图像语义分割 FCN图像分割网络网络详解
- 0、介绍
- 1、VGG16网络结构
- 2、转置卷积
- 3、FCN-32S、FCN-16S,FCN-8S网络结构
- 4、损失函数
- 5、膨胀卷积
- 6、FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)
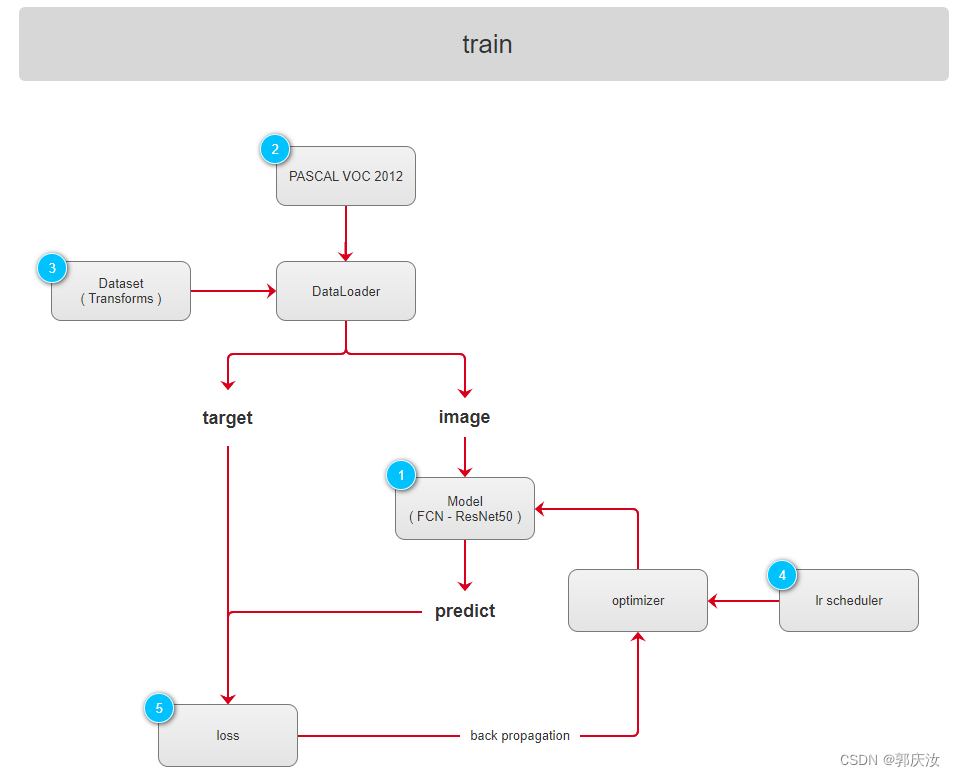
- 6.1 项目框架
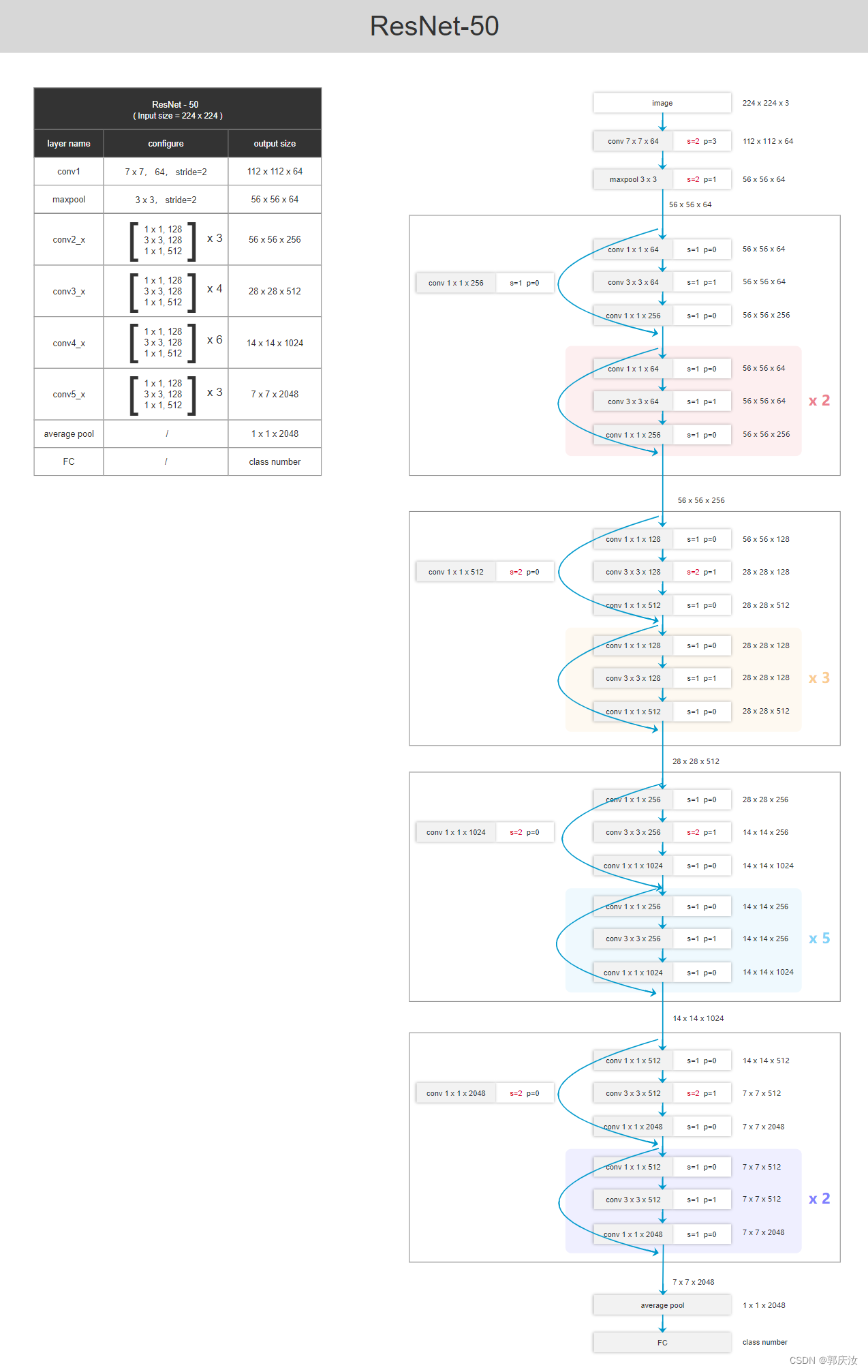
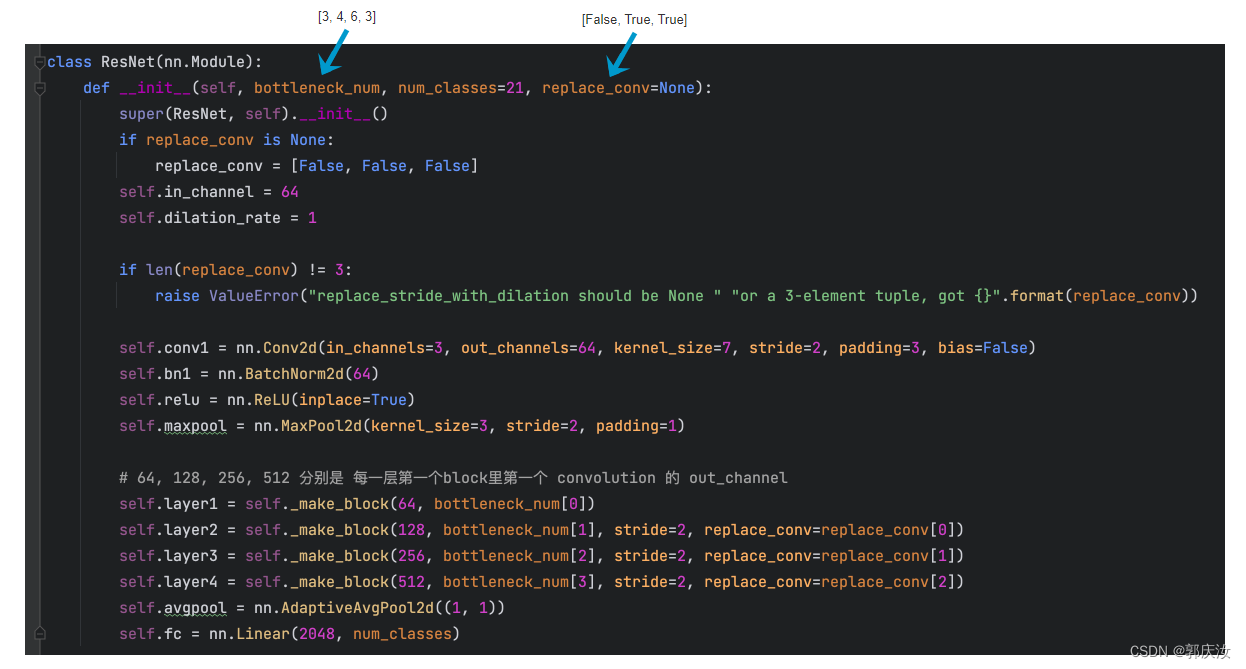
- 6.2 ResNet50网络结构
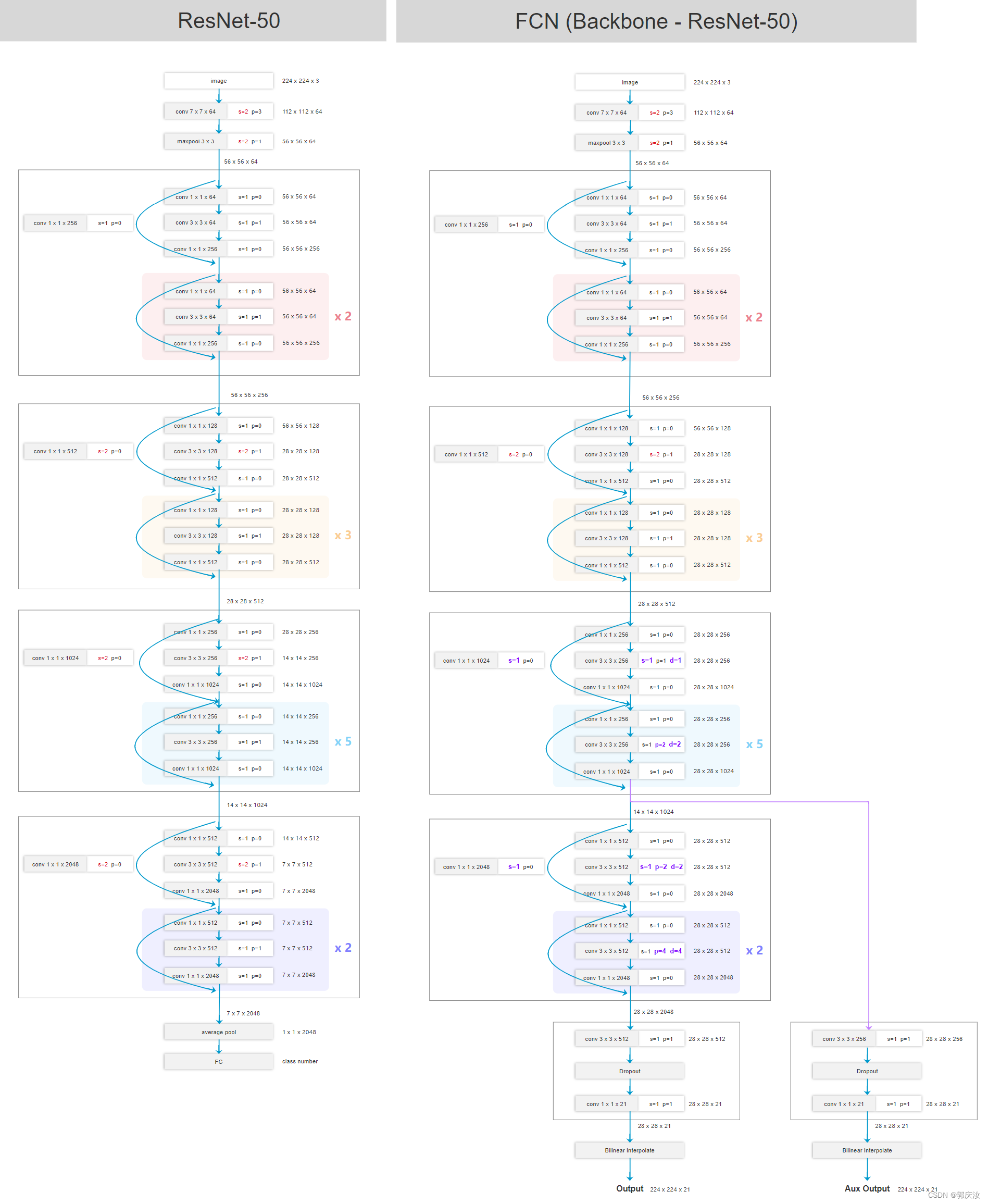
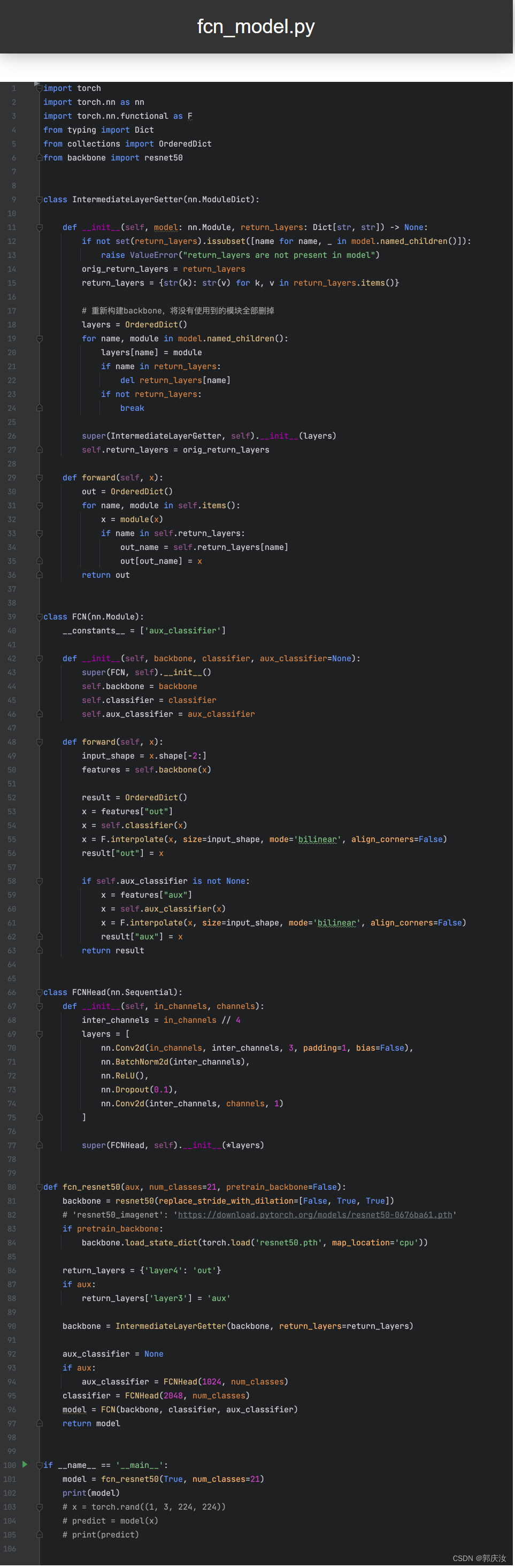
- 6.3 FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)网络结构
- 6.4 FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)模型搭建流程演示图
- 7、评价指标
- 8、数据集
- 8.1 数据集预处理
- 9、Loss损失函数
- 10、学习策略
- 11、测试效果
0、介绍

1、VGG16网络结构
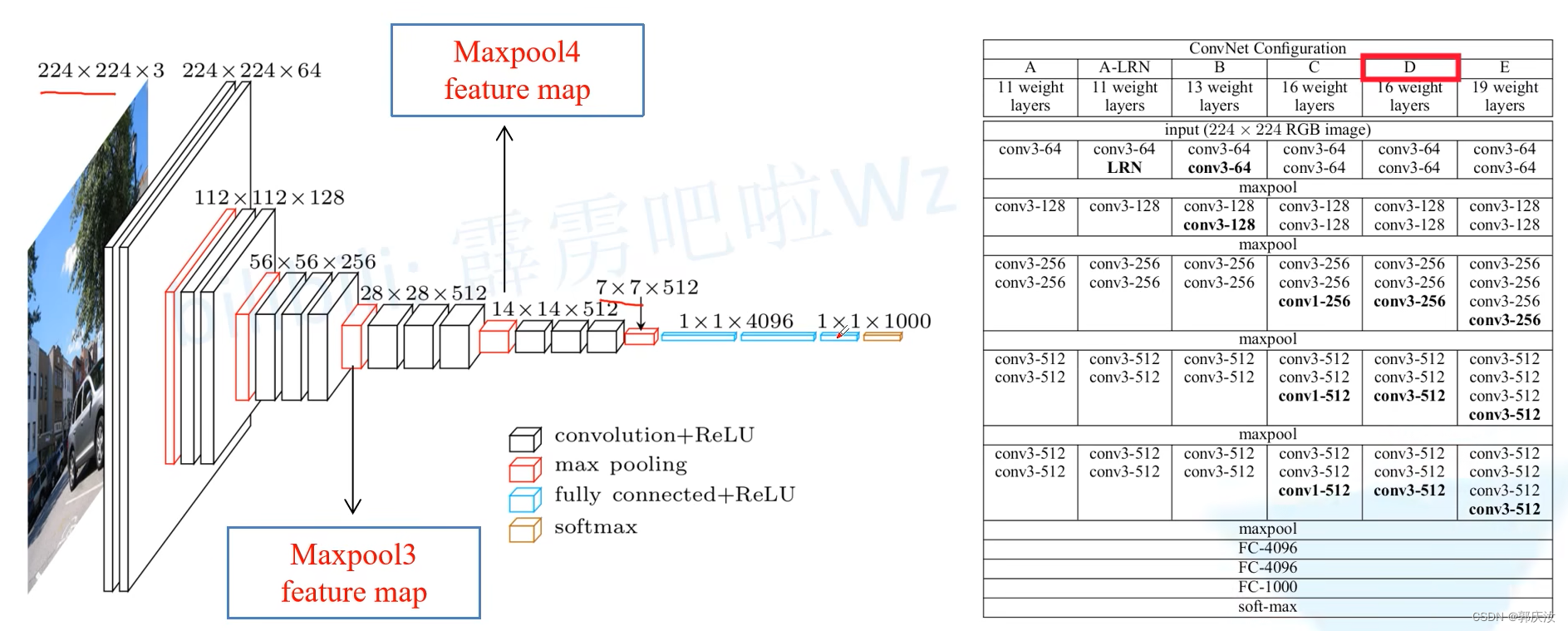
2、转置卷积
