- 任务分割
- 异步执行
- 让出执法权
文章目录
- 1.React的设计理念
- 1.1 Fiber
- 1.2 Scheduler
- 1.3 Lane
- 1.4 代数效应
- 2.React的源码架构
- 2.1 大概图示
- 2.2 jsx
- 2.3 Fiber双缓存
- 2.4 scheduler
- 2.5 Lane模型
- 2.6 reconciler
- 2.7 renderer
- 2.8 concurrent
- 3.React源码调试
1.React的设计理念
- Fiber: 即对应真实dom, 又作为分隔单元。
- Scheduler: 用js实现一套时间片运行的机制, 使得requestIdleCallback()的浏览器的兼容性和触发不稳定的问题解决。
- Lane: 异步调度有了, 需要细粒度的管理各个任务的优先级, 让高优先级的先执行, 各个Fiber工作单元还能比较优先级, 优先级相同的一起执行。
上面的机制能实现batchedUpdates批量更新和Suspense
1.1 Fiber
Fiber: react15的更新是同步的,因为它不能将任务分割,所以需要一套数据结构让它既能对应真实的dom又能作为分隔的单元,这就是Fiber。
- 对应真实dom。
- 作为分割单元。
let firstFiber
let nextFiber = firstFiber
let shouldYield = false
//firstFiber->firstChild->sibling
function performUnitOfWork(nextFiber){
//...
return nextFiber.next
}
function workLoop(deadline){
while(nextFiber && !shouldYield){
nextFiber = performUnitOfWork(nextFiber)
shouldYield = deadline.timeReaming < 1
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop)
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop)
1.2 Scheduler
Scheduler: 有了Fiber, 需要用浏览器的时间片异步执行这些Fiber的工作单元, 有一个Api是requestIdleCallback(), 可以在浏览器空闲的时候执行一些任务, 用这个api执行react的更新。requestIdleCallback存在着浏览器的兼容性和触发不稳定的问题, 需要用js实现一套时间片运行的机制, react称为Scheduler。
1.3 Lane
Lane: 异步调度有了, 需要细粒度的管理各个任务的优先级, 让高优先级的先执行, 各个Fiber工作单元还能比较优先级, 优先级相同的一起执行。
1.4 代数效应
除了cpu的瓶颈问题, 还存在一些副作用, 比如获取数据、文件操作等。不同设备性能和网络状况都不一样, react如何处理这些问题, 需要react可以有分离副作用的能力, 解耦, 这就是代数效应。
function getPrice(id) {
return fetch(`xxx.com?id=${productId}`).then((res)=>{
return res.price
})
}
async function getTotalPirce(id1, id2) {
const p1 = await getPrice(id1);
const p2 = await getPrice(id2);
return p1 + p2;
}
async function run(){
await getTotalPrice('001', '002');
}
getPrice()是一个异步获取数据的方法, 可以用async+await的方式获取数据, 但是会导致调用getTotalPrice的run方法也会变成异步函数, 这就是async的传染性(副作用)。
function usePrice(id) {
useEffect((id)=>{
fetch(`xxx.com?id=${productId}`).then((res)=>{
return res.price
})
}, [])
}
function TotalPirce({id1, id2}) {
const p1 = usePrice(id1);
const p2 = usePrice(id2);
return <TotalPirce props={...}>
}
getPrice换成usePrice, getTotalPirce换成TotalPirce组件, 这是hook的分离副作用能力。
generator: 也是有一定的传染性的, generator不能计算优先级, 排序优先级。
function getPrice(id) {
return fetch(`xxx.com?id=${productId}`).then((res)=>{
return res.price
})
}
function* getTotalPirce(id1, id2) {
const p1 = yield getPrice(id1);
const p2 = yield getPrice(id2);
return p1 + p2;
}
function* run(){
yield getTotalPrice('001', '002');
}
解耦副作用在函数式编程的实践中非常常见, 如react-saga, 将副作用从saga中分离, 自己不处理副作用, 发请求处理。
function* fetchUser(action) {
try {
