一边学习,一边总结,一边分享!
写在前面
关于GO背景基因集文件的制作,我们在很早以前也发过。近两天,自己在分析时候,也是被搞了头疼。想重新制作一份GO背景基因集,进行富集分析。但是结果,也不如意。以及在制作的过程中,也是跟随着以前的教程制作,发现以前整理的教程比较乱,那么借此机会,也进行整理,重新进行记录。
本期教程
直接访问链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/08hAZs24mi_KBOa4QZRLdQ
前言
我们在做转录组数据分析时,大多数都会进行功能富集分析,预测目的基因所具有的的功能。富集工具常用到的R语言中clusterProfiler包,里面包含了上千个功能富集的背景数据文件,功能非常强大,目前已经更新到V4.0版本。
在agriGO数据库中下载,
网址:http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/index.php

前期准备文件
- 所需注释的物种基因核酸序列或蛋白序列
- swissprot数据
- idmapping.tb.gz文件
- go-basic.obo文件
数据下载
你可以分别进去对应的网址下载最新的数据库即可。
- Swissprot数据库:https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA/

- dimapping数据:https://ftp.proteininformationresource.org/databases/idmapping/
wget -o GO_database/swissprot.gz https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA/swissprot.gz
wget -o GO_database/go-basic.obo http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/go/go-basic.obo
