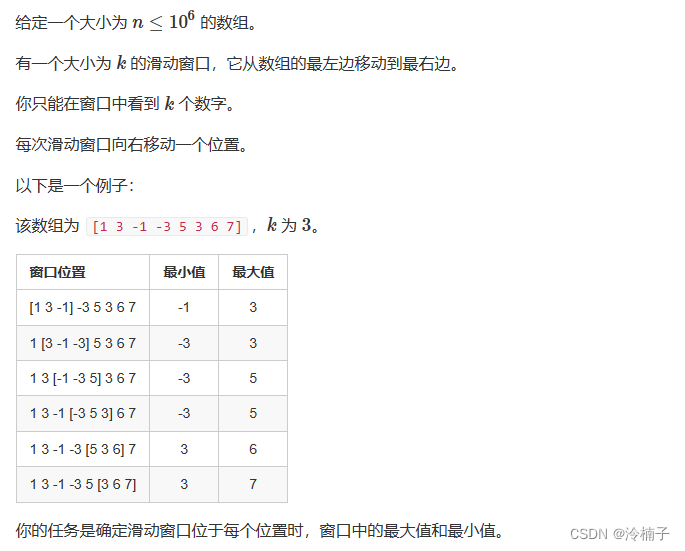
文章目录
- 1.概述
- 2.运行效果图
- 3.代码实现
- 3.1 扩展RecyclerView
- 3.2 扩展Adapter
- 3.3 RecyclerView装饰绘制
- 3.3.1 以图片实现分割线
- 3.3.2 画网格线
- 3.3.3空白的分割线
- 3.3.4 不同方向上的分割线
- 3.4 使用方法
1.概述
在一个开源项目上看到了一个Android Kotlin版的RecyclerView封装,个人觉得非常方便,所以就将这个封装摘了出来,记录下,方便以后使用,这个开源的项目叫DanDanPlayForAndroid点击链接可以查看具体的开源项目代码。
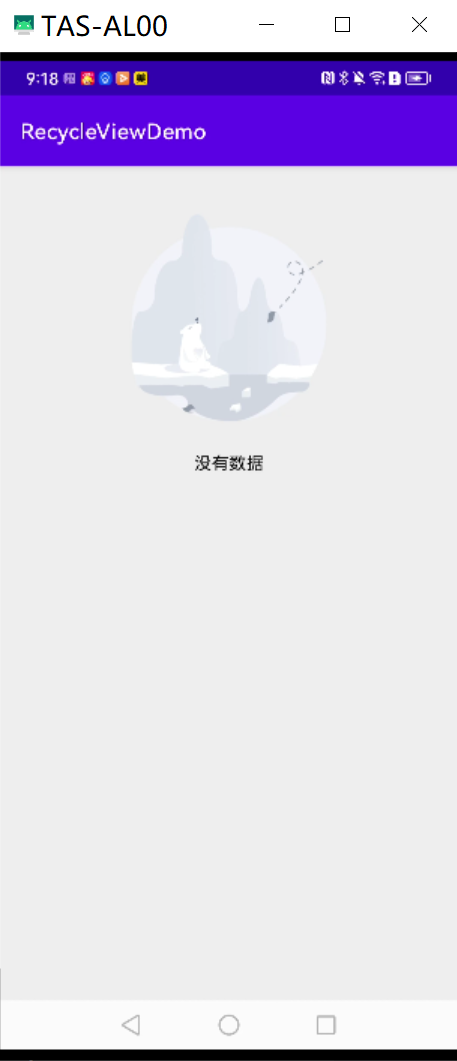
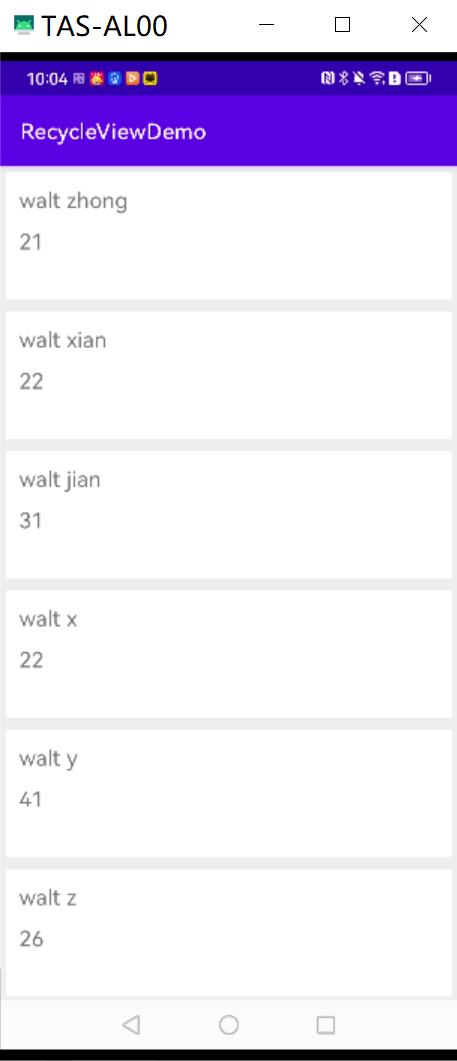
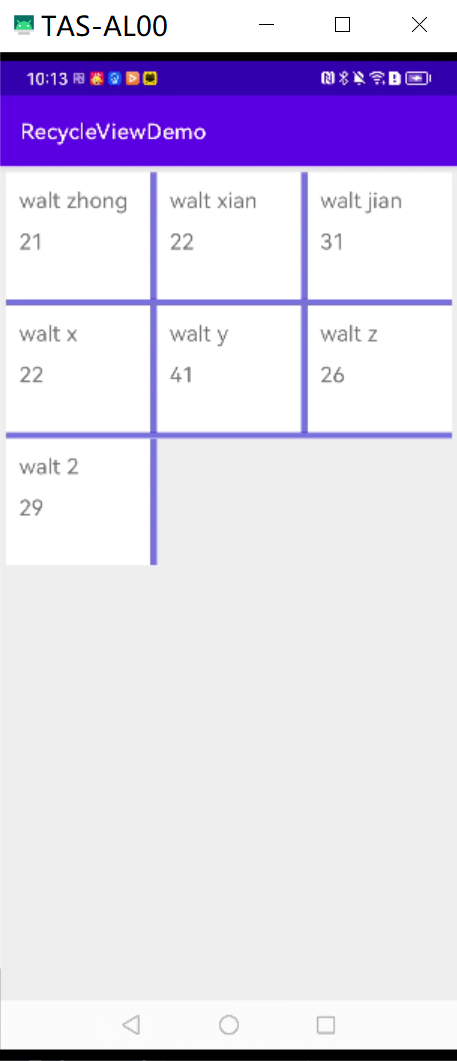
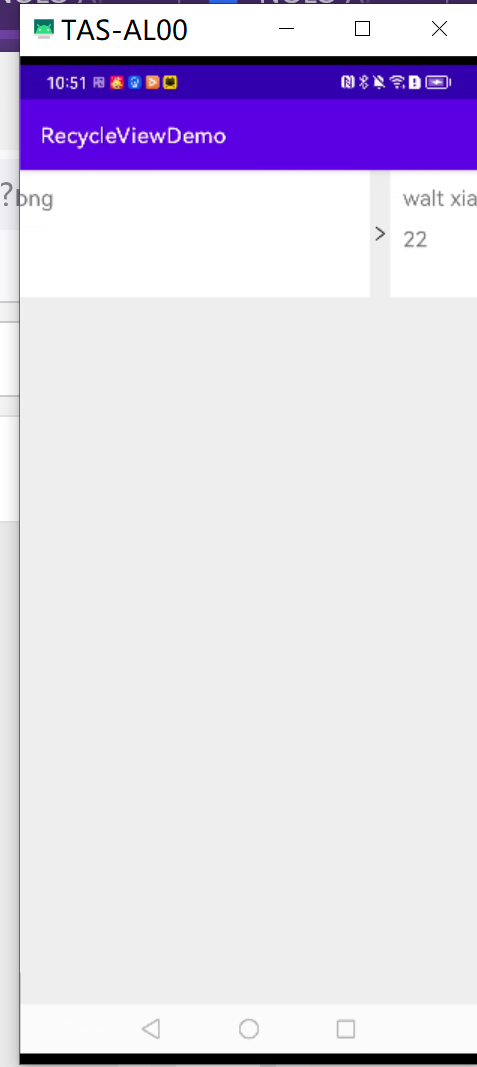
2.运行效果图
3.代码实现
3.1 扩展RecyclerView
我们可以通过Kotlin的扩展函数扩展RecycleView的布局方式,设置数据等功能,方便我们调用。代码如下:
fun RecyclerView.vertical(
reverse: Boolean = false
): LinearLayoutManager {
return LinearLayoutManager(
context,
LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL,
reverse
)
}
fun RecyclerView.horizontal(
reverse: Boolean = false
): LinearLayoutManager {
return LinearLayoutManager(
context,
LinearLayoutManager.HORIZONTAL,
reverse
)
}
fun RecyclerView.grid(
spanCount: Int
): GridLayoutManager {
return GridLayoutManager(context, spanCount)
}
fun RecyclerView.gridEmpty(spanCount: Int): GridLayoutManager {
return GridLayoutManager(context, spanCount).also {
it.spanSizeLookup = object : GridLayoutManager.SpanSizeLookup() {
override fun getSpanSize(position: Int): Int {
if (position == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
return 1
}
val viewType = adapter?.getItemViewType(position)
if (viewType != -1) {
return 1
}
return spanCount
}
}
}
}
fun RecyclerView.setData(itemData: List<Any>) {
(adapter as RVBaseAdapter).setData(itemData)
}
fun RecyclerView.requestIndexChildFocus(index: Int): Boolean {
scrollToPosition(index)
val targetTag = "tag_focusable_item"
val indexView = layoutManager?.findViewByPosition(index)
if (indexView != null) {
