请编写一段单词统计Python代码,统计下面两个Python三引号字符串里英文单词的词频。要求:
-
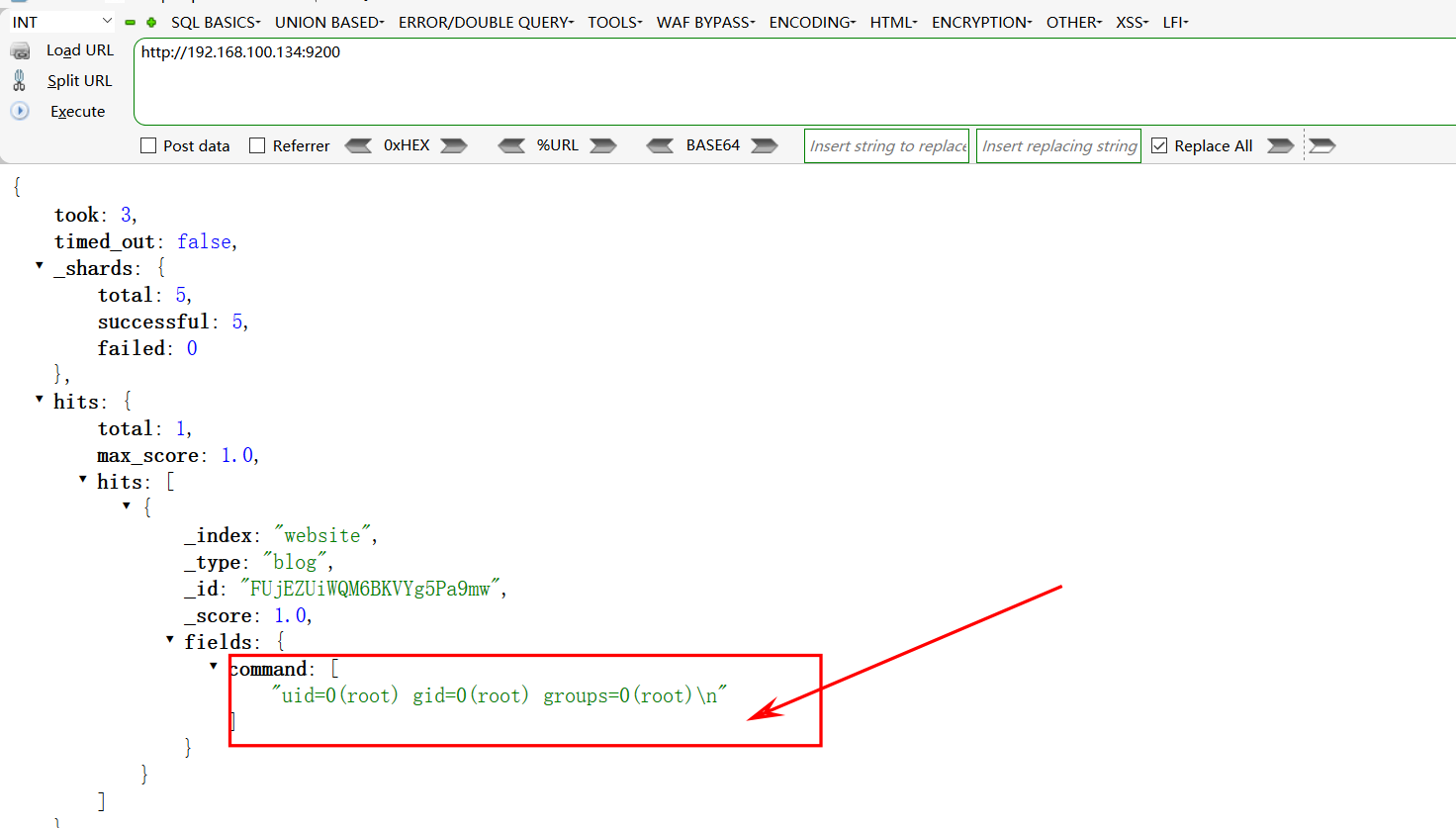
单词请忽略大小写 使用数组splits = ['\n', ' ', '-', ':', '/', '*', '_', '(', ')', '"', '”', '“',']','[']来切割单词 输出词频最高的5个单词和词频信息
'''
* Python 代码风格指南',
* [google-python-styleguide_zh_cn](https://zh-google-styleguide.readthedocs.io/en/latest/google-python-styleguide/python_style_rules /)
* [PEP8](https://legacy.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/)
* 代码风格和自动完成工具链
* 基本工具
* [pylint](https://pylint.org/)
* [autopep8](https://pypi.org/project/autopep8/)
* Visual Studio Code Python 开发基本插件
* Pylance
* Python Path
* Python-autopep8
''' '''
Every major open-source project has its own style guide: a set of conventions (sometimes arbitrary) about how to write code for that project. It is much easier to understand a large codebase when all the code in it is in a consistent style.
“Style” covers a lot of ground, from “use camelCase for variable names” to “never use global variables” to “never use exceptions.” This project (google/styleguide) links to the style guidelines we use for Google code. If you are modifying a project that originated at Google, you may be pointed to this page to see the style guides that apply to that project.
