函数对象
函数对象概念
重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常称为函数对象
函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:
函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数
函数对象使用
特点:
- 函数对象在使用时,可以想普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
- 函数对象可以作为参数传递
//函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
class MyAdd
{
public:
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
};
//函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
class MyPrint
{
public:
MyPrint()
{
this->m_Count = 0;
}
void operator()(string test)
{
cout << test << endl;
m_Count++;
}
int m_Count;
};
//函数对象可以作为参数传递
void doPrint(MyPrint& mp, string test)
{
mp(test);
}
void test01()
{
//函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
MyAdd add;
cout << add(10, 20) << endl;
//函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
MyPrint myPrint;
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
cout << "打印次数:" << myPrint.m_Count << endl;
//函数对象可以作为参数传递
doPrint(myPrint, "hello c++");
}谓词
谓词概念
返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
如果operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
如果operator()接受两个参数,那么叫做二元谓词
//返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
//一元谓词 - 大于5
class greaterFive
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), greaterFive());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到大于5的数为:" << *it << endl;
}
}二元谓词之前已经提过,排序的方式修改
内建函数对象
内建函数对象意义
STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
算术仿函数
关系仿函数
逻辑仿函数
用法:
这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同
使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件#include<fucntional>
算术仿函数
功能描述:
实现四则运算
其中negate是一元运算,其他都是二元运算
仿函数类型:

void test01()
{
negate<int>n;
cout<<n(30)<<endl;
plus<int>p;
cout<<p(10, 20)<<endl;
}注意:使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件#include<fucntional>
关系仿函数
功能描述:
实现关系对比
仿函数原型:

void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end();++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Larger
{
public:
bool operator()(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 > num2;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
printVector(v);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
printVector(v);
//从大到小排序
// 方法1. 自定义仿函数
// sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Larger());
//方法2. 内建关系仿函数
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
printVector(v);
}关系仿函数中最常用的就是greater<>大于
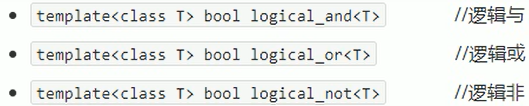
逻辑仿函数
实现逻辑运算
函数原型:
class print02
{
public:
void operator()(bool num)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
};
class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int num)
{
return num+1;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<bool>v;
v.push_back(true);
v.push_back(false);
v.push_back(true);
v.push_back(true);
for_each(v.begin(), v .end(), print02());
cout << endl;
//搬运
vector<bool>v2; //目标容器
v2.resize(v.size()); //目标容器,需要提前开辟空间
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<int>());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}STL-常用算法
- 算法主要是由头文件<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成。
- <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等
- <numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数
- <functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象。
常用遍历算法
for_each //遍历容器
transform //搬运容器到另一个容器中
for_each
函数原型:

//普通函数
void print01(int num)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
//仿函数
class print02
{
public:
void operator()(int num)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
//遍历算法
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);
cout << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
}
transform
函数原型:

class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int num)
{
return num+1;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
//搬运
vector<int>v2; //目标容器
v2.resize(v.size()); //目标容器,需要提前开辟空间
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), Transform());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}常用查找算法
算法简介:

find
功能描述:查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:

void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(14);
for_each(v.begin(), v .end(), print02());
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 20);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了:" << *it << endl;
}
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("top", 10);
Person p2("as", 32);
Person p3("bob", 43);
Person p4("tony", 38);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
Person pp("as", 32);
vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了,姓名:" << it->m_Name << ",年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}find_if
功能描述:
按条件查找元素
函数原型:

class greaterFive
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 15;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(14);
for_each(v.begin(), v .end(), print02());
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), greaterFive());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了:" << *it << endl;
}
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class greater20
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p)
{
return p.m_Age > 20;
}
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("top", 10);
Person p2("as", 32);
Person p3("bob", 43);
Person p4("tony", 38);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
Person pp("as", 32);
vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), greater20());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了,姓名:" << it->m_Name << ",年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}adjacent_find
查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:

void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(14);
v.push_back(14);
vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "未找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "已找到:" << *it << endl;
}
}binary_search
查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:

void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
bool judge = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 4);
if (judge)
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到" << endl;
}
}注意:二分查找法查找效率虽然高,但查找的容器中元素必须是有序序列
count
统计元素个数
函数原型:

void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(12);
v.push_back(34);
v.push_back(32);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(12);
v.push_back(12);
int sum = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 12);
cout << "12有" << sum << "个" << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("top", 10);
Person p2("as", 32);
Person p3("bob", 32);
Person p4("tony", 38);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
Person pp("sq", 32);
int sum = count(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
cout << "与sq同岁的人有" << sum << "个" << endl;
}count_if
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(12);
v.push_back(34);
v.push_back(32);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(16);
v.push_back(12);
int sum = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), greaterFive());
cout << "大于5有" << sum << "个" << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class AgeGreater20
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person&p)
{
return p.m_Age > 20;
}
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("top", 10);
Person p2("as", 32);
Person p3("bob", 32);
Person p4("tony", 38);
Person p5("pig", 43);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
Person pp("sq", 32);
int sum = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater20());
cout << "大于20的人有" << sum << "个" << endl;
}常用排序算法

sort
函数原型:

class print02
{
public:
void operator()(int num)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
};
class greaterInt
{
public:
bool operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(50);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());//升序
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
//降序
//sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greaterInt());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}random_shuffle
洗牌,指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:

void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
//利用洗牌算法 打乱顺序
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}random_shuffle洗牌算法较实用,记得加随机种子
merge
两个有序的容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
合并之后的容器依旧是有序的
函数原型:

reverse
反转元素
函数原型:

void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}常用拷贝和替换算法

copy
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());
void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
v2.resize(v.size());
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}replace

void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(2);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 2, 200);//将所有2改为200
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}replace_if
函数原型:

void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(2);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), greaterFive(), 6);//将所有大于5的改为6
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}swap
函数原型:

常用算术生成算法
算法生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含头文件#include<numeric>

accumulate
计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:

#include<numeric>
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//参数3是其实累加值
int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0); //5050
total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 1000);//6050
//for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << total<< endl;
}fill
向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:

void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.resize(10);//初始化10个0
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);//将0重新填充为100
}常用集合算法
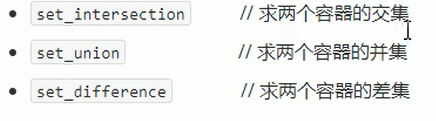
set_intersection
交集:
例:
v1: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
v2: 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
交集: 5 6 7 8 9 10

两个集合必须是有序序列!!
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
vector<int>vTarget;
//目标容器需要提前开辟空间
//最特殊情况也是占用空间最大情况:大容器包含小容器,
//故开辟空间时取最小容器的size
vTarget.resize(min(v.size(), v2.size()));
//获取交集
//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print02());
cout << endl;
}set_union
求集合并集
例:
v1: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
v2: 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
并集: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
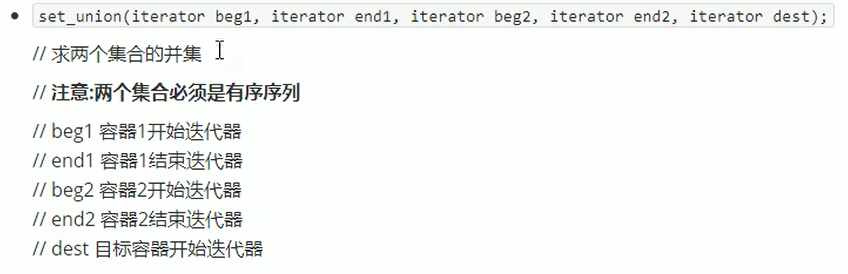
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
vector<int>vTarget;
//目标容器需要提前开辟空间
//最特殊情况也是占用空间最大情况:两个容器没有交集,
//并集就是两个容器size相加
vTarget.resize(v.size()+v2.size());
//获取并集
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print02());
cout << endl;
}set_difference
差集
例:
v1: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
v2: 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
v1和v2容器的差集: 0 1 2 3 4
v2和v1容器的差集:11 12 13 14 15

void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
vector<int>vTarget;
//目标容器需要提前开辟空间
//最特殊情况也是占用空间最大情况:两个容器没有交集,
//差集就是两个容器中大的size作为目标容器开辟空间
vTarget.resize(max(v.size(), v2.size()));
//获取v1和v2的差集
cout << "v1和v2的差集为:" << endl;
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print02());
cout << endl;
cout << "v2和v1的差集为:" << endl;
itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print02());
cout << endl;
}