一种更简洁的方式写出基于Promise的异步行为
async函数的返回值为一个promise,通过then和catch来捕获内部的返回值
1.特性:
1. async函数内部会返回一个promise对象,如果看起来不是promise,那么它将会隐式的包装在promise中(如果代码里返回的不是promise对象,会将其包装成promise对象)
async function fn () {
return 'hello world'
}
2. await能获取到promise状态改变后的值,如果后面不是一个promise,await 会把该值转换为已正常处理的Promise,结果为undefined
async function fn () {
await 1
}
3. await后面promise的状态是reject,则await后的代码不会执行,async函数将返回状态为reject的promise
async function fn() {
await cosle.log("sdf");
console.log(111);
}
console.log(fn());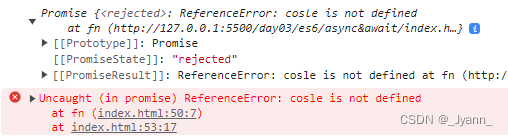
4. async函数内部如果存在await,await表达式会暂停整个async函数的执行,等当前位置promise状态改变后才能恢复
2.面试题分析:
async function fn() {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(1)
}, 0)
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4))
await setTimeout(function () {
console.log(5)
}, 0)
await Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(6))
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(7))
console.log(3)
}
fn()
//4 6 3 7 1 5分析:
宏任务:setTimeout 1;setTimeout 5
微任务: 4 6--》7
1.setTimeout 1会放在宏任务中
2.Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4))会放在微任务中
3.await setTimeout(function () {
console.log(5)
}, 0)
await后面跟的不是promise对象,会将其转为promise对象,并返回undefined
所以这段代码等价于:
await Promise.resolve(setTimeout(function(){ console.log(5) },0) 此时有个定时器,所以会放入宏任务中
4. await Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(6)) 执行后会将then后面放入微任务中,
***到此同步代码执行完(因为await会等待结果输出后再执行下面代码,所以下面的都不开始执行,而这个微任务在微任务4后面,所以需要先执行4,即打印4,6,
打印完后,await当前结果输出继续往下,将7设置进微任务
5.Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(7))放入微任务中
6. 打印console.log(3)
打印完3以后重新执行微任务7,在执行宏任务 1,5
最后为4,6,3,7,1,5