目录
- 一、简介
- 二、下载及安装
- 1.Linux 安装
- 2.Windows 安装
- 3.测试安装结果
- 三、jq用法
- 1.基本语法
- 2.常见用法
- 1)格式化 JSON
- 2)获取属性
- 3)属性不存在情况处理
- 4)数组遍历、截取、展开
- 5)管道、逗号、加号
- 6)数据构造
- 7)基础函数
- 8)过滤、排序、分组函数
- 9)字符串操作函数
- 10)日期函数
- 11)高级用法

- 官网地址: https://stedolan.github.io/jq/
- 官方文档: https://jqlang.github.io/jq/manual/
- GitHub: https://github.com/stedolan/jq
- 在线测试: https://jqplay.org/
一、简介
jq 是一个强大的命令行工具,用于处理 JSON 格式的数据。它可以帮助你查询、过滤、修改和处理 JSON 数据,使得再命令行环境下处理 JSON 变得非常方便。
二、下载及安装
官方下载地址: https://jqlang.github.io/jq/download/
1.Linux 安装
方式一:yum 命令
sudo yum install epel-releaseyum install -y jq
方式二:apt-get 命令
sudo apt-get install jq
方式三:dnf 命令
sudo dnf install jq
方式四:zypper 命令
sudo zypper install jq
方式五:pacman 命令
sudo pacman -S jq
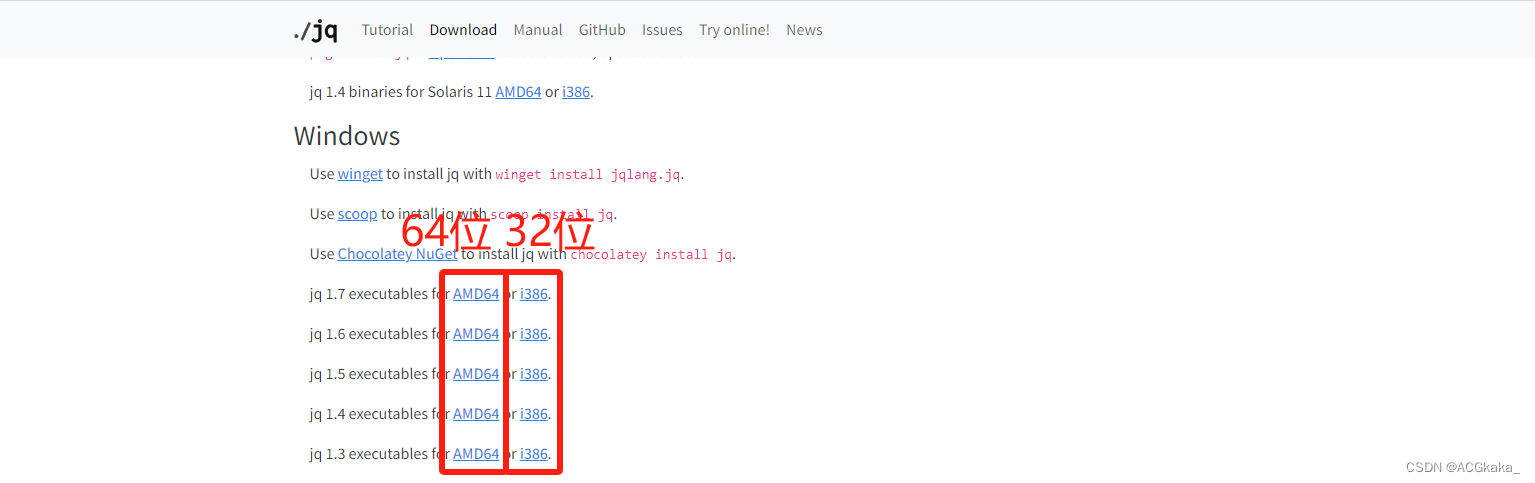
2.Windows 安装
Windows 安装,虽然下面命令很多,其实本质上都是从官网下载 exe 文件后,放到指定目录下,重命名为 jq.exe,然后再配置环境变量,自己手动操作也可以。
官方下载地址: https://jqlang.github.io/jq/download/
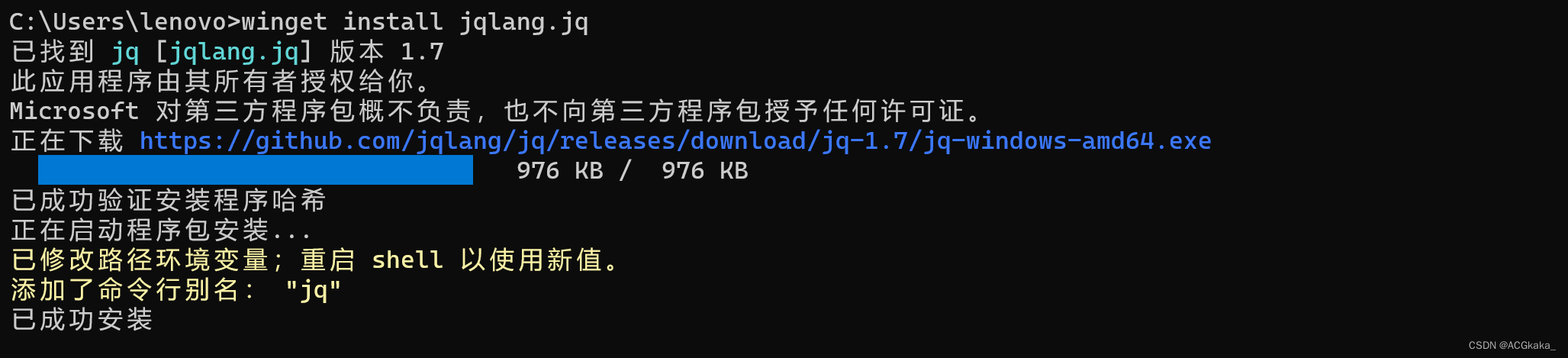
方式一:winget 命令
winget 是 Windows 自带的安装工具,可以直接在 PowerShell 或 CMD 控制台执行。
winget install jqlang.jq
需要注意的是,官方的下载地址国内无法访问,提示 InternetOpenUrl() failed. 这是网络问题导致的,需要自由发挥下。
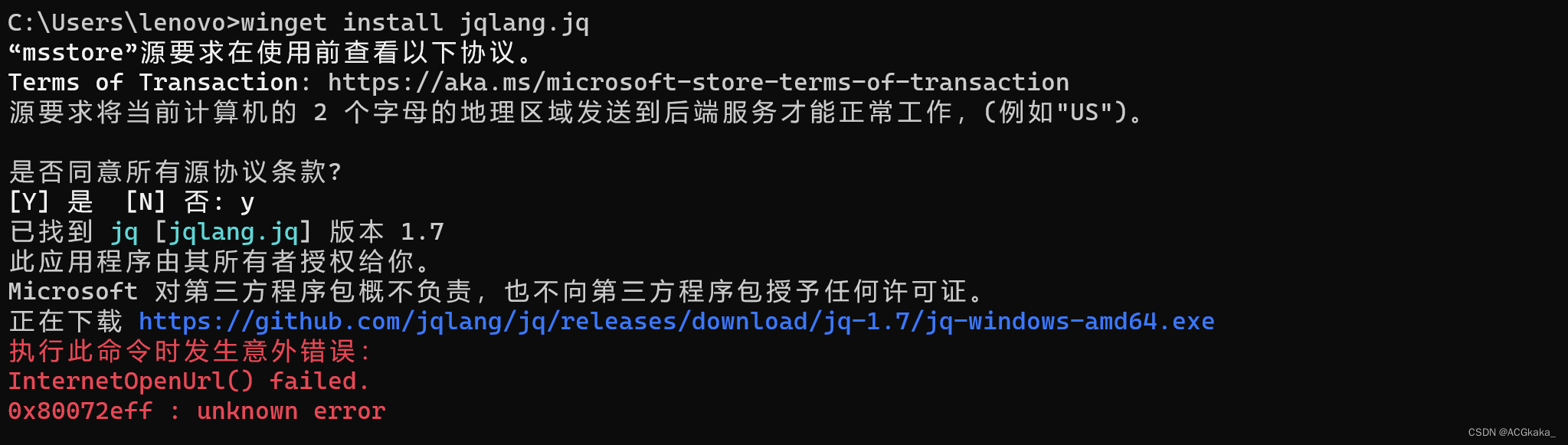
网络问题解决后,正常安装流程如下:
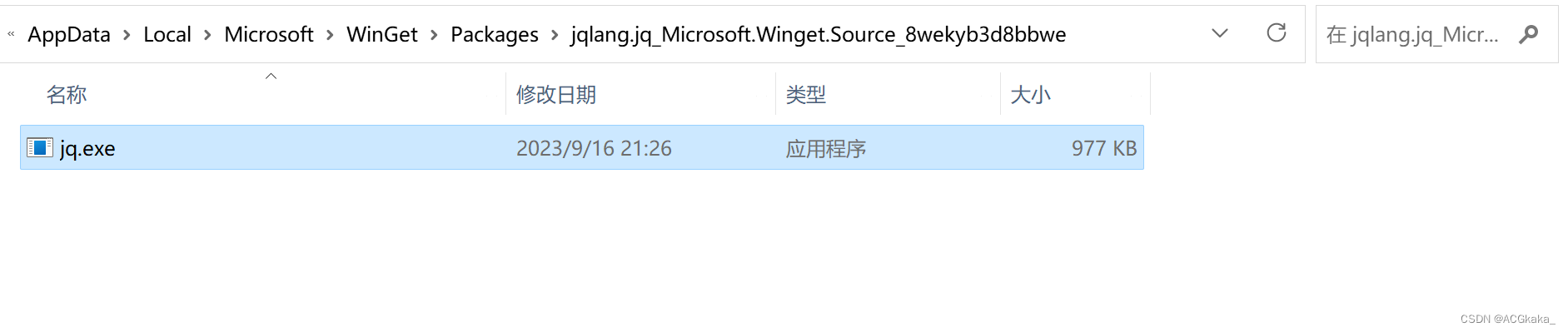
到这里还没完,因为默认安装的命令不是 jq,而是 jq-windows-amd64:

需要先去环境变量所在路径修改一下文件名为 jq.exe :