采用转置卷积的目的就是实现上采样,不过在FCN代码中采用的是双线性插值法
查看另一篇博文:
转置卷积部分
3、FCN-32S、FCN-16S,FCN-8S网络结构
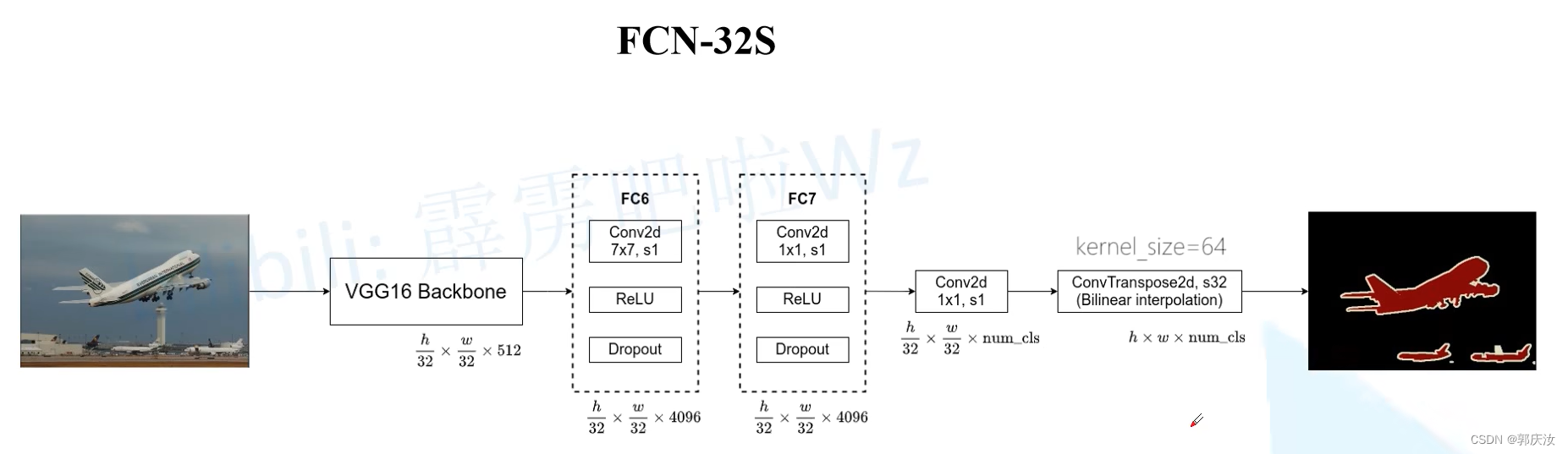
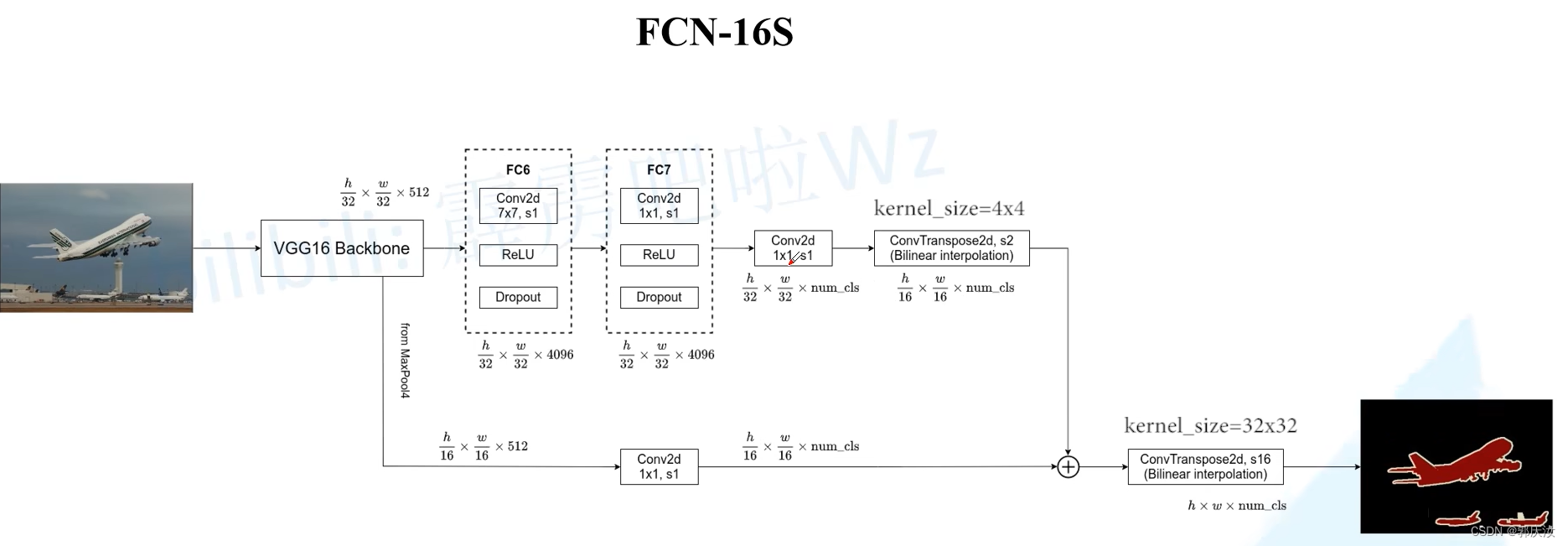
FCN-16S网络使用到了Maxpool4 feature map作为融合特征 ↑↑↑↑
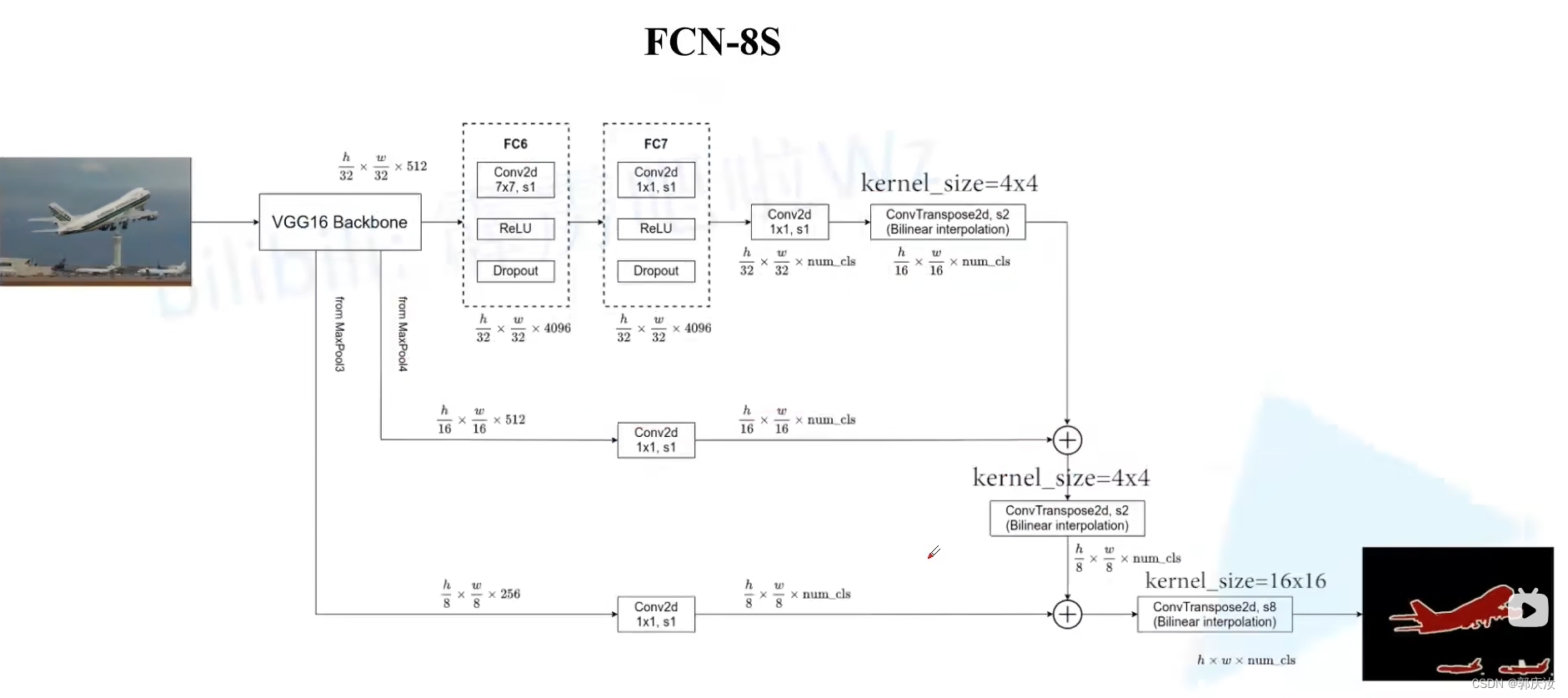
FCN-16S网络使用到了Maxpool4 feature map与Maxpool3 feature map作为融合特征 ↑↑↑↑
网络中的使用转置卷积的模块,在代码中实际采用的上采样模块实现
4、损失函数
损失函数采用Cross Entropy Loss
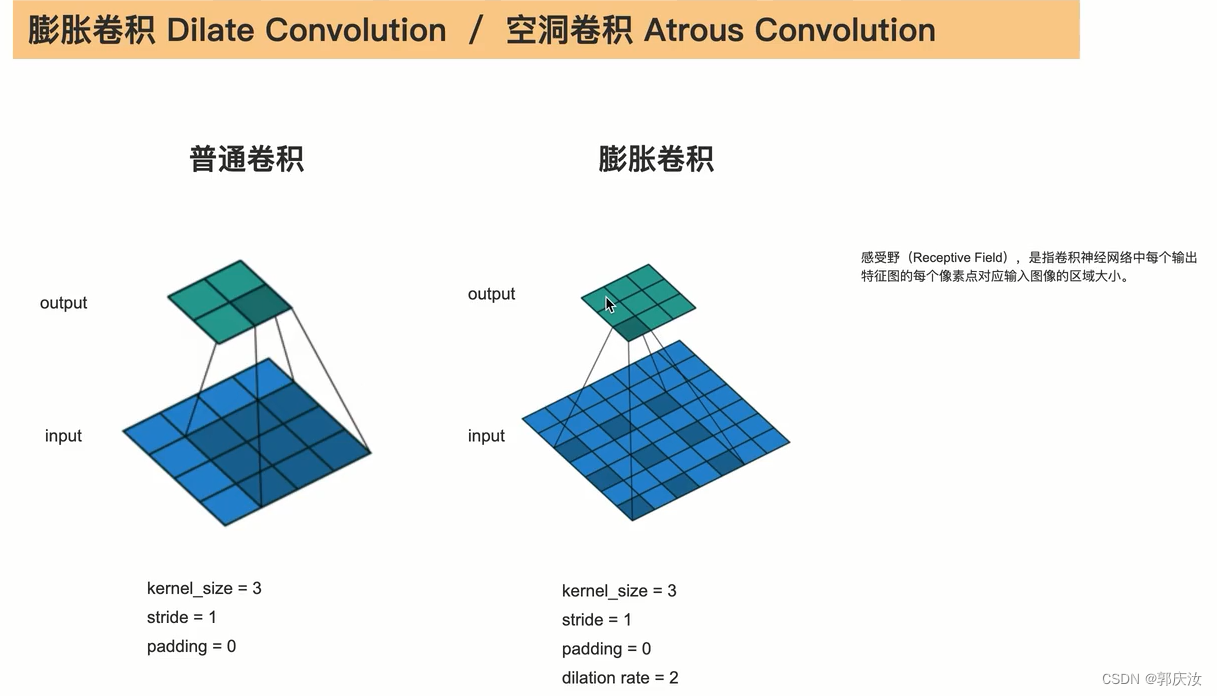
5、膨胀卷积
在进行语义分割过程中,通常需要分类网络作为网络的backbone进行一系列的下采样,再通过一系列的上采样还原回图像的原始尺寸;存在问题是在下采样过程中,如果采样倍率过大则对还原回原图是有很大影响的
膨胀卷积的优点:
- 增大感受野
- 保持原输入特征图的W、H


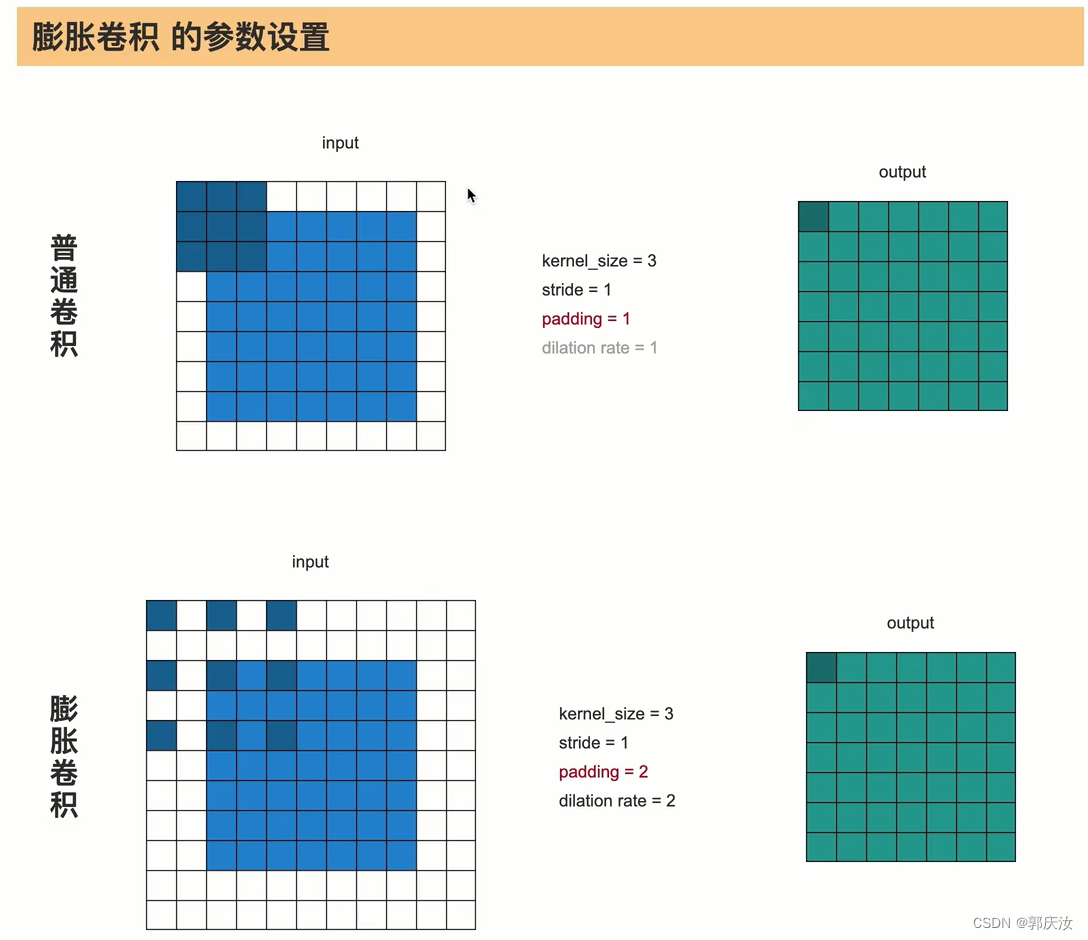
特征图中像素间的间隔数=dilation rate - 1

上图为空洞卷积的实现,参数填写为padding=dilation,dilation=dilation
