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]+idata[1];
return;
}
// in place reduction
idata[threadIdx.x] += idata[threadIdx.x + iStride];
// nested invocation to generate child grids
if(threadIdx.x == 0 && blockIdx.x == 0) {
gpuRecursiveReduce2 <<<gridDim.x,iStride/2>>>(
g_idata,g_odata,iStride/2,iDim);
}
}
编译运行:
./nestedReduce2 starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512 cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576 gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nestedNosyn elapsed 0.059125 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>> gpu nested2 elapsed 0.000797 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
从这个结果看,数据又好看了不少,可以猜测,大约是由于调用了较少的child grid,我们可以用nvprof来验证下:
$ nvprof ./nestedReduce2
部分输出结果如下,第二列上显示了dievice kernel 的调用次数,第一个和第二个创建了16384个child grid。gpuRecursiveReduce2八层nested Parallelism只创建了8个child。
Calls (host) Calls (device) Avg Min Max Name 1 16384 441.48us 2.3360us 171.34ms gpuRecursiveReduce 1 16384 51.140us 2.2080us 57.906ms gpuRecursiveReduceNosync 1 8 56.195us 22.048us 100.74us gpuRecursiveReduce2 1 0 352.67us 352.67us 352.67us reduceNeighbored
对于一个给定的算法,我们可以有很多种实现方式,避免大量的nested 调用可以提升很多性能。同步对算法的正确性至关重要,但也是一个消耗比较大的操作,block内部的同步操作倒是可以去掉。因为在device上运行nested程序需要额外的资源,nested调用是有限的。







![2023年中国汽车塑料模具市场规模、竞争格局及行业趋势分析[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/242fbb15e43dacf0782ca90523e11897.png)