C:\Users\用户名\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WinGet\Packages\jqlang.jq_Microsoft.Winget.Source_8wekyb3d8bbwe
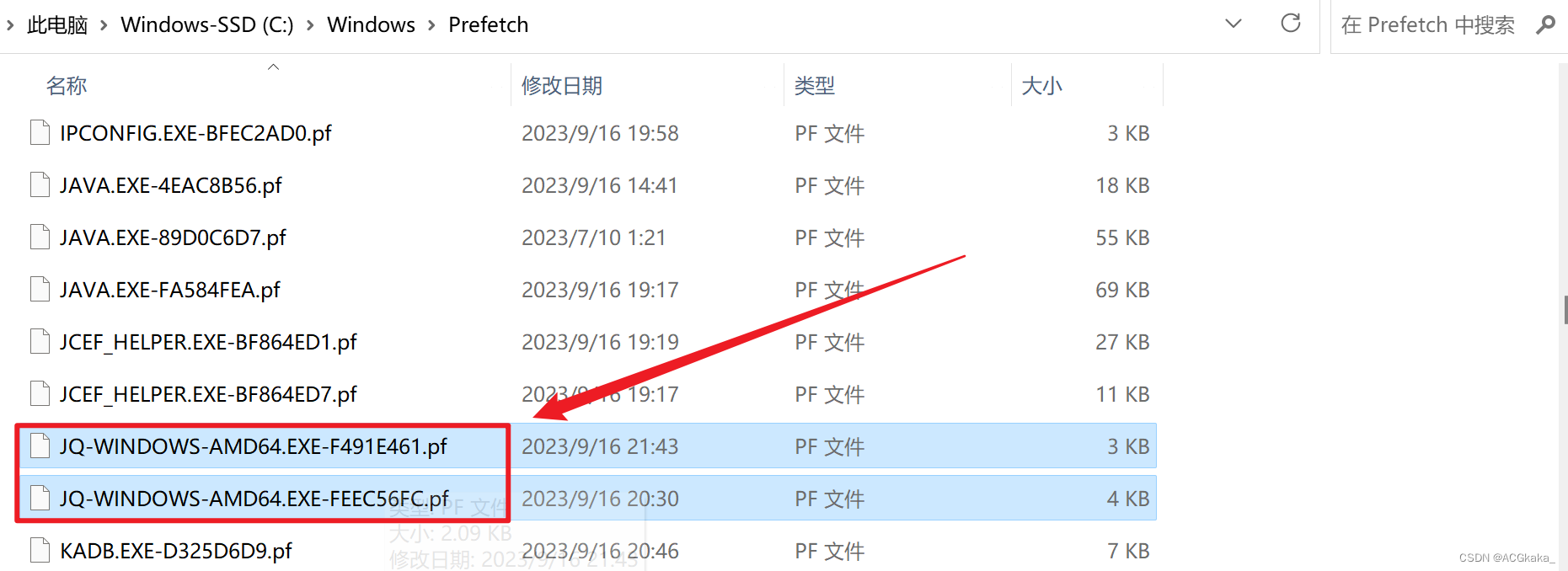
然后去 C:\Windows\Prefetch\ 下面删除 JQ-WINDOWS-AMD64 开头的文件,这是 Windows 操作系统生成缓存文件,需要清理下。
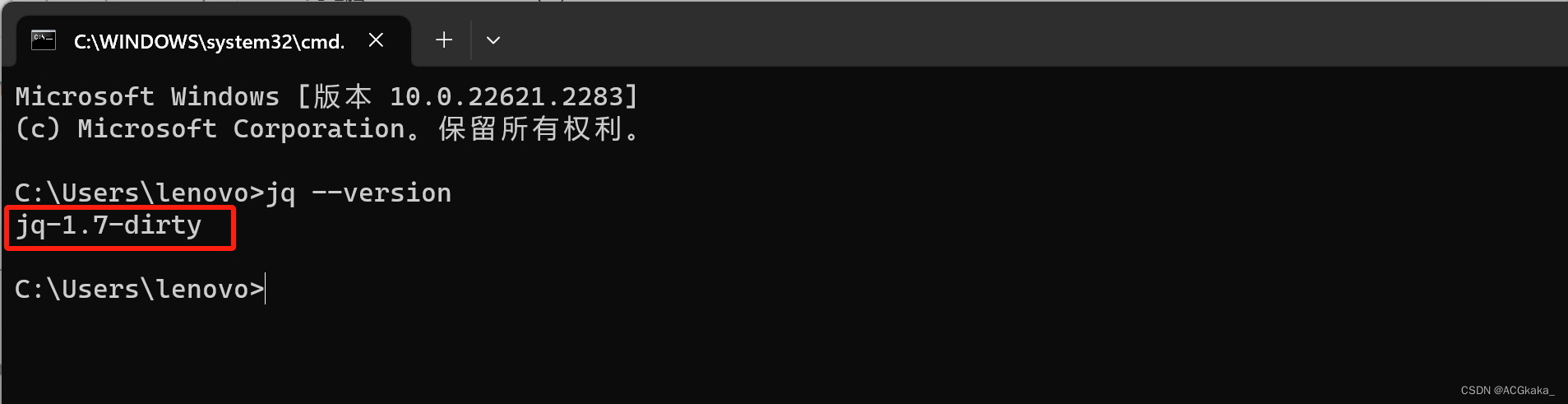
删除后,我们就可以去命令行里面执行 jq 命令了:
方式二:GitBash 命令
curl -L -o /usr/bin/jq.exe https://github.com/stedolan/jq/releases/latest/download/jq-win64.exe
这行命令主要做了以下操作:
1)下载 exe 执行文件;
2)重命名为 jq.exe;
3)将重命名后的文件放到 /usr/bin/ 目录下,也就是 Windows 的 C:\Users\用户名\Git\usr\bin\ 目录。(也可以放在 /mingw64/bin/ 目录下,对应 C:\Program Files\Git\mingw64\bin\,效果一样)
注意:这种方式安装之后,只能
方式三:Chocolatey 命令
choco install jq -y
方式四:scoop 命令
scoop install jq
