简介:Doctest 是 Python 标准库的一部分,它允许开发者通过在文档字符串(docstrings)中编写示例来进行测试。这不仅可以在确保代码正确性的同时编写文档,还可以让读者更容易理解代码的用法和期望的输出。
历史攻略:
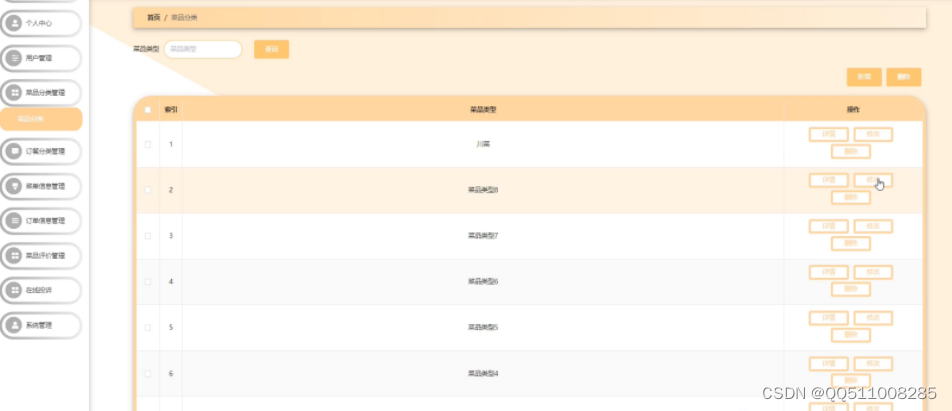
unittest:参数化ddt使用案例
Python:unittest-mock使用
pytest+allure安装和使用
pytest:并行和并发运行用例
让你的pytest日志更有序:配置和使用技巧
对比 unittest、pytest 优势:
1、简洁性:与 unittest 和 pytest 相比,Doctest 的语法更为简洁,它将测试示例写在文档字符串中,让测试看起来更清晰、易读。
2、直观性:通过阅读 Doctest 中的示例,开发者和用户能够快速理解函数或方法的用法。
3、易用性:Doctest 不需要额外的安装和配置,它是 Python 标准库的一部分,可以直接使用。
安装:Doctest 是 Python 的内置库,不需要额外的安装。
参数说明:常见的参数:
-v:启用详细模式,显示所有测试用例的输出结果。
doctest.testmod():运行当前模块中的所有 Doctest。
verbose 参数,如果设置为True则在执行测试的时候会输出详细信息。
默认是False,表示运行测试时,只有失败的用例会输出详细信息,成功的测试用例不会输出任何信息。
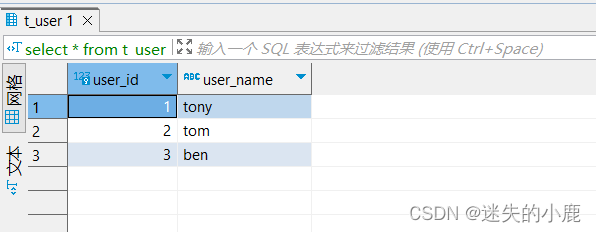
案例: 测试加法函数、测试字符串反转函数、在类对象方法的使用。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# time: 2023/9/26 0:47
# file: doctest_demo.py
# 公众号: 玩转测试开发
import doctest
def add(a, b):
"""
# case1 加法函数
This function adds two numbers and returns the sum.
>>> add(2, 3)
5
>>> add(-1, 1)
0
"""
return a + b
def reverse_string(s):
"""
# case2 翻转字符串函数
This function returns the reversed string.
>>> reverse_string('hello')
'olleh'
>>> reverse_string('Python')
'nohtyP'
"""
return s[::-1]
class Cat:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def fishing(self):
"""
>>> c = Cat('tom', 5)
>>> c.fishing()
tom is a cat, 5 years old, and now he is fishing.
True
>>> c = Cat('Lucy', 22)
>>> c.fishing()
Lucy is too old to fish.
False
>>> c = Cat('Lily', 1)
>>> c.fishing()
Lily is too young to fish yet.
False
"""
if 2 <= self.age <= 20:
print(f"{self.name} is a cat, {self.age} years old, and now he is fishing.")
return True
elif self.age < 2:
print(f"{self.name} is too young to fish yet.")
return False
else:
print(f"{self.name} is too old to fish.")
