文章目录
- 630. 课程表 III
- 解法——反悔贪心⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 1462. 课程表 IV⭐
- 解法1——拓扑排序预处理
- 解法2——Floyd算法判断是否存在路径
- 2596. 检查骑士巡视方案(方向模拟)
- 1222. 可以攻击国王的皇后(方向模拟)
- LCP 50. 宝石补给(简单模拟)
- 198. 打家劫舍(经典线性DP)
- 213. 打家劫舍 II(循环打家劫舍)
- 代码写法1——另写方法robR(l, r)
- 代码写法2——二维dp数组
630. 课程表 III
https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule-iii/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-11
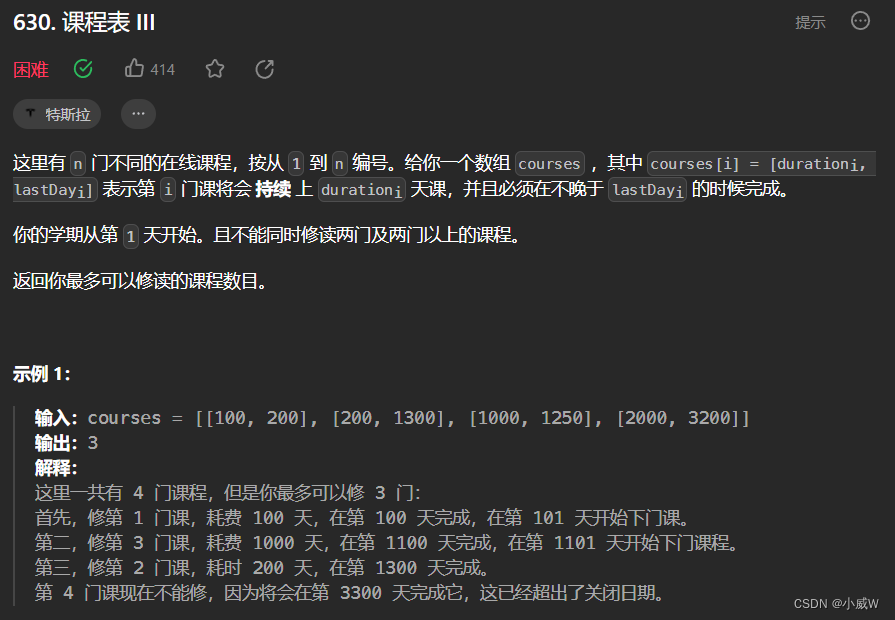
提示:
1 <= courses.length <= 10^4
1 <= durationi, lastDayi <= 10^4
解法——反悔贪心⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule-iii/solutions/2436667/tan-xin-huan-neng-fan-hui-pythonjavacgoj-lcwp/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-11
class Solution {
public int scheduleCourse(int[][] courses) {
// 按照截止时间从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(courses, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
// 最大堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
int day = 0; // 记录当前使用了多少天
for (int[] c: courses) {
int d = c[0], t = c[1];
if (day + d <= t) {
// 如果可以学,直接学
day += d;
pq.offer(d);
} else if (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek() > d) {
// 如果不可以学,检查已经选了的课程中有没有耗时更长的替换掉
day -= pq.poll() - d;
pq.offer(d);
}
}
// 最后的答案就是队列中已选课程的数量
return pq.size();
}
}
更多反悔贪心可见:
【算法】反悔贪心
【力扣周赛】第 357 场周赛(⭐反悔贪心)
1462. 课程表 IV⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule-iv/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-12
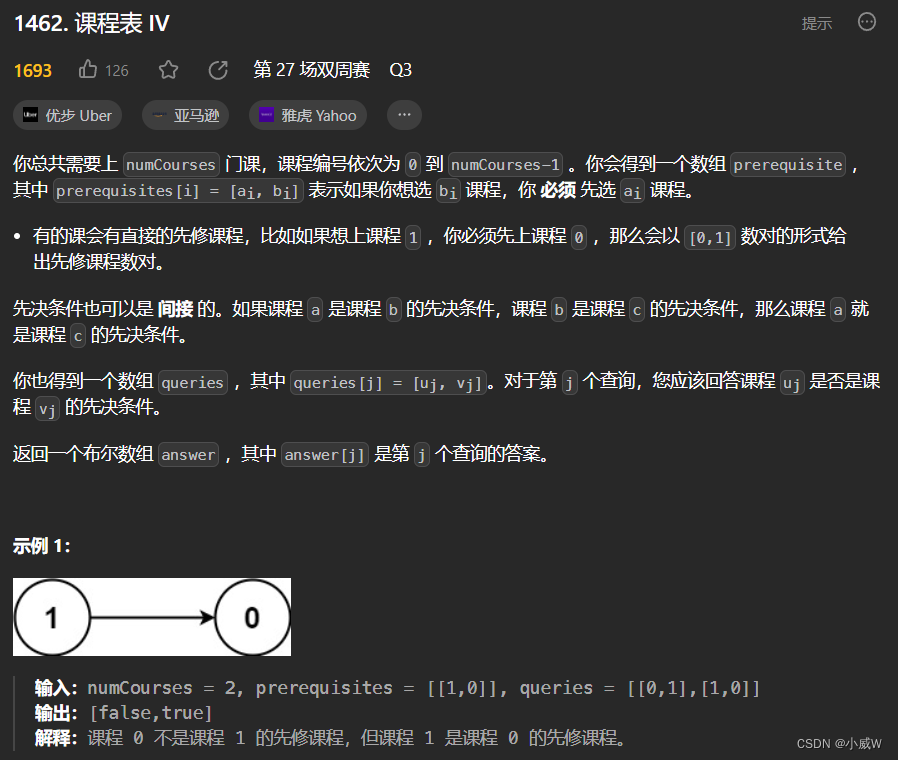
提示:
2 <= numCourses <= 100
0 <= prerequisites.length <= (numCourses * (numCourses - 1) / 2)
prerequisites[i].length == 2
0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1
ai != bi
每一对 [ai, bi] 都 不同
先修课程图中没有环。
1 <= queries.length <= 10^4
0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1
ui != vi
解法1——拓扑排序预处理
关于拓扑排序可见:【算法基础:搜索与图论】3.3 拓扑排序