3.测试安装结果
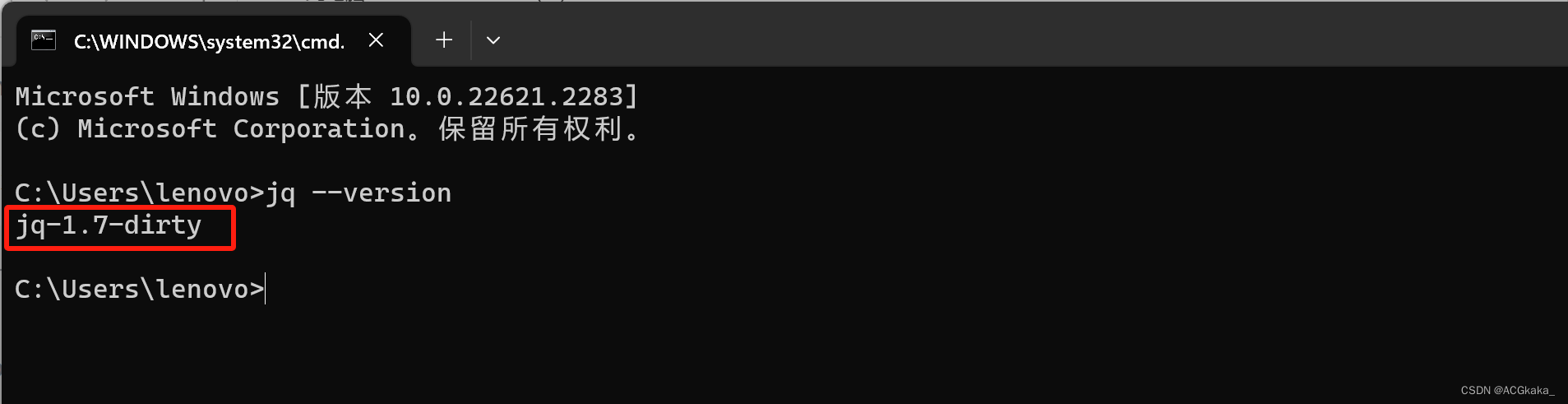
检查是否安装成功,执行如下命令:
jq --version
执行结果如下,则说明安装成功:
三、jq用法
在线测试地址: https://jqplay.org/
1.基本语法
jq [options] filter [file]
options:
-
-r:将结果按行分割,而不是 JSON 编码。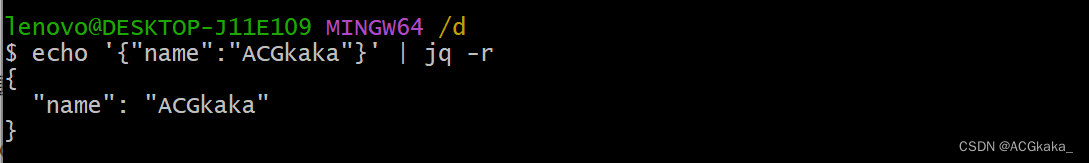
-
-c:输出时,输出原始格式。
-
-s:用于处理多个 JSON 对象的数组。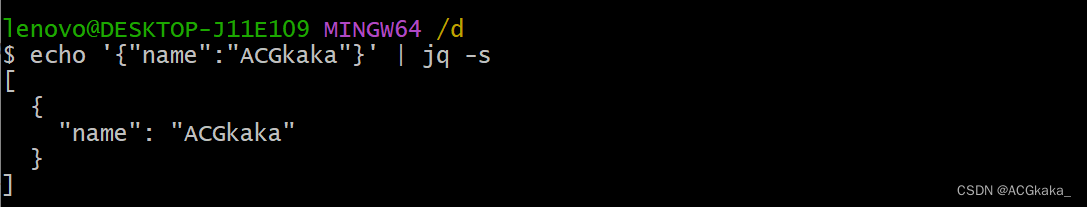
filter:
.:表示当前对象,用于访问字段或属性。例如 .fieldName 表示访问当前对象的 filedName 属性。[]:用于遍历数组元素。select(condition):根据条件选择元素。map(transform):对数组中的每个元素进行转换操作。
2.常见用法
1)格式化 JSON
按照 JSON 格式输出到多行:
echo '{"name":"ACGkaka"}' | jq
执行结果:
{
"name": "ACGkaka"
}
将 JSON 格式输出到一行:
<<eof 操作可以理解为:临时创建了一个文件并写入内容。
jq -c <<eof
{
"name": "ACGkaka"
}
eof
执行结果:
{"name":"ACGkaka"}
2)获取属性
获取对象属性:
$ echo '{"name":"ACGkaka"}' | jq .name
"ACGkaka"
获取对象属性,并去掉双引号:
$ echo '{"name":"ACGkaka"}' | jq -r .name
ACGkaka
获取数组中每个对象的属性:
$ echo '[{"name":"ACGkaka1"},{"name":"ACGkaka2"}]' | jq .[].name
"ACGkaka1"
"ACGkaka2"
获取数组中第1个对象的属性:
$ echo '[{"name":"ACGkaka1"},{"name":"ACGkaka2"}]' | jq .[0].name
"ACGkaka1"
3)属性不存在情况处理
# 从非对象类型中提取字段,会报错
$ echo -n '{"id":1, "name":"zhangsan", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq '.name.alias'
jq: error (at <stdin>:0): Cannot index string with string "alias"
# 使用?号可以避免这种报错
$ echo -n '{"id":1, "name":"zhangsan", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq '.name.alias?'