wget -o GO_database/idmapping.tb.gz https://ftp.proteininformationresource.org/databases/idmapping/idmapping.tb.gz
建库及文件提取
1. 使用diamond makedb建库
diamond makedb --in GO_database/swissprot.gz --threads 60 --db GO_database/swissprot
2. GO号与swissprot蛋白ID文件的提取
下载idmapping数据库
https://ftp.proteininformationresource.org/databases/idmapping/idmapping.tb.gz
解压idmapping.tb.gz文件
gunzip idmapping.tb.gz
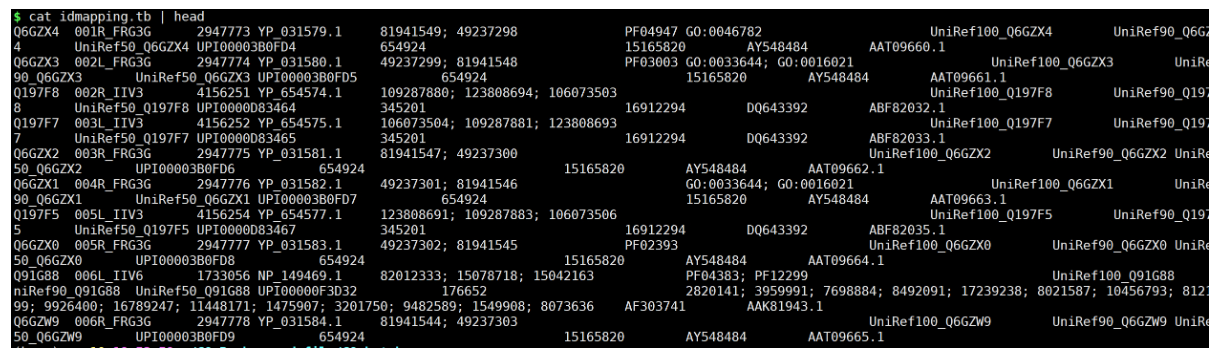
该文件的第一列为数据库ID,第八列为GO_ID,是我们这一次要与未知的结果进行转换的关键部分。
提取idmapping.tb.gz文件ID~GO.list file
awk -v FS="\t" -v OFS="\t" '{print $1,$8}' idmapping.tb | grep "GO" > idmapping.GO.list
使用Python脚本提取
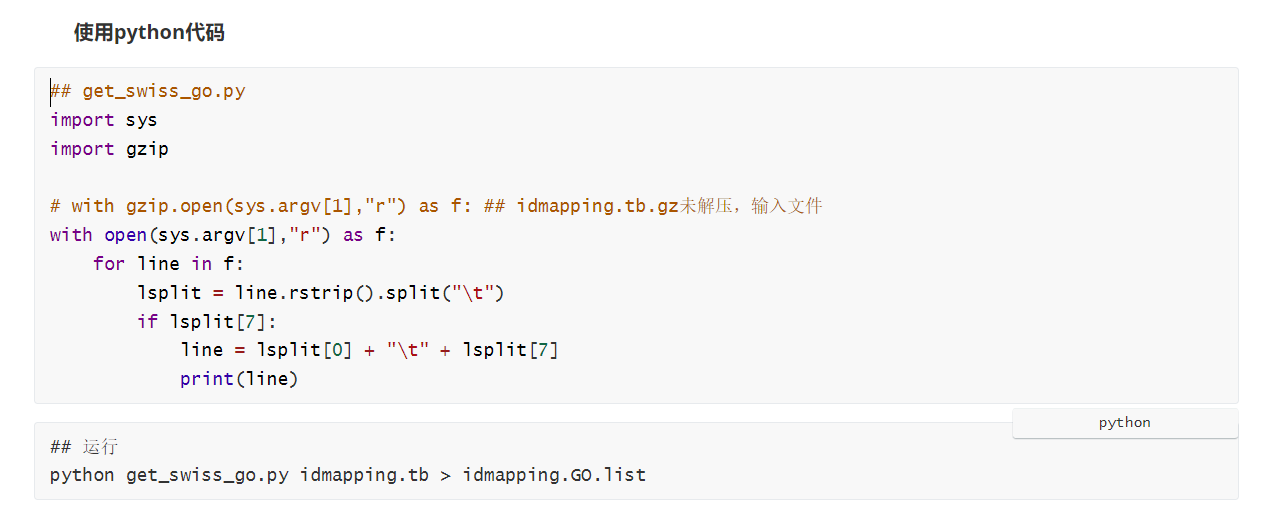
输出结果
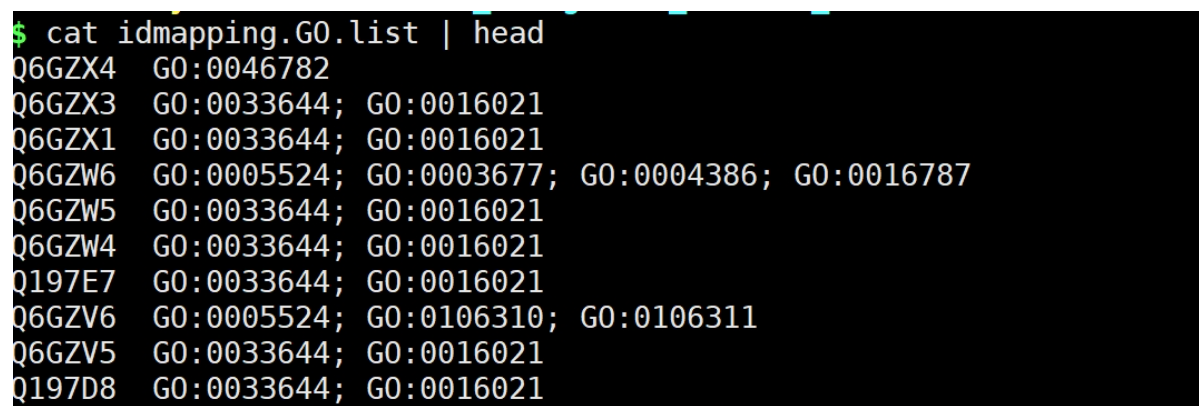
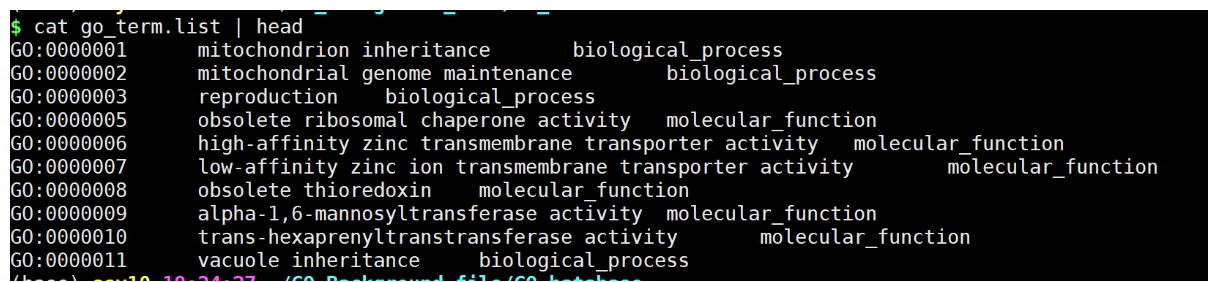
3. GO term文件提取
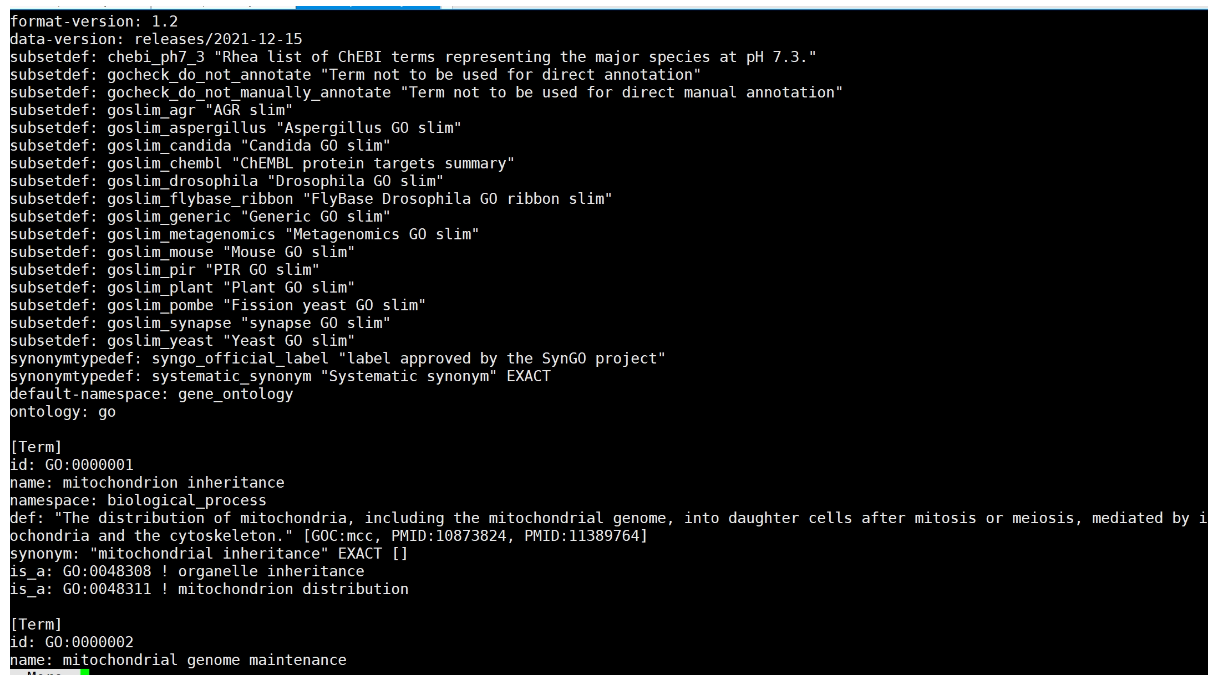
下载go-basi.obo,GO_Term
http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/go/go-basic.obo
原始go-basi.obo文件格式
脚本提取