This project holds the C++ Style Guide, C# Style Guide, Swift Style Guide, Objective-C Style Guide, Java Style Guide, Python Style Guide, R Style Guide, Shell Style Guide, HTML/CSS Style Guide, JavaScript Style Guide, TypeScript Style Guide, AngularJS Style Guide, Common Lisp Style Guide, and Vimscript Style Guide. This project also contains cpplint, a tool to assist with style guide compliance, and google-c-style.el, an Emacs settings file for Google style.
'''预期结果:
def top_words(splits, text, top_n=5):
i = 0
word_dict = {}
chars = []
while i < len(text):
c = text[i]
if c in splits:
# 过滤掉分隔字符串
while i+1 < len(text) and text[i+1] in splits:
i += 1
word = ''.join(chars).lower()
# 统计词频
# TODO(You): 请在此添加代码
word_info = word_dict.get(word)
if word_info is None:
word_info = {'word': word, 'count': 1}
word_dict[word] = word_info
else:
word_info['count'] += 1
chars = []
else:
chars.append(c)
i += 1
word_list = list(word_dict.values())
top_n = min(top_n, len(word_list))
word_list.sort(key=lambda word_info: word_info['count'], reverse=True)
return word_list[0:top_n]
if __name__ == '__main__':
google_style_guide = ...
python_style_guides = ...
splits = [' ', '-', ':', '/', '*', '_', '(', ')', '"', '”', '“']
tops = top_words(splits, google_style_guide+python_style_guides)
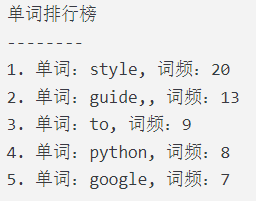
print('单词排行榜')
print('--------')
i = 0
while i < len(tops):
top = tops[i]
word = top['word']
count = top['count']
print(f'{i+1}. 单词:{word}, 词频:{count}')
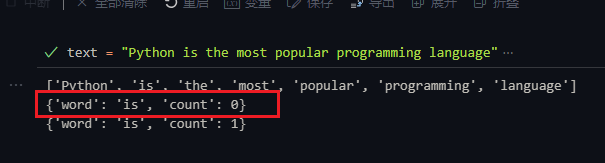
i += 1word_info = word_dict.get(word, {'word': word, 'count': 0})
word_info['count'] += 1
word_dict[word] = word_info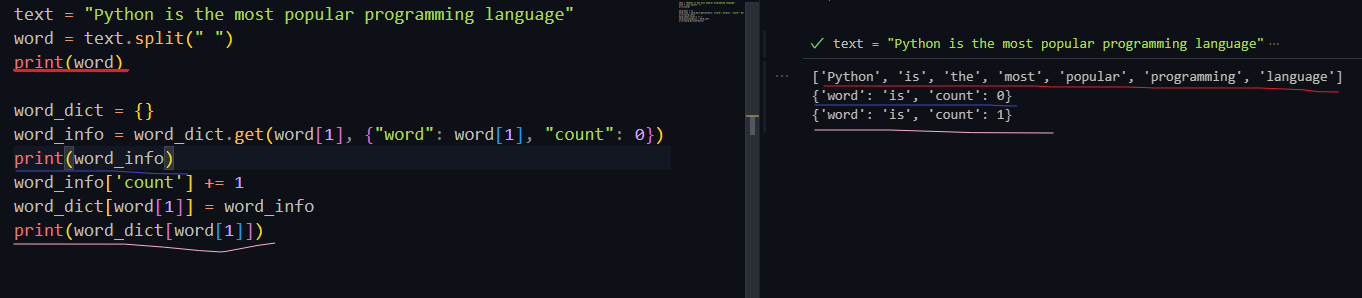
代码理解:
word_dict[word]是以word查找下标
word_info['count']是以count查找下标
类似于key和value里面的key值
word_info输出形式是
如下代码中的赋值看不懂
word_info = word_dict.get(word[1], {"word": word[1], "count": 0})
1. get()方法里面如果word_dict中不包含word会怎么执行?word_info的值为空吗?
如果键不在字典中,想要自己设置返回值
如果键不在字典中,想要自己设置返回值,可以这样处理,例如dict.get(‘键’,‘never’),键在字典中,则返回键对应的值,键不在字典中,则返回never。
dict1={'国家':'中国','首都':'北京'}
print(dict1.get('国家'))
print(dict1.get('首都','never'))
print(dict1.get('省会','never'))
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42709563/article/details/106593628
所以
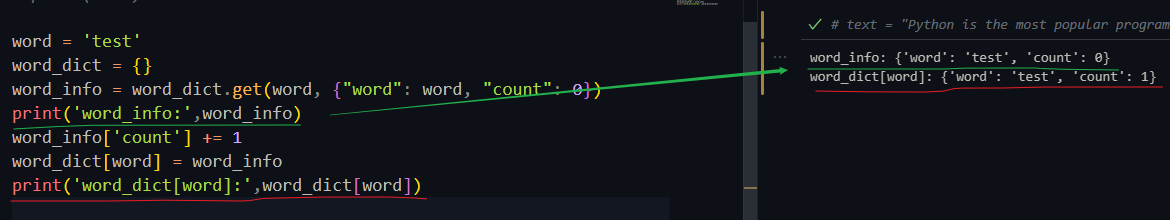
word = 'test'
word_dict = {}
word_info = word_dict.get(word, {"word": word, "count": 0})由于word的值(='test')不在word_dict(为空)字典里,所以get(word,{"word":word,"count":0}的含义是如果不在,直接返回word_info: {'word': 'test', 'count': 0}