推文作者:丰于杭
编者按
在“八月下旬特征选择专题期刊精选”中,我们有主题、有针对性地选择了MSOM, Operations Research, Management Science等管理科学杂志中一些有趣的文章,不仅对文章的内容进行了概括与点评,而且也对文章的结构进行了梳理,旨在激发广大读者的阅读兴趣与探索热情。在本期“论文精选”中,我们以“特征选择”为主题,分别探究了个性化医疗、肿瘤治疗目标选择、产品优化设计问题,涉及特征工程、医疗管理、产品管理等诸多知识。
推荐文章1
● 题目:A Contextual Ranking and Selection Method for Personalized Medicine
个性化医疗的情境排序和选择方法
● 期刊:Manufacturing & Service Operations Management
● 原文链接:https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/10.1287/msom.2022.0232
● 作者:Jianzhong Du, Siyang Gao, Chun-Hung Chen
● 关键词:个性化医疗, 上下文排序和选择, 仿真优化, 收敛速度
● 摘要:
Personalized medicine (PM) seeks the best treatment for each patient among a set of available treatment methods.
Since a specific treatment does not work well on all patients, traditionally, the best treatment was selected based on the doctor’s personal experience and expertise, which is subject to human errors. In the meantime, stochastic models have been well developed in the literature for a lot of major diseases.
In the meantime, stochastic models have been well developed in the literature for a lot of major diseases. This gives rise to a simulation-based solution for PM, which uses the simulation tool to evaluate the performance for pairs of treatment and patient biometric characteristics, and based on that, selects the best treatment for each patient characteristics.
个性化医疗(PM)在一组可用的治疗方法中为每位患者寻求最佳治疗。
由于一种特定的治疗方法并不是对所有的病人都有效,传统上,最好的治疗方法是根据医生的个人经验和专业知识来选择的,这容易受到人为错误的影响。与此同时,许多重大疾病的随机模型已经在文献中得到了很好的发展。
此外,这就产生了一种基于模拟的PM解决方案,该解决方案使用模拟工具来评估成对治疗和患者生物特征的性能,并在此基础上为每个患者特征选择最佳治疗。
● 文章结构:

● 核心解法及点评:
作者首先给出个性化医疗(PM)的三个客观度量指标。
指标:首先是通过正确选择的概率(PCS)来评估最佳治疗方案的选择质量。文中希望为所有m个上下文提供最好的处理方法,因此需要在整个上下文空间X上评估选择质量的度量。为了满足这一需求,考虑以下三个基于PCS的措施:

基于此,以及按照数据规模大小,作者给出了两种(小规模和大规模问题)不同的算法框架。
在本文中,作者将基于仿真的决策中的排序和选择(R&S)模型扩展到解决医疗项目管理问题,通过建立两种适用于小型和大型上下文空间的模拟预算分配模型,文章对这两个模型,确定了优化费率函数的费率最优预算分配规则,开发了方便的选择算法来实现,并展示了算法的一致性。文章同时也指出了未来的一些有趣的研究途径,比如需要在疾病进展过程中进行多次决策的问题和可以应用于更一般情况的CR&S算法以及将前两种框架(小型和大型上下文空间)和算法扩展到个性化医疗问题。
● 相关好文:
[1] Garnett, G. P., S. Cousens, T. B. Hallett, R. Steketee, N. Walker. 2011. Mathematical models in the evaluation of health programmes. Lancet.
[2] Chen, C. H., J. Lin, E. Y¨ucesan, S. E. Chick. 2000. Simulation budget allocation for further enhancing the efficiency of ordinal optimization. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems.
[3] Fu, M., J. Hu, C.-H. Chen, X. Xiong. 2007. Simulation allocation for determining the best design in the presence of correlated sampling. INFORMS Journal on Computing.
推荐文章2
● 题目:Objective Selection for Cancer Treatment: An Inverse Optimization Approach
肿瘤治疗的目的选择:一种逆优化方法
● 期刊:Operations Research
● 原文链接:https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/10.1287/opre.2021.2192
● 作者:Temitayo Ajayi, Taewoo Lee, Andrew J. Schaefer
● 关键词:目标选择, 特征选择, 逆优化, 贪婪算法, 多目标优化, 放射治疗计划
● 摘要:
In radiation therapy treatment-plan optimization, selecting a set of clinical objectives that are tractable and parsimonious yet effective is a challenging task.
In clinical practice, this is typically done by trial and error based on the treatment planner’s subjective assessment, which often makes the planning process inefficient and inconsistent. We develop the objective selection problem that infers a sparse set of objectives for prostate cancer treatment planning based on historical treatment data.
We formulate the problem as a non-convex bilevel mixed-integer program using inverse optimization and highlight its connection with feature selection to propose multiple solution approaches, including greedy heuristics, regularized problems, as well as application-specific methods that utilize anatomical information of the patients.
在放射治疗方案优化中,选择一组易于处理、简洁有效的临床目标是一项具有挑战性的任务。
在临床实践中,这通常是根据治疗计划者的主观评估通过试错来完成的,这往往使计划过程效率低下和不一致。我们发展了客观选择问题,根据历史治疗数据推断出前列腺癌治疗计划的稀疏目标集。
我们将该问题表述为使用逆优化的非凸双层混合整数规划,并强调其与特征选择的联系,提出多种解决方法,包括贪婪启发式,正则化问题以及利用患者解剖信息的特定应用方法。
● 文章结构:

● 核心解法及点评:
在特征选择方法的选取上,文中提出了三种前向选择方法来选择目标:一种方法是经典的贪婪算法,它优化目标选择问题的距离函数;第二种方法以贪婪的方式在每个ROI中迭代搜索最佳目标;第三种方法是贪婪算法的一种变体,它通过利用反映患者解剖特征的问题的独特结构来更有效地找到解决方案。
文章提出的这三种放射治疗方案选择方法:贪婪算法与正则化、基于解剖学的方法、批量输入目标选择。目标选择可以用来制定治疗计划程序,减少人工目标选择的时间密集负担,是相对较优的方法。作者证明了可以将客观选择框架扩展到多个患者,提出的客观选择问题的解决方法可以导致高效和简化的治疗计划,避免耗时和经常无指导的试验和错误。未来可能的工作包括探索限制逆问题的其他距离度量,以及进一步分析基于解剖的贪婪算法。
● 相关好文:
[1] G. Chandrashekar and F. Sahin. A survey on feature selection methods. Computers and Electrical Engineering.
[2] I. Guyon and A. Elisseeff. An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research.
推荐文章3
● 题目:Optimal Product Design by Sequential Experiments in High Dimensions
基于高维序贯实验的产品优化设计
● 期刊:Management Science
● 原文链接:https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/10.1287/mnsc.2018.3088
● 作者:Mingyu Joo, Michael L. Thompson, Greg M. Allenby
● 关键词:设计标准, 预期改善, 交互作用, 随机搜索变量选择
● 摘要:
The identification of optimal product and package designs is challenged when attributes and their levels interact. Firms recognize this by testing trial products and designs prior to launch where the effects of interactions are revealed. A difficulty in conducting analysis for product design is dealing with the high dimensionality of the design space and the selection of promising product configurations for testing. We propose an experimental criterion for efficiently testing product profiles with high demand potential in sequential experiments. The criterion is based on the expected improvement in market share of a design beyond the current best alternative.
We also incorporate a stochastic search variable selection method to selectively estimate relevant interactions among the attributes. A validation experiment confirms that our proposed method leads to improved design concepts in a high-dimensional space compared to alternative methods.
当属性及其水平相互作用时,最佳产品和包装设计的识别受到挑战。企业认识到这一点,通过在产品发布前测试试用产品和设计来揭示相互作用的影响。进行产品设计分析的一个难点是如何处理设计空间的高维性和选择有前景的产品结构进行测试。我们提出了一种在顺序实验中有效测试高需求潜力产品轮廓的实验准则。该标准是基于设计在当前最佳替代方案之外的市场份额的预期改进。
我们还结合了随机搜索变量选择方法来选择性地估计属性之间的相关相互作用。验证实验证实,与其他方法相比,我们提出的方法可以在高维空间中改进设计概念。
● 文章结构:
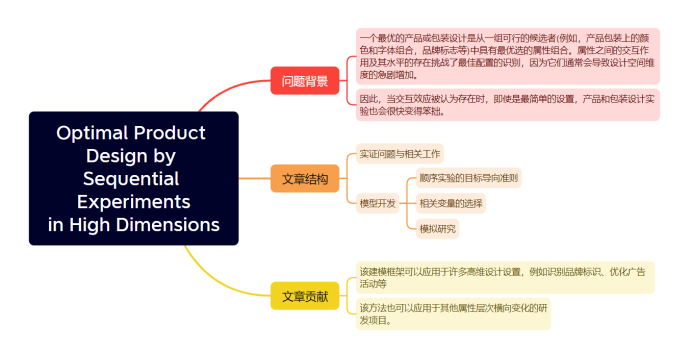
● 核心解法及点评:
此文中用到的特征选择方法是随机搜索变量选择(SSVS),该方法用于有选择地估计主效应和交互效应的相关协变量,它能有效地将不相关的协变量归零,并识别用于受访者对设计概念评估的协变量。基于此,作者使用SSVS评估了所提出的选择标准的预测性能,并对每轮不同数量的受访者和问题进行灵敏度分析。
文中提出了一种利用序列实验进行高维产品优化设计的新方法:如果产品简介能够改进当前最佳设计的结果,则优先考虑纳入,随机搜索变量选择方法通过选择相关变量来降低模型的维数,并且证明了所提出的框架确定了由一家大型包装商品公司进行的大规模研发项目的最佳设计。文中的建模框架可以应用于许多高维设计设置,例如识别品牌标识、优化广告活动等。其方法也可以应用于其他属性层次横向变化的研发项目。当设计属性包含大量的层次,并且所有潜在候选的评估是不可行的时候,提出的框架是特别有效的。
● 相关好文:
[1] George, Edward I., Robert E. McCulloch. 1993. Variable selection via gibbs sampling. Journal of the American Statistical Association.
[2] George, Edward I., Robert E. McCulloch. 1997. Approaches for bayesian variable selection. Statistica Sinica.
[3] Gilbride, Timothy J., Greg M. Allenby, Jeff D. Brazell. 2006. Models for heterogeneous variable selection. Journal of Marketing Research.