2. 资源管理
文章目录
- 2. 资源管理
- 2.1 资源管理介绍
- 2.2 YAML语言介绍
- 2.3 资源管理方式
- 2.2.1 命令式对象管理
- 2.2.2 命令式对象配置
- 2.2.3 声明式对象配置
- 2.4. 模拟使用普通用户来操作
2.1 资源管理介绍
在kubernetes中,所有的内容都抽象为资源,用户需要通过操作资源来管理kubernetes。
kubernetes的本质上就是一个集群系统,用户可以在集群中部署各种服务,所谓的部署服务,其实就是在kubernetes集群中运行一个个的容器,并将指定的程序跑在容器中。
kubernetes的最小管理单元是pod而不是容器,所以只能将容器放在
Pod中,而kubernetes一般也不会直接管理Pod,而是通过Pod控制器来管理Pod的。Pod可以提供服务之后,就要考虑如何访问Pod中服务,kubernetes提供了
Service资源实现这个功能。当然,如果Pod中程序的数据需要持久化,kubernetes还提供了各种
存储系统。
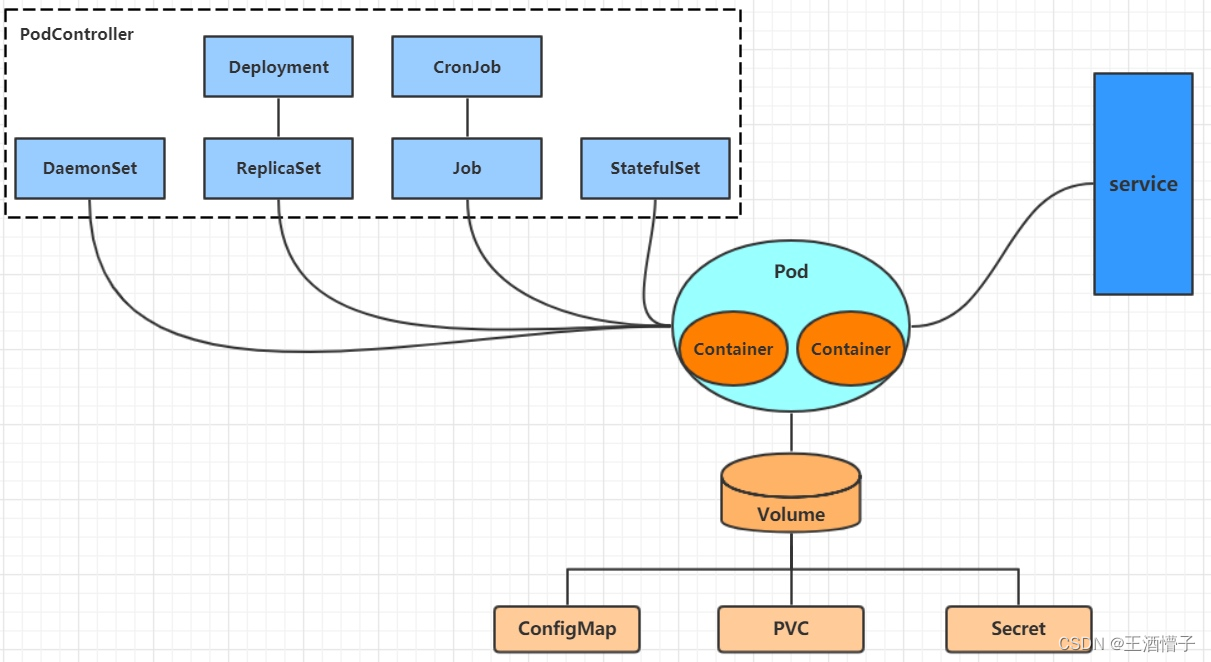
学习kubernetes的核心,就是学习如何对集群上的
Pod、Pod控制器、Service、存储等各种资源进行操作
2.2 YAML语言介绍
YAML是一个类似 XML、JSON 的标记性语言。它强调以数据为中心,并不是以标识语言为重点。因而YAML本身的定义比较简单,号称"一种人性化的数据格式语言"。
<wangqing>
<age>15</age>
<address>Wuhan</address>
</wangqing>
wangqing:
age: 15
address: Wuhan
YAML的语法比较简单,主要有下面几个:
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格( 低版本限制 )
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
YAML支持以下几种数据类型:
- 纯量:单个的、不可再分的值
- 对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hash) / 字典(dictionary)
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
# 纯量, 就是指的一个简单的值,字符串、布尔值、整数、浮点数、Null、时间、日期
# 1 布尔类型
c1: true (或者True)
# 2 整型
c2: 234
# 3 浮点型
c3: 3.14
# 4 null类型
c4: ~ # 使用~表示null
# 5 日期类型
c5: 2018-02-17 # 日期必须使用ISO 8601格式,即yyyy-MM-dd
# 6 时间类型
c6: 2018-02-17T15:02:31+08:00 # 时间使用ISO 8601格式,时间和日期之间使用T连接,最后使用+代表时区
# 7 字符串类型
c7: wangqing # 简单写法,直接写值 , 如果字符串中间有特殊字符,必须使用双引号或者单引号包裹
c8: line1
line2 # 字符串过多的情况可以拆成多行,每一行会被转化成一个空格
# 对象
# 形式一(推荐):
wangqing:
age: 15
address: Wuhan
# 形式二(了解):
wangqing: {age: 15,address: Wuhan}
# 数组
# 形式一(推荐):
address:
- 武昌
- 江夏
# 形式二(了解):
address: [武昌,江夏]
小提示:
1 书写yaml切记
:后面要加一个空格2 如果需要将多段yaml配置放在一个文件中,中间要使用
---分隔3 下面是一个yaml转json的网站,可以通过它验证yaml是否书写正确
https://www.json2yaml.com/convert-yaml-to-json
2.3 资源管理方式
-
命令式对象管理:直接使用命令去操作kubernetes资源
kubectl run nginx-pod --image=nginx:1.17.1 --port=80 -
命令式对象配置:通过命令配置和配置文件去操作kubernetes资源
kubectl create/patch -f nginx-pod.yaml -
声明式对象配置:通过apply命令和配置文件去操作kubernetes资源
kubectl apply -f nginx-pod.yaml
| 类型 | 操作对象 | 适用环境 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 命令式对象管理 | 对象 | 测试 | 简单 | 只能操作活动对象,无法审计、跟踪 |
| 命令式对象配置 | 文件 | 开发 | 可以审计、跟踪 | 项目大时,配置文件多,操作麻烦 |
| 声明式对象配置 | 目录 | 开发 | 支持目录操作 | 意外情况下难以调试 |
2.2.1 命令式对象管理
kubectl命令
kubectl是kubernetes集群的命令行工具,通过它能够对集群本身进行管理,并能够在集群上进行容器化应用的安装部署。kubectl命令的语法如下:
kubectl [command] [type] [name] [flags]
comand:指定要对资源执行的操作,例如create、get、delete
type:指定资源类型,比如deployment、pod、service
name:指定资源的名称,名称大小写敏感
flags:指定额外的可选参数
# 查看所有pod
kubectl get pod
# 查看某个pod
kubectl get pod pod_name
# 查看某个pod,以yaml格式展示结果
kubectl get pod pod_name -o yaml
资源类型
kubernetes中所有的内容都抽象为资源,可以通过下面的命令进行查看:
kubectl api-resources
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
nodes no v1 false Node
persistentvolumeclaims pvc v1 true PersistentVolumeClaim
persistentvolumes pv v1 false PersistentVolume
pods po v1 true Pod
podtemplates v1 true PodTemplate
replicationcontrollers rc v1 true ReplicationController
resourcequotas quota v1 true ResourceQuota
secrets v1 true Secret
serviceaccounts sa v1 true ServiceAccount