indexView.findViewWithTag<View>(targetTag)?.requestFocus()
return true
}
post {
layoutManager?.findViewByPosition(index)
?.findViewWithTag<View>(targetTag)
?.requestFocus()
}
return true
}
3.2 扩展Adapter
在扩展Adapter之前,我们需要先定义一个我们自己的Adapter,然后再基于我们自己的Adapter去做扩展,代码如下:
class RVBaseAdapter : RecyclerView.Adapter<RecyclerView.ViewHolder>() {
companion object{
// the data of empty layout
val EMPTY_ITEM = Any()
// view type of empty layout
const val VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY = -1
// number of max item
private const val NUMBER_OF_MAX_VIEW_TYPE = Int.MAX_VALUE -1
}
val itemData: MutableList<Any> = mutableListOf()
private val typeHolders =
SparseArrayCompat<BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>>()
override fun onCreateViewHolder(
parent: ViewGroup,
viewType: Int
): RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
return BaseViewHolder(
DataBindingUtil.inflate(
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context),
getHolderCreator(viewType).getResourceId(),
parent,
false
)
)
}
private fun getHolderCreator(viewType: Int):
BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding> {
return typeHolders.get(viewType)
?: throw java.lang.RuntimeException()
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int {
return itemData.size
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder,
position: Int) {
getHolderCreator(holder.itemViewType).apply {
initItemBinding(holder.itemView)
onBindViewHolder(itemData[position],position,this)
}
}
fun setData(dataList: List<Any>) {
itemData.clear()
itemData.addAll(dataList)
// show the empty layout when data is empty
if(itemData.isEmpty() && typeHolders.containsKey(VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY)){
itemData.add(EMPTY_ITEM)