# //符号用于,当前面的表达式取不到值时,执行后面的表达式
$ echo -n '{"id":1, "name":"zhangsan", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq '.alias//.name'
"zhangsan"
4)数组遍历、截取、展开
输出所有人的年龄:
$ echo '[{"name":"ACGkaka1","age":15},{"name":"ACGkaka2","age":20}]' | jq '.[] | .age'
15
20
截取前两位数字:
$ echo '[75, 85, 90, 95]' | jq .[:2]
[
75,
85
]
截取第2、3位数字:
(留头去尾)
$ echo '[75, 85, 90, 95]' | jq .[1:3]
[
85,
90
]
数组展开:
$ echo '[75, 85, 90]' | jq .[]
75
85
90
5)管道、逗号、加号
# 管道1.可以将值从前一个命令传送到后一个命令
$ echo '{"id":1, "name":"ACGkaka", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq '.attr|.height'
1.78
# 管道2.可以做一些简单的运算
$ echo '{"id":1, "name":"ACGkaka", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq '.attr|.height*100|tostring + "cm"'
"178cm"
# 逗号可以输出多个结果
$ echo '{"id":1, "name":"ACGkaka", "attr":{"height":1.78,"weight":"60kg"}}'|jq -r '.attr.height,.attr.weight'
1.78
60kg
# 加号可以进行拼接
$ echo '{"name":"ACGkaka", "city":"Beijing"}' | jq -r '.name+", "+.city'
ACGkaka, Beijing
6)数据构造
$ cat data.txt
id name age score
1 zhangsan 17 75
2 lisi 16 80
3 wangwu 18 85
4 zhaoliu 18 90
# 每行分割成数组,[]构造新的数组输出
$ tail -n+2 data.txt|jq -R '[splits("\\s+")]' -c
["1","zhangsan","17","75"]
["2","lisi","16","80"]
["3","wangwu","18","85"]
["4","zhaoliu","18","90"]
$ jq -n '{id:1, name:"zhangsan"}' -c
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan"}
# 每行转换为对象,{}构造新的对象格式输出
$ tail -n+2 data.txt|jq -R '[splits("\\s+")] | {id:.[0]|tonumber, name:.[1], age:.[2], score:.[3]}' -c
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","age":"16","score":"80"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","age":"18","score":"90"}
# \()字符串占位变量替换
$ cat data.json
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","age":"16","score":"80"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","age":"18","score":"90"}
$ cat data.json |jq '"id:\(.id),name:\(.name),age:\(.age),score:\(.score)"' -r
id:1,name:zhangsan,age:17,score:75
id:2,name:lisi,age:16,score:80
id:3,name:wangwu,age:18,score:85
id:4,name:zhaoliu,age:18,score:90
7)基础函数
# has函数,检测对象是否包含key
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}'|jq 'has("id")'
true
# del函数,删除某个属性
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}'|jq 'del(.id)' -c
{"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}
# map函数,对数组中每个元素执行表达式计算,计算结果组织成新数组
$ seq 4|jq -s 'map(. * 2)' -c
[2,4,6,8]
# 上面map函数写法,其实等价于这个写法
$ seq 4|jq -s '[.[]|.*2]' -c
[2,4,6,8]
# keys函数,列出对象属性
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}'|jq 'keys' -c
["age","id","name","score"]
# to_entries函数,列出对象键值对
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","score":"75"}'|jq 'to_entries' -c
[{"key":"id","value":1},{"key":"name","value":"zhangsan"},{"key":"age","value":"17"},{"key":"score","value":"75"}]
# length函数,计算数组或字符串长度
$ jq -n '[1,2,3,4]|length'
4
# add函数,计算数组中数值之和
$ seq 4|jq -s 'add'
10
# tostring与tonumber,类型转换
$ seq 4|jq 'tostring|tonumber'
1
2
3
4
# type函数,获取元素类型
$ jq 'type' <<eof
1
"zhangsan"
true
null
{"id":1}
[75, 80, 85]
eof
"number"
"string"
"boolean"
"null"
"object"
"array"
8)过滤、排序、分组函数
$ cat data.json
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","sex": 0, "age":"17","score":"75"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","sex": 1, "age":"16","score":"80"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","sex": 0, "age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","sex": 0, "age":"18","score":"90"}