const user = yield call(Api.fetchUser, action.payload.userId);
yield put({type: "USER_FETCH_SUCCEEDED", user: user});
} catch (e) {
yield put({type: "USER_FETCH_FAILED", message: e.message});
}
}
2.React的源码架构
- Scheduler(调度器): 排序优先级,让优先级高的任务先进行reconcile
- Reconciler(协调器): 找出哪些节点发生了改变,并打上不同的Flags(旧版本react叫Tag)
- Renderer(渲染器): 将Reconciler中打好标签的节点渲染到视图上

2.1 大概图示
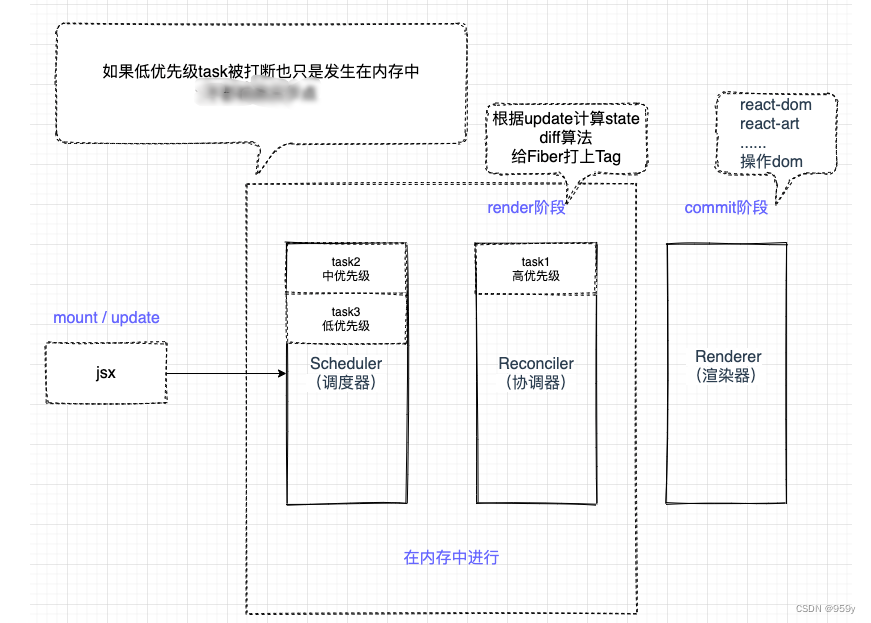
jsx(mount/update) -> scheduler(render) -> reconciler(render) -> rerender(commit)
2.2 jsx
jsx: React通过Babel解析, 将jsx转换成React.createElement, React.createElement方法返回virtual-dom对象React.createElement方法返回virtual-dom对象, 所有jsx本质上就是React.createElement的语法糖。
createElement -> ReactElement
export function createElement(type, config, children) {
let propName;
// Reserved names are extracted
const props = {};
let key = null;
let ref = null;
let self = null;
let source = null;
if (config != null) {
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref;
if (__DEV__) {
warnIfStringRefCannotBeAutoConverted(config);
}
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
key = '' + config.key;
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source;
// Remaining properties are added to a new props object
for (propName in config) {
if (
hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)
) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
const childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
const childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (let i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// Resolve default props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (key || ref) {
const displayName =
typeof type === 'function'
? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown'
: type;
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
}
}
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
self,
source,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props,
);
}
const ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
const element = {
// This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
if (__DEV__) {
// The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on
// an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object.
// This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in
// commonly used development environments.
element._store = {};
// To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make
// the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should
// include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework
// ignores it.
Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
value: false,
});
// self and source are DEV only properties.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: self,
});
// Two elements created in two different places should be considered
// equal for testing purposes and therefore we hide it from enumeration.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: source,
});
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(element.props);
Object.freeze(element);
}
}
return element;
};
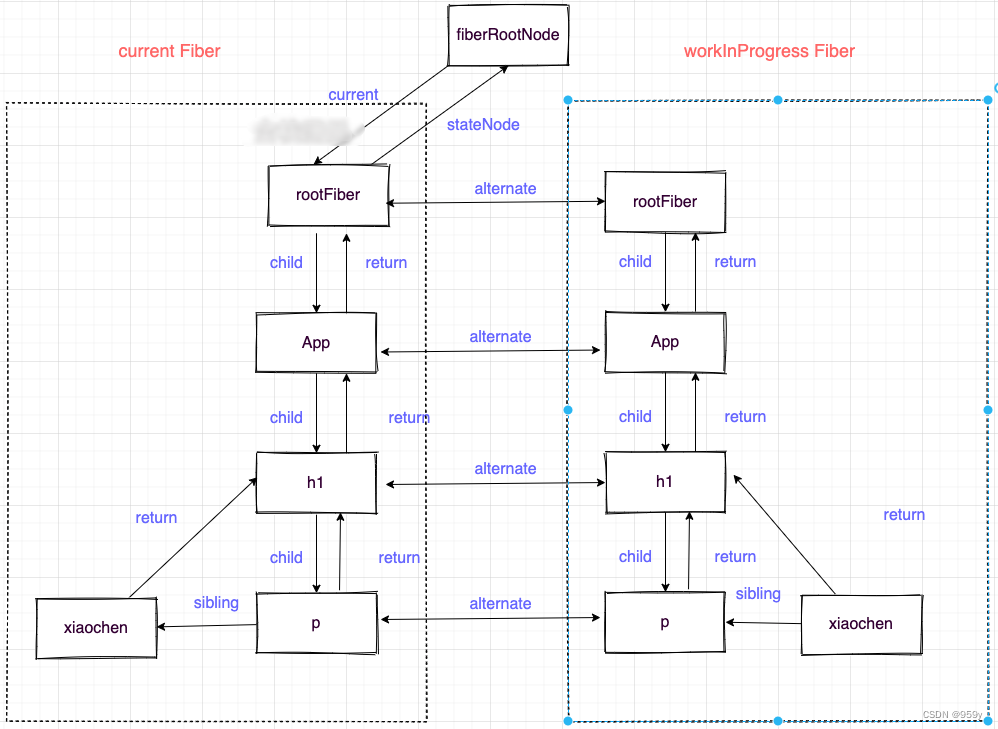
2.3 Fiber双缓存
Fiber对象上面保存了包括这个节点的属性, dom, 类型, 通过child, sibling, reture 形成fiber树, 保存了更新状态时用于计算state的updateQueue, updateQueue为一个链表, 上面存在未计算的update, update也是一个数据结构, 上面存有更新的数据、优先级等, 还有副作用的信息。
双缓存是指存在两颗Fiber树, current Fiber树描述了当前呈现的dom树, workInProgress Fiber是正在更新的Fiber树, 这两树都是存在于内存, 在workInProgress Fiber构建完成之后会将它作为current Fiber应用到dom上。
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<>
<h1 onClick={() => {
setCount(() => count + 1);
}}>
<p title={count}>{count}</p>
</h1>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));
2.4 scheduler
Scheduler的作用是调度任务。
在Scheduler中的每个任务的优先级使用过期时间表示的, 如果一个任务的过期时间离现在很近, 说明要过期了, 优先级很高。
没有过期的放在timerQueue中, 过期的放taskQueue, timerQueue和taskQueue都是小顶堆, 所以peek出的都是离现在时间最近也就是优先级最高的那个任务。
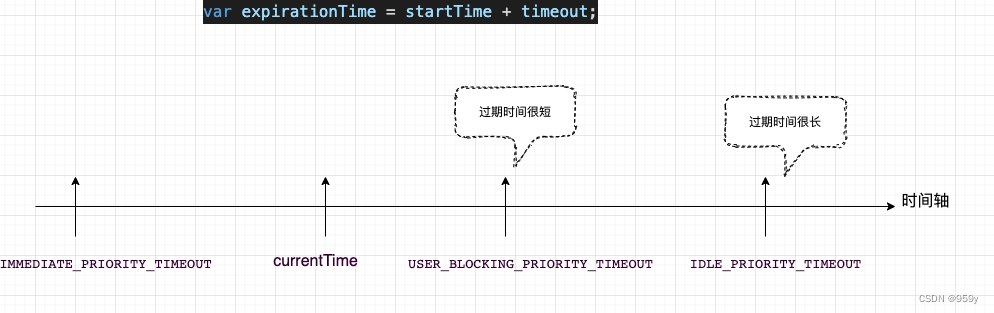
2.5 Lane模型