}
notifyDataSetChanged()
}
fun register(creator: BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>,
customViewType: Int? = null) {
apply {
var viewType = customViewType ?: typeHolders.size()
while (typeHolders.get(viewType) != null) {
viewType++
require(viewType < NUMBER_OF_MAX_VIEW_TYPE) {
"the number of view type has reached the maximum limit"
}
}
require(viewType < NUMBER_OF_MAX_VIEW_TYPE) {
"the number of view type has reached the maximum limit"
}
typeHolders.put(viewType, creator)
}
}
override fun getItemViewType(position: Int): Int {
if(itemData[position] == EMPTY_ITEM
&& typeHolders.containsKey(VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY)){
return VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY
}
// only one viewHolder
if(typeHolders.size() == 1){
return typeHolders.keyAt(0)
}
// more than one viewHolder
for (i in 0 until typeHolders.size()){
if(typeHolders.keyAt(i) == VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY){
continue
}
val holder = typeHolders.valueAt(i)
if(holder.isForViewType(itemData[position],position)){
return typeHolders.keyAt(i)
}
}
throw java.lang.IllegalStateException(
"no holder added that matches at position: $position in data source"
)
}
}
与上面代码相关联的抽象类:
class BaseViewHolder(binding: ViewDataBinding) :
RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
}
abstract class BaseViewHolderCreator<V : ViewDataBinding> {
abstract fun isForViewType(data: Any?, position: Int): Boolean
abstract fun getResourceId(): Int
abstract fun onBindViewHolder(
data: Any?,
position: Int,
creator: BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>
)
lateinit var itemDataBinding: V
fun initItemBinding(itemView: View) {
this.itemDataBinding = DataBindingUtil.getBinding(itemView)!!