services svc v1 true Service
mutatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false MutatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
customresourcedefinitions crd,crds apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 false CustomResourceDefinition
apiservices apiregistration.k8s.io/v1 false APIService
controllerrevisions apps/v1 true ControllerRevision
daemonsets ds apps/v1 true DaemonSet
deployments deploy apps/v1 true Deployment
replicasets rs apps/v1 true ReplicaSet
statefulsets sts apps/v1 true StatefulSet
tokenreviews authentication.k8s.io/v1 false TokenReview
localsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 true LocalSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectrulesreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectRulesReview
subjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SubjectAccessReview
horizontalpodautoscalers hpa autoscaling/v2 true HorizontalPodAutoscaler
cronjobs cj batch/v1 true CronJob
jobs batch/v1 true Job
certificatesigningrequests csr certificates.k8s.io/v1 false CertificateSigningRequest
leases coordination.k8s.io/v1 true Lease
endpointslices discovery.k8s.io/v1 true EndpointSlice
events ev events.k8s.io/v1 true Event
flowschemas flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 false FlowSchema
prioritylevelconfigurations flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 false PriorityLevelConfiguration
ingressclasses networking.k8s.io/v1 false IngressClass
ingresses ing networking.k8s.io/v1 true Ingress
networkpolicies netpol networking.k8s.io/v1 true NetworkPolicy
runtimeclasses node.k8s.io/v1 false RuntimeClass
poddisruptionbudgets pdb policy/v1 true PodDisruptionBudget
clusterrolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRoleBinding
clusterroles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRole
rolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true RoleBinding
roles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true Role
priorityclasses pc scheduling.k8s.io/v1 false PriorityClass
csidrivers storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSIDriver
csinodes storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSINode
csistoragecapacities storage.k8s.io/v1 true CSIStorageCapacity
storageclasses sc storage.k8s.io/v1 false StorageClass
volumeattachments storage.k8s.io/v1 false VolumeAttachment
//nodes no 缩写
pods po 缩写
经常使用的资源有下面这些:
| 资源分类 | 资源名称 | 缩写 | 资源作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 集群级别资源 | nodes | no | 集群组成部分 |
| namespaces | ns | 隔离Pod | |
| pod资源 | pods | po | 装载容器 |
| pod资源控制器 | replicationcontrollers | rc | 控制pod资源 |
| replicasets | rs | 控制pod资源 | |
| deployments | deploy | 控制pod资源 | |
| daemonsets | ds | 控制pod资源 | |
| jobs | 控制pod资源 | ||
| cronjobs | cj | 控制pod资源 | |
| horizontalpodautoscalers | hpa | 控制pod资源 | |
| statefulsets | sts | 控制pod资源 | |
| 服务发现资源 | services | svc | 统一pod对外接口 |
| ingress | ing | 统一pod对外接口 | |
| 存储资源 | volumeattachments | 存储 | |
| persistentvolumes | pv | 存储 | |
| persistentvolumeclaims | pvc | 存储 | |