即:dilation=dilation为空洞数
如果想保证输入特征图尺寸等于输出特征图尺寸,则需要padding=dilation,dilation=dilation
膨胀卷积的缺陷问题:
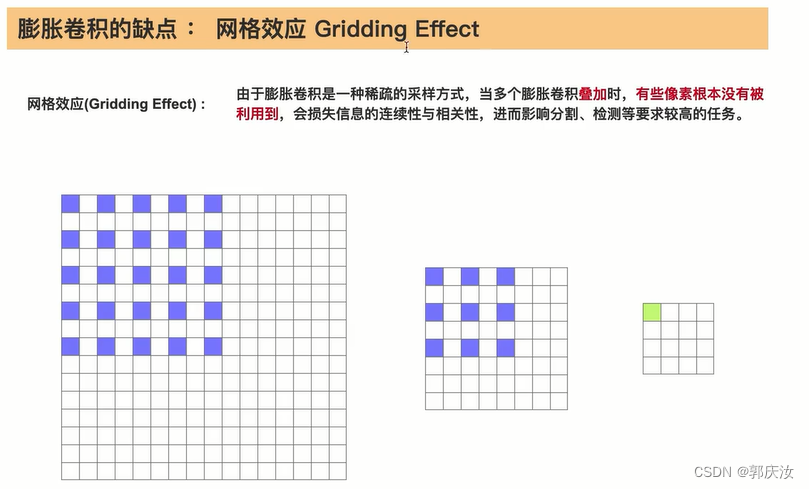

Gridding Effect问题↑↑↑↑↑
避免Gridding Effect的策略是:不要连续的使用膨胀卷积或将膨胀因子设置成锯齿结构
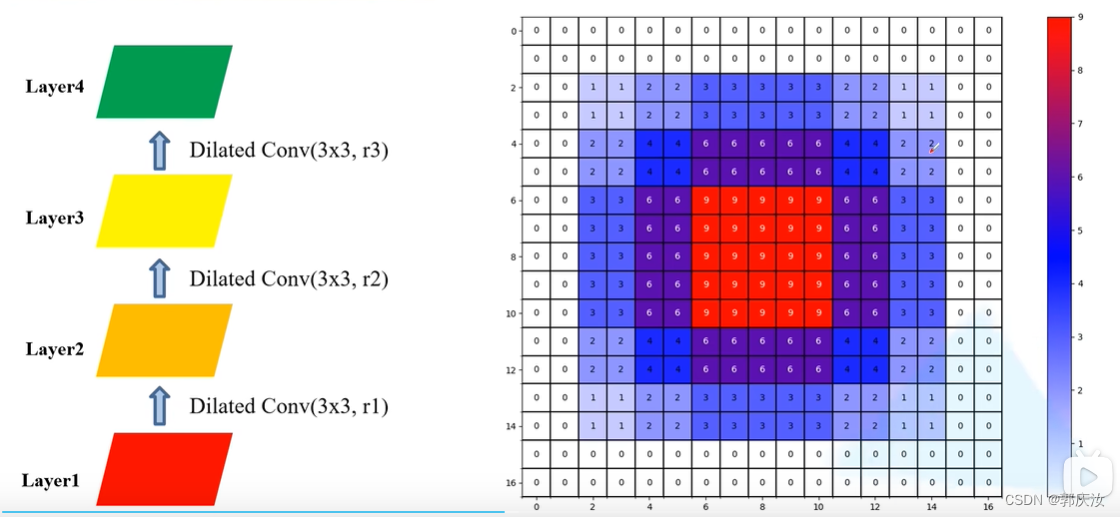
将膨胀因子设置成锯齿结构↑↑↑↑↑
6、FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)
6.1 项目框架
6.2 ResNet50网络结构
6.3 FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)网络结构
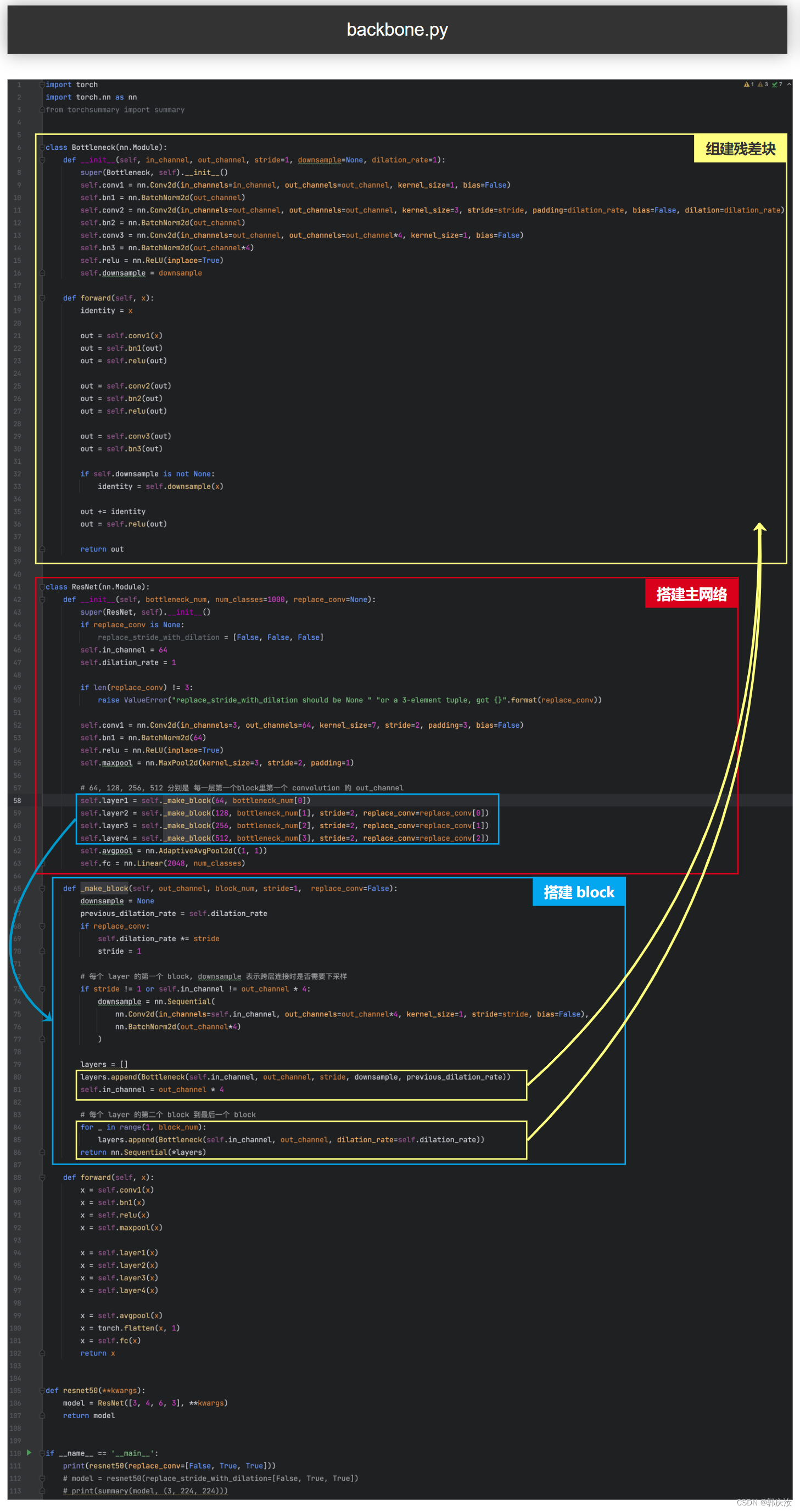
搭建主网络
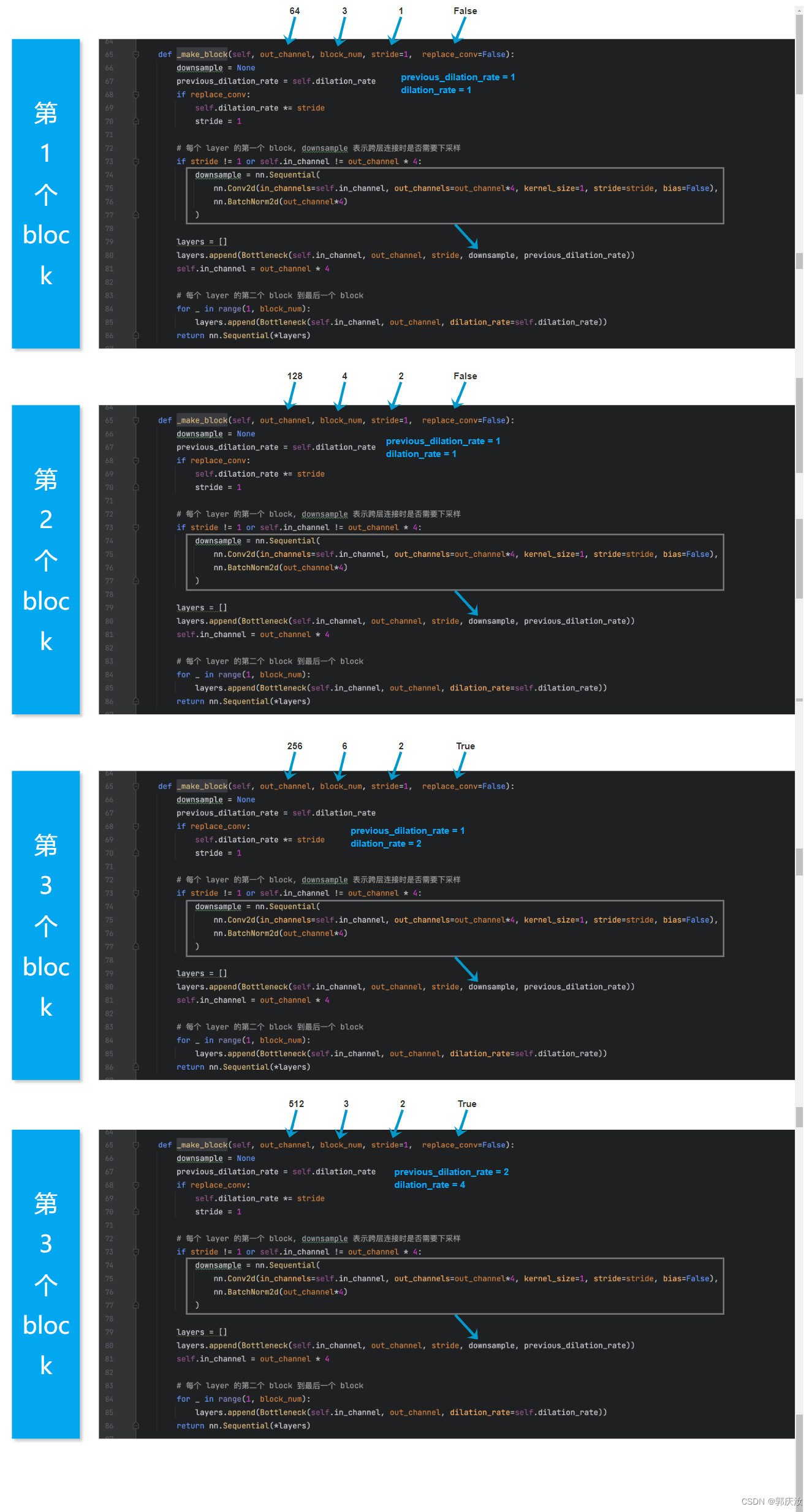
make_bolck
bottlneck
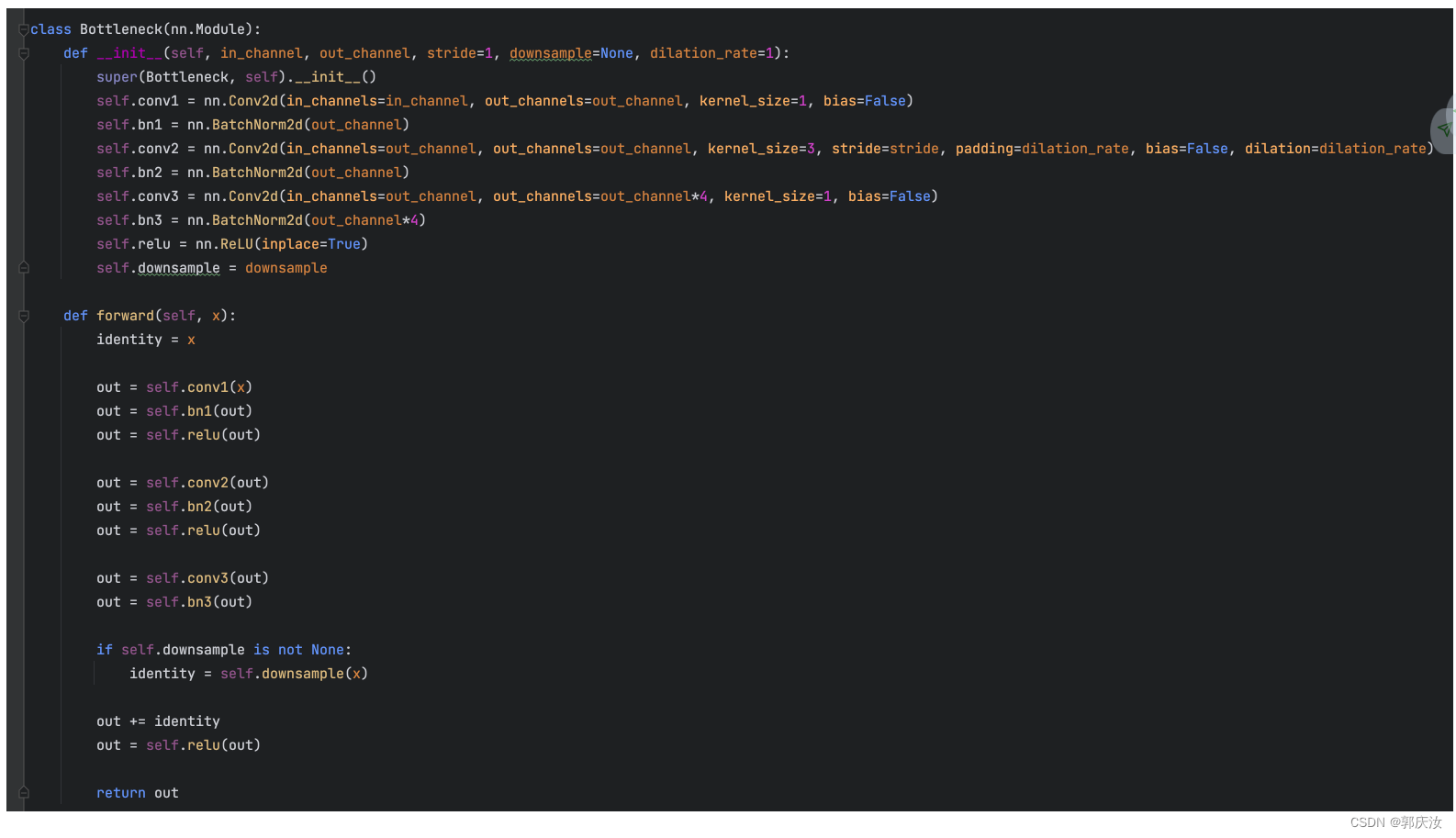
6.4 FCN(Backbone-ResNet-50)模型搭建流程演示图
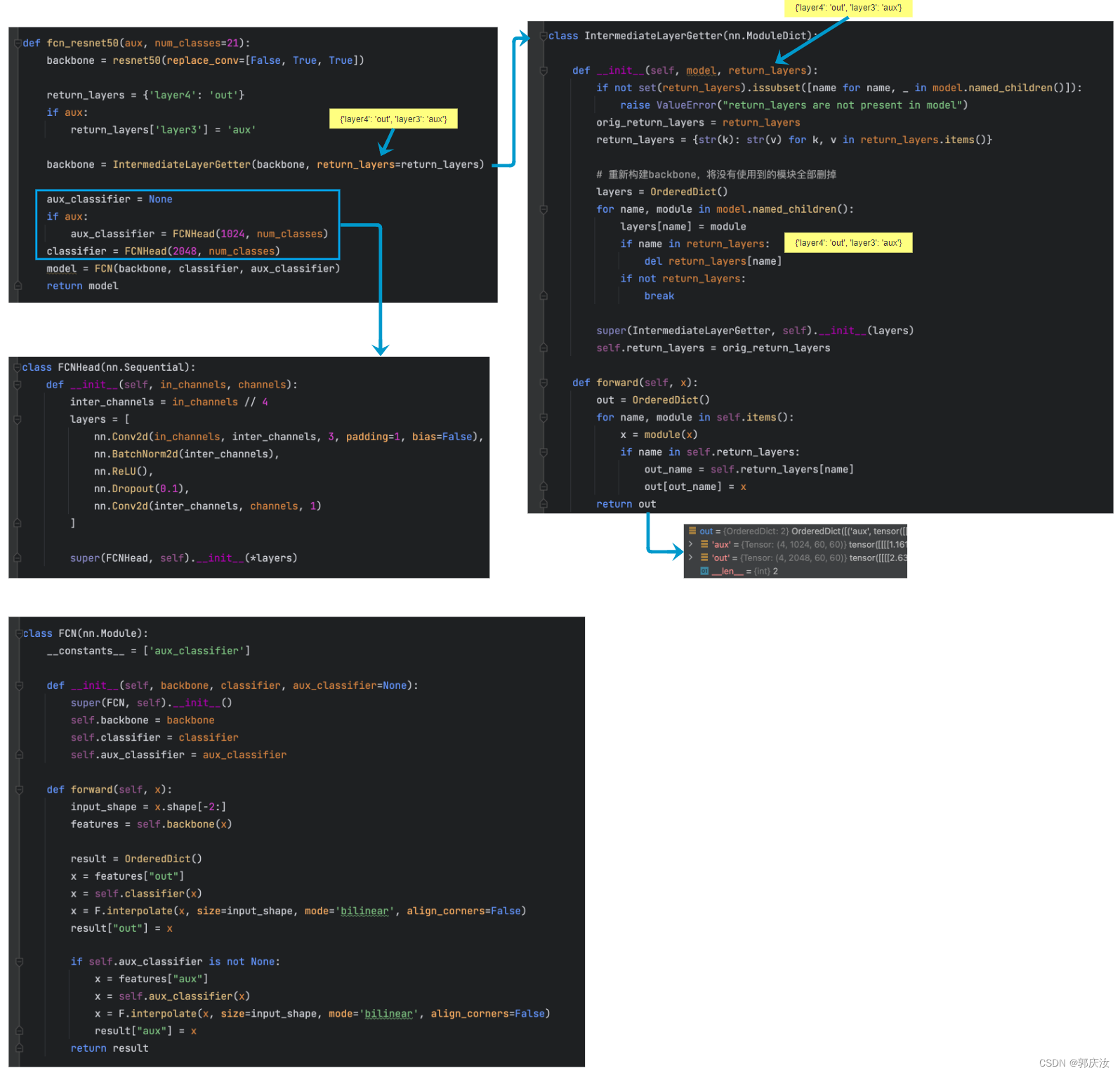
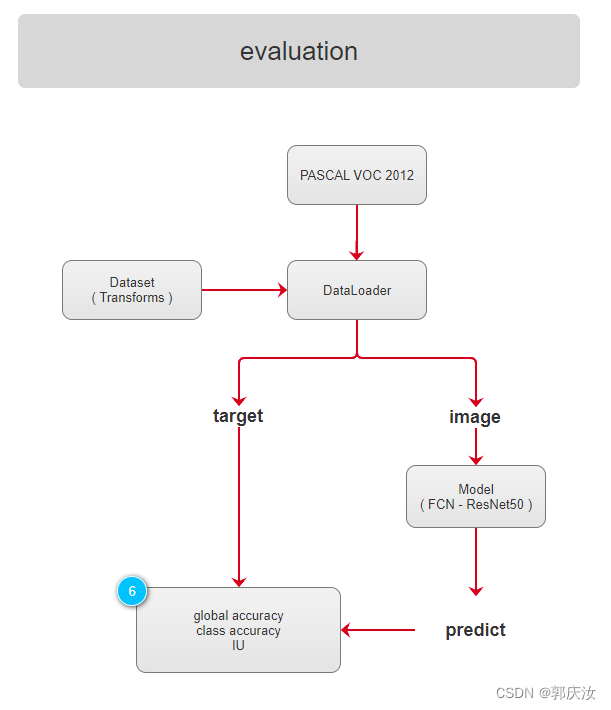
