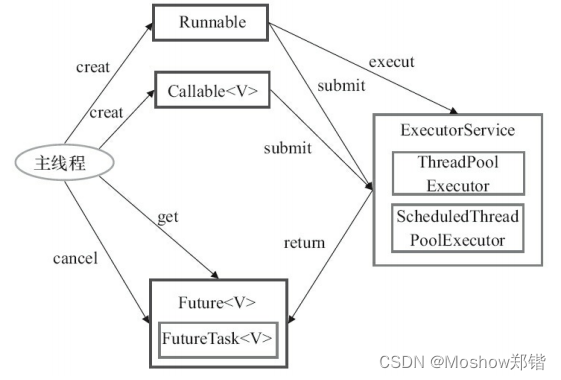
什么是ExecutorService
ExecutorService 是 Java 中的一个接口,它扩展了 Executor 接口,并提供了更多的方法来处理多线程任务。它是 Java 中用于执行多线程任务的框架之一,可以创建一个线程池,将多个任务提交到线程池中执行。ExecutorService 接口提供了许多方法,如 shutdown()、shutdownNow()、submit()、execute()、invokeAll() 等,可以更方便地提交任务、执行任务、关闭线程池等操作。同时,ExecutorService 还提供了线程池的管理和监控功能,可以更好地控制和管理线程池中的线程。在实际应用中,ExecutorService 通常与 Callable 和 Future 接口一起使用,可以实现更加灵活和高效的多线程编程。
by zhengkai.blog.csdn.net
ExecutorService基本原理
ExecutorService 的实现原理主要是基于线程池的概念。当我们创建一个 ExecutorService 对象时,实际上就是创建了一个线程池。线程池中包含了若干个线程,这些线程可以执行我们提交的任务。当线程池中的线程空闲时,它们会等待任务的到来,一旦有任务提交,就会从线程池中选择一个空闲的线程执行该任务。如果线程池中的线程都在执行任务,那么新的任务就会被暂时放在任务队列中,等待线程空闲时再来执行。
在 ExecutorService 的实现中,任务的提交和执行是异步的,也就是说,我们提交任务时不会阻塞当前线程,而是将任务交给线程池中的线程去执行。当任务执行完成后,线程会将执行结果返回给我们。同时,我们可以通过调用 ExecutorService 的方法来管理和控制线程池,如增加或减少线程数量、关闭线程池等。总之,ExecutorService 的实现原理是基于线程池的概念,通过管理和调度线程,提高程序的效率和性能,同时避免线程阻塞和死锁等问题,从而更好地管理和调度线程,提高应用程序的并发处理能力。
附加:线程池中的五种状态
线程池中有五种状态,分别是 RUNNING、STOP、SHUTDOWN、TIDYING 和 TERMINATED。它们的含义和区别如下:
- RUNNING:表示线程池处于运行状态,接受新的任务并且处理任务队列中的任务,直到线程池被显式地关闭。
- SHUTDOWN:表示线程池处于关闭状态,不再接受新的任务,但是会尝试执行任务队列中的任务,直到任务队列为空。在任务队列为空后,线程池会进入 TIDYING 状态。
- STOP:表示线程池处于停止状态,不再接受新的任务,也不会继续执行任务队列中的任务。此时,线程池会尝试中断正在执行的任务,并立即返回任务队列中的所有任务。在任务队列为空后,线程池会进入 TIDYING 状态。
- TIDYING:表示线程池正在进行线程回收的操作,此时线程池中的所有任务都已经执行完成,而线程池中的线程也已经被销毁。在线程回收完成后,线程池会进入 TERMINATED 状态。
- TERMINATED:表示线程池已经完全终止,不再接受任何任务,也不会执行任何任务。此时,线程池中的所有线程都已经被销毁,线程池对象也可以被垃圾回收。
总之,这五种状态代表了 ThreadPoolExecutor 在不同时间点的不同状态,分别表示线程池的运行状态、关闭状态、停止状态、回收状态和终止状态。它们的区别在于线程池在不同状态下的行为和状态转换。
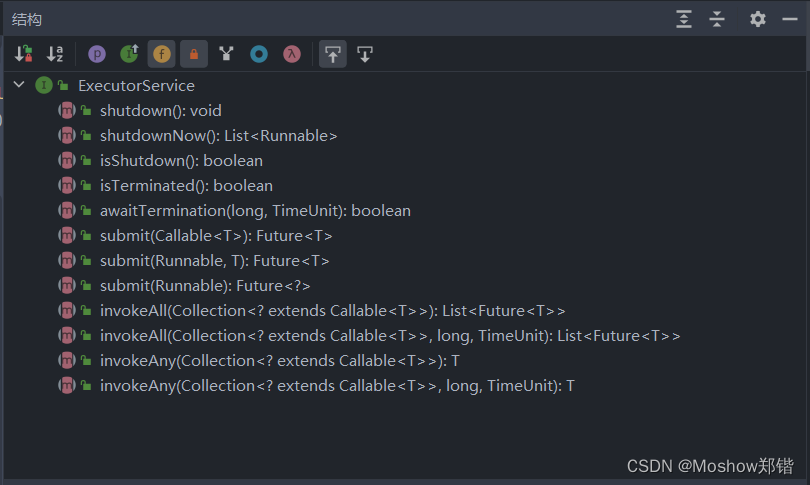
ExecuteService提供了什么方法
使用ExecuteService代表Executors创建线程池
- submit提交的是Callable方法,返回Future,说明submit是有返回值的
- execute执行的是Runnable方法,没有返回值
所以submit和execute的区别是提交的方法和是否有返回值,取决于你的业务需求。
/*
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
/*
* This file is available under and governed by the GNU General Public
* License version 2 only, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
* However, the following notice accompanied the original version of this
* file:
*
* Written by Doug Lea with assistance from members of JCP JSR-166
* Expert Group and released to the public domain, as explained at
* http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
*/
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
/**
* An {@link Executor} that provides methods to manage termination and
* methods that can produce a {@link Future} for tracking progress of
* one or more asynchronous tasks.
*
* <p>An {@code ExecutorService} can be shut down, which will cause
* it to reject new tasks. Two different methods are provided for
* shutting down an {@code ExecutorService}. The {@link #shutdown}
* method will allow previously submitted tasks to execute before
* terminating, while the {@link #shutdownNow} method prevents waiting
* tasks from starting and attempts to stop currently executing tasks.
* Upon termination, an executor has no tasks actively executing, no
* tasks awaiting execution, and no new tasks can be submitted. An