优先级表示方法Lane: Lane使用二进制的方式表示优先级, 1表示位置, 同一个二进制数可以有多个相同优先级的位, 这就可以表示‘批’的概念。低优先级的任务如果被高优先级的任务一直打断, 等到达它的时候, 优先级自动变为最高。
bit越多, 优先级越低。
//ReactFiberLane.js
export const NoLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const NoLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const SyncLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000001;
export const SyncBatchedLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000010;
export const InputDiscreteHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000100;
const InputDiscreteLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000011000;
const InputContinuousHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000100000;
const InputContinuousLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000011000000;
export const DefaultHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000100000000;
export const DefaultLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000111000000000;
const TransitionHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000001000000000000;
const TransitionLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000001111111110000000000000;
const RetryLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000011110000000000000000000000;
export const SomeRetryLane: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000010000000000000000000000000;
export const SelectiveHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000100000000000000000000000000;
const NonIdleLanes = /* */ 0b0000111111111111111111111111111;
export const IdleHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0001000000000000000000000000000;
const IdleLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0110000000000000000000000000000;
export const OffscreenLane: Lane = /* */ 0b1000000000000000000000000000000;
2.6 reconciler
Reconciler发生在render阶段, render分为节点执行beginWork和completeWork, 或是计算state, 对比节点的差异, 为节点赋值相应的effectFlags。
Reconciler会创建或者更新Fiber节点。在mount的时候会根据jsx生成Fiber对象,在update的时候会根据最新的state形成的jsx对象和current Fiber树对比构建workInProgress Fiber树, 对比就是diff算法。
diff算法发生在render阶段的reconcileChildFibers函数中, diff算法分为单节点的diff和多节点的diff, 单节点会根据节点的key和type, props判断节点是复用还是直接新创建节点, 多节点diff会涉及节点的增删和节点位置的变化。
reconcile时会在这些Fiber上打上Flags标签, 在commit阶段把这些标签应用到真实dom上, 这些标签代表了节点的增删改。
//ReactFiberFlags.js
export const Placement = /* */ 0b0000000000010;
export const Update = /* */ 0b0000000000100;
export const PlacementAndUpdate = /* */ 0b0000000000110;
export const Deletion = /* */ 0b0000000001000;
render阶段遍历Fiber树类似dfs的过程, ‘捕获’阶段发生在beginWork函数中, 该函数做的主要工作是创建Fiber节点, 计算state和diff算法, ‘冒泡’阶段发生在completeWork中, 该函数主要是做一些收尾工作, 例如处理节点的props、和形成一条effectList的链表, 该链表是被标记了更新的节点形成的链表。
function App() {
return (