| 配置资源 | configmaps | cm | 配置 |
| secrets | 配置 |
操作
kubernetes允许对资源进行多种操作,可以通过–help查看详细的操作命令
kubectl --help
经常使用的操作有下面这些:
| 命令分类 | 命令 | 翻译 | 命令作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基本命令 | create | 创建 | 创建一个资源 |
| edit | 编辑 | 编辑一个资源 | |
| get | 获取 | 获取一个资源 | |
| patch | 更新 | 更新一个资源 | |
| delete | 删除 | 删除一个资源 | |
| explain | 解释 | 展示资源文档 | |
| 运行和调试 | run | 运行 | 在集群中运行一个指定的镜像 |
| expose | 暴露 | 暴露资源为Service | |
| describe | 描述 | 显示资源内部信息 | |
| logs | 日志输出容器在 pod 中的日志 | 输出容器在 pod 中的日志 | |
| attach | 缠绕进入运行中的容器 | 进入运行中的容器 | |
| exec | 执行容器中的一个命令 | 执行容器中的一个命令 | |
| cp | 复制 | 在Pod内外复制文件 | |
| rollout | 首次展示 | 管理资源的发布 | |
| scale | 规模 | 扩(缩)容Pod的数量 | |
| autoscale | 自动调整 | 自动调整Pod的数量 | |
| 高级命令 | apply | rc | 通过文件对资源进行配置 |
| label | 标签 | 更新资源上的标签 | |
| 其他命令 | cluster-info | 集群信息 | 显示集群信息 |
| version | 版本 | 显示当前Server和Client的版本 |
下面以一个namespace / pod的创建和删除简单演示下命令的使用:
//查看当前有哪些namespace
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 64d //不指定名称空间,默认使用这个
kube-flannel Active 64d
kube-node-lease Active 64d
kube-public Active 64d
kube-system Active 64d
//创建一个名为dev的名称空间
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create namespace dev
namespace/dev created
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 64d
dev Active 4s //创建成功
kube-flannel Active 64d
kube-node-lease Active 64d
kube-public Active 64d
kube-system Active 64d
//在此namespace下创建并运行一个nginx的Pod
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl run pod --image=nginx:latest -n dev
pod/pod created
//查看新创建的pod
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev // -n 指定查看那个名称空间
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod 1/1 Running 0 35s
//删除指定的pod
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl delete pod pod -n dev
pod "pod" deleted
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
//删除指定的namespace
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl delete namespace dev
namespace "dev" deleted
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 64d
kube-flannel Active 64d
kube-node-lease Active 64d
kube-public Active 64d
kube-system Active 64d
// kubectl run httpd --image=httpd --port=80 // 自主式pod,删除不会有接替的
// kubectl create deployment httpd --image=httpd // 这个是使用deployment类型创建的
// kubectl expose deployment httpd --port=80 --type=NodePort // 暴露端口号
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-77b4fdf86c-xn5l9 1/1 Running 0 47h //这个是使用deployment类型创建的
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-77b4fdf86c-xn5l9 1/1 Running 0 47h
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1/1 1 1 47h
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl delete pod nginx-77b4fdf86c-xn5l9 //删除它,会自主替换 因为是deployment
pod "nginx-77b4fdf86c-xn5l9" deleted
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-77b4fdf86c-jsz8r 1/1 Running 0 5s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl delete deployment nginx //只有这样删除才不会出现替换
deployment.apps "nginx" deleted
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods
No resources found in default namespace.