* unused {@code ExecutorService} should be shut down to allow
* reclamation of its resources.
*
* <p>Method {@code submit} extends base method {@link
* Executor#execute(Runnable)} by creating and returning a {@link Future}
* that can be used to cancel execution and/or wait for completion.
* Methods {@code invokeAny} and {@code invokeAll} perform the most
* commonly useful forms of bulk execution, executing a collection of
* tasks and then waiting for at least one, or all, to
* complete. (Class {@link ExecutorCompletionService} can be used to
* write customized variants of these methods.)
*
* <p>The {@link Executors} class provides factory methods for the
* executor services provided in this package.
*
* <h2>Usage Examples</h2>
*
* Here is a sketch of a network service in which threads in a thread
* pool service incoming requests. It uses the preconfigured {@link
* Executors#newFixedThreadPool} factory method:
*
* <pre> {@code
* class NetworkService implements Runnable {
* private final ServerSocket serverSocket;
* private final ExecutorService pool;
*
* public NetworkService(int port, int poolSize)
* throws IOException {
* serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
* pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(poolSize);
* }
*
* public void run() { // run the service
* try {
* for (;;) {
* pool.execute(new Handler(serverSocket.accept()));
* }
* } catch (IOException ex) {
* pool.shutdown();
* }
* }
* }
*
* class Handler implements Runnable {
* private final Socket socket;
* Handler(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; }
* public void run() {
* // read and service request on socket
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* The following method shuts down an {@code ExecutorService} in two phases,
* first by calling {@code shutdown} to reject incoming tasks, and then
* calling {@code shutdownNow}, if necessary, to cancel any lingering tasks:
*
* <pre> {@code
* void shutdownAndAwaitTermination(ExecutorService pool) {
* pool.shutdown(); // Disable new tasks from being submitted
* try {
* // Wait a while for existing tasks to terminate
* if (!pool.awaitTermination(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
* pool.shutdownNow(); // Cancel currently executing tasks
* // Wait a while for tasks to respond to being cancelled
* if (!pool.awaitTermination(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
* System.err.println("Pool did not terminate");
* }
* } catch (InterruptedException ex) {
* // (Re-)Cancel if current thread also interrupted
* pool.shutdownNow();
* // Preserve interrupt status
* Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions in a thread prior to the
* submission of a {@code Runnable} or {@code Callable} task to an
* {@code ExecutorService}
* <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"><i>happen-before</i></a>
* any actions taken by that task, which in turn <i>happen-before</i> the
* result is retrieved via {@code Future.get()}.