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
doctest.testmod(verbose=True)
运行结果:
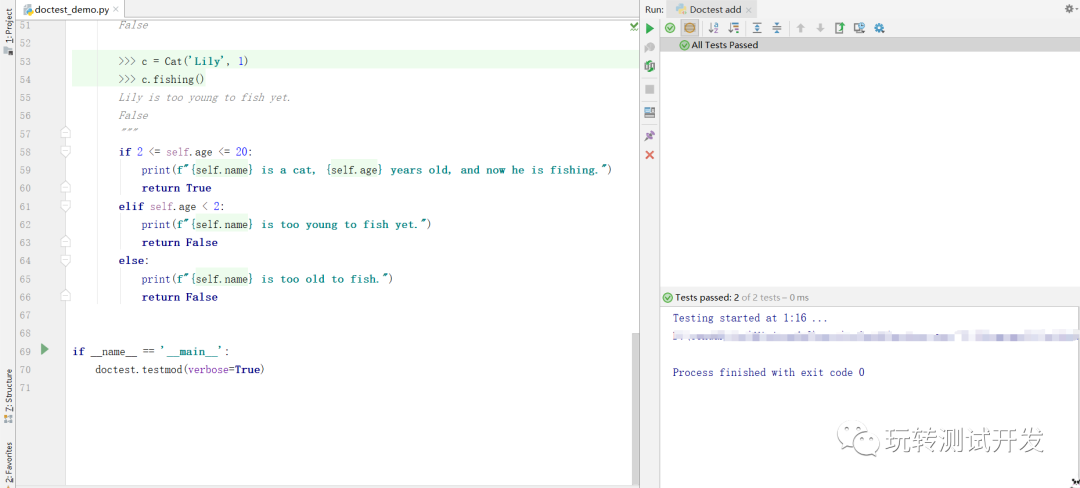
不符合预期时:
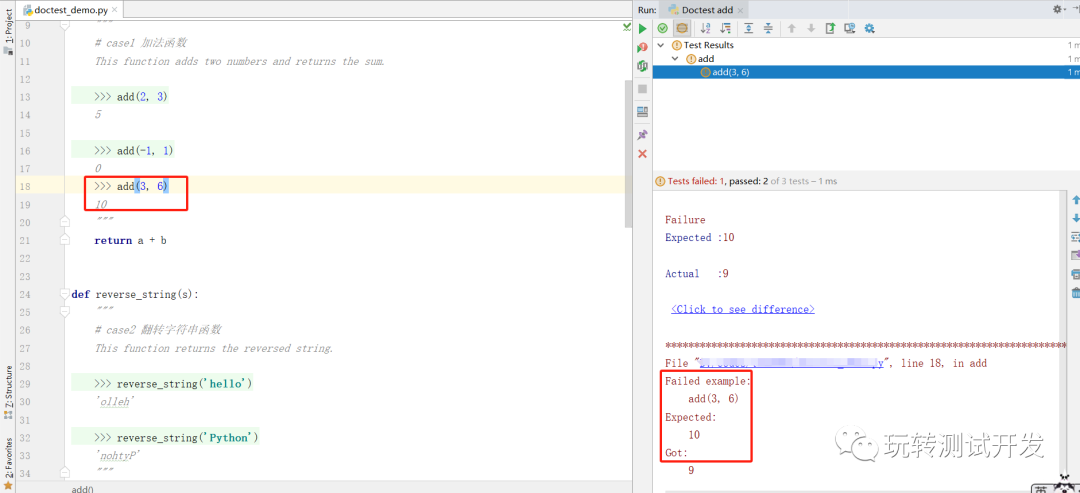
注意事项:确保测试用例的输出结果与示例中的完全匹配,包括空格和换行。Doctest 更适用于简单的、不需要太多设置和清理的测试场景。
总结:Doctest 是一个简单、直观、易用的测试框架,它通过文档字符串中的示例让你能够快速编写和理解测试。与其他测试框架相比,Doctest 为简单的测试场景提供了一个清晰、高效的解决方案。在日常的 Python 开发中,合理利用 Doctest 可以帮助你更好地保证代码的正确性和质量。