输出结果

基因文件序列的准备
下载所需的背景基因序列,核酸序列或蛋白序列度都可以
我们这里以番茄基因组4.0版本为例子。
#!/bin/bash
## download the tomato reference geneome to 4.1
wget https://solgenomics.net/ftp//tomato_genome/annotation/ITAG4.0_release/ITAG4.0_gene_models.gff
wget https://solgenomics.net/ftp//tomato_genome/assembly/build_4.00/S_lycopersicum_chromosomes.4.00.fa
gffread ITAG4.0_gene_models.gff -T -o ITAG4.0_gene_models.gtf
##
gffread ITAG4.0_gene_models.gff -T -o ITAG4.0_gene_models.gtf
##
gffread -w tomato_4.0.fa -g S_lycopersicum_chromosomes.4.00.fa ITAG4.0_gene_models.gtf
注意:若你不想这用操作,下载蛋白序列即可
1. 比对
diamond blastx -d GO_database/swissprot.dmnd -q ../Tomato_4.0/tomato_4.00.fa -k 1 -e 0.00001 -o tomato.gene.m8
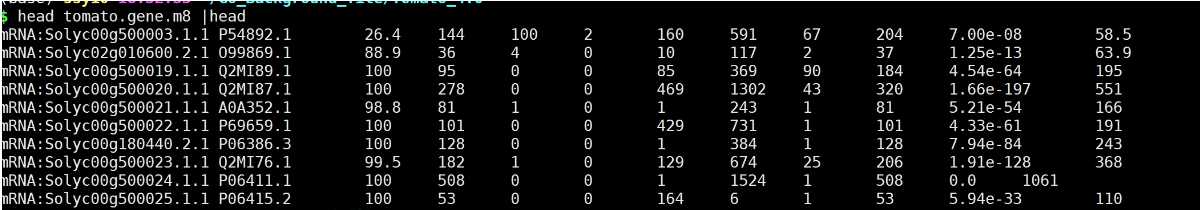
2. 筛选出最佳结果
这步,若你认为有必要进行,那就进行筛选。筛选的参数可以自己调整。
使用*.pl教程
die "perl $0 *.m8 *.m8.out\n" if(@ARGV!=2);
open IN, "$ARGV[0]" or die "can not open file: $ARGV[0]\n";
open OA, ">$ARGV[1]" or die "can not open file: $ARGV[1]\n";
my ($line,@inf,%score_data,%m8_data,%order);
my $n=1;
while($line=<IN>){
chomp $line;
@inf=split /\t/,$line;
if($inf[11]>$score_data{$inf[0]}){
$score_data{$inf[0]}=$inf[11];
$m8_data{$inf[0]}=$line;
}
else{
next;
}
$order{$line}=$n++;
}
foreach my $i (sort {$order{$a}<=>$order{$b}} keys %order){
@inf=split /\t/,$i;
if(exists $m8_data{$inf[0]}){
print OA "$m8_data{$inf[0]}\n";
}
}
close IN;
close OA;
运行
perl m8_best_pick.pl tomato.gene.m8 tomato.gene.m8.best.out
3. 提取最佳结果ID文件
使用Python脚本:

或,你可以使用wak命令提取就可以。
运行
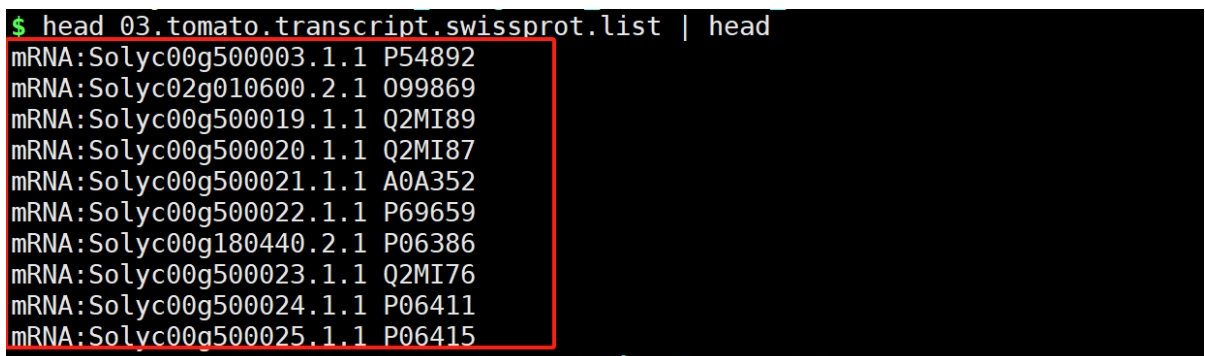
python ../get_blastx_wiss_id.py 02.tomato.gene.best.m8 > 03.tomato.transcript.swissprot.list
结果文件:
4. 合并文件,获得目标基因-GO ID

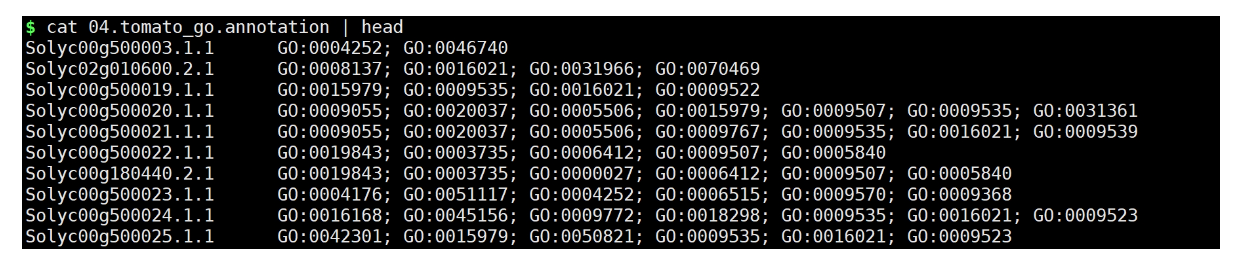
运行:
python get_go_annotation.py GO_batabase/idmapping.GO.list 03.tomato.transcript.swissprot.list
结果文件:
5. 拆分文件

注意:
我们的基因ID中,没有以mRNA:Solyc00g500003.1.1命名,如Solyc00g500003.1.1.我们需要将split_with_go.py进行适当修改即可。

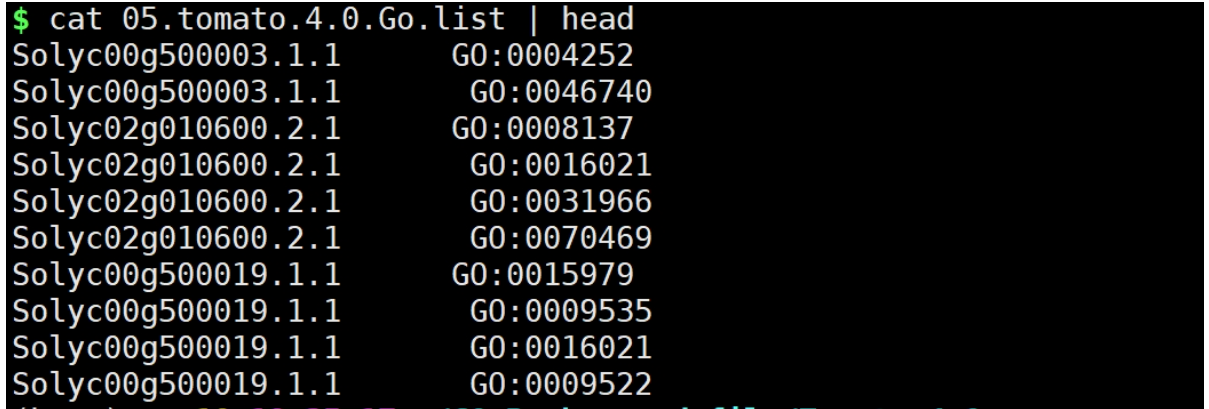
运行:
python ../split_with_go.py 04.tomato_go.annotation 05.tomato.4.0.Go.list
结果文件:
到这里基本结束了,你获得Gene ID与对应GO ID。
富集分析
你可以使用相关的云平台做GO功能富集分析,例如使用基迪奥生信平台的GO功能富集工具
在线网址:OmicShare Tools - 基迪奥生信云工具:
上传背景基因