}
}
抽象类的实现:
class BaseViewHolderDSL<T : Any, V : ViewDataBinding>(
private val resourceId: Int,
private val clazz: KClass<T>
) : BaseViewHolderCreator<V>() {
private var checkViewType: ((data: Any, position: Int) -> Boolean)? = null
private var viewHolder: (
(data: T, position: Int, creator:
BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>) -> Unit
)? = null
private var emptyViewHolder: (() -> Unit)? = null
override fun isForViewType(data: Any?, position: Int): Boolean {
if(data == null){
return false
}
if(checkViewType != null){
return checkViewType!!.invoke(data,position)
}
return clazz.isInstance(data)
}
/**
* judge the type of current item data according to position
*/
fun checkType(viewType:(data:Any,position:Int) ->Boolean){
this.checkViewType = viewType
}
fun initView(
holder:(
data:T,
position:Int,
holder:BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>
)->Unit
){
this.viewHolder = holder
}
override fun getResourceId(): Int {
return resourceId
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(
data: Any?,
position: Int,
creator: BaseViewHolderCreator<out ViewDataBinding>
) {
// empty layout
if(data == RVBaseAdapter.EMPTY_ITEM){
emptyViewHolder?.invoke()
return
}
data ?: return
viewHolder?.invoke(data as T,position,creator)
}
}
RVBaseAdapter类的扩展
fun buildAdapter(init: RVBaseAdapter.() -> Unit): RVBaseAdapter {
return RVBaseAdapter().apply {
init()
}
}
inline fun <reified T : Any, V : ViewDataBinding> RVBaseAdapter.addItem(
resourceID: Int,
init: BaseViewHolderDSL<T, V>.() -> Unit
) {
register(
BaseViewHolderDSL<T, V>(resourceID, T::class).apply { init() }
)
}
inline fun RVBaseAdapter.addEmptyView(
resourceID: Int,
init: (BaseViewHolderDSL<Any, LayoutEmptyBinding>.() -> Unit) = {}
) {
register(
BaseViewHolderDSL<Any, LayoutEmptyBinding>(resourceID, Any::class)
.apply {
init()
},
customViewType = RVBaseAdapter.VIEW_TYPE_EMPTY
)
setData(listOf(RVBaseAdapter.EMPTY_ITEM))
}
3.3 RecyclerView装饰绘制
RecyclerView可以继承自ItemDecoration类绘制自己想要的分割线和装饰,这里做了几个例子,代码如下:
3.3.1 以图片实现分割线
/**
* 分割线(以图片实现)
*/
class MyItemDecoration(divider: Drawable, dividerSize: Int) :
RecyclerView.ItemDecoration() {
private val mDivider = divider
private val mDividerSize = dividerSize
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas, parent: RecyclerView, state:
RecyclerView.State) {
canvas.save()
//居中显示
val top = (parent.height - mDividerSize) / 2
val bottom = top + mDividerSize
val mBounds = Rect()
//只在中间绘制
for (i in 0 until parent.childCount - 1) {
val child = parent.getChildAt(i)
parent.layoutManager!!.getDecoratedBoundsWithMargins(child, mBounds)
val right = mBounds.right + child.translationX.roundToInt()
val left = right - mDividerSize
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom)
mDivider.draw(canvas)
}
canvas.restore()
}
override fun getItemOffsets(
outRect: Rect,
view: View,
parent: RecyclerView,
state: RecyclerView.State
) {
outRect.set(0, 0, mDividerSize, 0)
}
}
3.3.2 画网格线
class ItemGridDecorationDrawable : ItemDecoration {
private var leftRight: Int
private var topBottom: Int
private var mDivider: Drawable?