在拓扑排序过程中多加一层循环,用来处理各个节点之间是否为先决条件。 回复查询时只需要
O
(
1
)
O(1)
O(1)查询。
class Solution {
public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites, int[][] queries) {
List<Boolean> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[numCourses];
int[] in = new int[numCourses];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<Integer>());
boolean[][] isPre = new boolean[numCourses][numCourses];
for (int[] p: prerequisites) {
g[p[0]].add(p[1]);
in[p[1]]++;
isPre[p[0]][p[1]] = true;
}
// 拓扑排序预处理出n^2各个节点是否是其它节点的先决条件
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if (in[i] == 0) q.offer(i);
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.poll();
for (int y: g[x]) {
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
isPre[i][y] |= isPre[i][x];
}
if (--in[y] == 0) q.offer(y);
}
}
// O(1) 回答查询
for (int[] query: queries) {
ans.add(isPre[query[0]][query[1]]);
}
return ans;
}
}
解法2——Floyd算法判断是否存在路径
关于Floyd算法可见:【算法基础:搜索与图论】3.4 求最短路算法(Dijkstra&bellman-ford&spfa&Floyd)
class Solution {
public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites, int[][] queries) {
boolean[][] g = new boolean[numCourses][numCourses];
for (int[] p: prerequisites) {
g[p[0]][p[1]] = true;
}
// Floyd三重循环
for (int k = 0; k < numCourses; ++k) {
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < numCourses; ++j) {
g[i][j] = g[i][j] | (g[i][k] & g[k][j]);
}
}
}
// 回复查询
List<Boolean> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] q: queries) {
ans.add(g[q[0]][q[1]]);
}
return ans;
}
}
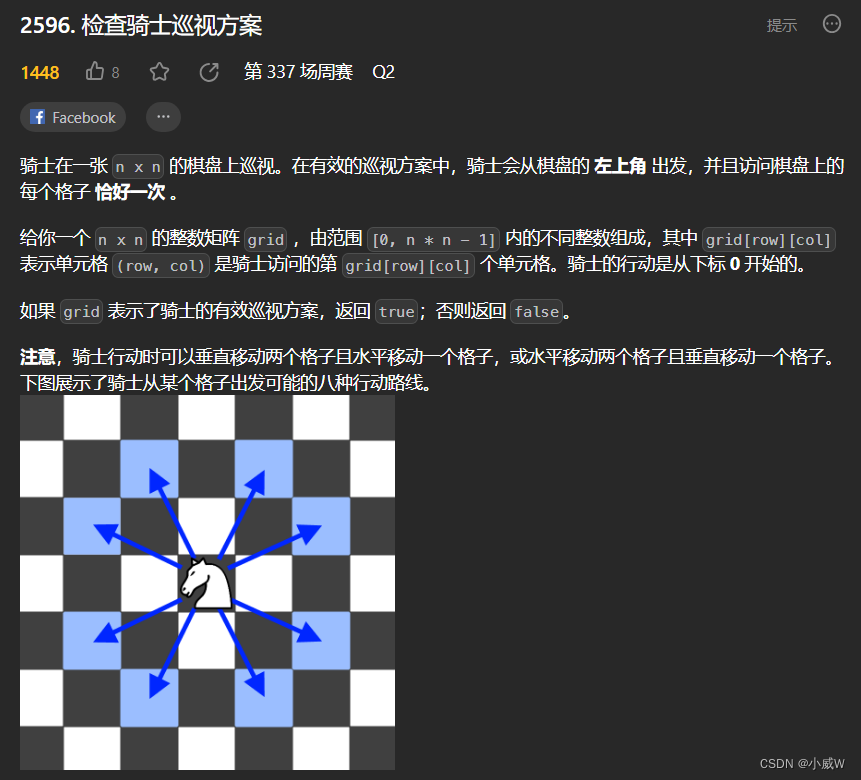
2596. 检查骑士巡视方案(方向模拟)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/check-knight-tour-configuration/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-13
提示:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length
3 <= n <= 7
0 <= grid[row][col] < n * n
grid 中的所有整数 互不相同
按题意模拟八个方向即可。
class Solution {