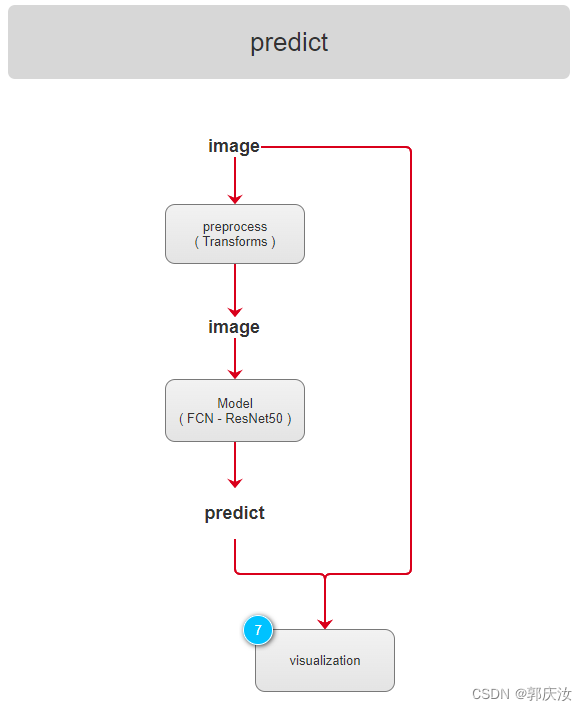
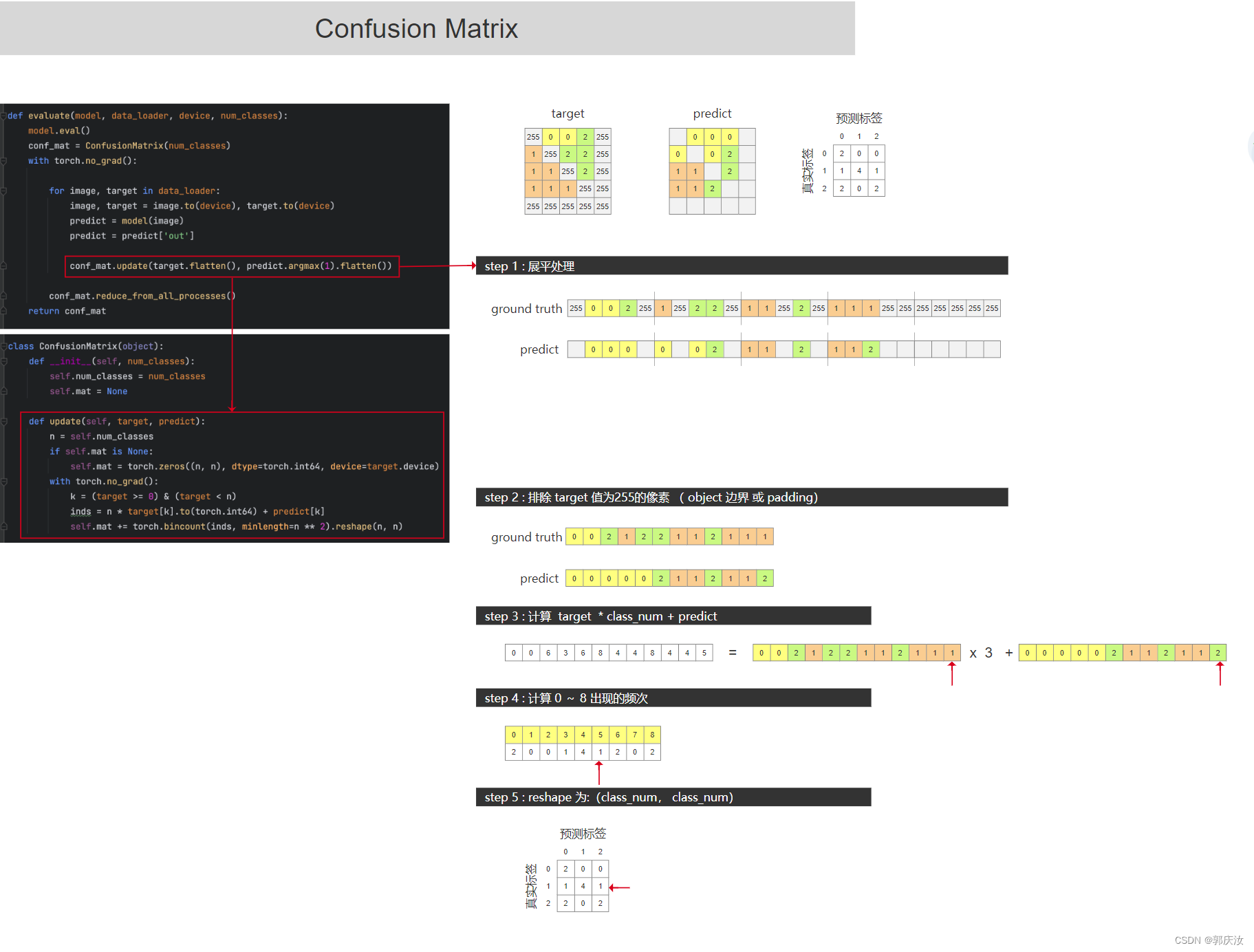
7、评价指标
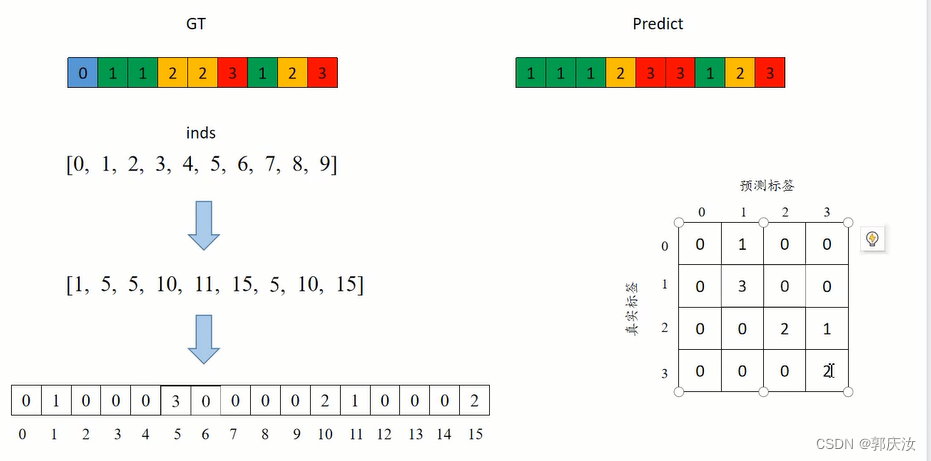
上图中假设类别为n_class=4(包含背景类别)
第一步:假定真实的GT标签为GT=[0,1,1,2,2,3,1,2,3]
真是标签列表索引为GT_inds=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
第二步:将类别数n_class x GT + Predict (得到对应像素在混淆矩阵展平后的位置)
得到location=[1,5,5,10,11,15,5,10,15]
第三步:在用统计直方图的方法统计location中每一个数值出现的频次
torch.bincount(inds, minlength=n**2).reshape(n, n)
得到混淆矩阵:
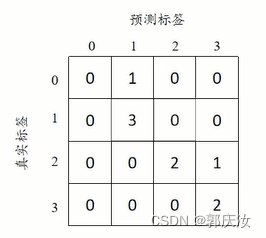
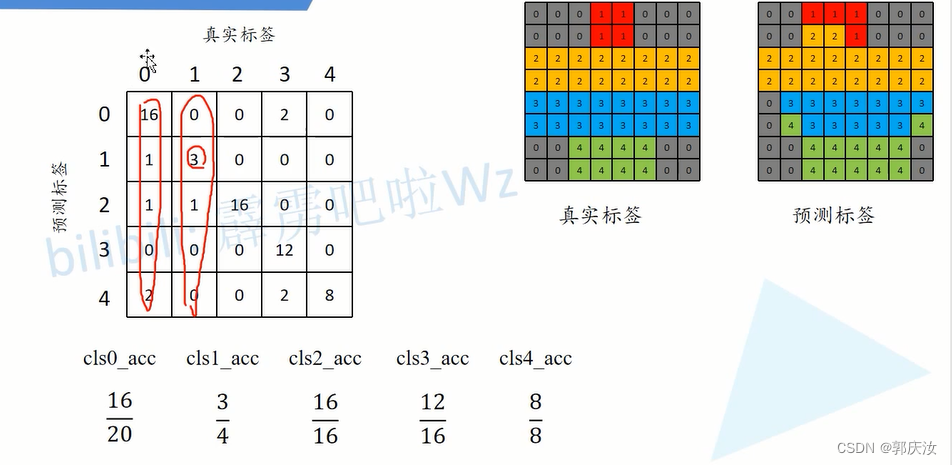
求得每一类别对应的准确率:
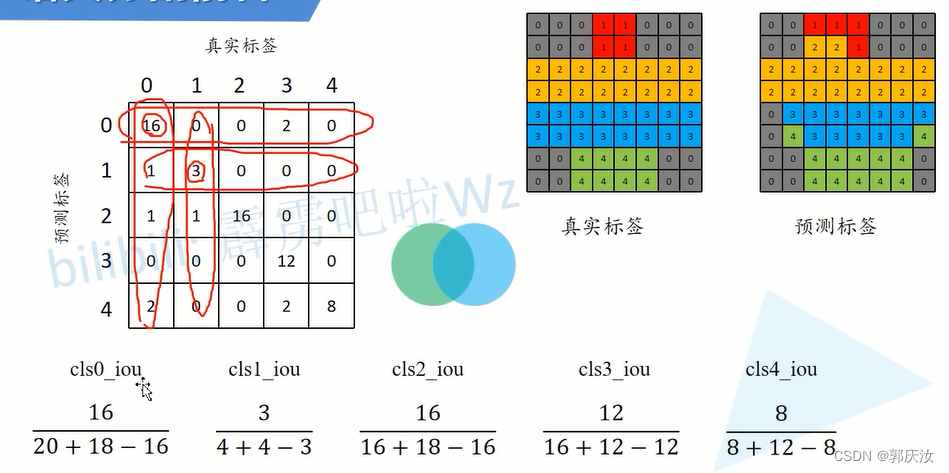
计算每个类别预测与真实目标的iou
代码实现:
class ConfusionMatrix(object):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.mat = None