<>
<h1>
<p>count</p> xiaochen
</h1>
</>
)
}
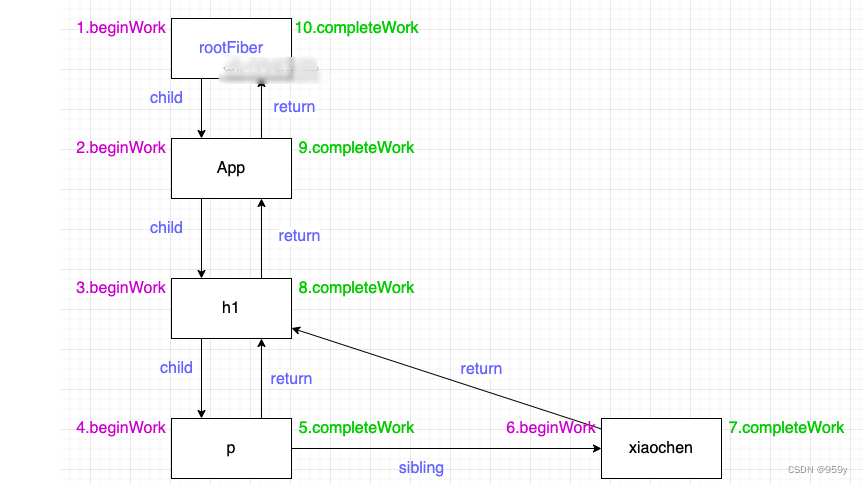
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<>
<h1
onClick={() => {
setCount(() => count + 1);
}}
>
<p title={count}>{count}</p> xiaochen
</h1>
</>
)
}
如果p和h1节点更新了则effectList如下, rootFiber->h1->p, fiberRoot是整个项目的根节点, rootFiber为应用的根节点, 可以有多个。
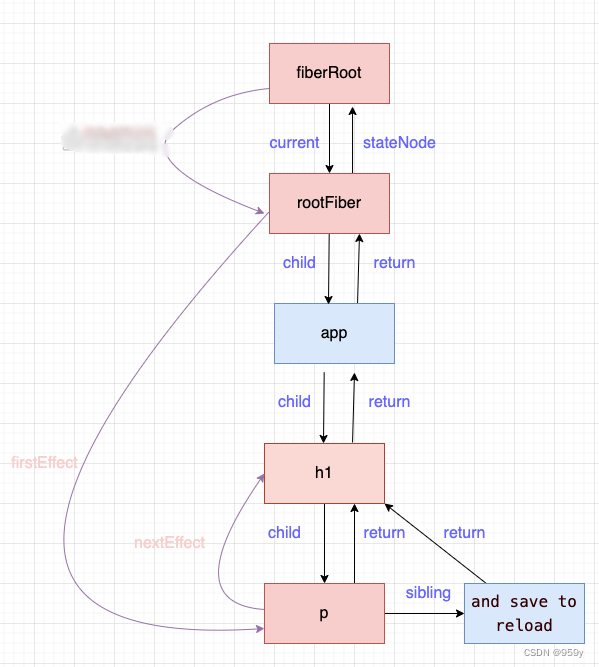
2.7 renderer
Renderer发生在commit阶段, commit阶段遍历effectList执行对应的dom操作或部分生命周期。并执行真实dom节点的操作和一些生命周期, 不同的平台对应的Renderer不同, 浏览器对应的是react-dom。
commit阶段发生在commitRoot函数中, 遍历effectList, 三个函数来处理effectList上的节点, commitBeforeMutationEffects, commitMutationEffects, commitLayoutEffects。
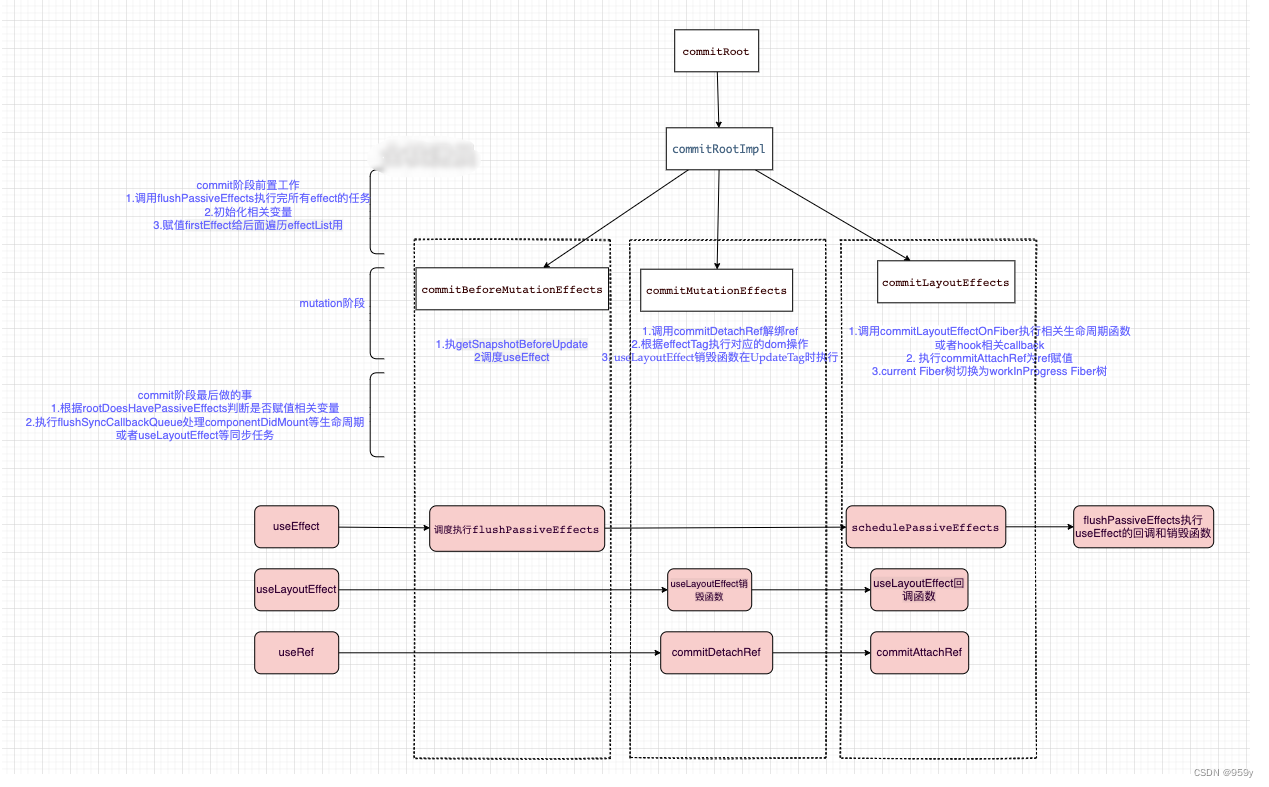
2.8 concurrent
一类功能的合集(如fiber、schduler、lane、suspense), 目的是为了提高应用的响应速度, 使应用cpu密集型的更新不在那么卡顿, 核心是实现了一套异步可中断、带优先级的更新。
3.React源码调试

- fixtures:为代码贡献者提供的测试React
- packages:主要部分,包含Scheduler,reconciler等
- scripts:react构建相关
-
react:核心Api如:React.createElement、React.Component都在这
-
和平台相关render相关的文件夹:
react-art:如canvas svg的渲染
react-dom:浏览器环境
react-native-renderer:原生相关 react-noop-renderer:调试或者fiber用 -
试验性的包
react-server: ssr相关
react-fetch: 请求相关
react-interactions: 和事件如点击事件相关
react-reconciler: 构建节点
shared:包含公共方法和变量 -
辅助包:
react-is : 判断类型
react-client: 流相关
react-fetch: 数据请求相关 -
react-refresh: 热加载相关
-
scheduler:调度器相关
-
React-reconciler:在render阶段用它来构建fiber节点