2.2.2 命令式对象配置
命令式对象配置就是使用命令配合配置文件一起来操作kubernetes资源。
1) 创建一个nginxpod.yaml,内容如下:
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir inventory //创建inventory目录存放yaml文件
[root@k8s-master ~]# cd inventory/
[root@k8s-master inventory]# ls
[root@k8s-master inventory]# vi nginx.yaml
apiVersion: v1 //版本v1
kind: Namespace //类型名称空间
metadata:
name: dev //名称空间叫dev
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod //类型是pod类型
metadata:
name: nginxpod //pod名字叫nginxpod
namespace: dev //这个pod 跑在dev 名称空间里
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-containers // 这个pod 里面跑的容器叫 nginx-containers
image: nginx:latest // 用的镜像是 nginx:latest
//创建 Pod 查找方式
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl explain --help
List the fields for supported resources.
This command describes the fields associated with each supported API resource. Fields are identified via a simple
JSONPath identifier:
<type>.<fieldName>[.<fieldName>]
Add the --recursive flag to display all of the fields at once without descriptions. Information about each field is
retrieved from the server in OpenAPI format.
Use "kubectl api-resources" for a complete list of supported resources.
Examples:
# Get the documentation of the resource and its fields
kubectl explain pods //第一步
# Get the documentation of a specific field of a resource
kubectl explain pods.spec.containers //第二步
Options:
--api-version='':
Get different explanations for particular API version (API group/version)
--output='plaintext':
Format in which to render the schema (plaintext, plaintext-openapiv2)
--recursive=false:
Print the fields of fields (Currently only 1 level deep)
Usage:
kubectl explain RESOURCE [options]
Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl explain pods
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is
created by clients and scheduled onto hosts.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object.
Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and
may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <ObjectMeta>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <PodSpec>
Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
status <PodStatus>
Most recently observed status of the pod. This data may not be up to date.
Populated by the system. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl explain pods.apiVersion //查看版本
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
FIELD: apiVersion <string>
DESCRIPTION:
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object.
Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and
may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
//创建控制器的查找方式
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl explain deployment
GROUP: apps
KIND: Deployment
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Deployment enables declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object.
Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and
may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <ObjectMeta>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <DeploymentSpec>
Specification of the desired behavior of the Deployment.
status <DeploymentStatus>
Most recently observed status of the Deployment.
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl explain deployment.spec
GROUP: apps
KIND: Deployment
VERSION: v1
FIELD: spec <DeploymentSpec>
DESCRIPTION:
Specification of the desired behavior of the Deployment.
DeploymentSpec is the specification of the desired behavior of the
Deployment.
FIELDS:
minReadySeconds <integer>
Minimum number of seconds for which a newly created pod should be ready
without any of its container crashing, for it to be considered available.
Defaults to 0 (pod will be considered available as soon as it is ready)
paused <boolean>
Indicates that the deployment is paused.
progressDeadlineSeconds <integer>
The maximum time in seconds for a deployment to make progress before it is
considered to be failed. The deployment controller will continue to process
failed deployments and a condition with a ProgressDeadlineExceeded reason
will be surfaced in the deployment status. Note that progress will not be
estimated during the time a deployment is paused. Defaults to 600s.
replicas <integer>
Number of desired pods. This is a pointer to distinguish between explicit
zero and not specified. Defaults to 1.
revisionHistoryLimit <integer>
The number of old ReplicaSets to retain to allow rollback. This is a pointer
to distinguish between explicit zero and not specified. Defaults to 10.
selector <LabelSelector> -required- //出现这个是必须要用的
Label selector for pods. Existing ReplicaSets whose pods are selected by
this will be the ones affected by this deployment. It must match the pod
template's labels.
strategy <DeploymentStrategy>
The deployment strategy to use to replace existing pods with new ones.
