目录
1 文件I/O 介绍
2 文件I/O – 文件描述符fd(File Descriptor)
3 文件I/O – open
4 文件I/O – close
5 文件I/O – read
6 文件I/O – write
7 文件IO – lseek
8 标准I/O – 思考和练习
掌握文件描述符的含义
1 文件I/O 介绍
什么是文件I/O?
posix(可移植操作系统接口)定义的一组函数
不提供缓冲机制,每次读写操作都引起系统调用
核心概念是文件描述符
访问各种类型文件
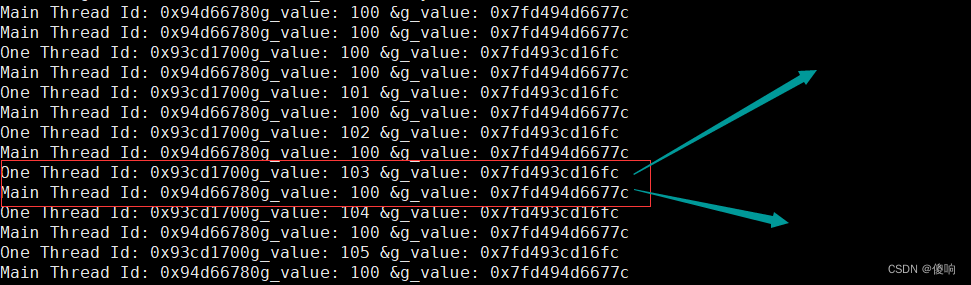
Linux下, 标准IO基于文件IO实现,文件IO与操作系统有关,每个操作系统不一样
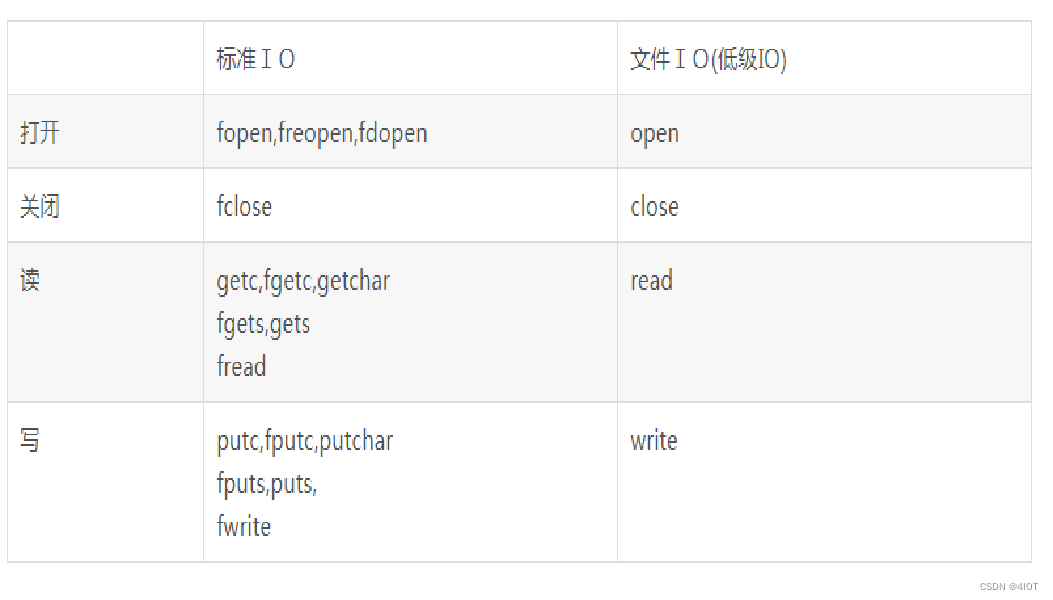
建议操作字符串还是使用标准IO,两者不能混用
2 文件I/O – 文件描述符fd(File Descriptor)
- 每个打开的文件都对应一个文件描述符。
- 文件描述符是一个非负整数。Linux为程序中每个打开的文件分配一个文件描述符。
- 文件描述符从0开始分配,依次递增。
- 文件IO操作通过文件描述符来完成。
- 0, 1, 2 的含义?