def update(self, a, b):
n = self.num_classes # gqr:其包含背景类别
if self.mat is None:
# 创建混淆矩阵
self.mat = torch.zeros((n, n), dtype=torch.int64, device=a.device)
with torch.no_grad():
# 寻找GT中为目标的像素索引
k = (a >= 0) & (a < n) # gqr:利用(a < n)忽略掉值为255的像素
# 统计像素真实类别a[k]被预测成类别b[k]的个数(这里的做法很巧妙)
inds = n * a[k].to(torch.int64) + b[k]
self.mat += torch.bincount(inds, minlength=n**2).reshape(n, n)
def reset(self):
if self.mat is not None:
self.mat.zero_()
def compute(self):
h = self.mat.float()
# 计算全局预测准确率(混淆矩阵的对角线为预测正确的个数)
acc_global = torch.diag(h).sum() / h.sum()
# 计算每个类别的准确率
acc = torch.diag(h) / h.sum(1)
# 计算每个类别预测与真实目标的iou
iu = torch.diag(h) / (h.sum(1) + h.sum(0) - torch.diag(h))
return acc_global, acc, iu
def reduce_from_all_processes(self):
if not torch.distributed.is_available():
return
if not torch.distributed.is_initialized():
return
torch.distributed.barrier()
torch.distributed.all_reduce(self.mat)
def __str__(self):
acc_global, acc, iu = self.compute()
return (
'global correct: {:.1f}\n'
'average row correct: {}\n'
'IoU: {}\n'
'mean IoU: {:.1f}').format(
acc_global.item() * 100,
['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (acc * 100).tolist()],
['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (iu * 100).tolist()],
iu.mean().item() * 100)
[epoch: 183]
train_loss: 0.3513
lr: 0.000010