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
/**
* Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted
* tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted.
* Invocation has no additional effect if already shut down.
*
* <p>This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to
* complete execution. Use {@link #awaitTermination awaitTermination}
* to do that.
*
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager exists and
* shutting down this ExecutorService may manipulate
* threads that the caller is not permitted to modify
* because it does not hold {@link
* java.lang.RuntimePermission}{@code ("modifyThread")},
* or the security manager's {@code checkAccess} method
* denies access.
*/
void shutdown();
/**
* Attempts to stop all actively executing tasks, halts the
* processing of waiting tasks, and returns a list of the tasks
* that were awaiting execution.
*
* <p>This method does not wait for actively executing tasks to
* terminate. Use {@link #awaitTermination awaitTermination} to
* do that.
*
* <p>There are no guarantees beyond best-effort attempts to stop
* processing actively executing tasks. For example, typical
* implementations will cancel via {@link Thread#interrupt}, so any
* task that fails to respond to interrupts may never terminate.
*
* @return list of tasks that never commenced execution
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager exists and
* shutting down this ExecutorService may manipulate
* threads that the caller is not permitted to modify
* because it does not hold {@link
* java.lang.RuntimePermission}{@code ("modifyThread")},
* or the security manager's {@code checkAccess} method
* denies access.
*/
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this executor has been shut down.
*
* @return {@code true} if this executor has been shut down
*/
boolean isShutdown();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if all tasks have completed following shut down.
* Note that {@code isTerminated} is never {@code true} unless
* either {@code shutdown} or {@code shutdownNow} was called first.
*
* @return {@code true} if all tasks have completed following shut down
*/
boolean isTerminated();
/**
* Blocks until all tasks have completed execution after a shutdown
* request, or the timeout occurs, or the current thread is
* interrupted, whichever happens first.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @return {@code true} if this executor terminated and
* {@code false} if the timeout elapsed before termination
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
*/
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Submits a value-returning task for execution and returns a
* Future representing the pending results of the task. The
* Future's {@code get} method will return the task's result upon
* successful completion.
*
* <p>
* If you would like to immediately block waiting
* for a task, you can use constructions of the form
* {@code result = exec.submit(aCallable).get();}
*
* <p>Note: The {@link Executors} class includes a set of methods
* that can convert some other common closure-like objects,
* for example, {@link java.security.PrivilegedAction} to
* {@link Callable} form so they can be submitted.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @param <T> the type of the task's result
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
/**
* Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future
* representing that task. The Future's {@code get} method will
* return the given result upon successful completion.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @param result the result to return
* @param <T> the type of the result
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
/**
* Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future
* representing that task. The Future's {@code get} method will
* return {@code null} upon <em>successful</em> completion.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning a list of Futures holding
* their status and results when all complete.
* {@link Future#isDone} is {@code true} for each
* element of the returned list.
* Note that a <em>completed</em> task could have
* terminated either normally or by throwing an exception.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
*
* @param tasks the collection of tasks
* @param <T> the type of the values returned from the tasks
* @return a list of Futures representing the tasks, in the same
* sequential order as produced by the iterator for the
* given task list, each of which has completed
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting, in
* which case unfinished tasks are cancelled
* @throws NullPointerException if tasks or any of its elements are {@code null}
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if any task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
*/
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning a list of Futures holding
* their status and results
* when all complete or the timeout expires, whichever happens first.
* {@link Future#isDone} is {@code true} for each
* element of the returned list.
* Upon return, tasks that have not completed are cancelled.
* Note that a <em>completed</em> task could have
* terminated either normally or by throwing an exception.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
*
* @param tasks the collection of tasks
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @param <T> the type of the values returned from the tasks
* @return a list of Futures representing the tasks, in the same
* sequential order as produced by the iterator for the
* given task list. If the operation did not time out,
* each task will have completed. If it did time out, some
* of these tasks will not have completed.