应用程序运行时自动打开,0标准输入流 1标准输入流 2标准错误流
3 文件I/O – open
open函数用来创建或打开一个文件:
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags); //文件存在,传入2个参数
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); //文件存在,需要3个参数创建
- 成功时返回文件描述符;出错时返回EOF
- 打开文件时使用两个参数
- 创建文件时第三个参数指定新文件的权限,(只有在建立新文件时有效)此外真正建文件时的权限会受到umask 值影响,实际权限是mode-umaks
- 可以打开设备文件,但是不能创建设备文件(创建设备mknode 驱动部分会讲)
man 2 open 查看文档
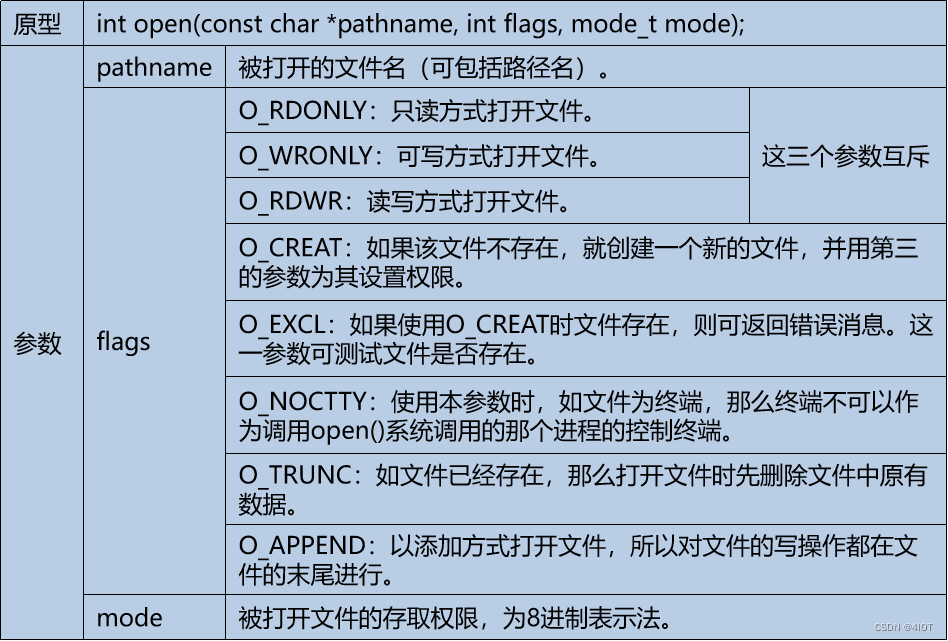
O_NOCTTY 在串口用的时候比较多,在某些情况下,我们希望打开终端设备时不将其作为进程的控制终端。这时可以使用 O_NOCTTY 标记来避免这种情况发生。
r O_RDONLY
r+ O_RDWR
w O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664
w+ O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664
a O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0664
a+ O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0664
- umask :用来设定文件或目录的初始权限
- 文件和目录的真正初始权限
- 文件或目录的初始权限 = 文件或目录的最大默认权限 - umask权限
普通用户 666 - 0002 =664
root用户 666 - 0022 =644
![]()
对于标准IO是没有权限参数的,只有文件IO有。
示例
以只写方式打开文件1.txt。如果文件不存在则创建,如果文件存在则清空:
int fd;
if ((fd = open(“1.txt”, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0666)) < 0) {
perror(“open”);
return -1;
}
……
以读写方式打开文件1.txt。如果文件不存在则创建,如果文件存在则报错:
int fd;
if ((fd = open(“1.txt”, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_EXCL, 0666)) < 0) {
if (errno == EEXIST) {
perror(“exist error”);
} else {
perror(“other error”);
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd;
int ret;
fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0666);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file err\n");
return 0;
}
printf("sucess,fd=%d\n",fd);
ret= close(fd);
if(ret<0){
printf("close failed\n");
}
ret=close(fd);
printf("ret=%d\n",ret);
}
4 文件I/O – close
close函数用来关闭一个打开的文件:
#include <unistd.h>
int close(int fd);
- 成功时返回0;
- 出错时返回EOF 程序结束时自动关闭所有打开的文件
- 文件关闭后,文件描述符不再代表文件
5 文件I/O – read
read函数用来从文件中读取数据:
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
- 成功时返回实际读取的字节数;出错时返回EOF
- 读到文件末尾时返回0
- buf是接收数据的缓冲区
- count不应超过buf大小
示例
从指定的文件(文本文件)中读取内容并统计大小
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
{
int fd, n, total = 0;
char buf[64];
if (argc < 2) {
printf(“Usage : %s <file>\n”, argv[0]); return -1;
}
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror(“open”); return -1;
}
while ((n = read(fd, buf, 64)) > 0) {
total += n;
}
……
6 文件I/O – write
write函数用来向文件写入数据:
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
- 成功时返回实际写入的字节数;出错时返回EOF
- buf是发送数据的缓冲区
- count不应超过buf大小
示例