云平台支持的背景文件的数据格式
<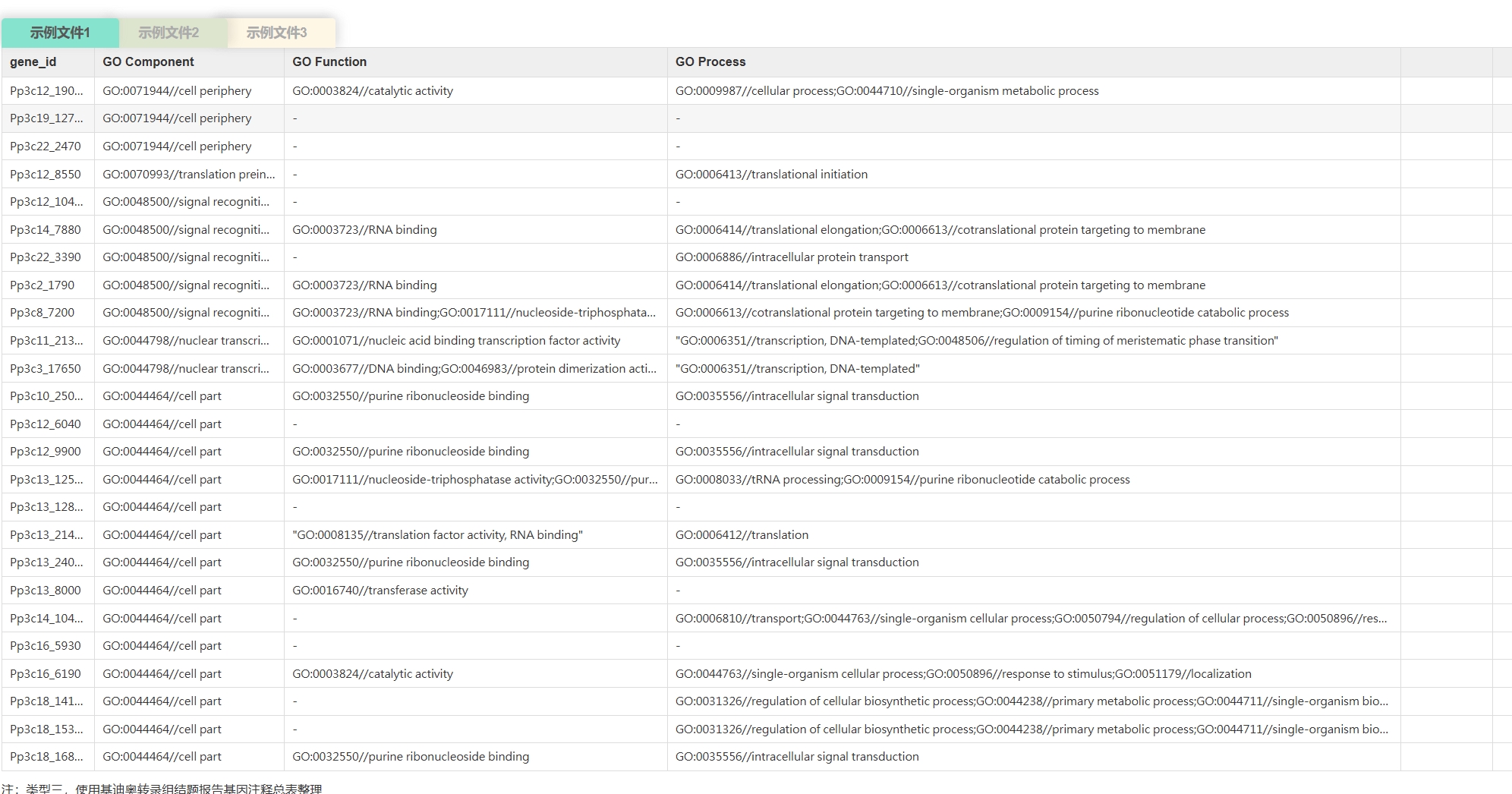 ,
,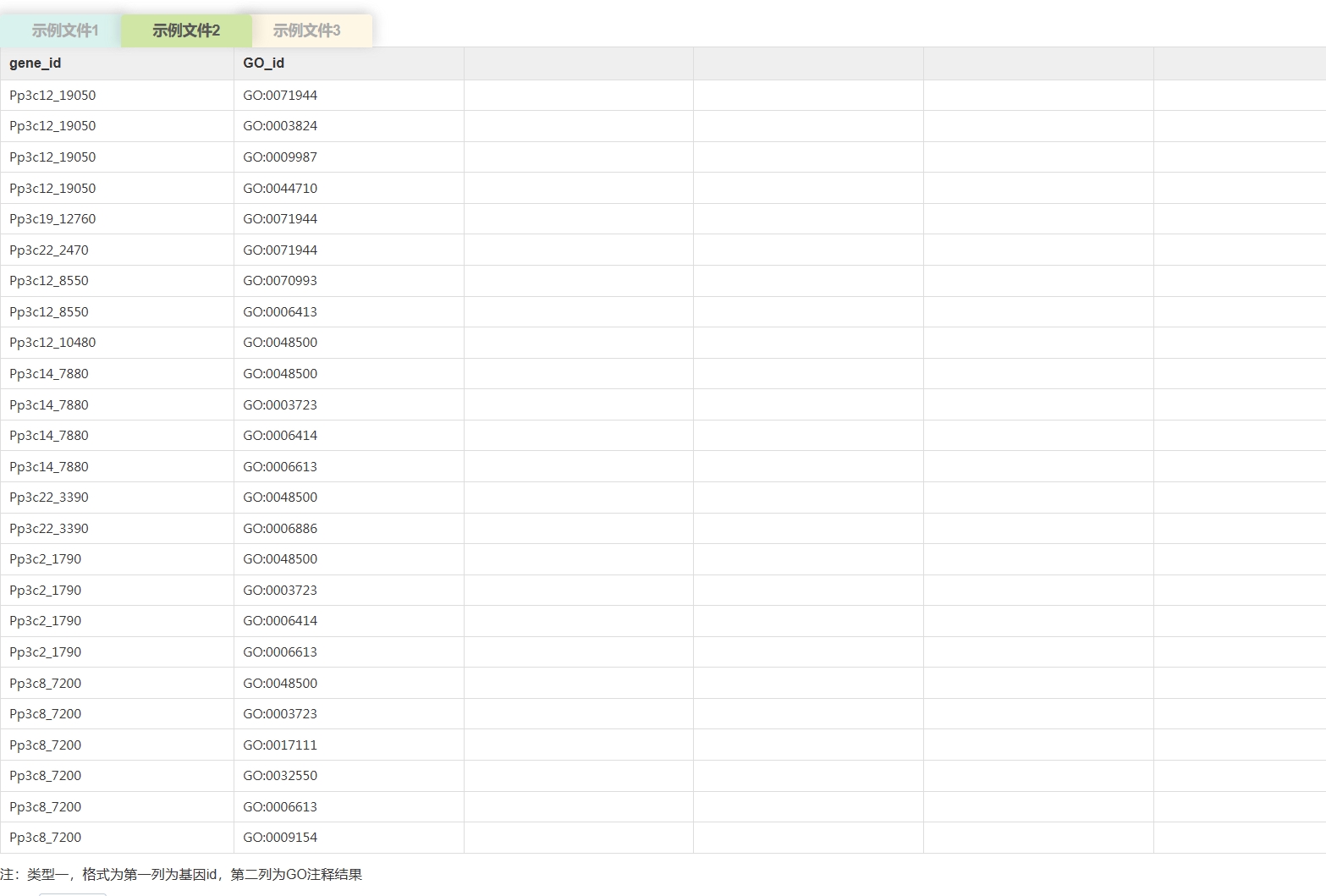 >
>
自己进行GO term的提取
下载go-basi.obo,GO_Term
http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/go/go-basic.obo
原始go-basi.obo文件格式
Python脚本:

运行:
python get_go_term.py go-basic.obo
使用R进行合并
library(clusterProfiler)
## 加载背景基因文件“gene-GO"
go_anno <- read.delim('tomato_go.annotation.new', header = FALSE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
names(go_anno) <- c("gene_id", "GO_ID")
head(go_anno)
### 导入GO注释文件
go_class <- read.delim("go_term.list", header = F, stringsAsFactors = F)
names(go_class) <- c("GO_ID", "Description","Ontology")
head(go_class)
## 合并背景基因
go_ann <- merge(go_anno, go_class, by = 'GO_ID', all.x = F)
head(go_ann)

开始富集分析:
# 导入差异基因
gene_list <- read.table("tomato.gene.5000.txt", stringsAsFactors = F)
head(gene_list)
names(gene_list) <- c("gene_id")
gene_select <- gene_list$gene_id
## 富集分析
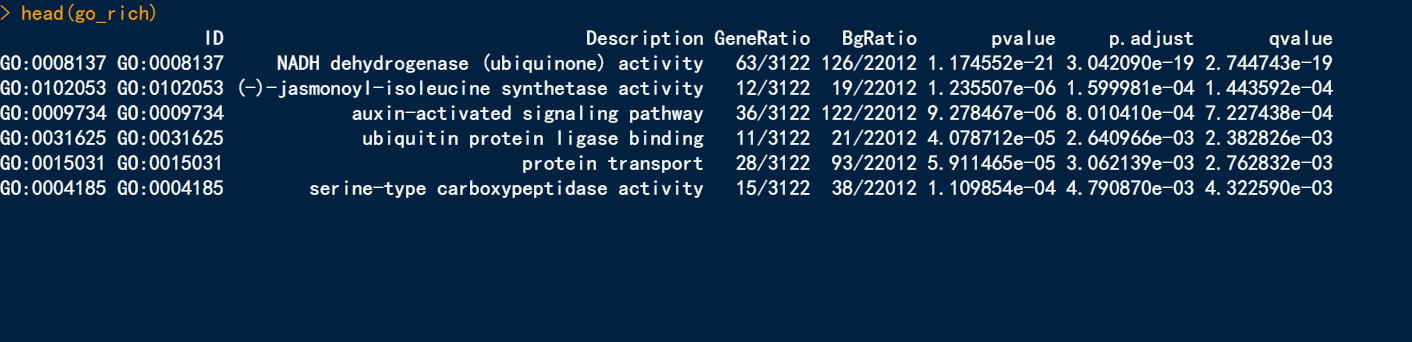
go_rich <- enricher(gene = gene_select,
TERM2GENE = go_ann[c('GO_ID','gene_id')],
TERM2NAME = go_ann[c('GO_ID','Description')],
pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
pAdjustMethod = 'BH',
qvalueCutoff = 0.2,
maxGSSize = 200)
head(go_rich)
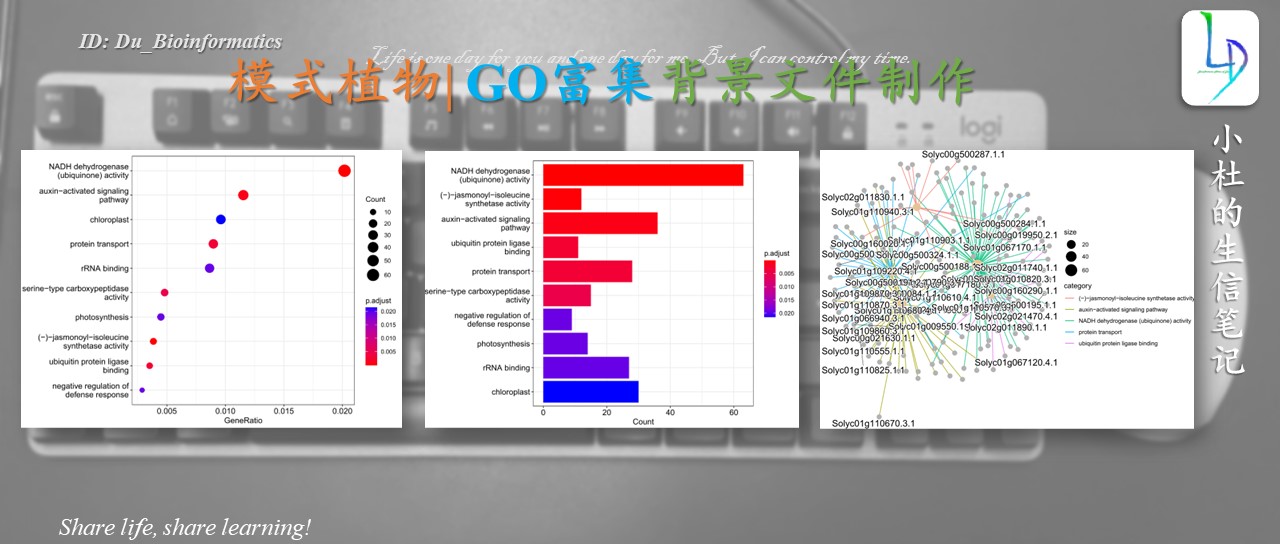
**柱状图**
barplot(go_rich,
drop=T,
showCategory = 10)

**气泡图**
dotplot(go_rich)

网络图
enrichplot::cnetplot(go_rich,circular = F, colorEdge = T)

