完整程序请查看博主主页置顶博客(专享优惠)
主要内容:
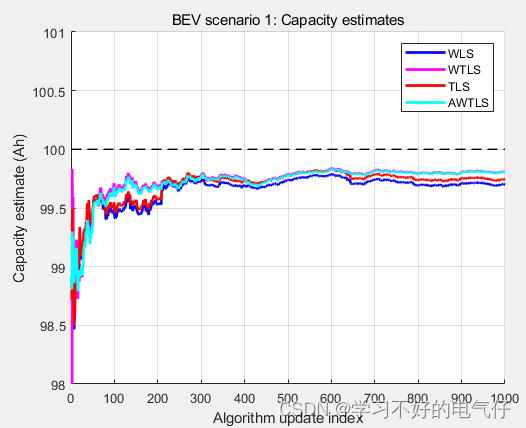
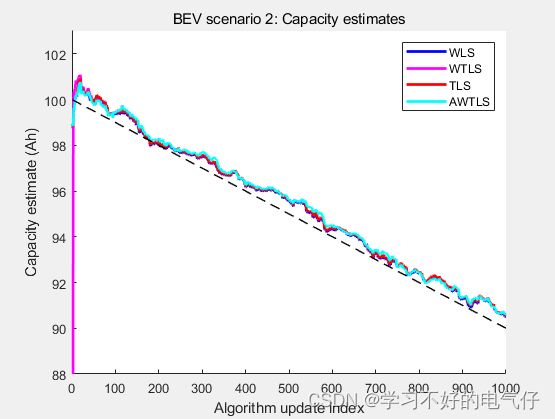
健康状态 SOH采用平均加权最小二乘法(AWTLS)进行估计,并对比了加权最小二乘 (WLS)、总最小二乘法(TLS)以及加权总最小二乘法(WTLS)算法。
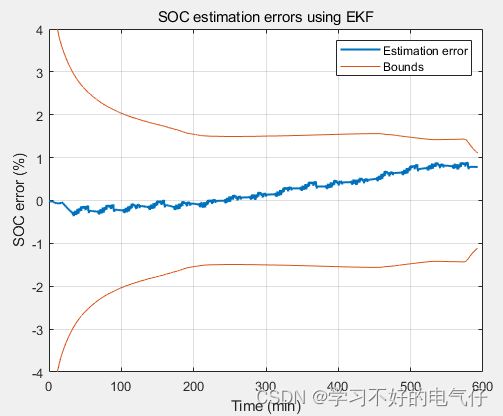
充电状态SOC采用扩展卡尔曼滤波算法进行估计。
部分代码:
binsize = 2*maxI/precisionI; % resolution of current sensor
rn1 = ones(n,1); % init std. dev. for each measurement
sx = socnoise*rn1; % scale Gaussian std. dev.
if theCase == 1, % the typical case
rn2 = rn1; % same scale on y(i) as x(i) noise
sy = binsize*sqrt(m/12)/3600*rn2; % std. dev. for y(i)
else % this case will be discussed for BEV case 2
mu = log(mode)+sigma^2;
m = 3600*lognrnd(mu,sigma,n,1);
sy = binsize*sqrt(m/12)/3600; % std.dev. for y(i)
end
x = x + sx.*randn(n,1); % measured x(i) data, including noise
y = y + sy.*randn(n,1); % measured y(i) data, including noise
% Execute the algorithms for BEV case 2
[QhatBEV3,SigmaQBEV3] = xLSalgos(x,y,sx.^2,sy.^2,gamma,Qnom,sy(1)^2);
% Plot estimates of capacity for BEV case 2
hold on; Qhat = QhatBEV3; SigmaQ = SigmaQBEV3;
plot(Qhat(:,1),'b','linewidth',2); % WLS
plot(Qhat(:,2),'m','linewidth',2); % WTLS
plot(Qhat(:,3),'r','linewidth',2); % TLS
plot(Qhat(:,4),'c','linewidth',2); % AWTLS
plot(1:length(x),Q,'k--','linewidth',1); % Plot true capacity
ylim([88 103]);
xlabel('Algorithm update index');
ylabel('Capacity estimate (Ah)');
title(sprintf('%s: Capacity estimates',plotTitle));
legend('WLS','WTLS','TLS','AWTLS','location','northeast');
% Compute RMS estimation error for all methods
errWLS = Q - QhatBEV3(:,1); rmsErrWLS = sqrt(mean(errWLS.^2))
errWTLS = Q - QhatBEV3(:,2); rmsErrWTLS = sqrt(mean(errWTLS.^2))
errTLS = Q - QhatBEV3(:,3); rmsErrTLS = sqrt(mean(errTLS.^2))
errAWTLS = Q - QhatBEV3(:,4); rmsErrAWTLS = sqrt(mean(errAWTLS.^2))
健康状态 SOH运行结果:
充电状态SOC估计结果:











![[N0wayback 2023春节红包题] happyGame python反编译](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8d35300b5a184df2b5a8a67da4984148.png)