constructor(spacePx: Int) {
leftRight = spacePx
topBottom = spacePx
mDivider = ColorDrawable(Color.WHITE)
}
constructor(leftRight: Int, topBottom: Int) {
this.leftRight = leftRight
this.topBottom = topBottom
mDivider = ColorDrawable(Color.WHITE)
}
constructor(leftRight: Int, topBottom: Int, mColor: Int) {
this.leftRight = leftRight
this.topBottom = topBottom
mDivider = ColorDrawable(mColor)
}
override fun onDraw(
c: Canvas,
parent: RecyclerView,
state: RecyclerView.State
) {
val layoutManager = parent.layoutManager
as GridLayoutManager? ?: return
val lookup = layoutManager.spanSizeLookup
if (mDivider == null || layoutManager.childCount == 0) {
return
}
//判断总的数量是否可以整除
val spanCount = layoutManager.spanCount
var left: Int
var right: Int
var top: Int
var bottom: Int
val childCount = parent.childCount
if (layoutManager.orientation == GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
for (i in 0 until childCount) {
val child = parent.getChildAt(i)
//将带有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
val centerLeft =
((layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child) + layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(
child
)).toFloat()
* spanCount / (spanCount + 1) + 1 - leftRight) / 2
val centerTop =
(layoutManager.getBottomDecorationHeight(child)
+ 1 - topBottom) / 2f
//得到它在总数里面的位置
val position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(child)
//获取它所占有的比重
val spanSize = lookup.getSpanSize(position)
//获取每排的位置
val spanIndex = lookup.getSpanIndex(position,
layoutManager.spanCount)
//判断是否为第一排
val isFirst =
layoutManager.spanSizeLookup.getSpanGroupIndex(position,
spanCount) == 0
//画上边的,第一排不需要上边的,只需要在最左边的那项的时候画一次就好
if (!isFirst && spanIndex == 0) {
left = layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child)
right = parent.width -
layoutManager.getLeftDecorationWidth(child)
top = (child.top - centerTop).toInt() - topBottom
bottom = top + topBottom
mDivider!!.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom)
mDivider!!.draw(c)
}
//最右边的一排不需要右边的
val isRight = spanIndex + spanSize == spanCount
if (!isRight) { //计算右边的
left = (child.right + centerLeft).toInt()
right = left + leftRight
top = child.top
if (!isFirst) {
top -= centerTop.toInt()
}
bottom = (child.bottom + centerTop).toInt()
mDivider!!.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom)
mDivider!!.draw(c)
}
}
} else {
for (i in 0 until childCount) {
val child = parent.getChildAt(i)
//将带有颜色的分割线处于中间位置
val centerLeft =
(layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(child)
+ 1 - leftRight) / 2f
val centerTop =
((layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child) + layoutManager.getBottomDecorationHeight(
child
)).toFloat()
* spanCount / (spanCount + 1) - topBottom) / 2
//得到它在总数里面的位置
val position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(child)
//获取它所占有的比重
val spanSize = lookup.getSpanSize(position)
//获取每排的位置
val spanIndex = lookup
.getSpanIndex(position, layoutManager.spanCount)
//判断是否为第一列
val isFirst =
layoutManager.spanSizeLookup
.getSpanGroupIndex(position, spanCount) == 0
//画左边的,第一排不需要左边的,只需要在最上边的那项的时候画一次就好
if (!isFirst && spanIndex == 0) {
left = (child.left - centerLeft).toInt() - leftRight
right = left + leftRight
top = layoutManager.getRightDecorationWidth(child)
bottom = parent.height - layoutManager.getTopDecorationHeight(child)
mDivider!!.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom)
mDivider!!.draw(c)
}
//最下的一排不需要下边的
val isRight = spanIndex + spanSize == spanCount
if (!isRight) { //计算右边的
left = child.left
if (!isFirst) {
left -= centerLeft.toInt()
}
right = (child.right + centerTop).toInt()
top = (child.bottom + centerLeft).toInt()
bottom = top + leftRight
mDivider!!.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom)
