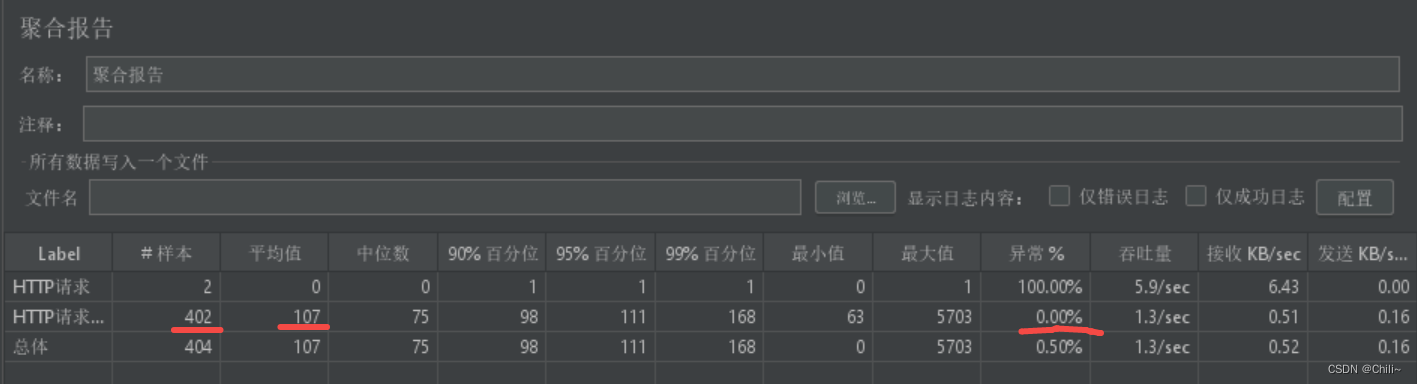
数值极限
提供查询所有基础数值类型的性质的接口
定义于头文件 <limits>
template< class T > class numeric_limits;numeric_limits 类模板提供查询各种算术类型属性的标准化方式(例如 int 类型的最大可能值是 std::numeric_limits<int>::max() )。
返回 1.0 与给定类型的下个可表示值的差
std::numeric_limits<T>::epsilon| static T epsilon() throw(); | (C++11 前) | |
| static constexpr T epsilon() noexcept; | (C++11 起) |
返回机器 epsilon ,即 1.0 与浮点类型 T 的下个可表示值的差。它仅若 std::numeric_limits<T>::is_integer == false 才有意义。
返回值
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::epsilon() |
| /* non-specialized */ | T() |
| bool | false |
| char | 0 |
| signed char | 0 |
| unsigned char | 0 |
| wchar_t | 0 |
| char8_t | 0 |
| char16_t | 0 |
| char32_t | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| unsigned short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| unsigned int | 0 |
| long | 0 |
| unsigned long | 0 |
| long long | 0 |
| unsigned long long | 0 |
| float | FLT_EPSILON |
| double | DBL_EPSILON |
| long double | LDBL_EPSILON |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>
struct SName
{
};
//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};
namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent = FLT_MIN_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent10 = FLT_MIN_10_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent10 = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool traps = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool tinyness_before = true;
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
min() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
lowest() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
max() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MAX ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
epsilon() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return LDBL_EPSILON ; }
};
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<short>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<int>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<float>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::epsilon() << std::endl;
//必须偏特化
// std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::epsilon(): "
// << std::numeric_limits<SName>::epsilon() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::epsilon(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::epsilon() << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出

返回给定浮点类型的最大舍入误差
std::numeric_limits<T>::round_error| static T round_error() throw(); | (C++11 前) | |
| static constexpr T round_error() noexcept; | (C++11 起) |
返回以 ULP (最后位置单位)表示的最大可能舍入错误,其为 ISO 10967 定义,可以从 0.5 (舍入到最近位)变化到 1.0 (舍入到零或无穷大)。它仅若 std::numeric_limits<T>::is_integer == false 才有意义。
返回值
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::round_error() |
| /* non-specialized */ | T() |
| bool | false |
| char | 0 |
| signed char | 0 |
| unsigned char | 0 |
| wchar_t | 0 |
| char8_t | 0 |
| char16_t | 0 |
| char32_t | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| unsigned short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| unsigned int | 0 |
| long | 0 |
| unsigned long | 0 |
| long long | 0 |
| unsigned long long | 0 |
| float | 0.5F |
| double | 0.5 |
| long double | 0.5L |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>
struct SName
{
};
//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};
namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent = FLT_MIN_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent10 = FLT_MIN_10_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent10 = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool traps = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool tinyness_before = true;
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
min() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