写在最后,为了方便,我将前面的步骤进行分别写在一个脚本中。只要前期的数据准备好,输入所需的物种序列的序列即可。
算是比较方便。

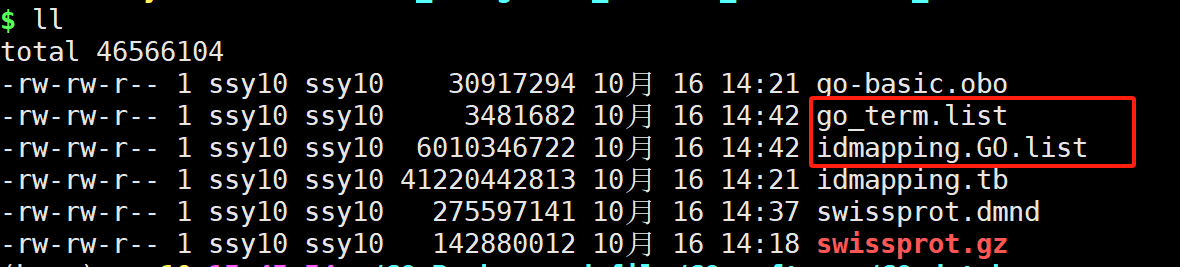
准备文件GO_database
- swissprot.gz
- go-basic.obo
- idmapping.tb
运行脚本:
sh 01.run.swissprot.sh
结果文件:
- go_term.list
- idmapping.GO.list
GO注释文件脚本:
sh 02_run.GO_enrichment_file.sh test.fa
- test.fa为注释文件序列
**注意:**若你不更改blast的脚本,这里默认只支持核酸序列。
结果文件:
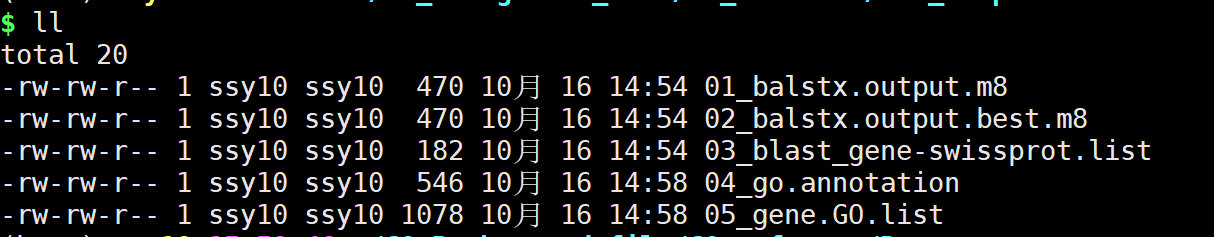
在结果文件中05_gene.GO.list即最终结果文件。
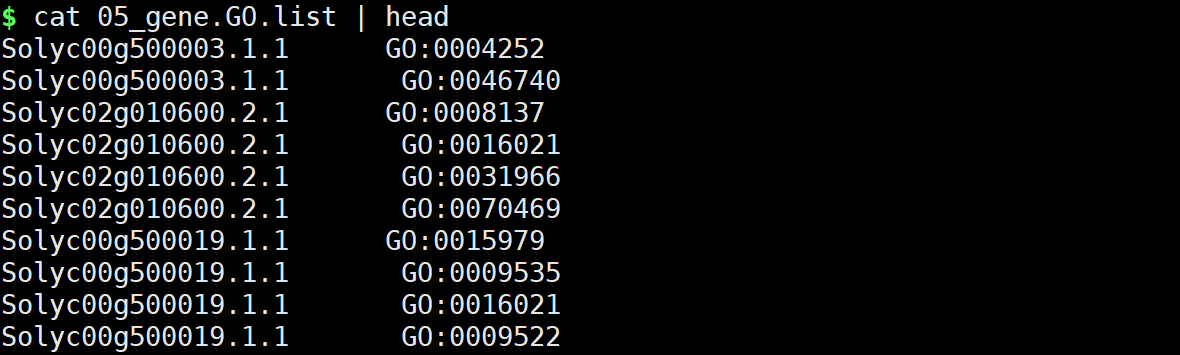
后面的分析与前面的一致。
若你不想制作,我们这里提供完整的
GO_database文件夹中的文件。你只需要在此基础上,运行你所需的物种序列即可。
直接访问链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/08hAZs24mi_KBOa4QZRLdQ
往期文章:
1. 复现SCI文章系列专栏
2. 《生信知识库订阅须知》,同步更新,易于搜索与管理。

3. 最全WGCNA教程(替换数据即可出全部结果与图形)
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码一
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码二
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程代码分享 | 代码三
4. 精美图形绘制教程
- 精美图形绘制教程
5. 转录组分析教程
转录组上游分析教程[零基础]
小杜的生信筆記,主要发表或收录生物信息学的教程,以及基于R的分析和可视化(包括数据分析,图形绘制等);分享感兴趣的文献和学习资料!!