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting, in
* which case unfinished tasks are cancelled
* @throws NullPointerException if tasks, any of its elements, or
* unit are {@code null}
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if any task cannot be scheduled
* for execution
*/
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning the result
* of one that has completed successfully (i.e., without throwing
* an exception), if any do. Upon normal or exceptional return,
* tasks that have not completed are cancelled.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
*
* @param tasks the collection of tasks
* @param <T> the type of the values returned from the tasks
* @return the result returned by one of the tasks
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
* @throws NullPointerException if tasks or any element task
* subject to execution is {@code null}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if tasks is empty
* @throws ExecutionException if no task successfully completes
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if tasks cannot be scheduled
* for execution
*/
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning the result
* of one that has completed successfully (i.e., without throwing
* an exception), if any do before the given timeout elapses.
* Upon normal or exceptional return, tasks that have not
* completed are cancelled.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
*
* @param tasks the collection of tasks
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @param <T> the type of the values returned from the tasks
* @return the result returned by one of the tasks
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
* @throws NullPointerException if tasks, or unit, or any element
* task subject to execution is {@code null}
* @throws TimeoutException if the given timeout elapses before
* any task successfully completes
* @throws ExecutionException if no task successfully completes
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if tasks cannot be scheduled
* for execution
*/
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
new ExecutorService的创建
创建一个什么样的ExecutorService的实例(即线程池)需要g根据具体应用场景而定,不过Java给我们提供了一个Executors工厂类,它可以帮助我们很方便的创建各种类型ExecutorService线程池,Executors一共可以创建下面这四类线程池:
- newCachedThreadPool 创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。
- newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
- newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
- newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
注意:Executors只是一个工厂类,它所有的方法返回的都是ThreadPoolExecutor、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor这两个类的实例。
execute(Runnable)
这个方法接收一个Runnable实例,并且异步的执行,缺点就是只负责执行不负责返回:
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Asynchronous task");
}
});
executorService.shutdown();submit(Runnable)
submit(Runnable)和execute(Runnable)区别是前者可以返回一个Future对象,通过返回的Future对象,我们可以检查提交的任务是否执行完毕,请看下面执行的例子:
Future future = executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Asynchronous task");
}
});
future.get();
//如果返回了空,则代表没有任务正在执行中,任务已经运行完毕
如果任务执行完成,future.get()方法会返回一个null。注意,future.get()方法会产生阻塞。
submit(Callable)
submit(Callable)和submit(Runnable)类似,也会返回一个Future对象,但是除此之外,submit(Callable)接收的是一个Callable的实现,Callable接口中的call()方法有一个返回值,可以返回任务的执行结果,而Runnable接口中的run()方法是void的,没有返回值。请看下面实例:
Future future = executorService.submit(new Callable(){
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Asynchronous Callable");
return "Callable Result";
}
});
System.out.println("future.get() = " + future.get());
如果任务执行完成,future.get()方法会返回Callable任务的执行结果。注意,future.get()方法会产生阻塞。
invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)方法接收的是一个Callable的集合,执行这个方法不会返回Future,但是会返回所有Callable任务中其中一个任务的执行结果。这个方法也无法保证返回的是哪个任务的执行结果,反正是其中的某一个。
以下代码每次执行都会返回一个结果,并且返回的结果是变化的,可能会返回“Task2”也可是“Task1”或者“Task3”。
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Set<Callable<String>> callables = new HashSet<Callable<String>>();
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 1";
}
});
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 2";
}
});
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 3";
}
});
String result = executorService.invokeAny(callables);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
executorService.shutdown();
invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