lowest() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
max() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MAX ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
epsilon() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return LDBL_EPSILON ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR double
round_error() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return 0.5F ; }
};
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<short>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<int>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<float>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::round_error() << std::endl;
//必须偏特化
// std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::round_error(): "
// << std::numeric_limits<SName>::round_error() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::round_error(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::round_error() << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出
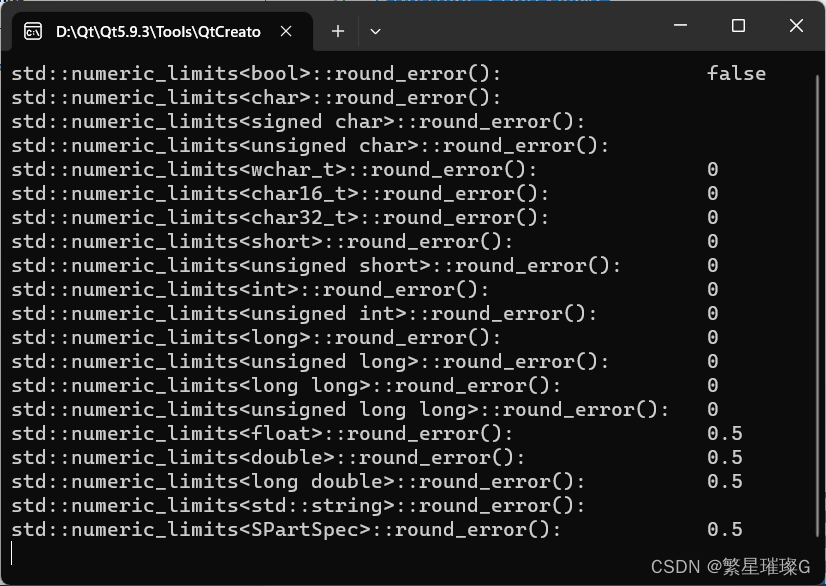
返回给定类型的正无穷大值
std::numeric_limits<T>::infinity| static T infinity() throw(); | (C++11 前) | |
| static constexpr T infinity() noexcept; | (C++11 起) |
返回浮点类型 T 所表示的特殊值“正无穷大”。仅若 std::numeric_limits<T>::has_infinity == true 才有意义。在最常见的浮点数二进制表示 IEEE 754 中,正无穷大是所有指数位为 1 而所有尾数位为 0 的值。
返回值
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::infinity() |
| /* non-specialized */ | T() |
| bool | false |
| char | 0 |
| signed char | 0 |
| unsigned char | 0 |
| wchar_t | 0 |
| char8_t | 0 |
| char16_t | 0 |
| char32_t | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| unsigned short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| unsigned int | 0 |
| long | 0 |
| unsigned long | 0 |
| long long | 0 |
| unsigned long long | 0 |
| float | HUGE_VALF |
| double | HUGE_VAL |
| long double | HUGE_VALL |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>
#include <cmath>
struct SName
{
};
//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};
namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent = FLT_MIN_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent10 = FLT_MIN_10_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_exponent10 = FLT_MAX_EXP;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool traps = true;
static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool tinyness_before = true;
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
min() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
lowest() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MIN ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
max() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return CHAR_MAX ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR int
epsilon() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return LDBL_EPSILON ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR double
round_error() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return 0.5F ; }
static _GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR double
infinity() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return HUGE_VAL ; }
};
}
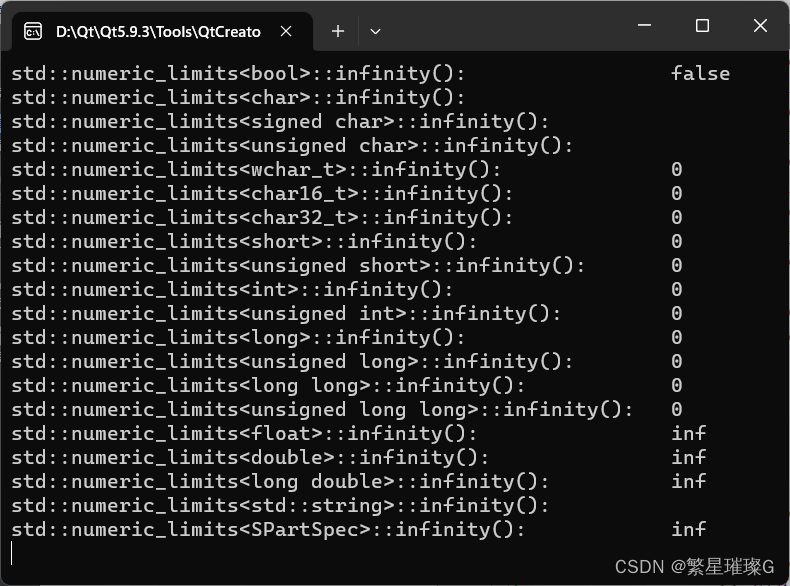
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<short>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<int>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::infinity() << std::endl;
//必须偏特化
// std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::infinity(): "
// << std::numeric_limits<SName>::infinity() << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::infinity(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::infinity() << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出




![[计算机提升] 系统及用户操作](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/41c7cc1f36a14ee3b326d149e405752f.png)