# select函数用于过滤,类似SQL中的where
$ cat data.json |jq 'select( (.id>1) and (.age|IN("16","17","18")) and (.name != "lisi") or (has("attr")|not) and (.score|tonumber >= 90) )' -c
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"90"}
# 有一些简化的过滤函数,如arrays, objects, iterables, booleans, numbers, normals, finites, strings, nulls, values, scalars
# 它们根据类型过滤,如objects过滤出对象,values过滤出非null值等
$ jq -c 'objects' <<eof
1
"zhangsan"
true
null
{"id":1}
[75, 80, 85]
eof
{"id":1}
$ jq -c 'values' <<eof
1
"zhangsan"
true
null
{"id":1}
[75, 80, 85]
eof
1
"zhangsan"
true
{"id":1}
[75,80,85]
# 选择出id与name字段,类似SQL中的select id,name
$ cat data.json|jq -s 'map({id,name})[]' -c
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu"}
# 提取前2行,类似SQL中的limit 2
$ cat data.json|jq -s 'limit(2; map({id,name})[])' -c
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi"}
# 按照age、id排序,类似SQL中的order by age,id
$ cat data.json|jq -s 'sort_by((.age|tonumber), .id)[]' -c
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","sex":1,"age":"16","score":"80"}
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","sex":0,"age":"17","score":"75"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"90"}
# 根据sex与age分组,并每组聚合计算count(*)、avg(score)、max(id)
$ cat data.json |jq -s 'group_by(.sex, .age)[]' -c
[{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","sex":0,"age":"17","score":"75"}]
[{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"85"},{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","sex":0,"age":"18","score":"90"}]
[{"id":2,"name":"lisi","sex":1,"age":"16","score":"80"}]
$ cat data.json |jq -s 'group_by(.sex, .age)[]|{sex:.[0].sex, age:.[0].age, count:length, avg_score:map(.score|tonumber)|(add/length), scores:map(.score)|join(","), max_id:map(.id)|max }' -c
{"sex":0,"age":"17","count":1,"avg_score":75,"scores":"75","max_id":1}
{"sex":0,"age":"18","count":2,"avg_score":87.5,"scores":"85,90","max_id":4}
{"sex":1,"age":"16","count":1,"avg_score":80,"scores":"80","max_id":2}
9)字符串操作函数
# contains函数,判断是否包含,实际也可用于判断数组是否包含某个元素
$ echo hello | jq -R 'contains("he")'
true
# 判断是否以he开头
$ echo hello | jq -R 'startswith("he")'
true
# 判断是否以llo结尾
$ echo hello | jq -R 'endswith("llo")'
true
# 去掉起始空格
$ echo ' hello '|jq -R 'ltrimstr(" ")|rtrimstr(" ")'
"hello"
# 大小写转换
$ echo hello|jq -R 'ascii_upcase'
"HELLO"
$ echo HELLO|jq -R 'ascii_downcase'
"hello"
# 字符串数组,通过逗号拼接成一个字符串
$ seq 4|jq -s 'map(tostring)|join(",")'
"1,2,3,4"
# json字符串转换为json对象
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","attr":"{\"weight\":56,\"height\":178}"}'|jq '.attr = (.attr|fromjson)' -c
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","attr":{"weight":56,"height":178}}
# json对象转换为json字符串
$ echo -n '{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","age":"17","attr":{"weight":56,"height":178}}'|jq '.attr = (.attr|tojson)'
{
"id": 1,
"name": "zhangsan",
"age": "17",
"attr": "{\"weight\":56,\"height\":178}"
}
$ cat data.txt
id:1,name:zhangsan,age:17,score:75
id:2,name:lisi,age:16,score:80
id:3,name:wangwu,age:18,score:85
id:4,name:zhaoliu,age:18,score:90
# 正则表达式过滤,jq使用的是PCRE
$ cat data.txt|jq -R 'select(test("id:\\d+,name:\\w+,age:\\d+,score:8\\d+"))' -r
id:2,name:lisi,age:16,score:80
id:3,name:wangwu,age:18,score:85
# 正则拆分字符串
$ cat data.txt|jq -R '[splits(",")]' -cr
["id:1","name:zhangsan","age:17","score:75"]
["id:2","name:lisi","age:16","score:80"]
["id:3","name:wangwu","age:18","score:85"]