2)执行create命令,创建资源:
[root@k8s-master inventory]# pwd
/root/inventory
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl create -f nginx.yaml
namespace/dev created
pod/nginxpod created
此时发现创建了两个资源对象,分别是namespace和pod
3)执行get命令,查看资源:
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -f nginx.yaml
NAME STATUS AGE
namespace/dev Active 33s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 33s
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 64d
dev Active 73s // 刚创建的 dev 名称空间
kube-flannel Active 64d
kube-node-lease Active 64d
kube-public Active 64d
kube-system Active 64d
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -n dev pods // 查看所有在dev 的pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 94s
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -n dev pod nginxpod // 指定查看哪个pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 106s
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -n dev pods -o wide //查看所有容器在那个主机上运行、IP是多少
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.244.1.3 k8s-node1 <none> <none>
这样就显示了两个资源对象的信息
4)执行delete命令,删除资源:
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml
namespace "dev" deleted
pod "nginxpod" deleted
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -n dev pods
No resources found in dev namespace.
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 64d
kube-flannel Active 64d
kube-node-lease Active 64d
kube-public Active 64d
kube-system Active 64d
此时发现两个资源对象被删除了
总结:
命令式对象配置的方式操作资源,可以简单的认为:命令 + yaml配置文件(里面是命令需要的各种参数)
2.2.3 声明式对象配置
声明式对象配置跟命令式对象配置很相似,但是它只有一个命令apply。
# 首先执行一次kubectl apply -f yaml文件,发现创建了资源
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
namespace/dev created
pod/nginxpod created
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get -n dev pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 68s
# 再次执行一次kubectl apply -f yaml文件,发现说资源没有变动
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
namespace/dev unchanged//已经存在
pod/nginxpod unchanged //已经存在
总结:
其实声明式对象配置就是使用apply描述一个资源最终的状态(在yaml中定义状态)
使用apply操作资源:
如果资源不存在,就创建,相当于 kubectl create
如果资源已存在,就更新,相当于 kubectl patch
扩展:kubectl可以在node节点上运行吗 ?
kubectl的运行是需要进行配置的,它的配置文件是$HOME/.kube,如果想要在node节点运行此命令,需要将master上的.kube文件复制到node节点上,即在master节点上执行下面操作:
scp -r HOME/.kube node1: HOME/ # 哪个普通用户就放到哪个的对应用户里
2.4. 模拟使用普通用户来操作
使用k8s-node1来模拟
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
[root@k8s-master ~]# useradd tom
[root@k8s-master ~]# id tom
uid=1000(tom) gid=1000(tom) groups=1000(tom)
[root@k8s-master ~]# su - tom
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get nodes // 普通用户使用不了 kubectl
error: error loading config file "/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf": open /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf: permission denied
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ ls -a
. .. .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .kube
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ su //使用 root 不然没有权限
Password:
[root@k8s-master tom]# cd
[root@k8s-master ~]# cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf ~tom/.kube/config
[root@k8s-master ~]# chown -R tom.tom ~tom/.kube/
[root@k8s-master ~]# su tom
[tom@k8s-master root]$ cd
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ ll .kube/ -d
drwxrwxr-x 2 tom tom 20 Oct 5 14:05 .kube/
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ ll .kube/
total 8
-rw------- 1 tom tom 5638 Oct 5 14:05 config
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ echo $KUBECONFIG // 因为之前使用管理员做的,所以需要把管理员做的那一步骤取消掉
/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ export KUBECONFIG=
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ echo $KUBECONFIG
[tom@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get nodes // 设置完成之后就可以使用 kubectl
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane 71d v1.27.0
k8s-node1 Ready <none> 71d v1.27.0
k8s-node2 Ready <none> 71d v1.27.0
创建/更新资源 使用声明式对象配置 kubectl apply -f XXX.yaml
删除资源 使用命令式对象配置 kubectl delete -f XXX.yaml
查询资源 使用命令式对象管理 kubectl get(describe) 资源名称
模拟k8s节点出现宕机的情况
[root@k8s-master inventory]# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-77b4fdf86c-mt7wg 1/1 Running 0 26s 10.244.1.5 k8s-node1 <none> <none>
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes //k8s-node1已经关机了
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane 71d v1.27.0
k8s-node1 NotReady <none> 71d v1.27.0
k8s-node2 Ready <none> 71d v1.27.0
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide //可以看到k8s-node2已经替代了k8s-node1
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-77b4fdf86c-mt7wg 1/1 Terminating 0 32m 10.244.1.5 k8s-node1 <none> <none>
nginx-77b4fdf86c-pk5rh 1/1 Running 0 17m 10.244.2.4 k8s-node2 <none> <none>
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-77b4fdf86c-mt7wg 1/1 Terminating 0 34m
pod/nginx-77b4fdf86c-pk5rh 1/1 Running 0 19m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 71d
service/nginx NodePort 10.110.234.211 <none> 80:31982/TCP 9d