int[] dx = {-1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1}, dy = new int[]{-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2};
public boolean checkValidGrid(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n * n - 1; ++i) { // 检查每一步
boolean f = false;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; ++k) { // 尝试8个方向
int nx = x + dx[k], ny = y + dy[k];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < n && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] == grid[x][y] + 1) {
x = nx;
y = ny;
f = true;
break;
}
}
if (!f) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
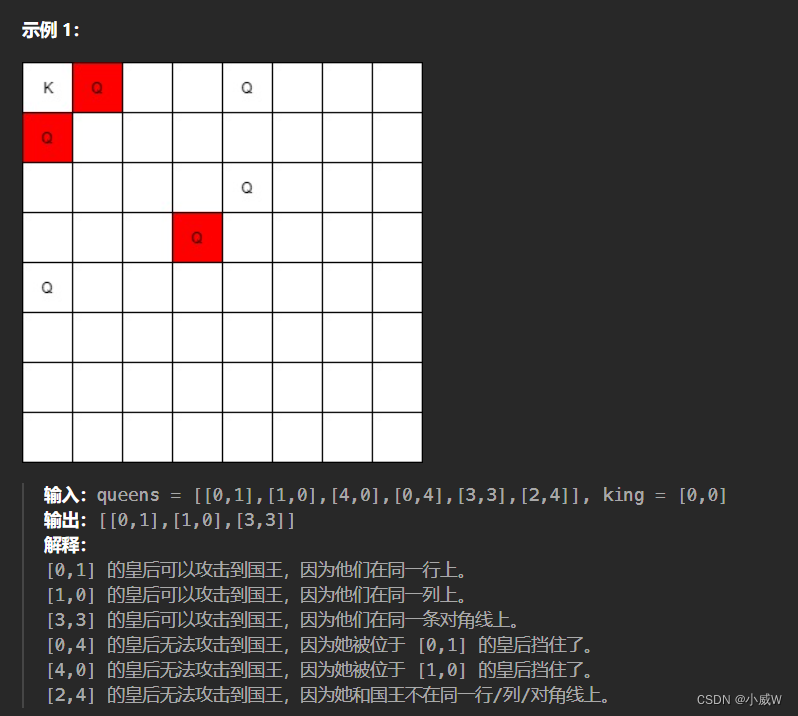
1222. 可以攻击国王的皇后(方向模拟)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/queens-that-can-attack-the-king/description/
提示:
1 <= queens.length <= 63
queens[i].length == 2
0 <= queens[i][j] < 8
king.length == 2
0 <= king[0], king[1] < 8
一个棋盘格上最多只能放置一枚棋子。
将所有皇后放入一个哈希集合中。
从国王位置开始,枚举8个方向,走8步,如果遇到的位置存在于皇后集合中,则将其加入答案。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> queensAttacktheKing(int[][] queens, int[] king) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] q: queens) s.add(q[0] * 10 + q[1]);
int[] dx = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1}, dy = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
int x = king[0], y = king[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) { // 枚举8个方向
for (int k = 1; k < 8; ++k) { // 枚举8步
int nx = x + dx[i] * k, ny = y + dy[i] * k;
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < 8 && ny < 8) {
if (s.contains(nx * 10 + ny)) {
ans.add(List.of(nx, ny));
break;
}
} else break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
LCP 50. 宝石补给(简单模拟)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/WHnhjV/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-15
提示:
2 <= gem.length <= 10^3
0 <= gem[i] <= 10^3
0 <= operations.length <= 10^4
operations[i].length == 2
