零.声明
本专栏文章我们会以连载的方式持续更新,本专栏计划更新内容如下:
第一篇:蓝牙综合介绍 ,主要介绍蓝牙的一些概念,产生背景,发展轨迹,市面蓝牙介绍,以及蓝牙开发板介绍。
第二篇:Transport层介绍,主要介绍蓝牙协议栈跟蓝牙芯片之前的硬件传输协议,比如基于UART的H4,H5,BCSP,基于USB的H2等
第三篇:传统蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙芯片的介绍,包括射频层(RF),基带层(baseband),链路管理层(LMP)等
第四篇:传统蓝牙host介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙的协议栈,比如HCI,L2CAP,SDP,RFCOMM,HFP,SPP,HID,AVDTP,AVCTP,A2DP,AVRCP,OBEX,PBAP,MAP等等一系列的协议吧。
第五篇:低功耗蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍低功耗蓝牙芯片,包括物理层(PHY),链路层(LL)
第六篇:低功耗蓝牙host介绍,低功耗蓝牙协议栈的介绍,包括HCI,L2CAP,ATT,GATT,SM等
第七篇:蓝牙芯片介绍,主要介绍一些蓝牙芯片的初始化流程,基于HCI vendor command的扩展
第八篇:附录,主要介绍以上常用名词的介绍以及一些特殊流程的介绍等。
另外,开发板如下所示,对于想学习蓝牙协议栈的最好人手一套。以便更好的学习蓝牙协议栈,相信我,学完这一套视频你将拥有修改任何协议栈的能力(比如Linux下的bluez,Android下的bluedroid)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
蓝牙视频教程(跟韦东山老师合作):
https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z10.1-c-s.w4004-22329603896.20.5aeb41f98e267j&id=693788592796
蓝牙交流扣扣群:765961169
Github代码:GitHub - sj15712795029/bluetooth_stack: 这是一个开源的双模蓝牙协议栈(bluetooth.stack)(btstack),可以运行在STM32,Linux.,包含HCI,L2CAP,SDP,RFCOMM,HFP,SPP,A2DP,AVRCP,AVDTP,AVCTP,OBEX,PBAP等协议,后续会继续维护,以达到商用的目的
入手开发板:https://shop220811498.taobao.com/category-1542116976.htm?spm=a1z10.5-c-s.w4010-22329603913.7.39ca7dbe2EA0K3&search=y&catName=%C0%B6%D1%C0%BF%AA%B7%A2%B0%E5#bd
蓝牙学习目录:一篇文章足够你学习蓝牙技术,提供史上最全的蓝牙技术(传统蓝牙/低功耗蓝牙)文章总结,文档下载总结(2020/12/11更新)_Wireless_Link的博客-CSDN博客_蓝牙eir
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一. AVRCP概念
AVRCP(Audio/Video Remote Control Profile)定义了蓝牙设备和audio/video控制功能通信的特点和过程,另用于远程控制音视频设备,底层传输基于AVCTP传输协议。该Profile定义了AV/C数字命令控制集。命令和信息通过AVCTP(Audio/Video Control Transport Protocol)协议进行传输。浏览功能通过AVCTP的第二个channel而不是AV/C。传输媒体信息通过基于OBEX协议的BIP(Bluetooth Basic Imaging Profile)协议。架构如下:

在我们协议栈的位置是:

二.AVRCP角色
The following roles are defined for devices that comply with this profile:
The controller (CT) is a device that initiates a transaction by sending a command frame to a target. Examples for CT are a personal computer, a PDA, a mobilephone, a remote controller or an AV device (such as an in car system, headphone, player/recorder, timer, tuner, monitor etc.).
The target (TG) is a device that receives a command frame and accordingly generates a response frame. Examples for TG are an audio player/recorder, a video player/recorder, a TV, a tuner, an amplifier or a headphone。
说白了就是发送命令控制的就是AVRCP controller,那么接受命令的就是AVRCP target.

并且AVRCP定义了4中类别:
1)Category 1: Player/Recorder,播放器/录音器
Basic operations of a player or a recorder are defined, regardless of the type of media
(tape, disc, solid state, etc.) or the type of contents (audio or video, etc.).
2)Category 2: Monitor/Amplifier,显示器/放大器
The category 2 is to define basic operations of a video monitor or an audio amplifier.
3)Category 3: Tuner,调试器
The category 3 defines the basic operation of a video tuner or an audio tuner.
4)Category 4: Menu,菜单
The basic operations for a menu function are defined in category 4. The method to display
menu data is not specified. It may be a display panel of the device itself, or on-screen
display (OSD) on an external monitor.
角色有以下几种应用场景:
1)单独充当AVRCP controller的设备
 其中遥控器只是发送Category 1的command的指令来控制播放器,然后播放器把音乐发送给耳机(音频协议不再本章范围内)
其中遥控器只是发送Category 1的command的指令来控制播放器,然后播放器把音乐发送给耳机(音频协议不再本章范围内)
2)车载娱乐系统

其中车载IVI来通过Category 1的command的指令来控制手机,手机发送音乐给IVI(音频协议不再本章范围内)
3)两个设备之间的远程控制以及Audio流

这个跟第二种情况类似,是一种情况的升级版,也就是把控制跟接受音频放在了同一个设备上,其中Headphone只发送Category 1的指令来控制
4)每个设备都充当AVRCP双角色的设备
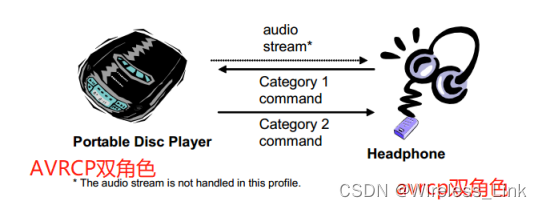
以上两个设备都是AVRCP双角色(controller,target),耳机通过Category 1的指令充当控制播放暂停等(此时Headphone就是AVRCP controller,Disc Player是AVRCP target),Disc Player通过Category 2来控制音量(此时Disc Player是AVRCP controller,此时Headphone就是AVRCP target)
5)带有LCD的远程控制

此耳机带有LCD显示功能,此时可以通过Category 1的命令不仅可以做常规的play/pause等功能,还可以通过Browing来浏览目录文件夹等。
6)全功能显示的车载系统
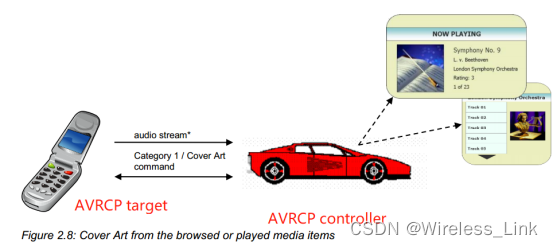
车机通过Category 1来进行常规的play/pause/browing功能,还可以通过Cover Art来下载专辑图片等功能。