global correct: 92.7
average row correct: ['97.1', '84.3', '70.9', '81.5', '67.0', '82.2', '77.7', '89.9', '93.2', '59.5', '50.4', '69.8', '80.4', '62.5', '86.1', '95.0', '70.8', '78.9', '62.9', '83.2', '88.4']
IoU: ['93.7', '82.7', '58.1', '75.1', '61.4', '69.4', '74.8', '77.8', '76.2', '37.3', '47.8', '57.7', '57.7', '56.9', '77.3', '87.9', '60.7', '63.9', '45.8', '71.9', '70.0']
mean IoU: 66.9

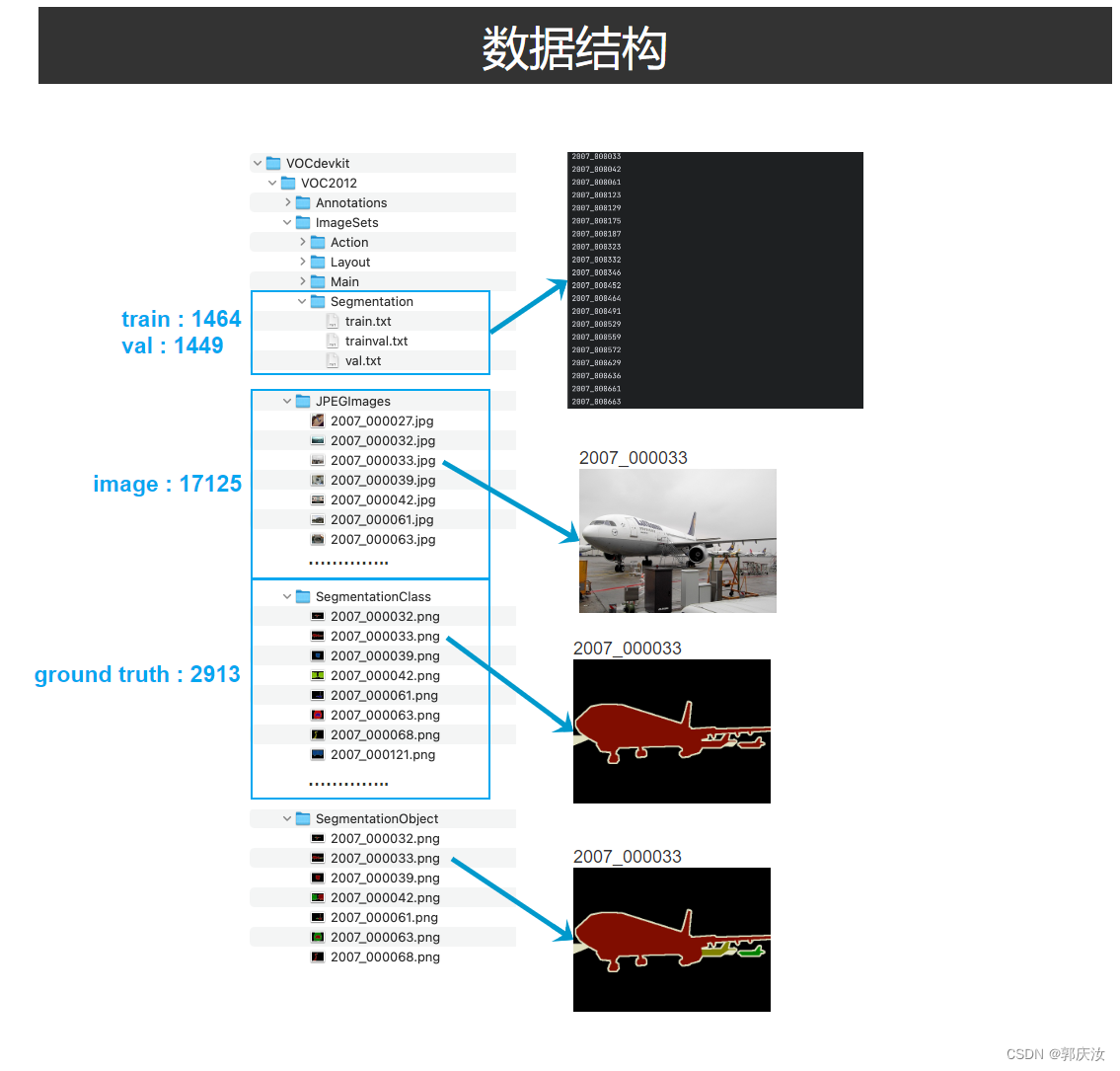
8、数据集
参照博文:
PASCAL VOC2012数据集详细介绍-5、语义分割任务

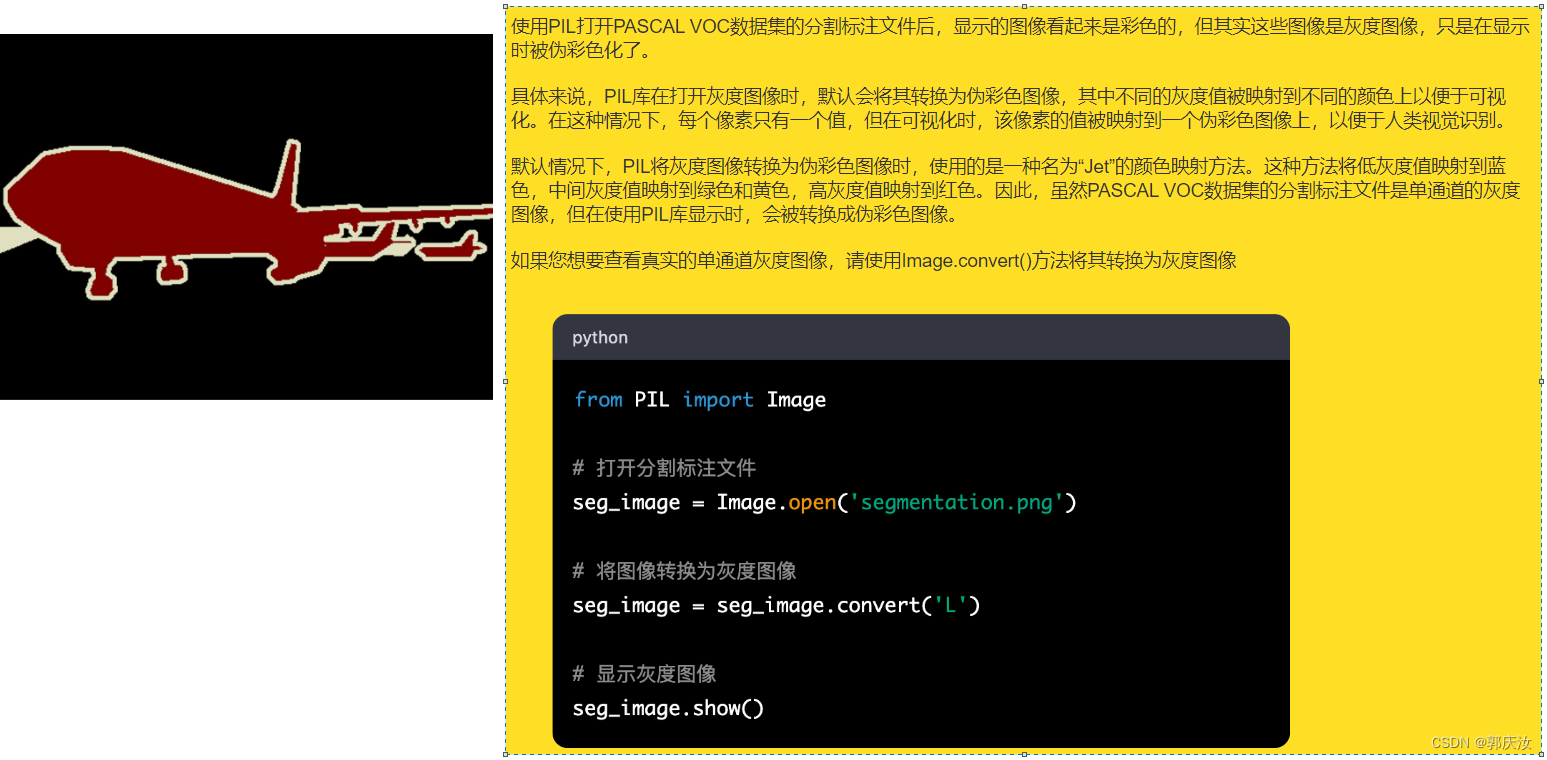
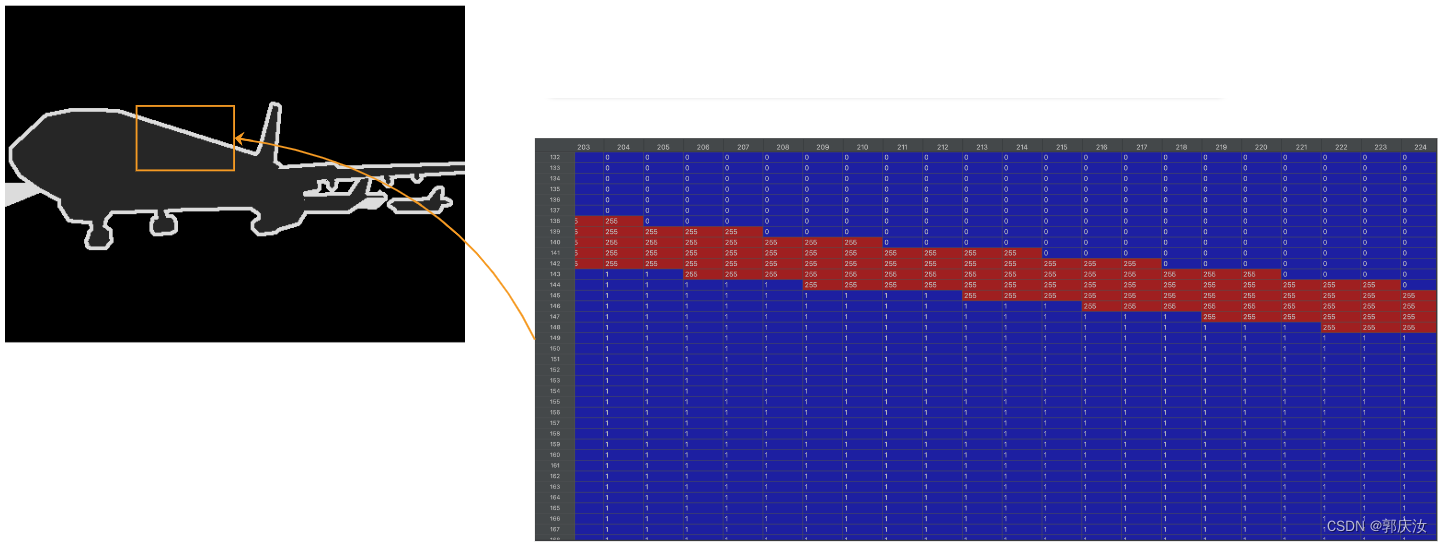
8.1 数据集预处理
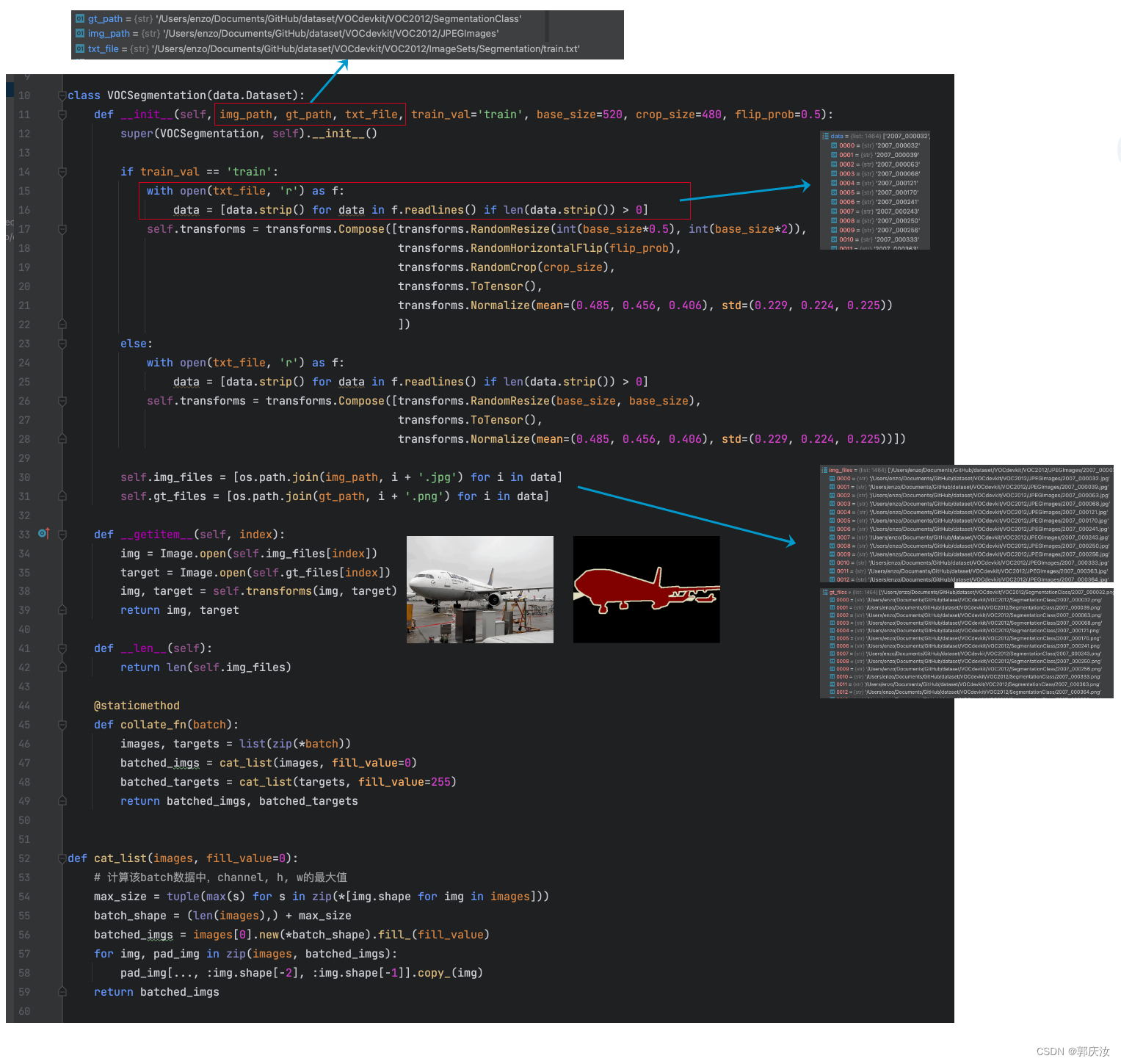
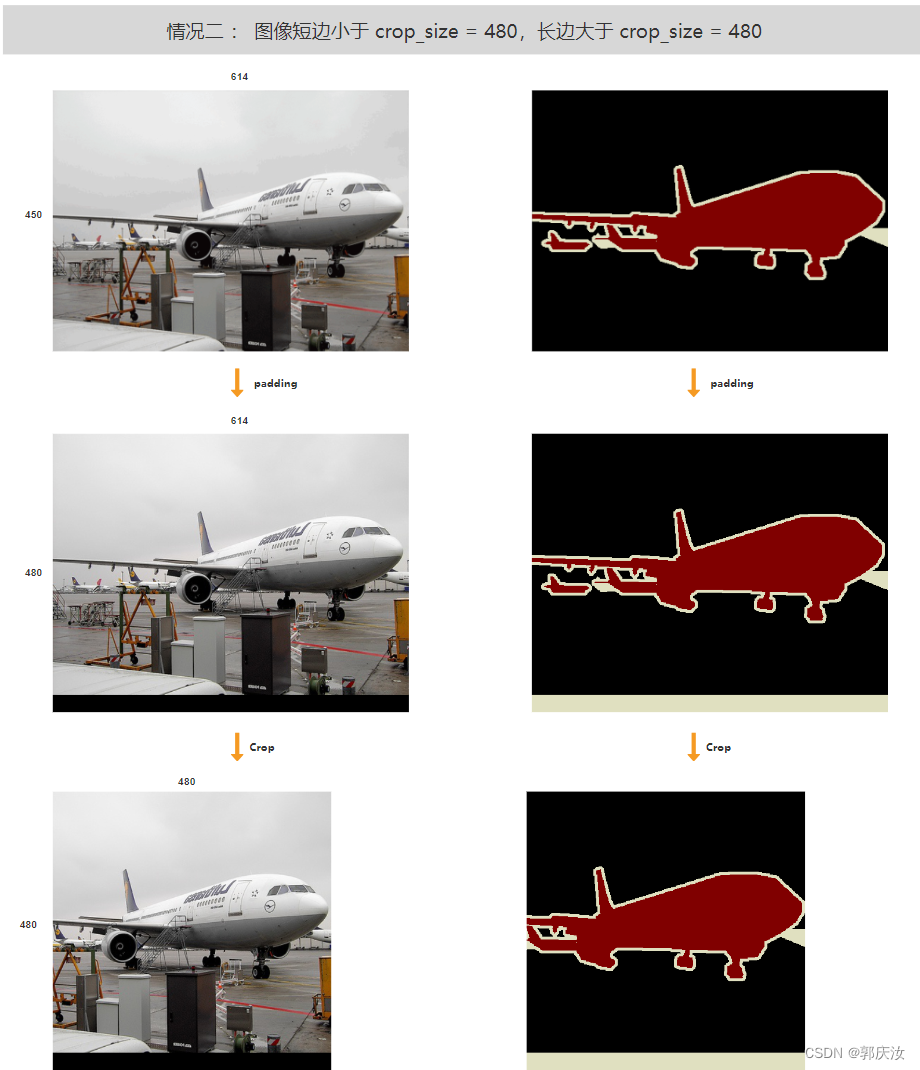
Random Resize
