哈希本质是的值和位置建立关联起来,这种关联关系就是哈希函数
示例:除留余数:对输入的数字取模。
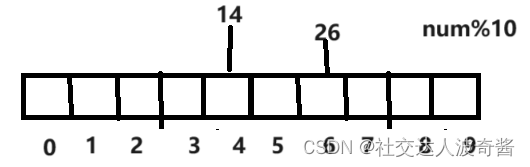
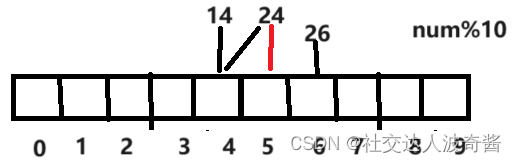
哈希冲突:多个不同的值指向同一个位置

解决方法:
闭散列:开发地址法。
把24放在下一个位置
哈希桶
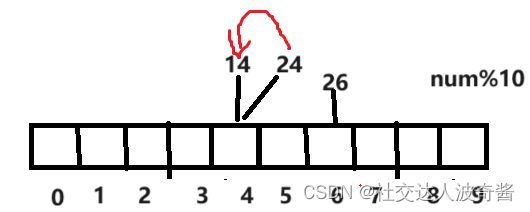
闭散列法
闭散列的负载因子:表元素个数/散列表长度(size),当负载因子达到一定范围时就进行扩容。
扩容会涉及重新映射,取模的范围变大了。
闭散列的元素搜索:闭散列的元素搜索到空截止,要搜索的值只可能往后延,不可能提前,所以如果为空,说明没有。
闭散列的删除:不能直接置空,而是要设置一个状态值表示是否删除。
enum STATE
{
EXIST,
EMPTY,
DELETE
};对于其他类型string,可以选择仿函数来取哈希值,算法上的难点是取哈希值的方式。
其中一个算法
template<>
struct DefaultHashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
// BKDR
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
完整代码
namespace myhashtable {
enum STATE
{
EXIST,
EMPTY,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
STATE _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class K>
struct DefaultHashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefaultHashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
// BKDR
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V,class HashFunc=DefaultHashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(10);
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//扩容
if ((double)_n * 10 / (double)_table.size() >= 0.7)
{
size_t newSize = _table.size() * 2;
// 扩容以后映射关系变了
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._table.resize(newSize);
// 遍历旧表的数据插入新表就可以了
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i]._state == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(_table[i]._kv);
}
}
_table.swap(newHT._table);
}
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi =hf( kv.first) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state == EXIST)
{
++hashi;
hashi %= _table.size();
}
_table[hashi]._kv = kv;
_table[hashi]._state = EXIST;
++_n;
return true;
}
HashData<const K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_table[hashi]._state == EXIST
&& _table[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return (HashData<const K, V>*) & _table[hashi]._kv;
}
++hashi;
hashi %= _table.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashData<const K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<HashData<K, V>> _table;
size_t _n =0;
};
}
哈希桶方法
关键点:哈希表存节点地址,用单链表存冲突的哈希值
namespace bush_bucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V> kv)
{
_kv = kv;
_next = nullptr;
}
};
template<class K,class V>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(10,nullptr);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i= 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
// 扩容
if (_n == _table.size())
{
size_t newSize = _table.size()*2;
vector<Node*> newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newSize;
cur->_next = newTable[hashi];
newTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newTable);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _table.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key% _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _table.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_table[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
printf("[%d]->", i);
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->_kv.first << "->";
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("null");
printf("\n");
}
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table; //指针数组
size_t _n=0;
};
}






![[PwnThyBytes 2019]Baby_SQL - 代码审计+布尔盲注+SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS利用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/428b3ba8ad314ce89825aab1a50a18fe.png#pic_center)