将键盘输入的内容写入文件,直到输入quit
int fd;
char buf[20];
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0666)) < 0) {
perror(“open”); return -1;
}
while (fgets(buf, 20, stdin) != NULL) {
if (strcmp(buf, “quit\n”) == 0) break;
write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
}
……
7 文件IO – lseek
lseek函数用来定位文件:
#include <unistd.h>
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, intt whence);
param whence:SEEK_SET头偏移 SEEK_CUR当前位置偏移 SEEK_END尾部偏移
- 成功时返回当前的文件读写位置;出错时返回EOF
- 参数offset和参数whence同fseek完全一样(可正、可负)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd;
int ret;
char buf[32] = "hello world";
char buf2[32]={0};
fd = open("test.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT|O_APPEND, 0666);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file err\n");
return 0;
}
printf("sucess,fd=%d\n",fd);
ret=write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); //注意写字符串不能用sizeof,用strlen
if(ret<0){
perror("write");
goto END;
}
printf("write count=%d\n",ret);
lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);
ret = read(fd,buf2,32);
if(ret<0){
perror("read");
goto END;
}
buf2[31]=0; // '/0'可以避免超过32位有乱码出现的情况
printf("read buf2=%s\n",buf2);
END:
close(fd);
}
注意:
写字符串不能用sizeof ,用strlen,不能使用标准函数的定位。如果没有定位,关闭再打开读取,会从首字符读取。
8 标准I/O – 思考和练习
利用文件IO实现文件的复制
文件名通过命令行参数指定
打开文件的方式?
如何判断读到源文件的末尾?
练习
使用文件IO实现“每隔1秒向文件1.txt写入当前系统时间,行号递增”
#include "stdio.h"
#include "time.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "string.h"
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int fd;
time_t ticks;
struct tm * curtime;
int linecount = 0;
char buf[256];
int ret;
fd = open("text.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0666);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open file err\n");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
while(1)
{
ticks = time(&ticks);
curtime = localtime(&ticks);
//printf("cur=%d\n",(int)ticks);
printf("%d,%4d-%2d-%2d %2d:%2d:%2d\n",linecount\
,curtime->tm_year+1900\
,curtime->tm_mon+1\
,curtime->tm_mday\
,curtime->tm_hour\
,curtime->tm_min\
,curtime->tm_sec);
sprintf(buf,"%d,%4d-%2d-%2d %2d:%2d:%2d\n",linecount\
,curtime->tm_year+1900\
,curtime->tm_mon+1\
,curtime->tm_mday\
,curtime->tm_hour\
,curtime->tm_min\
,curtime->tm_sec);
ret = write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
buf[255] = 0;
if(ret < 0)
{
perror("write");
goto END;
}
linecount++;
sleep(1);
}
END:
close(fd);
return 0;
}