0 <= operations[i][0], operations[i][1] < gem.length
按照题意模拟即可,注意向下取整的用法。
class Solution {
public int giveGem(int[] gem, int[][] operations) {
// 模拟
for (int[] op: operations) {
gem[op[1]] += gem[op[0]] / 2;
gem[op[0]] = (gem[op[0]] + 1) / 2;
}
int mn = gem[0], mx = gem[0];
for (int g: gem) {
mn = Math.min(mn, g);
mx = Math.max(mx, g);
}
return mx - mn;
}
}
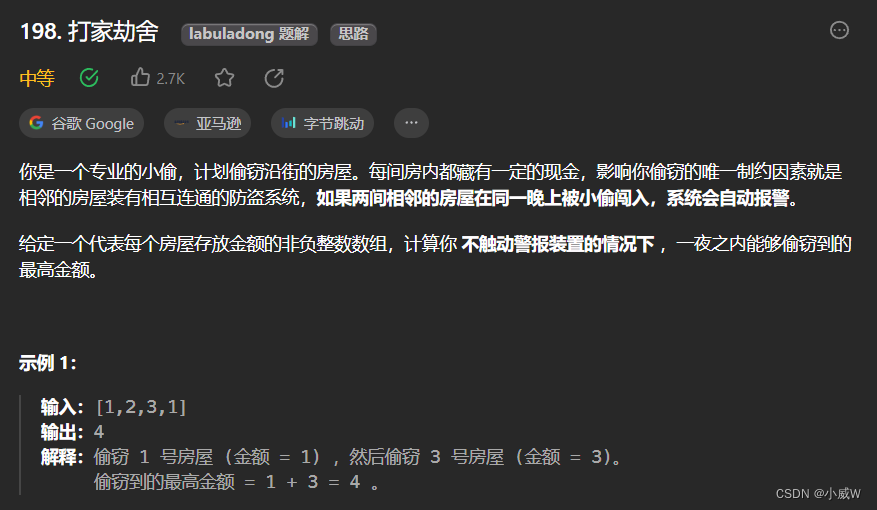
198. 打家劫舍(经典线性DP)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-16
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 400
经典线性规划嘛——
要么偷当前位置,要么不偷当前位置,取两者最大的。
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1) return nums[0];
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], nums[i] + dp[i - 2]);
return dp[n - 1];
}
}
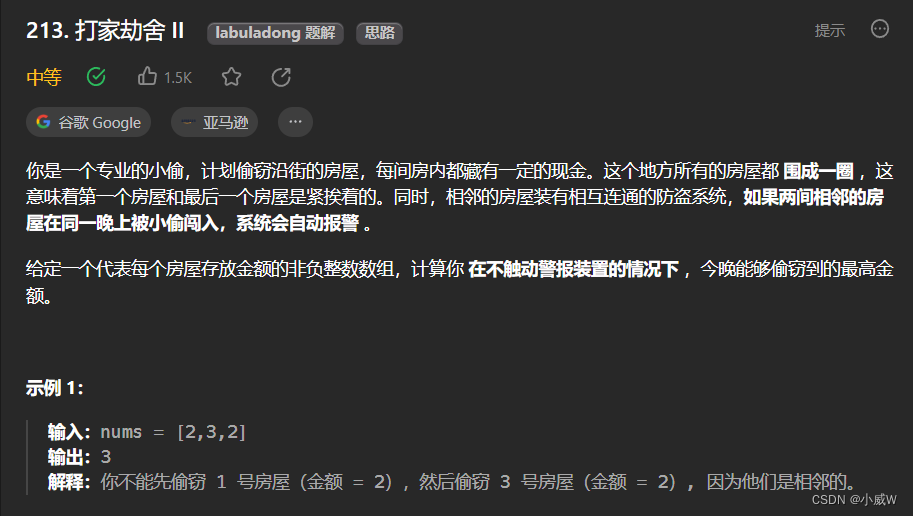
213. 打家劫舍 II(循环打家劫舍)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-ii/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-09-17
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
代码写法1——另写方法robR(l, r)
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1) return nums[0];
return Math.max(robR(nums, 0, n - 2), robR(nums, 1, n - 1));
}
public int robR(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return nums[l];
int[] dp = new int[r - l + 1];
dp[0] = nums[l];
dp[1] = Math.max(dp[0], nums[l + 1]);
for (int i = l + 2; i <= r; ++i) {
dp[i - l] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 - l], dp[i - 2 - l] + nums[i]);
}
return dp[r - l];
}
}
代码写法2——二维dp数组
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1) return nums[0];
int[] dp1 = new int[n], dp2 = new int[n];
dp1[0] = nums[0];
dp1[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
dp2[1] = nums[1];
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
dp1[i] = Math.max(dp1[i - 1], dp1[i - 2] + nums[i]);
dp2[i] = Math.max(dp2[i - 1], dp2[i - 2] + nums[i]);
}
return Math.max(dp1[n - 2], dp2[n - 1]);
}
}
两种写法见仁见智吧。