mDivider!!.draw(c)
}
}
}
}
override fun getItemOffsets(
outRect: Rect,
view: View,
parent: RecyclerView,
state: RecyclerView.State
) {
val layoutManager = parent.layoutManager as GridLayoutManager? ?: return
val lp =
view.layoutParams as GridLayoutManager.LayoutParams
val childPosition = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view)
val spanCount = layoutManager.spanCount
if (layoutManager.orientation == GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL) {
//判断是否在第一排
if (layoutManager.spanSizeLookup.getSpanGroupIndex(
childPosition,
spanCount
) == 0
) { //第一排的需要上面
outRect.top = topBottom
}
outRect.bottom = topBottom
//这里忽略和合并项的问题,只考虑占满和单一的问题
if (lp.spanSize == spanCount) { //占满
outRect.left = leftRight
outRect.right = leftRight
} else {
outRect.left =
((spanCount - lp.spanIndex).toFloat() / spanCount * leftRight).toInt()
outRect.right =
(leftRight.toFloat() * (spanCount + 1) / spanCount - outRect.left).toInt()
}
} else {
if (layoutManager.spanSizeLookup.getSpanGroupIndex(
childPosition,
spanCount
) == 0
) { //第一排的需要left
outRect.left = leftRight
}
outRect.right = leftRight
//这里忽略和合并项的问题,只考虑占满和单一的问题
if (lp.spanSize == spanCount) { //占满
outRect.top = topBottom
outRect.bottom = topBottom
} else {
outRect.top =
((spanCount - lp.spanIndex).toFloat() / spanCount * topBottom).toInt()
outRect.bottom =
(topBottom.toFloat() * (spanCount + 1) / spanCount - outRect.top).toInt()
}
}
}
}
3.3.3空白的分割线
/**
* 空白的分割线
*
*/
class ItemDecorationSpace : ItemDecoration {
private var top: Int
private var left: Int
private var right: Int
private var bottom: Int
private var spanCount: Int
constructor(space: Int) : this(space, space, space, space)
constructor(spaceLR: Int, spaceTB: Int) : this(spaceTB, spaceLR, spaceLR,
spaceTB)
constructor(top: Int, left: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) {
this.top = top
this.left = left
this.right = right
this.bottom = bottom
spanCount = 0
}
constructor(top: Int, left: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int, spanCount: Int) {
this.top = top
this.left = left
this.right = right
this.bottom = bottom
this.spanCount = spanCount
}
override fun getItemOffsets(
outRect: Rect, view: View,
parent: RecyclerView, state: RecyclerView.State
) {
outRect.top = top
outRect.left = left
outRect.bottom = bottom
if (spanCount != 0) {
val position = parent.getChildLayoutPosition(view)
if ((position + 1) % spanCount == 0) {
outRect.right = 0
} else {
outRect.right = right
}
} else {
outRect.right = right
}
}
}
3.3.4 不同方向上的分割线
/**
* 不同方向上的分割线
*/
class ItemDecorationOrientation : ItemDecoration {
private val dividerPx: Int
private val headerPx: Int
private val footerPx: Int
private val orientation: Int
constructor(dividerPx: Int, @RecyclerView.Orientation orientation: Int)
: this(
dividerPx,
dividerPx,
orientation
)
constructor(
dividerPx: Int,
headerFooterPx: Int,
@RecyclerView.Orientation orientation: Int
) : this(dividerPx, headerFooterPx, headerFooterPx, orientation)
constructor(
dividerPx: Int,
headerPx: Int,
footerPx: Int,
@RecyclerView.Orientation orientation: Int
) {
this.dividerPx = dividerPx
this.headerPx = headerPx
this.footerPx = footerPx
this.orientation = orientation
}
override fun getItemOffsets(
outRect: Rect,
view: View,
parent: RecyclerView,
state: RecyclerView.State
) {
if (orientation == RecyclerView.VERTICAL) {
getItemOffsetsVertical(outRect, view, parent)
} else {
getItemOffsetsHorizontal(outRect, view, parent)
}
}
private fun getItemOffsetsVertical(outRect: Rect, view: View,
parent: RecyclerView) {
val itemCount = parent.adapter?.itemCount ?: return
val position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view)
if (position == 0) {
outRect.top = headerPx
} else {
outRect.top = position * dividerPx / itemCount
}