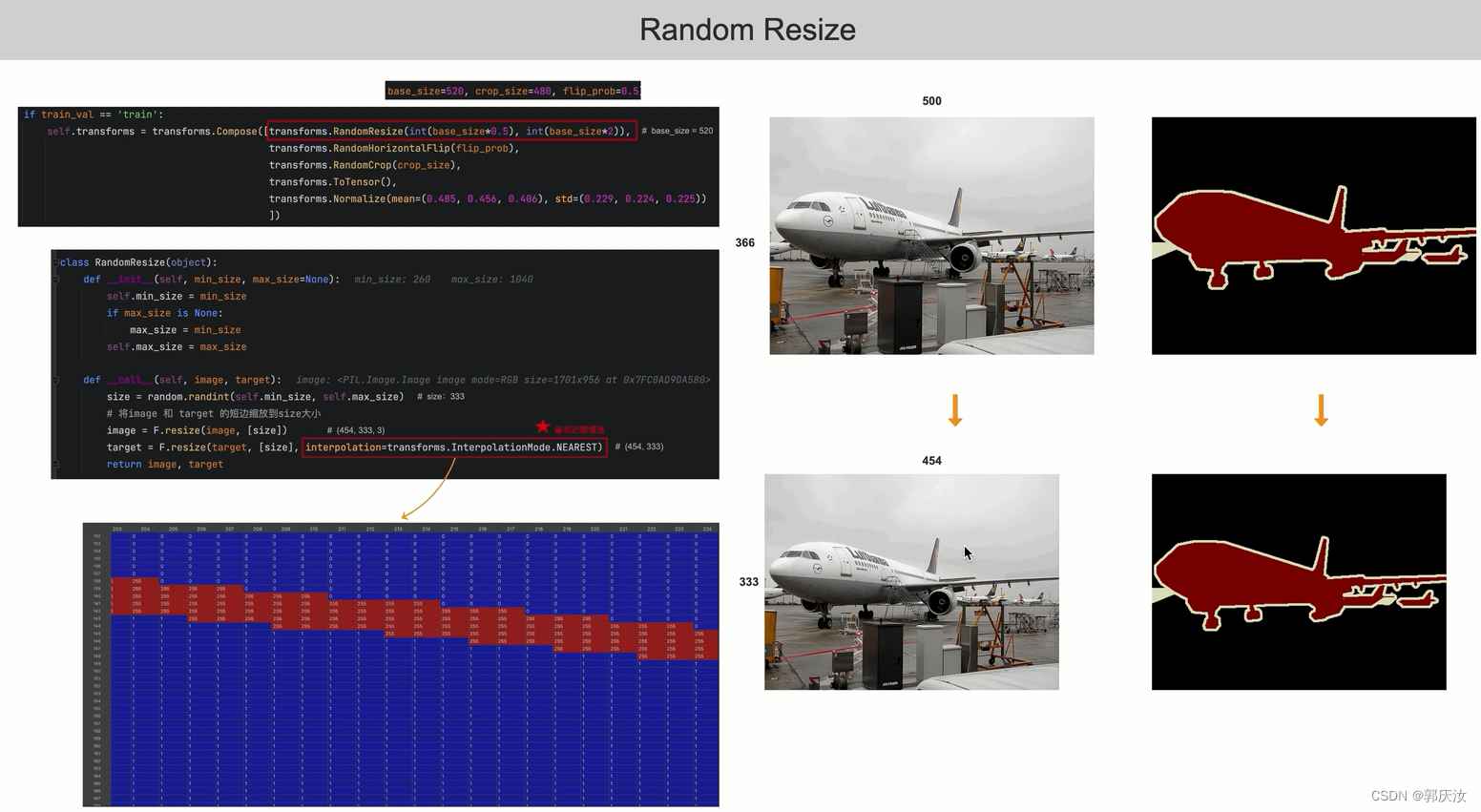
在对mask图像进行缩放时,必须采用最邻近插值法,以为如果采用双线性插值,回出现引入杂乱的像素值
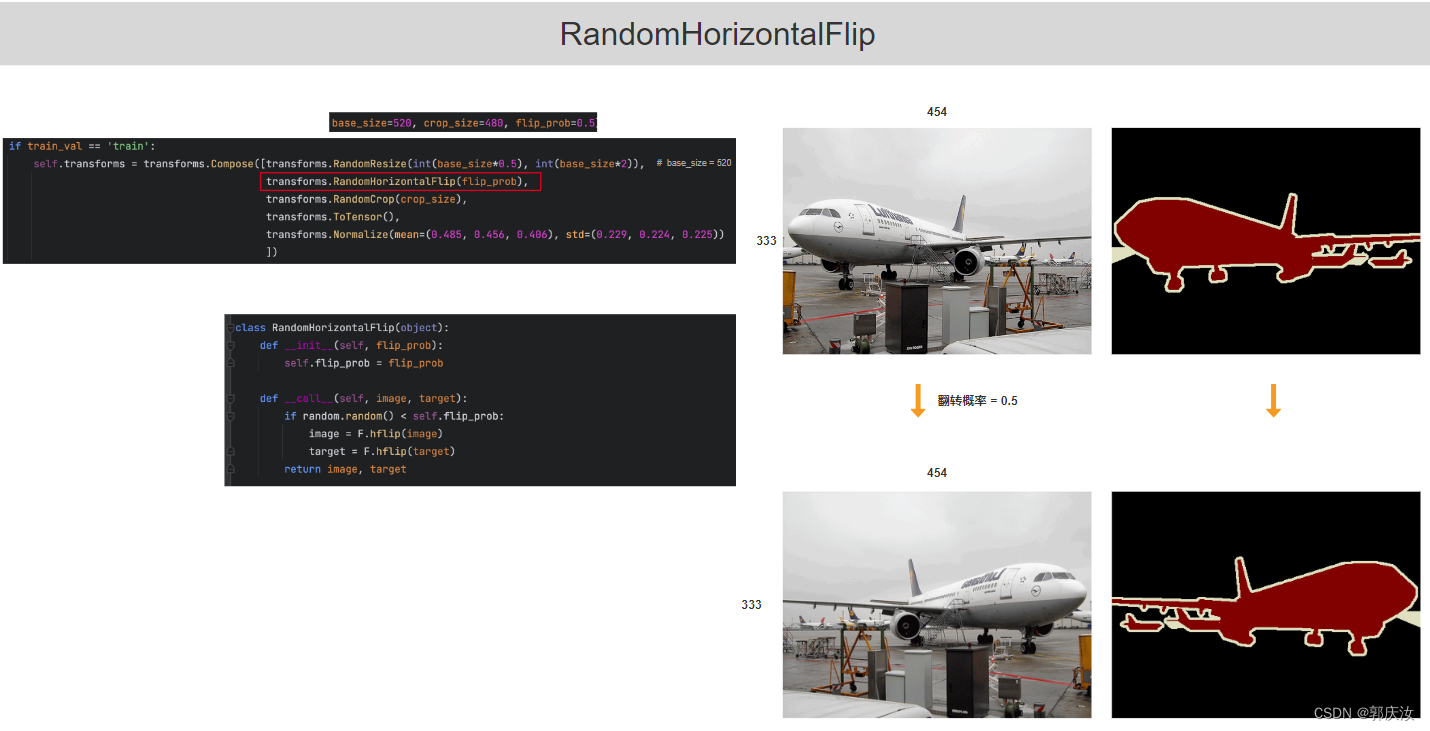
RandomHorizontalFlip
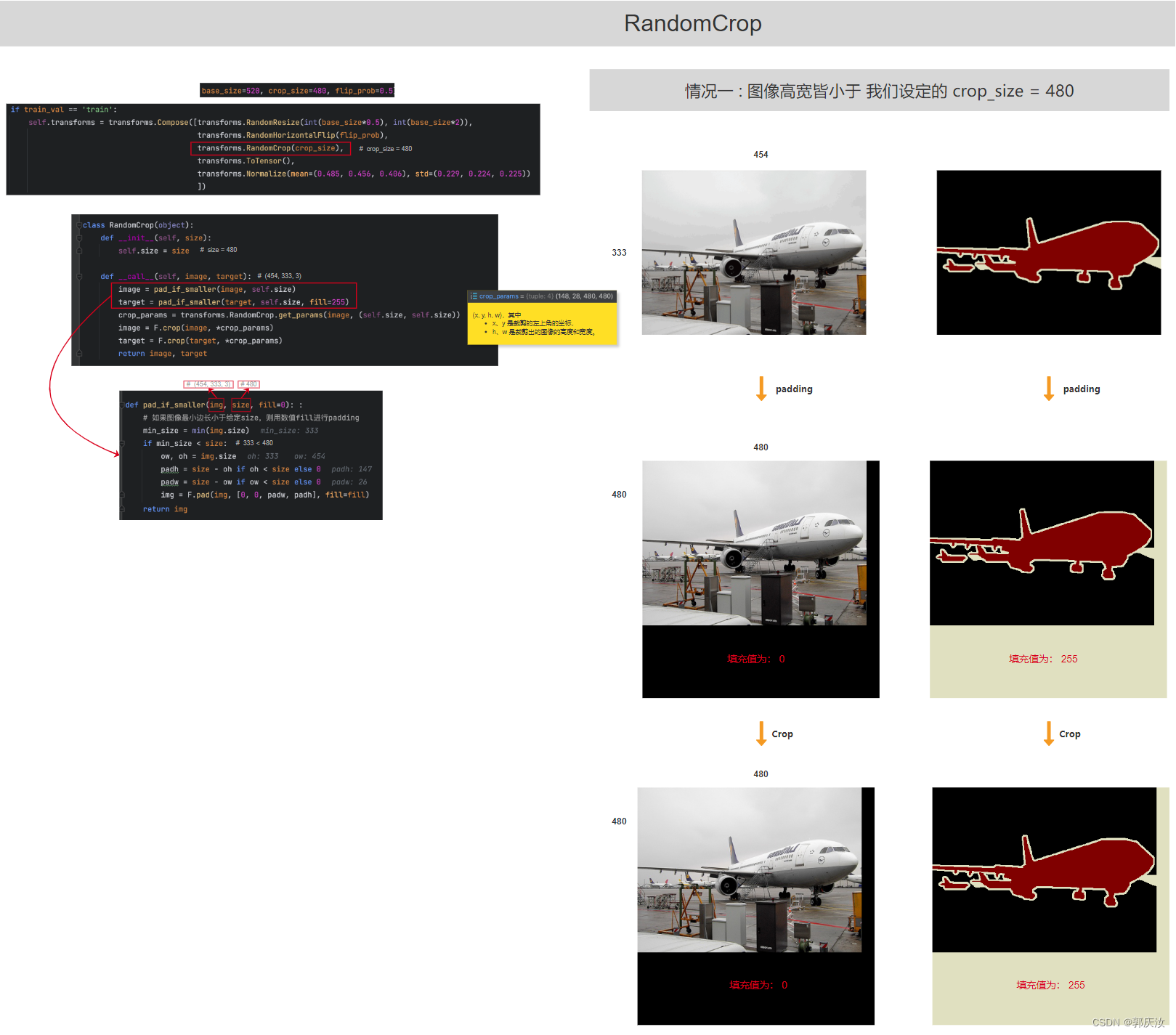
RandomCrop
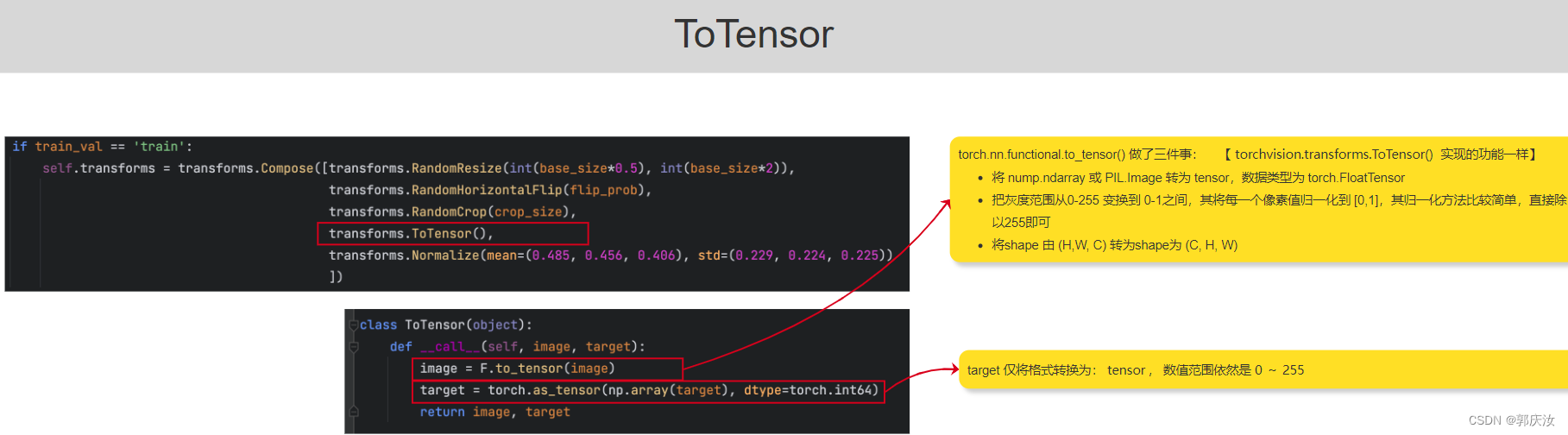
ToTensor
Normalize

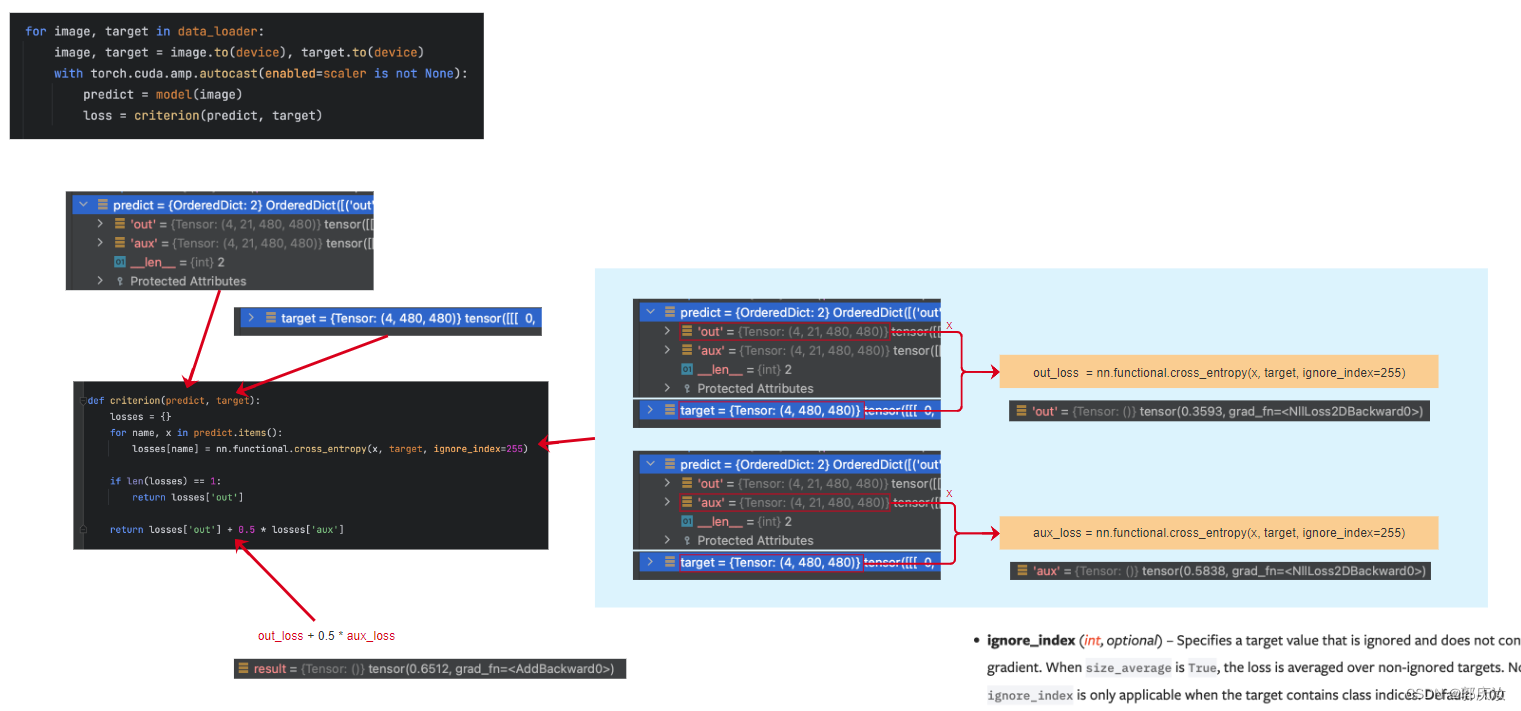
9、Loss损失函数
采用交叉熵损失函数
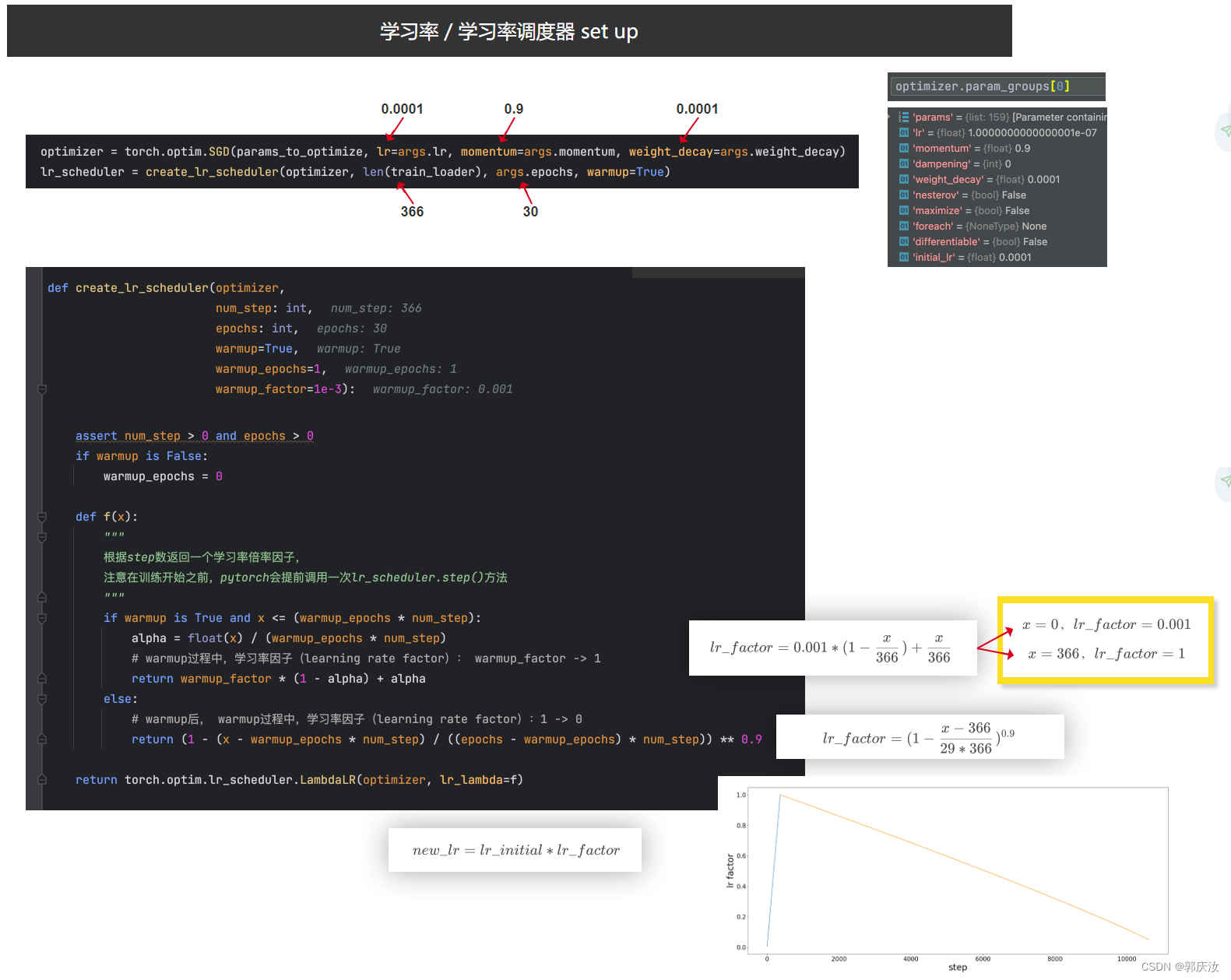
10、学习策略
采用warm up热身训练,
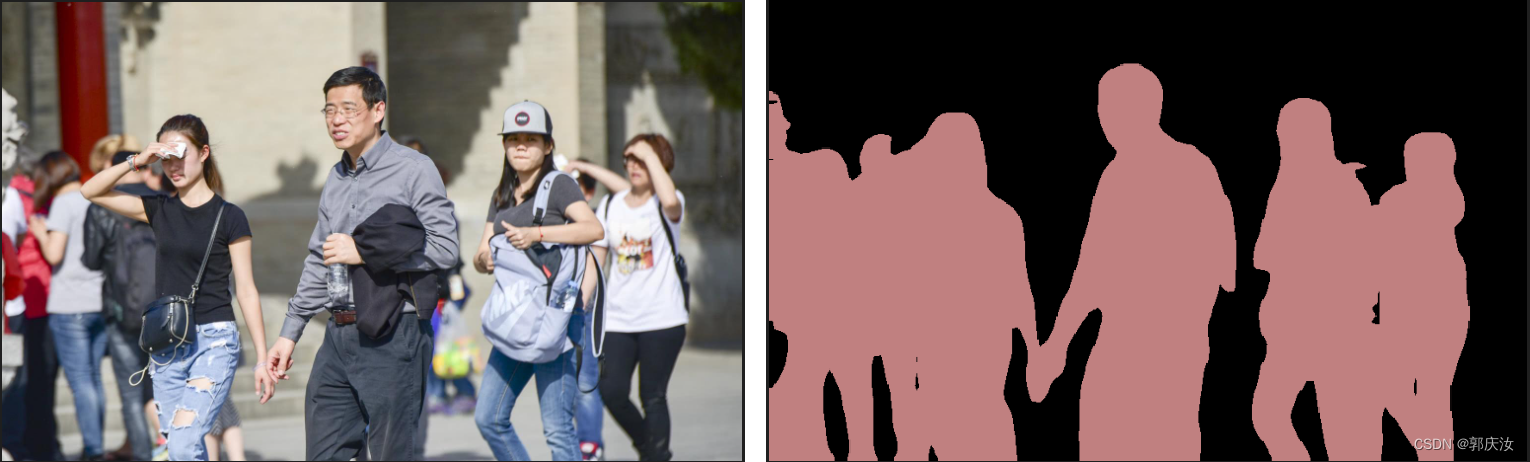
11、测试效果

多GPU训练指令
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=2 --use_env train_multi_GPU.py






![[补题记录] Atcoder Beginner Contest 321(E)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a4681635982f43759f9707a3c0398d7e.png)