["id:4","name:zhaoliu","age:18","score:90"]
# 正则替换字符串
$ cat data.txt |jq -R 'gsub("name"; "nick")' -r
id:1,nick:zhangsan,age:17,score:75
id:2,nick:lisi,age:16,score:80
id:3,nick:wangwu,age:18,score:85
id:4,nick:zhaoliu,age:18,score:90
# 正则表达式捕获数据
$ cat data.txt|jq -R 'match("id:(?<id>\\d+),name:(?<name>\\w+),age:\\d+,score:8\\d+")' -cr
{"offset":0,"length":30,"string":"id:2,name:lisi,age:16,score:80","captures":[{"offset":3,"length":1,"string":"2","name":"id"},{"offset":10,"length":4,"string":"lisi","name":"name"}]}
{"offset":0,"length":32,"string":"id:3,name:wangwu,age:18,score:85","captures":[{"offset":3,"length":1,"string":"3","name":"id"},{"offset":10,"length":6,"string":"wangwu","name":"name"}]}
# capture命名捕获,生成key是捕获组名称,value是捕获值的对象
$ cat data.txt|jq -R 'capture("id:(?<id>\\d+),name:(?<name>\\w+),age:\\d+,score:8\\d+")' -rc
{"id":"2","name":"lisi"}
{"id":"3","name":"wangwu"}
# 正则扫描输入字符串
$ cat data.txt|jq -R '[scan("\\w+:\\w+")]' -rc
["id:1","name:zhangsan","age:17","score:75"]
["id:2","name:lisi","age:16","score:80"]
["id:3","name:wangwu","age:18","score:85"]
["id:4","name:zhaoliu","age:18","score:90"]
10)日期函数
# 当前时间缀
$ jq -n 'now'
1653820640.939947
# 将时间缀转换为0时区的分解时间(broken down time),形式为 年 月 日 时 分 秒 dayOfWeek dayOfYear
$ jq -n 'now|gmtime' -c
[2022,4,29,10,45,5.466768980026245,0,148]
# 将时间缀转换为本地时区的分解时间(broken down time)
$ jq -n 'now|localtime' -c
[2022,4,29,18,46,5.386353015899658,0,148]
# 分解时间转换为时间串
$ jq -n 'now|localtime|strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")' -c
"2022-05-29T18:50:33"
# 与上面等效
$ jq -n 'now|strflocaltime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")'
"2022-05-29T19:00:40Z"
# 时间串解析为分解时间
$ date +%FT%T|jq -R 'strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")' -c
[2022,4,29,18,51,27,0,148]
# 分解时间转换为时间缀
$ date +%FT%T|jq -R 'strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")|mktime'
1653850310
11)高级用法
$ cat data.json
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","sex": 0, "age":"17","score":"75"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","sex": 1, "age":"16","score":"80"}
{"id":3,"name":"wangwu","sex": 0, "age":"18","score":"85"}
{"id":4,"name":"zhaoliu","sex": 0, "age":"18","score":"90"}
# 单变量定义
$ cat data.json| jq '.id as $id|$id'
1
2
3
4
# 对象展开式变量定义
$ cat data.json |jq '. as {id:$id,name:$name}|"id:\($id),name:\($name)"'
"id:1,name:zhangsan"
"id:2,name:lisi"
"id:3,name:wangwu"
"id:4,name:zhaoliu"
$ cat data.json
["1","zhangsan","17","75"]
["2","lisi","16","80"]
["3","wangwu","18","85"]
["4","zhaoliu","18","90"]
# 数组展开式变量定义
$ cat data.json|jq '. as [$id,$name]|"id:\($id),name:\($name)"'
"id:1,name:zhangsan"
"id:2,name:lisi"
"id:3,name:wangwu"
"id:4,name:zhaoliu"
# 分支结构
$ cat data.json|jq '. as [$id,$name]|if ($id>"1") then "id:\($id),name:\($name)" else empty end'
"id:2,name:lisi"
"id:3,name:wangwu"
"id:4,name:zhaoliu"
# 循环结构,第一个表达式条件满足时,执行只每二个表达式
# 循环结构除了while,还有until、recurse等
$ echo 1|jq 'while(.<100; .*2)'
1
2
4
8
16
32
64
# 自定义计算3次方的函数
$ echo 2|jq 'def cube: .*.*. ; cube'
8
整理完毕,完结撒花~ 🌻
参考地址:
1.Linux jq 命令讲解与实战操作(json字符串解析工具),https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1773731505742878774&wfr=spider&for=pc
2.如何在 Windows 上安装和使用“jq”,https://mwell.tech/archives/7140
3.windows的gitbash使用jq,https://blog.csdn.net/xiaolixi199311/article/details/116834056
4.Linux之jq命令,https://www.cnblogs.com/yangjianbo/articles/17667460.html