invokeAll(...)与 invokeAny(...)类似也是接收一个Callable集合,但是前者执行之后会返回一个Future的List,其中对应着每个Callable任务执行后的Future对象。r
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Set<Callable<String>> callables = new HashSet<Callable<String>>();
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 1";
}
});
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 2";
}
});
callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Task 3";
}
});
List<Future<String>> futures = executorService.invokeAll(callables);
for(Future<String> future : futures){
System.out.println("future.get = " + future.get());
}
executorService.shutdown();优雅的关闭ExecutorService
如果的应用程序是通过main()方法启动的,在这个main()退出之后,如果应用程序中的ExecutorService没有关闭,这个应用将一直运行。之所以会出现这种情况,是因为ExecutorService中运行的线程会阻止JVM关闭。
如果要关闭ExecutorService中执行的线程,我们可以调用ExecutorService.shutdown()方法。在调用shutdown()方法之后,ExecutorService不会立即关闭,但是它不再接收新的任务,直到当前所有线程执行完成才会关闭,所有在shutdown()执行之前提交的任务都会被执行。
如果我们想立即关闭ExecutorService,我们可以调用ExecutorService.shutdownNow()方法。这个动作将跳过所有正在执行的任务和被提交还没有执行的任务。但是它并不对正在执行的任务做任何保证,有可能它们都会停止,也有可能执行完成。
优雅一点就是
//使用这种方式,ExecutorService 首先停止执行新任务,等待指定的时间段完成所有任务。如果该时间到期,则立即停止执行。
executorService.shutdown();
try {
if (!executorService.awaitTermination(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
SpringBoot中注入ExecutorService
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* 多线程池配置
*/
@Slf4j
@EnableAsync
@Configuration
public class ThreadExecutorConfig {
/**
* SpringBoot会优先使用名称为"taskExecutor"的线程池。
* 如果没有找到,才会使用其他类型为TaskExecutor或其子类的线程池。
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Executor taskExecutor() {
log.info("start taskExecutor");
int size = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
//return new ThreadPoolExecutor(size, size, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new VisiableThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 配置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(8);
// 设置队列容量
executor.setQueueCapacity(20);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(0);
// 配置线程池中的线程的名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("executor-");
// 设置拒绝策略
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
// CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是有调用者所在的线程来执行
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 执行初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
//Bean销毁时会执行线程池销毁方法
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public ExecutorService executorService() {
return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
}
}@AutoWired
private ExecutorService executorService;使用Callable+FutureTask
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种方式
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(task);
executor.submit(futureTask);
executor.shutdown();
//第二种方式,注意这种方式和第一种方式效果是类似的,只不过一个使用的是ExecutorService,一个使用的是Thread
/*Task task = new Task();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(task);
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("主线程在执行任务");
try {
System.out.println("task运行结果"+futureTask.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("所有任务执行完毕");
}
}
class Task implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("子线程在进行计算");
Thread.sleep(3000);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
}Future 接口
submit() 方法和 invokeAll() 方法返回一个 Future 接口的对象或 Future 类型的对象集合。这些 Future 接口的对象允许我们获取任务执行的结果或检查任务的状态 ( 是正在运行还是执行完毕 )。
Future 接口 get() 方法
Future 接口提供了一个特殊的阻塞方法 get(),它返回 Callable 任务执行的实际结果,但如果是 Runnable 任务,则只会返回 null。
因为 get() 方法是阻塞的。如果调用 get() 方法时任务仍在运行,那么调用将会一直被执阻塞,直到任务正确执行完毕并且结果可用时才返回。
而且更重要的是,正在被执行的任务随时都可能抛出异常或中断执行。因此我们要将 get() 调用放在 try catch 语句块中,并捕捉 InterruptedException 或 ExecutionException 异常。
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(callableTask);
String result = null;
try {
result = future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}因为 get() 方法是阻塞的,而且并不知道要阻塞多长时间。因此可能导致应用程序的性能降低。如果结果数据并不重要,那么我们可以使用超时机制来避免长时间阻塞。
String result = future.get(200, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
这个 get() 的重载,第一个参数为超时的时间,第二个参数为时间的单位。上面的实例所表示就的就是等待 200 毫秒。
注意,这个 get() 重载方法,如果在超时时间内正常结束,那么返回的是 Future 类型的结果,如果超时了还没结束,那么将抛出 TimeoutException 异常。
除了 get() 方法之外,Future 还提供了其它很多方法,我们将几个重要的方法罗列在此
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| isDone() | 检查已分配的任务是否已处理 |
| cancel() | 取消任务执行 |
| isCancelled() | 检查任务是否已取消 |
这些方法的使用方式如下
boolean isDone = future.isDone(); boolean canceled = future.cancel(true); boolean isCancelled = future.isCancelled();