if (position == itemCount - 1) {
outRect.bottom = footerPx
} else {
outRect.bottom = dividerPx - (position + 1) * dividerPx / itemCount
}
}
private fun getItemOffsetsHorizontal(outRect: Rect, view: View, parent:
RecyclerView) {
val itemCount = parent.adapter?.itemCount ?: return
val position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view)
if (position == 0) {
outRect.left = headerPx
} else {
outRect.left = position * dividerPx / itemCount
}
if (position == itemCount - 1) {
outRect.right = footerPx
} else {
outRect.right = dividerPx - (position + 1) * dividerPx / itemCount
}
}
}
3.4 使用方法
使用的时候去掉代码中对应的注释,体验各种风格
class RecyclerViewActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var dataBinding: ActivityRecyclerViewBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
initDataBinding()
initRV()
val dataList = listOf<UserData>(
UserData("walt zhong", 21),
UserData("walt xian", 22),
UserData("walt jian", 31),
UserData("walt x", 22),
UserData("walt y", 41),
UserData("walt z", 26),
UserData("walt 2", 29),
)
// val dataList = emptyList<UserData>()
dataBinding.rvList.setData(dataList)
}
private fun initRV() {
dataBinding.rvList.apply {
// layoutManager = gridEmpty(3) //网格布局
// layoutManager = vertical(false) // 垂直布局
layoutManager = horizontal(false) // 水平布局
adapter = buildAdapter {
addEmptyView(R.layout.layout_empty)
addItem<UserData, RvItemBinding>(R.layout.rv_item) {
initView { data, position, _ ->
itemDataBinding.apply {
tvName.text = data.name
tvAge.text = data.age.toString()
itemLayout.setOnClickListener {
Log.d("zhongxj", "click item: $position")
}
}
}
}
}
// val pxValue = dp2px(5)
//
// addItemDecoration(
// ItemGridDecorationDrawable(
// pxValue,
// pxValue,
// R.color.purple_200
// )
// )
// addItemDecoration(
// ItemDecorationSpace(
// pxValue
// )
// )
// addItemDecoration(
// ItemDecorationOrientation(
// dividerPx = pxValue,
// headerFooterPx = 0,
// orientation = RecyclerView.HORIZONTAL
// )
// )
val dividerSize = dp2px(16)
val divider = ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, R.drawable.ic_arrow)
if(divider != null){
addItemDecoration(
MyItemDecoration(
divider,
dividerSize
)
)
}
}
}
private fun initDataBinding() {
dataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(
this,
R.layout.activity_recycler_view
)
dataBinding.lifecycleOwner = this@RecyclerViewActivity
}
/**
* 单位转换,将DP转为PX
*/
fun dp2px(dpValue: Int): Int {
val scale = Resources.getSystem().displayMetrics.density
return (dpValue * scale + 0.5f).toInt()
}
}
data class UserData(var name:String,var age:Int)
布局文件:
RcyclerViewActivity布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:background="#eeeeee"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".RecyclerViewActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv_list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
RecyclerView item布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:background="@color/white"
android:padding="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:id="@+id/item_layout"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="walt"
android:id="@+id/tv_name"/>
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="24"
android:id="@+id/tv_age"/>
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
没有数据时的空布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/empty_iv"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_empty_data"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.382" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/empty_tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:text="没有数据"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/empty_iv" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
里面对应的图片读者自己找喜欢的替换上就可以啦,本文主要是记录,代码也不难,读者可以自行跟着敲一遍,加深映像,熟悉这种封装方法,后面可以使用在项目的其他部分的封装。